Mysql优化
Mysql优化
版本
select @@version; select version();
5.7.23
一、准备Sql
1、创建表结构
t_test:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_test`; CREATE TABLE `t_test` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `user_level` int(1) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `type` int(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `y_score` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `t_score` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 1 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
user_id字段添加唯一索引;type字段添加普通索引
ALTER TABLE `db_cold`.`t_test` ADD UNIQUE INDEX `idx_user_id`(`user_id`) USING BTREE; ALTER TABLE `db_cold`.`t_test` ADD INDEX `idx_type`(`type`) USING BTREE;
t_type:
-- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for t_type -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_type`; CREATE TABLE `t_type` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `type_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 1 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of t_type -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `t_type` VALUES (1, '类型1');
2、使用存储过程插入1w条数据
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `proc_auto_insertdata`( IN `rownum` INT ) BEGIN DECLARE index_num INTEGER DEFAULT 1; WHILE index_num <= rownum DO -- insert INSERT INTO `db_cold`.`t_test` (`user_id`, `user_level`, `type`, `y_score`, `t_score` ) VALUES ( index_num + 1, IF(index_num <= rownum/2, 10, 20), CASE index_num%3 WHEN 0 THEN 0 WHEN 1 THEN 1 WHEN 2 THEN 2 ELSE 10 END, CONCAT( "Y", index_num + 10 ), CONCAT( "T", index_num + 100 ) ); SET index_num = index_num + 1; END WHILE; END
CALL proc_auto_insertdata ( 10000 ) > OK > 时间: 348.543s
二、使用Explain分析SQL
1、Explain的一些内容
参考 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008131735
示例:
mysql> EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type = 1\G; *************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1 select_type: SIMPLE table: t partitions: NULL type: ref possible_keys: idx_type key: idx_type key_len: 5 ref: const rows: 3334 filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
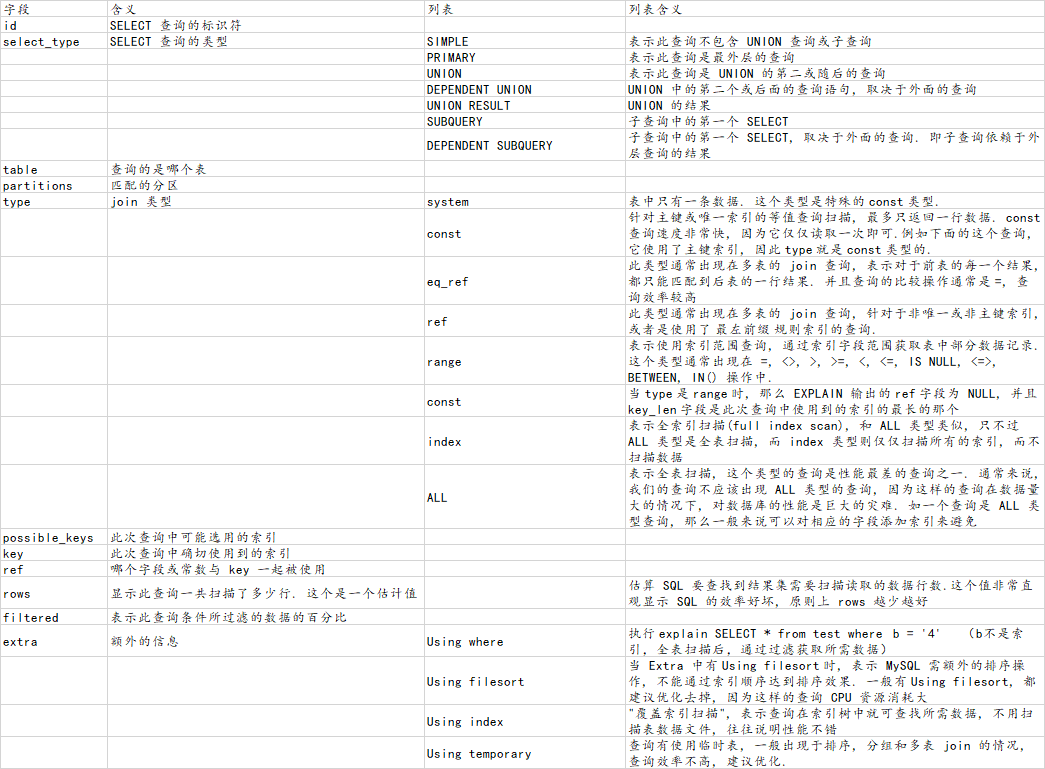
1.1 select_type
1.1.1
EXPLAIN select * from t_test t;
id select_type table 1 SIMPLE t
SIMPLE,单表查询。
1.1.2
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t1 WHERE t1.type = ( SELECT t2.id FROM t_test t2 WHERE t2.id = 1 );
id select_type table 1 PRIMARY t1 2 SUBQUERY t2
t1外层查询 对应的是PRIMARY,t2子查询对应的是SUBQUERY
1.1.3
EXPLAIN select * from t_test t1 where t1.id=1 UNION select * from t_test t2 where t2.id=1;
id select_type table 1 PRIMARY t1 2 UNION t2 UNION RESULT <union1,2>
UNION左边(第一个SELECT)对应PRIMARY,UNION右边(第二个以及之后的查询)对应UNION,最后合并的操作对应UNION RESULT
1.1.4
EXPLAIN select * from t_test t1 where t1.id in (select t2.id from t_test t2 where t2.id=1 UNION select t3.id from t_test t3 where t3.id=2 );
id select_type table 1 PRIMARY t1 2 DEPENDENT SUBQUERY t2 3 DEPENDENT UNION t3 UNION RESULT <union2,3>
in 查询的子查询(下划线部分)与1.1.3一致,对于整个查询而言,子查询的PRIMARY是整个查询的DEPENDENT SUBQUERY,子查询的UNION是整个查询的DEPENDENT UNION,DEPENDENT SUBQUERY和DEPENDENT UNION都依赖于外层的结果,原因在与Mysql优化器会自动优化上面的语句为 :
select * from t_test t1 where t1.id in (select t2.id from t_test t2 where t2.id=1 and t1.id=t2.id UNION select t3.id from t_test t3 where t3.id=2 and t1.id=t3.id);
也就说明了子查询的subquery和union确实依赖于外层的sql
1.2 type(参考 https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/explain-output.html#explain-join-types)
执行效率从低到高: all < index < range < index_subquery < unique_subquery < index_merge < ref_or_null < ref < eq_ref < const<system
1.2.1 null
MySQL不访问任何表或索引,直接返回结果
EXPLAIN select 1;
EXPLAIN select CURRENT_DATE();
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE No tables used
1.2.1 const/system
单条记录,系统会把匹配行中的其他列作为常数处理,如主键或唯一索引查询。
system是const的特例,表中只有一行数据。
主键索引:
EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id = 2;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t const PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 const 1 100.00
唯一索引:
EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id = 2;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t const idx_user_id idx_user_id 5 const 1 100.00
1.2.2 eq_ref
SQL_1_1:
EXPLAIN SELECT t1.* FROM t_test t1, t_type t2 WHERE 1 = 1 AND t1.id = t2.id;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t2 index PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 2 100.00 Using index 1 SIMPLE t1 eq_ref PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 db_cold.t2.id 1 100.00
SQL_1_2:相比SQL_1_1,多了t1 字段 type的过滤条件
EXPLAIN SELECT t1.* FROM t_test t1, t_type t2 WHERE 1 = 1 AND t1.id = t2.id AND t1.type = 1;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t2 index PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 2 100.00 Using index 1 SIMPLE t1 eq_ref PRIMARY,idx_type PRIMARY 4 db_cold.t2.id 1 32.91 Using where
SQL_2:
EXPLAIN SELECT t2.* FROM t_type t1, t_test t2 WHERE 1 = 1 AND t1.id = t2.id AND t2.type = 1;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t1 index PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 2 100.00 Using index 1 SIMPLE t2 eq_ref PRIMARY,idx_type PRIMARY 4 db_cold.t1.id 1 32.91 Using where
left join
SQL_3:
EXPLAIN SELECT t1.* FROM t_test t1 LEFT JOIN t_type t2 ON t1.id = t2.id WHERE 1 = 1;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t1 ALL 10130 100.00 1 SIMPLE t2 eq_ref PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 db_cold.t1.id 1 100.00 Using index
SQL_4:
EXPLAIN SELECT t1.* FROM t_test t1 LEFT JOIN t_type t2 ON t1.id = t2.id WHERE 1 = 1 AND t1.type = 3;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t1 ref idx_type idx_type 5 const 1 100.00 1 SIMPLE t2 eq_ref PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 db_cold.t1.id 1 100.00 Using index
总结:
以下面的执行计划为例
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE t1 ref idx_type idx_type 5 const 1 100.00
1 SIMPLE t2 eq_ref PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 db_cold.t1.id 1 100.00 Using index
前面t1的每一行数据,t2(type==eq_ref)表中都有唯一的一行记录与之匹配,t1和t2链接规则为主键索引或者不为null的唯一索引。
1.2.3 ref
单表:
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE t.type = 1;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t ref idx_type idx_type 5 const 3334 100.00
多表:
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t1 LEFT JOIN t_type t2 ON t1.type = t2.id WHERE 1 = 1 AND t1.type = 1;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t1 ref idx_type idx_type 5 const 3334 100.00 1 SIMPLE t2 const PRIMARY PRIMARY 4 const 1 100.00
总结:type为 ref 表示 匹配当前表中的多行数据
1.2.2 index
最典型的就是查询的列是索引列
EXPLAIN SELECT t.type FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t index idx_type 5 10130 100.00 Using index
1.2.1 all
全表扫描
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t ALL 10130 100.00
1.2.1 range(封闭区间检索,只使用<或者>不会使用Range)
唯一索引:
BETWEEN(range)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1 AND t.user_id BETWEEN 1 AND 2;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t range idx_user_id idx_user_id 5 1 100.00 Using index condition
IN(range)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1 AND t.user_id IN ( 1, 2 );
1 SIMPLE t range idx_user_id idx_user_id 5 2 100.00 Using index condition
< >(range)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1 AND t.user_id > 10 AND t.user_id < 100;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t range idx_user_id idx_user_id 5 89 100.00 Using index condition
普通索引:
BETWEEN(all)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1 AND t.type BETWEEN 1 AND 2;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t ALL idx_type 10130 65.81 Using where
IN(all)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1 AND t.type IN ( 1, 2 );
