C++Primer第五版 第九章 顺序容器
知识点1:所有的容器类都共享公共的接口,不同容器按不同方式对其进行扩展,每种容器提供了不同的性能和功能的权衡
vector:可变大小,支持快速随机访问,尾位置删除\插入速度很快,其余很慢,将元素保存在连续的内存空间
deque:双端队列。支持快速随机访问,头尾部插入\删除数据很快
list:双向链表。只支持双向顺序访问,在其任何位置插入\删除数据都很快,不支持元素随机访问(访问一个元素得历遍整个容器,内存开销大)
array:固定大小数组,不能添加或删除元素(不是普通的内置数组)
string:专门用于保存字符,随机访问快,在尾部插入\删除速度快,将元素保存在连续的内存空间
平常就使用vector,C++程序应该使用标准库容器,而不是原始的数据结构如:内置数组。
习题9.1
(a)list,因为可能需要在容器的中间位置插入元素
(b)deque,因为需要在头部进行元素的删除,deque效率更高
(c)vector,无具体的删除插入操作,未知数量,vector是个不错的选择。
知识点2:一个容器的元素类型可以是另一个容器
c.empty():c中存储了元素,返回false.
c.cbegin():返回const_iterator
c.clear():清空容器
c.swap(b):交换c与b中的元素
要访问顺序容器和关联容器中的元素,需要通过“迭代器(iterator)”进行。
迭代器是一个变量,相当于容器和操纵容器的算法之间的中介。迭代器可以指向容器中的某个元素,通过迭代器就可以读写它指向的元素。
习题9.2
list<deque<int>> li;
习题9.3
迭代器指向同一个容器或者最后一个元素之后的位置,可以反复递增begin直到end
迭代器指向的元素范围是左闭合区间,注意end指向的是最后一个元素之后的位置。 如:[begin,end)
习题9.4
bool findInt(vector<int>&vec, int c){
for (auto i : vec){
if (i == c){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
习题9.5
int findInt(vector<int>&vec, int c){
for (auto i : vec){
if (i == c){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
习题9.6
两个迭代器不在统一容器内不能直接比较
程序修改为:
while(iter1!=iter2)
习题9.7
vector<int>::size_type;
习题9.8
list<string>::const_iterator;
list<string>::iterator;
习题9.9
begin返回容器的iterator类型
cbegin返回容器的const_iterator类型
习题9.10
P298 一个const成员,返回容器的const_iterator类型。另一个非常量成员,返回容器的iterator类型。
知识点3:当一个容器初始化为另一个容器的拷贝时,两个容器的容器类型和元素类型都必须相同。
不过,当传递迭代器参数来拷贝一个范围时,就不要求容器类型是相同。如下:
forwar_list<string> words(articles.begin(),articles.end());
知识点4:为了使用array类型,我们必须同时指定元素类型和大小:
array<int,42> i; //类型为:保存42个int的数组
array<string,10> j; //类型为:保存10个string的数组
习题9.11
vector<int> vec; // 0
vector<int> vec(0); //0
vector<int> vec(10,1); //10个1
vector<int> vec{1,2,3,4,5};//1,2,3,4,5
vector<int> vec(other_vec);//same as other_vec
vector<int> vec(other_vec.begin(),other_end());//same as other_vec
习题9.12
当一个容器初始化为另一个容器的拷贝时,两个容器的类型和元素型必须相同。使用迭代器,则不要求类型相同。
接受迭代器创建拷贝,拷贝的是两个迭代器之间的内容,而直接接受一个容器,就是拷贝整个容器的内容了。
习题9.13
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//目标初试化的容器
vector<int> vec1(5,5);
list<int> vec2(2,2);
//创建初始化容器
vector<double> vec3(vec1.begin(), vec1.end());
vector<double> vec4(vec2.begin(), vec2.end());
/验证
for (auto i : vec3){
cout << i << " ";
}
for (auto j : vec4){
cout << j << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}

知识点5:赋值运算符和swap要求左右的运算对象有相同的类型,assign操作不适用于关联容器和array
习题9.14
list<string> names;
vector<const char*> oldstyle;
names.assign(oldstyle.cbegin(),oldstyle.cend());
知识点6:关系运算符左右的运算对象必须是相同类型的容器,且必须保持相同类型的元素
1.如果两个容器具有相同大小且所有元素都两两对应相等,则这两个容器相等,否则不相等
2.如果两个容器大小不同,但小的容器中的每个元素都大于大的容器,则小的容器大于大的容器
3.如果两个容器都不是另一个容器的前缀子序列,则它们的比较结果取决于第一个不相等的元素比较结果
4.只有当其元素类型也定义了相应的比较运算符时,我们才可以使用关系运算符来比较两个容器
习题9.15
bool isEquel(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b) {
if (a == b) return true;
else return false;
}
习题9.16
bool isEquel(vector<int> &a, list<int> &b) {
vector<int> c(b.begin(), b.end());
if (a == c) return true;
else return false;
}
习题9.17
只有当其元素类型也定义了相应的比较运算符时,我们才可以使用关系运算符来比较两个容器
知识点7:顺序容器操作
push_back 将一个元素追加到一个容器的尾部,除了array和forwar_list之外,每个顺序容器都支持push_back,放入容器中的是对象值的一个拷贝,而不是对象本身
push_front 将一个元素追加到一个容器的头部,vector不支持这个
insert 将一个元素插入到特定位置,支持插入范围内的元素
emplace 在容器中直接构造元素。传递给empalce函数的参数必须与元素类型的构造函数相匹配
习题9.18
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
deque<string> deq;
while (cin >> s) {
deq.push_back(s);
}
for (auto it:deq) {
cout << it << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.19
将deque改成list
习题9.20
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int main() {
list<int> s = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
deque<int> odd, even;
for (auto i:s){
if (i % 2 ){
odd.push_back(i);
}
else
{
even.push_back(i);
}
}
cout << "odd中的奇数为:";
