Net6 EFcore框架介绍
1、简介
EFcore,可用使得开发人员不需要再去关注数据库的实现,全都由代码进行生成
这样有利于减少工作量、数据库快速迁移...
2、上手搭建架构
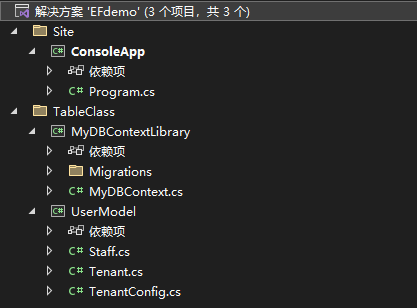
(这个图是做完本章内容的完整图,我们一步步深入即可)
在写EF之前,先安装好数据库,我选择在本地安装Sqlserver
我们先执行最核心的两步,将EF和数据库跑通
1)类&表的定义:基本上会保持class和数据库的table字段保持一致,如上UserModel,我定义了Staff、Tenant两个类,会自动生成两个表
UserModel需要安装
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
Staff
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; namespace UserModel { public class Staff { public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; } public string Description { get; set; } public string? PhoneNumber { get; set; } public string? Email { get; set; } } }
Tenant
namespace UserModel { public class Tenant { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public string Description { get; set; } } }
2)上下文定义:负责关联实体类、访问数据库配置,提供后续生成数据库支持,如上MyDBContextLibrary
MyDBContextLibrary需要安装
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
MyDBContext
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; namespace UserModel { public class MyDBContext : DbContext { public DbSet<Staff> Staffs { get; set; } public DbSet<Tenant> Tenants { get; set; } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder); optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=master;Integrated Security=True;TrustServerCertificate=yes"); } } }
准备完毕!!
打开【程序包管理器控制台】
项目指定到MyDBContext

Add-Migration Ini #添加一个迁移 Ini是为这个迁移起的备注名 Update-database #更新到数据库,执行了才会同步迁移到数据库
=======================================================
#扩展
Update-datebase A #指定更新到A脚本
Remove-migration #删除最近一次迁移脚本
Script-migration #生成脚本对应的SQL,可手动到数据库执行,Update-datebase命令就是执行这串代码更新数据库的
#疑问来了:为啥需要这个?答:正常Update-database适合更新开发环境,生产环境需要生产SQL脚本来更新
Script-migration A B #生成版本A更新到版本B的SQL脚本
Script-migration A #生成版本A更新到最新的SQL脚本
到此,简单的EF框架已经跑起来了
3、扩展
EF是一个十分强大的框架,我们逐渐扩展知识点。
1)属性定义
有两种方式
其一:Data Annotations(数据注解),利用特性进行定义,如对Staff属性进行定义
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; //Data Annotations例子 namespace UserModel { [Table("Staff")]//可用加特性指定表名 public class Staff { public int Id { get; set; } [Required]//必填 [MaxLength(10)]//最大长度为10 public string Name { get; set; } [Required] public string Description { get; set; } public string? PhoneNumber { get; set; } //可空 public string? Email { get; set; } } }
PS:提醒一点,Id / 类名+Id 在迁移到数据库表的时候,会默认为递增序列
其二:Fluent API,微软官方提供的API,如对Tenant属性进行定义
在MyDBContext,重写OnModelCreating方法
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; namespace UserModel { public class MyDBContext : DbContext { public DbSet<Staff> Staffs { get; set; } public DbSet<Tenant> Tenants { get; set; } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder); optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=master;Integrated Security=True;TrustServerCertificate=yes"); } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);modelBuilder.Entity<Tenant>().Property(x=>x.Description).IsRequired(false); /*指定Description非必填*/ } } }
当然,我们容易看到,如果实体很多,属性直接写在这里代码太冗长了
改变一下方法,添加一个TenantConfig类
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Builders; namespace UserModel { public class TenantConfig : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Tenant> { public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Tenant> builder) { builder.ToTable("Tenant");//可重新指定表名 builder.HasKey(x => x.Id); builder.Property(x=>x.Name).IsRequired().HasColumnType("nvarchar(100)"); builder.Property(x=>x.Description).IsRequired(false); } } }
然后 DbContext:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; namespace UserModel { public class MyDBContext : DbContext { public DbSet<Staff> Staffs { get; set; } public DbSet<Tenant> Tenants { get; set; } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder); optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=master;Integrated Security=True;TrustServerCertificate=yes"); } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);modelBuilder.ApplyConfigurationsFromAssembly(typeof(Tenant).Assembly); //利用反射,加载Tenant程序集下的IEntityTypeConfiguration } } }
完成,再次生成一个迁移到数据库看看!!!
