高性能计算实验报告
高性能计算实验报告
第一部分 实验介绍
1.1 实验基础
需要使用slurm系统进行太原国家高算的资源调度,使用mpi进行并行计算。
1.2 实验目的及其意义
本实验将利用mpi实现一个大数据量的排序算法(PSRS)。
第二部分 算法分析
2.1 算法介绍:正则采样排序PSRS的MPI算法
如果注意到一个好的串行排序算法的时间复杂度为O那么,容易证得上述PSRS算法的时间复杂度为O。
PS:正则采样,就是从原数组中尽量等间隔的取出采样点。
2.2 算法流程
假设有p个进程,有N条数据需要排序
2.2.1均匀划分
将N个数据平均分为p段,其中i号进程处理(i*N)/p到((i+1)*N)/p-1行(行号从0开始计算)。
例如:18个数据划分为3个进程
#define BLOCK_LOW(my_rank, comm_sz, T) ((my_rank)*(T)/(comm_sz)) #define BLOCK_SIZE(my_rank, comm_sz, T) (BLOCK_HIGH(my_rank,comm_sz,T) - BLOCK_LOW(my_rank,comm_sz,T) + 1) // 打开文件 ifstream fin(fileName, ios::binary); // 计算各进程读取文件的起始行号和大小 unsigned long myDataStart = BLOCK_LOW(my_rank, comm_sz, dataLength); unsigned long myDataLength = BLOCK_SIZE(my_rank, comm_sz, dataLength); // 将文件指针移动到起始行号 fin.seekg((myDataStart)*sizeof(unsigned long), ios::beg); unsigned long *myData = new unsigned long[myDataLength]; // 读取数据 for(unsigned long i=0; i<myDataLength; i++) fin.read((char*)&myData[i], sizeof(unsigned long)); fin.close();
PS:本人并未在源代码中设计读取部分,故这部分代码引用Henry_Liu_的代码
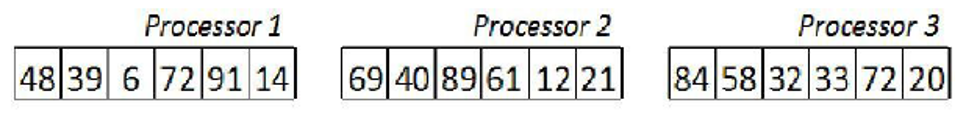
2.2.2局部排序
各个进程对各自的数据进行排序
例如:下图各数据对各自有序
int cmp(const void* a, const void* b) { if (*(int*)a < *(int*)b) return -1; if (*(int*)a > *(int*)b) return 1; else return 0; } void phase1(int* array, int N, int startIndex, int subArraySize, int* pivots, int p) { // 对子数组进行局部排序 qsort(array + startIndex, subArraySize, sizeof(array[0]), cmp);
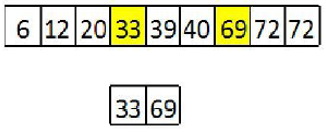
2.2.3选取样本(正则采样)
p个进程中,每个进程需要选取出p个样本(regular samples),选取规则为(i*dataLength)/p , dataLength是进程各自的数据长度。
PS:这时候选取的样本也是有序的。
// 正则采样 for (i = 0; i < p; i++) { pivots[i] = array[startIndex + (i * (N / (p * p)))]; } return;
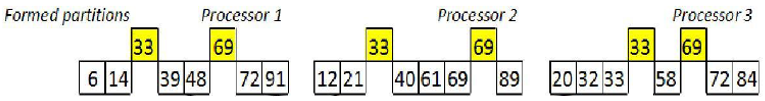
2.2.4样本排序
用一个进程对p个进程的p*p个样本排序,此时样本都是局部有序的,使用归并能减少时间复杂度。
例如:processor 1将9个样本排序
//收集消息,根进程在它的接受缓冲区中包含所有进程的发送缓冲区的连接。 MPI_Gather(pivots, p, MPI_INT, collectedPivots, p, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD); if (myId == 0) { qsort(collectedPivots, p * p, sizeof(pivots[0]), cmp); //对正则采样的样本进行排序 // 采样排序后进行主元的选择 for (i = 0; i < (p - 1); i++) { phase2Pivots[i] = collectedPivots[(((i + 1) * p) + (p / 2)) - 1]; } }
2.2.5 主元选取
一个进程从排好序的样本中选取p-1个主元。选取方法是i*p。
// 采样排序后进行主元的选择 for (i = 0; i < (p - 1); i++) { phase2Pivots[i] = collectedPivots[(((i + 1) * p) + (p / 2)) - 1];
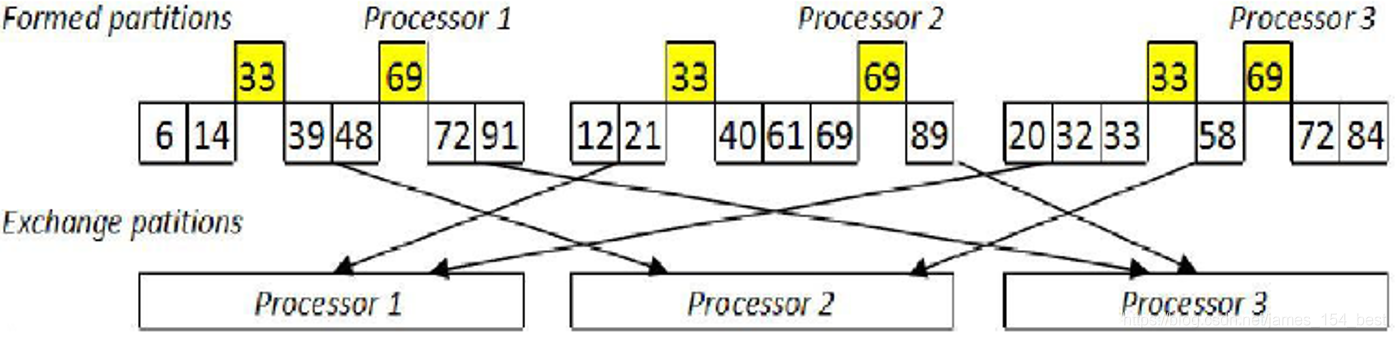
2.2.6 主元划分
p个进程的数据按照p-1个主元划分为p段
例如:3个进程的数据都被2个主元划分为3段
在具体的实现中,0号进程要将p-1个主元广播到其他进程。然后所有进程按照主元划分。
