wxPython 绘图演示——模拟雷达信号图(2)
参考此前 wxpython 实现简易画板(1),wxPython 实现绘图有直接法和缓冲法。推荐使用缓冲法来避免屏闪。
1.1. 基本框架
下面以“雷达信号图”为例,回顾 wxPython 的绘图的基本框架:
class RadarGraph(wx.Window):
def __init__(self, *args, **kw):
super().__init__(*args, **kw)
# 自定义的数据
# Add your codes
# 设置并重绘缓冲区
self.buffer = None # 缓冲区
self.InitBuffer()
# 绑定事件
self.Bind(wx.EVT_SIZE, self.OnSize)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_PAINT, self.OnPaint)
# add other events you need
def InitBuffer(self):
'''设置并重绘缓冲区'''
w, h = self.GetClientSize()
self.buffer = wx.Bitmap(w, h)
dc = wx.BufferedDC(wx.ClientDC(self), self.buffer)
# 你的绘制内容
self.DrawGraph(dc)
def DrawGraph(self, dc:wx.BufferedPaintDC):
pass
# ----- 事件响应函数 -----
def OnSize(self, event):
"""响应窗口大小改变"""
# 每次窗口大小变换,都需要重新设置缓冲区大小,重绘窗口
self.InitBuffer()
def OnPaint(self, event):
"""响应Paint Event"""
wx.BufferedPaintDC(self, self.buffer)
1.2. 运行结果
设置了一个定时器 wx.Timer,让数据随着时间而变化,形成一个动图效果。
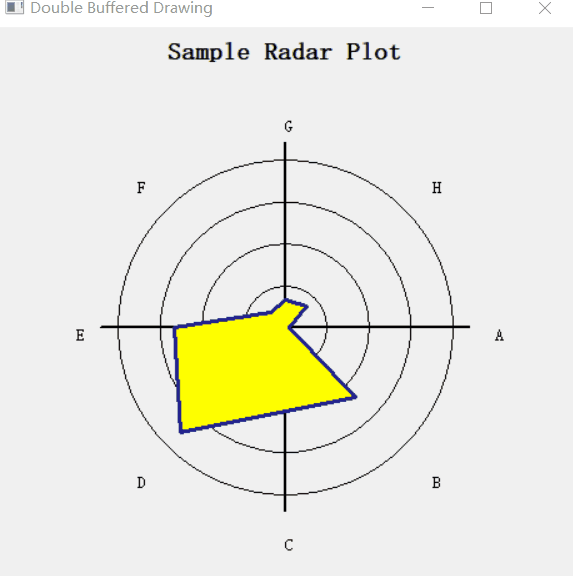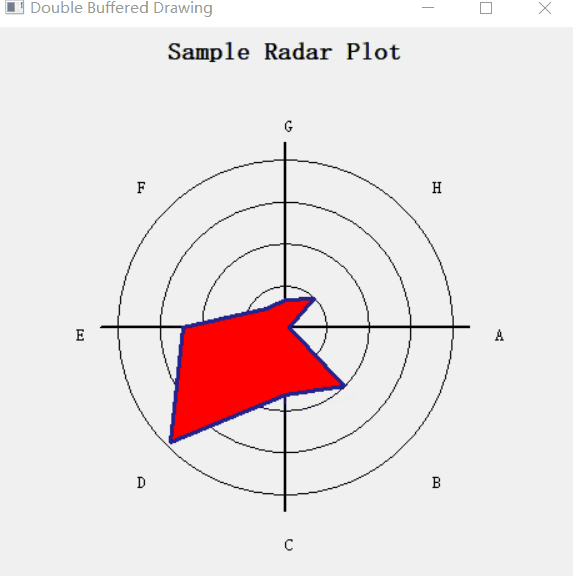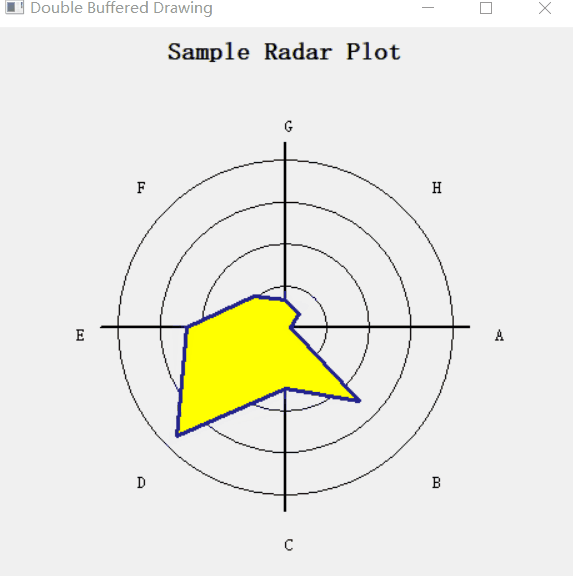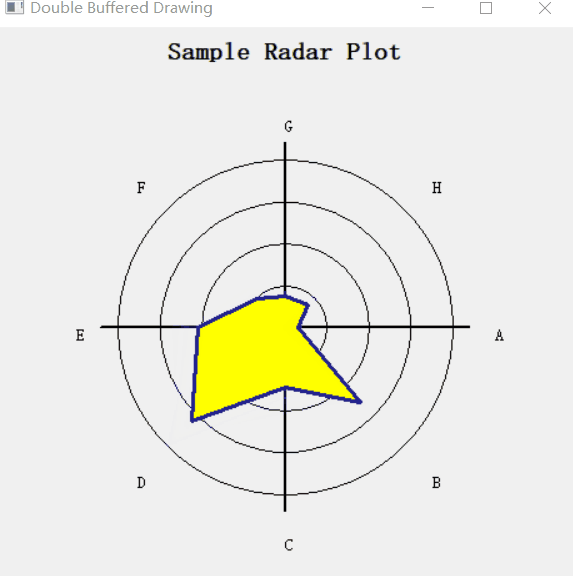
1.3. 完整代码
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-
# Python 3.9.6 64bit
'''
@File : a_sample_radar_graph.py
@Time : 2022/01/04 11:02
@Author : Wreng
@Description : 雷达信号图,参考 Python in action / Chapter 12 / example 12.2
@Other : version - Python 3.9.6 64bit, wxPython 4.1.1
'''
import wx
import math
import random
class RadarGraph(wx.Window):
def __init__(self, parent, title, labels):
super().__init__(parent)
# 窗口标题
self.title = title
self.titleFont = wx.Font(14, wx.FONTFAMILY_SWISS, wx.FONTSTYLE_NORMAL, wx.FONTWEIGHT_BOLD)
# 图中的标签
self.labels = labels
self.labelFont = wx.Font(10, wx.FONTFAMILY_SWISS, wx.FONTSTYLE_NORMAL, wx.FONTWEIGHT_NORMAL)
self.data = [0.0] * len(labels)
self.xy = None
self.buffer = None # 缓冲区