代码不会一步到位的,大家逐步测试严重,这边我就不贴数据库的截图了
4、然后说明一下ConsoleApp
Program
using UserModel; using(var ctx = new MyDBContext()) { var s = new Staff() { Name = "kxy2", Description = "三好员工", PhoneNumber = "1234567890" }; ctx.Staffs.Add(s); var t = new Tenant() { Name = "ccc", }; ctx.Tenants.Add(t); ctx.SaveChanges(); } Console.ReadLine();
测试数据而已,怎么方便怎么来
PS:有个点,如果设置ConsoleApp为启动项,迁移的时候会验证启动项的依赖,从而产生错误
ConsoleApp需要安装
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
至此,完成!!
5、日志输出
EF会翻译成SQL,然后到数据库执行,尝试一下在控制台输出EF的SQL代码。
安装nuget包
Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Console
MyDBContext,添加
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; namespace UserModel { public class MyDBContext : DbContext { private static ILoggerFactory _loggerFactory = LoggerFactory.Create(build => { build.AddConsole(); }); public DbSet<Staff> Staffs { get; set; } public DbSet<Tenant> Tenants { get; set; } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder); optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=master;Integrated Security=True;TrustServerCertificate=yes"); optionsBuilder.UseLoggerFactory(_loggerFactory); } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder); modelBuilder.ApplyConfigurationsFromAssembly(typeof(Tenant).Assembly); //指定其他类库下的程序集 } } }
完成,执行一下代码,查看输出

6.导航属性
EF有单向导航属性和双向导航属性两种,主要是方便EF框架本身的操作,对数据库表结构并没有影响
究其本质,就是希望通过一个主体查询/新增另一个主体的信息
1)单向导航属性:我们要求查出一个员工,并查看该员工所属商场
定义 Mall
namespace UserModel { public class Mall { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } }
定义 Staff
namespace UserModel { public class Staff { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public string? Description { get; set; } public string? PhoneNumber { get; set; } public string? Email { get; set; } public Mall TheMall { get; set; } } }
StaffConfig 定义单向导航
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Builders; namespace UserModel { public class StaffConfig : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Staff> { public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Staff> builder) { builder.ToTable("Staff"); builder.HasKey(x => x.Id); builder.Property(x => x.Name).IsRequired().HasColumnType("nvarchar(100)"); builder.HasOne<Mall>(x => x.TheMall).WithMany().IsRequired(); } } }
这样做的好处是什么?
新增的时候,可用指定该员工所属商场,所以这是必要的:
var staff = new Staff() { Name = "员工3", //TheMall = new Mall() { Id = 1 },//new的话会新增一个mall TheMall = ctx.Mall.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == 1) }; ctx.Staffs.Add(staff); ctx.SaveChanges();
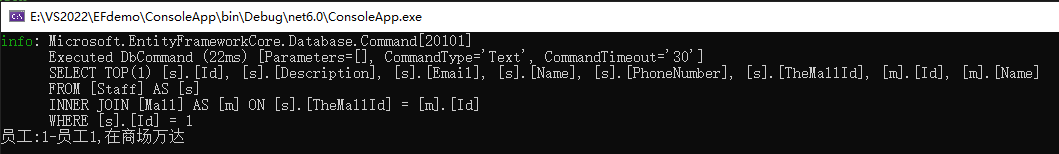
查询:可用通过一条SQL查询出员工1信息及所属商场
var staff = ctx.Staffs.Include(x=>x.TheMall).FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == 1); Console.WriteLine($"员工:{staff.Id}-{staff.Name},在商场{staff.TheMall.Name}");
结果如图:(其实就是告诉SQL进行Join操作)
2)双向导航属性:那如果,我们要通过商场查员工呢
Mall
namespace UserModel { public class Mall { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public List<Staff> Staffs { get; set; } //加一个导航属性 } }