for (auto i : odd){
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl << "even中的偶数为:";
for (auto i : even){
cout << i << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.21
不改变
习题9.22
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void func(vector<int> &iv, int some_val) {
int extra = 0;
vector<int>::iterator iter = iv.begin();
while (iter != (iv.begin() + iv.size() / 2 + extra)) {
if (*iter == some_val) {
iter = iv.insert(iter, 2 * some_val);
++extra;
++iter;
}
++iter;
}
}
int main() {
vector<int> iv = { 1,2,3,4 };
func(iv, 2);
for (auto i : iv) {
cout << i << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
知识点8:访问元素
迭代器end指向的是容器尾元素之后的(不存在)的元素。
在调用front和back(或者解引用begin和end返回的迭代器)之前,要保证容器为非空,否则操作的行为将是未定义的,是严重的程序设计错误。
在容器中访问元素的成员函数(如front、back、下标和at)返回的都是引用,如果使用auto来保存函数的返回值,必须将变量定义为引用类型。
为了确保下标是合法的,可以使用at成员函数,如果下标越界,at会抛出一个out_of_range异常。
习题9.23
四个值都是*c.begin(),即第一个元素
习题9.24
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> vec;
int a = vec.at(0),
b = vec[0],
c = vec.front();
auto d = vec.begin();
cout << "a: " << a << endl;
cout << "b: " << b << endl;
cout << "c: " << c << endl;
cout << "d: " << *d << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
知识点9:删除元素
pop_front和pop_back成员函数分别删除首元素和尾元素,vector和string不支持。
成员函数erase从容器中指定位置删除元素。
习题9.25
如果elem1与elem2相等,则一个元素都不会删除。
如果elem2是尾后迭代器,则会从elem1元素删除到最后一个元素。
如果elem1与elem2都是尾后迭代器,则一个元素都不会删除。
习题9.26
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int ia[] = { 0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,55,89 };
vector<int> vec(ia, end(ia));
list<int> li(ia, end(ia));
for (auto it = li.begin(); it != li.end();) {
if (*it % 2 == 1) {
it = li.erase(it);
}
else {
++it;
}
}
for (auto i : li) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto it = vec.begin();it != vec.end();) {
if (*it % 2 == 0) {
it = vec.erase(it);
}
else {
++it;
}
}
for (auto i : vec) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
知识点10:
forward_list的相关操作比较特殊,有其自己特殊的删除和插入操作
习题9.27
#include<iostream>
#include<forward_list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
forward_list<int> flst = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
auto prev = flst.before_begin();
auto curr = flst.begin();
while (curr != flst.end()) {
if (*curr % 2) {
curr = flst.erase_after(prev);
}
else {
prev = curr;
++curr;
}
}
for (auto i : flst) {
cout << i << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.28
#include<forward_list>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void func(forward_list<string> &flst, string a, string b) {
auto it = flst.begin();
auto prev = flst.before_begin();
bool flag = false;
while (it != flst.end()) {
if (*it == a) {
it = flst.insert_after(it, b);
flag = true;
break;
}
else {
prev = it;
++it;
}
}
if (!flag) flst.insert_after(prev, b);
}
int main() {
forward_list<string> flst = { "abc","bcd","eee" };
string a = "eee", b = "fff";
func(flst, a, b);
for (auto i : flst) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
知识点11:改变容器大小
resize可以增大或缩小容器,array不支持
习题9.29
vec.resize(100)会将75个值为0的元素添加到vec的末尾。
vec.resize(10)会从vec末尾删除90个元素。
习题9.30
元素类型必须提供一个默认构造函数
知识点12:容器操作可能会使迭代器失效
1.向容器中添加元素和从容器中删除元素的操作都可能会使指向容器元素的指针、引用或者迭代器失效。
2.必须保证每次改变容器的操作之后都正确地重新定位迭代器。
3.对于list和forward_list,变动之后指向容器的迭代器(包括首前迭代器、尾后迭代器)、指针和引用仍然有效。
4.不要保存end返回的迭代器。
习题9.31
list
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
list<int> lst = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
auto iter = lst.begin();
while (iter != lst.end()) {
if (*iter % 2) {
iter = lst.insert(iter, *iter);
++iter;
++iter;
}
else {
iter = lst.erase(iter);
}
}
for (auto i : lst) {
cout << i << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
forward_list