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t ALL idx_type 10130 65.81 Using where
< >(range)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1 AND t.type > 10 AND t.type < 100;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t range idx_type idx_type 5 1 100.00 Using index condition
非主键 开区间检索:> 或者<
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_test t WHERE 1 = 1 AND t.user_id > 10;
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra 1 SIMPLE t ALL idx_user_id 10130 98.63 Using where
主键索引:
type SQL
const: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id = 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id > 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id >= 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id < 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id <= 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id <> 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id != 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and (t.id = 1 or t.id = 2); range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id BETWEEN 1 and 2; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id like '%1'; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id like '1%'; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id like '%1%'; const: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id in (2); range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id not in (1); NULL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id is null; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id is not null;
普通索引
type SQL
ref: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type = 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type > 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type >= 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type < 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type <= 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type <> 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type != 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and (t.type = 1 or t.type = 2); ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type BETWEEN 1 and 2; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type like '%1'; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type like '1%'; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type like '%1%'; ref: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type in (2); ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type not in (1); ref: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type is null; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.type is not null;
唯一索引
type SQL
NULL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id = 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id > 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id >= 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id < 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id <= 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id <> 1; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id != 1; range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and (t.user_id = 1 or t.user_id = 2); range: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id BETWEEN 1 and 2; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id like '%1'; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id like '1%'; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id like '%1%'; const: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id in (2); ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id not in (1); ref: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.user_id is null; ALL: EXPLAIN select * from t_test t where 1=1 and t.id is not null;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号