# 设置并重绘缓冲区
self.InitBuffer()
# 绑定事件
self.Bind(wx.EVT_SIZE, self.OnSize)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_PAINT, self.OnPaint)
def InitBuffer(self):
'''创建缓冲区'''
w, h = self.GetClientSize()
self.buffer = wx.Bitmap(w, h)
dc = wx.BufferedDC(wx.ClientDC(self), self.buffer)
# 你的绘制内容
self.DrawGraph(dc)
def DrawGraph(self, dc:wx.BufferedPaintDC):
'''绘制图形'''
spacer = 10
scaledmax = 150.0
dc.SetBackground(wx.Brush(self.GetBackgroundColour()))
dc.Clear()
dw, dh = dc.GetSize()
# 绘制标题
dc.SetFont(self.titleFont)
tw, th = dc.GetTextExtent(self.title)
dc.DrawText(self.title, (dw-tw)/2, spacer)
# 找到中心点
th = th + 2*spacer
cx = dw / 2
cy = (dh - th)/2 + th
# 计算比率
mindim = min(cx, (dh - th)/2)
scale = mindim / scaledmax
# 绘制轴线,以25为刻度
dc.SetPen(wx.Pen("black", 1))
dc.SetBrush(wx.TRANSPARENT_BRUSH)
dc.DrawCircle(cx, cy, 25*scale)
dc.DrawCircle(cx, cy, 50*scale)
dc.DrawCircle(cx, cy, 75*scale)
dc.DrawCircle(cx, cy, 100*scale)
dc.SetPen(wx.Pen("black", 2))
dc.DrawLine(cx-110*scale, cy, cx+110*scale, cy)
dc.DrawLine(cx, cy-110*scale, cx, cy+110*scale)
# 寻找了每个点的坐标,绘制标签以及最大的数据点
dc.SetFont(self.labelFont)
maxval = 0
angle = 0
polypoints = []
for i, label in enumerate(self.labels):
val = self.data[i]
point = self.PolarToCartesian(val*scale, angle, cx, cy) # 将极坐标转化为直角坐标
polypoints.append(point)
x, y = self.PolarToCartesian(125*scale, angle, cx, cy)
dc.DrawText(label, x, y) # 绘制标签
if val > maxval:
maxval = val
angle = angle + 360 / len(self.labels)
# 根据最大值确定brush的颜色, green is good; red is bad
c = "forest green"
if maxval > 70:
c = "yellow"
if maxval > 95:
c = "red"
dc.SetBrush(wx.Brush(c)) # 设置画刷的颜色
dc.SetPen(wx.Pen("navy", 3))
dc.DrawPolygon(polypoints) # 绘制采集的形状
def PolarToCartesian(self, radius, angle, cx,cy):
'''将极坐标转化为直角坐标'''
x = radius * math.cos(math.radians(angle))
y = radius * math.sin(math.radians(angle))