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<forward_list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
forward_list<int> lst = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
auto iter = lst.begin();
auto prev = lst.before_begin();
while (iter != lst.end()) {
if (*iter % 2) {
iter = lst.insert_after(iter, *iter);
prev = iter;
++iter;
}
else {
iter = lst.erase_after(prev);
}
}
for (auto i : lst) {
cout << i << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.32
不合法的原因:解引运算符和递增的优先级一样,结合律从右往左,函数实参求值顺序不定
习题9.33
程序会崩溃,因为begin迭代器的值在插入一个元素之后已经失效
习题9.34
程序是为了复制奇数,但是由于每次插入奇数后返回的是仍是同一个奇数,于是会进入无限循环,所以应在每次插入奇数后跳两次。
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> v = { 1,2,3,4,5};
auto iter = v.begin();
while (iter != v.end()) {
if (*iter % 2) {
iter = v.insert(iter, *iter);
++iter;
}
++iter;
}
for (auto i : v) {
cout << i << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
知识点13:vector对象是如何增长的
vector将元素连续存储,当没有内存空间时,会分配比新空间需求更大的内存空间。
容器的size是指它保存了多少元素,capacity是指容器的最大容量。后者至少和前者一样大,具体会分配多少额外空间得看标准库的具体实现。
可以调用shrink_to_fit来要求vector将超出当前大小的多余内存退还给系统。
习题9.35
容器的size是指它已经保存元素的个数,capacity指的是不分配内存空间的前提下它最多可以保存的元素。
习题9.36
不可能
9.37
vector中的元素在内存中是连续存放的,所以需要capacity,list的元素不是连续存放的,不需要capacity,array的大小是固定的。
习题9.38
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<string> v;
for (string buffer; cin >> buffer; v.push_back(buffer))
cout << v.size() << " " << v.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
习题9.39
首先为svec预留了1024的空间,其次将输入添加到svec中,最后将svec的size增大当前的一半。
习题9.40
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void func(int val){
vector<string> svec;
string s = "string";
svec.reserve(1000);
for (int i = 0; i < val; i++)
{
svec.push_back(s);
}
svec.resize(svec.size() + svec.size() / 2);
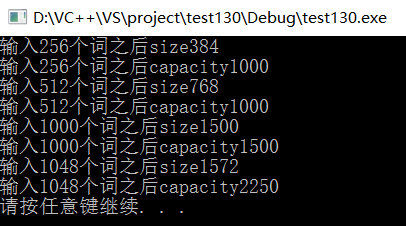
cout << "输入" << val << "个词之后size" << svec.size() << endl;
cout << "输入" << val << "个词之后capacity" << svec.capacity() << endl;
}
int main() {
func(256);
func(512);
func(1000);
func(1048);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.41
vector<char> v = { 'a','b','c' };
string s(v.begin(), v.end());
习题9.42
利用reverse()操作预留足够的内存,这样就不用在过程中进行修改内存的操作。
string s;
s.reserve(100);
知识点14:append和replace函数
append()直接在字符串之后加上相关的参数
replace函数提供了两种指定删除元素范围的方式
习题9.43
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void func(string &s, string &oldVal, string &newVal) {
auto iter = s.begin();
while (iter + oldVal.size() != s.end()) {
if (oldVal == string(iter, iter + oldVal.size())) {
iter = s.erase(iter, iter + oldVal.size());
iter = s.insert(iter, newVal.begin(), newVal.end());
iter += newVal.size();
}
else {
++iter;
}
}
}
int main() {
string s("though,you don't love me");
string oldVal("though");
string newVal("tho");
func(s, oldVal, newVal);
cout << s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.44
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void func(string &s, string &oldVal, string &newVal) {
string::size_type i = 0;
auto s_len = s.size(), old_len = oldVal.size();
while (i + old_len <= s_len) {
if (oldVal == s.substr(i, i + old_len)) {
s.replace(i, i + old_len, newVal);
i += newVal.size();
}
else {
++i;
}
}
}
int main() {
string s("though,you don't love me");
string oldVal("though");
string newVal("tho");
func(s, oldVal, newVal);
cout << s << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.45
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void func(string &name, string &pre, string &post) {
name.insert(0, pre);
name.append(post);
}
int main() {
string nm = "Allen", pre = "Mr.", post = " Jr.";
func(nm, pre, post);
cout << nm;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.46
void func(string &name, string &pre, string &post) {