//发送广播 MPI_Bcast(phase2Pivots, p - 1, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD); // 进行主元划分,并计算划分部分的大小 for (i = 0; i < subArraySize; i++) { if (array[startIndex + i] > phase2Pivots[index]) { //如果当前位置的数字大小超过主元位置,则进行下一个划分 index += 1; } if (index == p) { //最后一次划分,子数组总长减掉当前位置即可得到最后一个子数组划分的大小 partitionSizes[p - 1] = subArraySize - i + 1; break; } partitionSizes[index]++; //划分大小自增 } free(collectedPivots); free(phase2Pivots); return; } void phase3(int* array, int startIndex, int* partitionSizes, int** newPartitions, int* newPartitionSizes, int p) { int totalSize = 0; int* sendDisp = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); int* recvDisp = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); // 全局到全局的发送,每个进程可以向每个接收者发送数目不同的数据. MPI_Alltoall(partitionSizes, 1, MPI_INT, newPartitionSizes, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_COMM_WORLD); // 计算划分的总大小,并给新划分分配空间 for (i = 0; i < p; i++) { totalSize += newPartitionSizes[i]; } *newPartitions = (int*)malloc(totalSize * sizeof(int)); // 在发送划分之前计算相对于sendbuf的位移,此位移处存放着输出到进程的数据 sendDisp[0] = 0; recvDisp[0] = 0; //计算相对于recvbuf的位移,此位移处存放着从进程接受到的数据 for (i = 1; i < p; i++) { sendDisp[i] = partitionSizes[i - 1] + sendDisp[i - 1]; recvDisp[i] = newPartitionSizes[i - 1] + recvDisp[i - 1]; }
2.2.7 全局交换
进程i将第j段发送给进程j。也就是每个进程都要给其它所有进程发送数据段,并且还要从其它所有进程中接收数据段,所以称为全局交换。
例如:
//发送数据,实现n次点对点通信 MPI_Alltoallv(&(array[startIndex]), partitionSizes, sendDisp, MPI_INT, *newPartitions, newPartitionSizes, recvDisp, MPI_INT, MPI_COMM_WORLD); free(sendDisp); free(recvDisp); return; } void phase4(int* partitions, int* partitionSizes, int p, int myId, int* array) { int* sortedSubList; int* recvDisp, * indexes, * partitionEnds, * subListSizes, totalListSize; indexes = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); partitionEnds = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); indexes[0] = 0; totalListSize = partitionSizes[0]; for (i = 1; i < p; i++) { totalListSize += partitionSizes[i]; indexes[i] = indexes[i - 1] + partitionSizes[i - 1]; partitionEnds[i - 1] = indexes[i]; } partitionEnds[p - 1] = totalListSize; sortedSubList = (int*)malloc(totalListSize * sizeof(int)); subListSizes = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); recvDisp = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int));
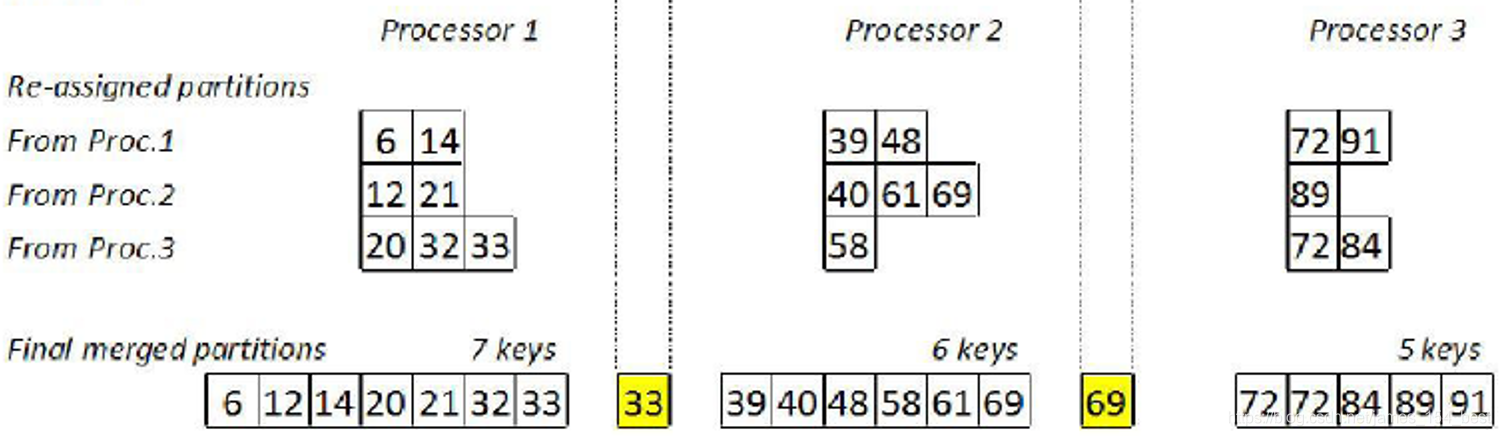
2.2.8 归并排序
各处理器对接收到的p个数据段进行归并,因为p个数据段已经是局部有序的。
例如:
// 归并排序 for (i = 0; i < totalListSize; i++) { int lowest = INT_MAX; int ind = -1; for (j = 0; j < p; j++) { if ((indexes[j] < partitionEnds[j]) && (partitions[indexes[j]] < lowest)) { lowest = partitions[indexes[j]]; ind = j; } } sortedSubList[i] = lowest; indexes[ind] += 1; }
源代码