return (int(cx+x+0.5), int(cy+y+0.5)) # 四舍五入转化为整数
def GetData(self):
return self.data
def SetData(self, newData):
assert len(newData) == len(self.data)
self.data = newData[:]
# 数据改变了,因此更新缓冲和窗口
dc = wx.BufferedDC(wx.ClientDC(self), self.buffer)
self.DrawGraph(dc)
# ====================================================================
# 事件响应函数
# ====================================================================
def OnSize(self, event):
"""响应窗口大小改变"""
# 每次窗口大小变换,都需要重新设置缓冲区大小,重绘窗口
self.InitBuffer()
def OnPaint(self, event):
"""响应Paint Event"""
wx.BufferedPaintDC(self, self.buffer)
class TestFrame(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self):
wx.Frame.__init__(self, None, title="Double Buffered Drawing", size=(480, 480))
self.plot = RadarGraph(self, "Sample Radar Plot", ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H'])
data = []
for d in self.plot.GetData():
data.append(random.randint(0, 75))
self.plot.SetData(data)
# 设置一个定时器,使数据随时间随机变化
self.timer = wx.Timer(self)
self.timer.Start(500) # 每 500ms 触发一次 EVT_TIMER
self.Bind(wx.EVT_TIMER, self.OnTimeout)
def OnTimeout(self, event):
data = []
for d in self.plot.GetData():
val = d + random.uniform(-5, 5)
if val < 0:
val = 0
if val > 110:
val = 110
data.append(val)
self.plot.SetData(data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = wx.App()
frm = TestFrame()
frm.Show()
app.MainLoop()
1.4. 相关参考
- https://docs.wxpython.org/
- wxpython 实现简易画板(1)
- wxPython in Action by Noel Rappin, Robin Dunn, Chapter 12
- 蓝奏云下载:https://wwe.lanzoup.com/b01oz824f,密码:g7np
- 书中的代码可以在这找到:https://github.com/freephys/wxPython-In-Action
本文作者:Wreng
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wreng/p/15761776.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。


 wxPython绘图实战——模拟雷达信号图
wxPython绘图实战——模拟雷达信号图