name.insert(0, pre);
name.insert(name.size(), post);
}
习题9.47
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str("ab2c3d7R4E6");
string numbers{ "123456789" };
string alphabet{ "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" };
string::size_type pos = 0;
while ((pos = str.find_first_of(numbers, pos)) != string::npos) {
cout << str[pos] << " ";
++pos;
}
cout << endl;
pos = 0;
while ((pos = str.find_first_of(alphabet, pos)) != string::npos) {
cout << str[pos] << " ";
++pos;
}
cout << endl;
pos = 0;
while ((pos = str.find_first_not_of(alphabet, pos)) != string::npos) {
cout << str[pos] << " ";
++pos;
}
cout << endl;
pos = 0;
while ((pos = str.find_first_not_of(numbers, pos)) != string::npos) {
cout << str[pos] << " ";
++pos;
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.48
string::npos
习题9.49
#include<fstream>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string FileName;
cout << "请输入要打开的单词文件:" << endl;
cin >> FileName;
ifstream inFile(FileName);
if (!inFile) {
cout << "打开失败!" << endl;
return 0;
}
vector<string> ans;
string up("bdfhklt"), down("gjpqy"), s;
string::size_type pos = 0,poschar;
while (inFile >> s) {
if ((pos = s.find_first_of(up)) == string::npos) {
if ((pos = s.find_first_of(down)) == string::npos) {
ans.push_back(s);
}
}
}
for (auto i : ans) {
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.50
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<string> vec = { "2","3","4","50" };
int sum = 0;
for (auto i : vec) {
sum += stoi(i);
}
cout << sum << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.51
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
const string mm[12] = { "Jan","Feb","Mar","Apr","May","Jun","Jul","Aug","Sept","Oct","Nov","Dec" };
int findmonth(const string &mon) {
int pos;
for (int i = 0;i < 12;++i) {
if ((pos = mon.find(mm[i])) != string::npos) {
return i + 1;
}
}
}
class Date {
public:
Date(const string &str) {
string data_str = str;
string::size_type index1 = 0;
string::size_type index2 = 0;
if (str.find(',') != string::npos) {
index1 = str.find(' ');
index2 = str.find(',',index1+1);
string mon = str.substr(0, index1 - 1);
month = findmonth(mon);
day = stoi(str.substr(index1 + 1, index2));
year = stoi(str.substr(index2 + 1));
}
else if (str.find('/') != string::npos) {
index1 = str.find_first_of('/');
index2 = str.find_first_of('/', index1 + 1);
year = stoi(str.substr(index2 + 1));
month = stoi(str.substr(index1 + 1, index2 - 1));
day = stoi(str.substr(0, index1));
}
else {
index1 = str.find_first_of(' ');
index2 = str.find_first_of(' ', index1 + 1);
string mon = str.substr(0, index1);
month = findmonth(mon);
day = stoi(str.substr(index1 + 1, index2 - 1));
year = stoi(str.substr(index2 + 1));
}
}
void getdate() {
cout << "Year:" << year << " " << "Month:" << month << " " << "Day:" << day << endl;
}
private:
unsigned year, month, day;
};
int main() {
string d1 = "January 1,1900", d2 = "1/1/1990", d3 = "Jan 1 1900";
Date a(d1), b(d2), c(d3);
a.getdate();
b.getdate();
c.getdate();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
习题9.52
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
bool isnum(char a) {
if (a >= '0'&&a <= '9') {
return true;
}
else return false;
}
int main() {
string expr("(1+2)+(3+4)+5");
stack<char> st;
int sum = 0;
int len = expr.size();
for (int i = 0;i < len;i++) {
if (expr[i] == '('|| isnum((expr[i]))) {
st.push(expr[i]);
}
else if (expr[i] == '+') {
continue;
}
else if (expr[i] == ')') {
while (st.top() != '(') {
sum += st.top() - '0';
st.pop();
}
st.pop();
}
}
while (!st.empty()) {
sum += st.top() - '0';
st.pop();
}
cout << sum << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号