StaffConfig
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Builders; namespace UserModel { public class StaffConfig : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Staff> { public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Staff> builder) { builder.ToTable("Staff"); builder.HasKey(x => x.Id); builder.Property(x => x.Name).IsRequired().HasColumnType("nvarchar(100)"); builder.HasOne<Mall>(x => x.TheMall).WithMany(x => x.Staffs).IsRequired(); } } }
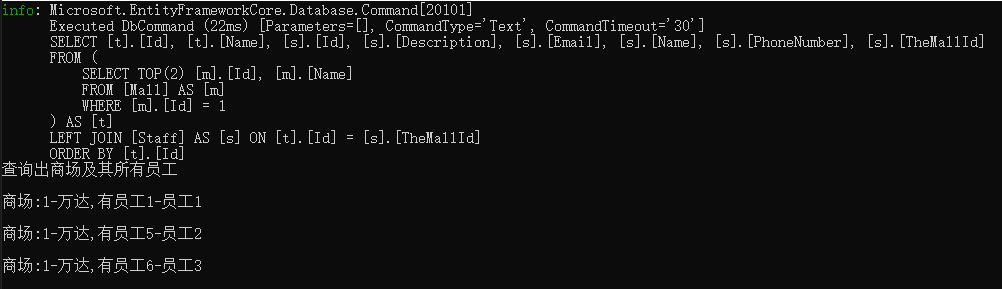
查询商场ID=1的所有员工
var mall = ctx.Mall.Include(x => x.Staffs).Single(x => x.Id == 1); Console.WriteLine("查询出商场及其所有员工 \n"); foreach (var staff in mall.Staffs) { Console.WriteLine($"商场:{mall.Id}-{mall.Name},有员工{staff.Id}-{staff.Name} \n"); }
结果如图:告诉SQL,进行子查询
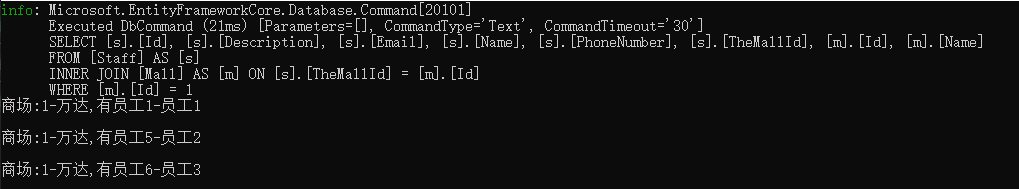
也可以这样写
var staffs = ctx.Staffs.Include(x=>x.TheMall).Where(x => x.TheMall.Id== 1); foreach (var staff in staffs) { Console.WriteLine($"商场:{staff.TheMall.Id}-{staff.TheMall.Name},有员工{staff.Id}-{staff.Name} \n"); }
结果:(这样写语法效率更好,避免了子查询)
总结:不管是单向还是双向导航,都是希望通过一个主体带出/新增另一个主体的信息。
7、IEnumerable和IQueryable
//普通List的LINQ返回IEnumerable var list = new List<Staff>(); IEnumerable<Staff> staffs1 = list.Where(x => x.Id == 1); //EF语法的LINQ返回IQueryable var ctx = new MyDBContext(); IQueryable<Staff> staffs2 = ctx.Staffs.Where(x => x.Id== 1);
Enumerable:可枚举的
Queryable:可查询的
IQueryable对比IEnumerable,没有功能上的扩充,EF为什么大费周章的引进IQueryable呢!
答:为了加入了延迟访问数据库机制,IQueryable相当于一个可访问数据库对象,而不是立马去访问数据库,当IQueryable遇到终结方法的时候,才会执行数据库操作
非终结方法:Where()、GroupBy()、OrderBy()、Inclede()、Skip()、Take()等数据库操作
终结方法:ToList()、ToArray()、Min()、Max()、Count()等非数据操作或统计操作
总结:返回结果非IQueryable的时候,就会到数据库执行
PS:执行For循环读取数据的时候,也是终结方法,示例:
//EF语法的LINQ返回IQueryable IQueryable<Staff> staffs2 = ctx.Staffs.Include(x=>x.TheMall).Where(x => x.Id > 0); Console.WriteLine("还没进入foreach"); foreach (var staff in staffs2) { Console.WriteLine("进入foreach"); Console.WriteLine($"商场:{staff.TheMall.Id}-{staff.TheMall.Name},有员工{staff.Id}-{staff.Name} \n"); }
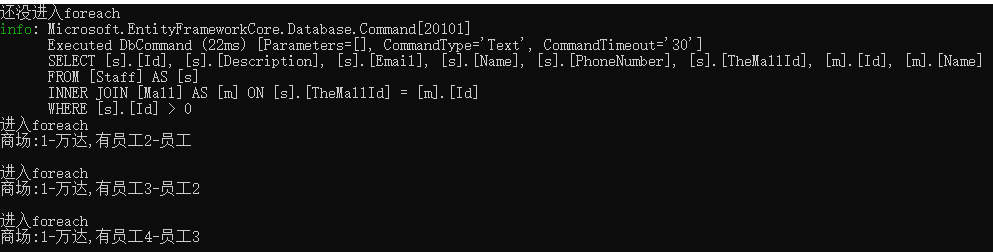
可见,访问数据库是在需要for循环staffs2的时候执行的
这就是延迟访问。。
8、事务域
一个域内,只有执行了Complete,才会提交事务
如果多个事务中有一个发生错误,所有事务都会一起回滚
using(TransactionScope tx=new TransactionScope()) { var staff = new Staff() { Name = "员工", TheMall = ctx.Mall.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == 1) }; ctx.Staffs.Add(staff); ctx.SaveChanges(); //这是一个事务 var staff3 = new Staff() { Name = "员工333333333333333333333333333333333",//名字长度超过允许最大长度 TheMall = ctx.Mall.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == 1) }; ctx.Staffs.Add(staff3); ctx.SaveChanges(); //这是另一个事务 tx.Complete(); }
PS:异步情况需要指定变量存储位置
ThreadLocal:当前线程全局变量上下文
AsyncLocal:当前异步流全局变量上下文
域内有异步函数,需要加参数,告诉TransactionScope把事务信息保存在AsyncLocal
using(TransactionScope tx=new TransactionScope(TransactionScopeAsyncFlowOption.Enabled))