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <limits.h> #include <assert.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <unistd.h> #include "mpi.h" int i, j, k; int N = 36; int cmp(const void* a, const void* b) { if (*(int*)a < *(int*)b) return -1; if (*(int*)a > *(int*)b) return 1; else return 0; } void phase1(int* array, int N, int startIndex, int subArraySize, int* pivots, int p) { // 对子数组进行局部排序 qsort(array + startIndex, subArraySize, sizeof(array[0]), cmp); // 正则采样 for (i = 0; i < p; i++) { pivots[i] = array[startIndex + (i * (N / (p * p)))]; } return; } void phase2(int* array, int startIndex, int subArraySize, int* pivots, int* partitionSizes, int p, int myId) { int* collectedPivots = (int*)malloc(p * p * sizeof(pivots[0])); int* phase2Pivots = (int*)malloc((p - 1) * sizeof(pivots[0])); //主元 int index = 0; //收集消息,根进程在它的接受缓冲区中包含所有进程的发送缓冲区的连接。 MPI_Gather(pivots, p, MPI_INT, collectedPivots, p, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD); if (myId == 0) { qsort(collectedPivots, p * p, sizeof(pivots[0]), cmp); //对正则采样的样本进行排序 // 采样排序后进行主元的选择 for (i = 0; i < (p - 1); i++) { phase2Pivots[i] = collectedPivots[(((i + 1) * p) + (p / 2)) - 1]; } } //发送广播 MPI_Bcast(phase2Pivots, p - 1, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD); // 进行主元划分,并计算划分部分的大小 for (i = 0; i < subArraySize; i++) { if (array[startIndex + i] > phase2Pivots[index]) { //如果当前位置的数字大小超过主元位置,则进行下一个划分 index += 1; } if (index == p) { //最后一次划分,子数组总长减掉当前位置即可得到最后一个子数组划分的大小 partitionSizes[p - 1] = subArraySize - i + 1; break; } partitionSizes[index]++; //划分大小自增 } free(collectedPivots); free(phase2Pivots); return; } void phase3(int* array, int startIndex, int* partitionSizes, int** newPartitions, int* newPartitionSizes, int p) { int totalSize = 0; int* sendDisp = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); int* recvDisp = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); // 全局到全局的发送,每个进程可以向每个接收者发送数目不同的数据. MPI_Alltoall(partitionSizes, 1, MPI_INT, newPartitionSizes, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_COMM_WORLD); // 计算划分的总大小,并给新划分分配空间 for (i = 0; i < p; i++) { totalSize += newPartitionSizes[i]; } *newPartitions = (int*)malloc(totalSize * sizeof(int)); // 在发送划分之前计算相对于sendbuf的位移,此位移处存放着输出到进程的数据 sendDisp[0] = 0; recvDisp[0] = 0; //计算相对于recvbuf的位移,此位移处存放着从进程接受到的数据 for (i = 1; i < p; i++) { sendDisp[i] = partitionSizes[i - 1] + sendDisp[i - 1]; recvDisp[i] = newPartitionSizes[i - 1] + recvDisp[i - 1]; } //发送数据,实现n次点对点通信 MPI_Alltoallv(&(array[startIndex]), partitionSizes, sendDisp, MPI_INT, *newPartitions, newPartitionSizes, recvDisp, MPI_INT, MPI_COMM_WORLD); free(sendDisp); free(recvDisp); return; } void phase4(int* partitions, int* partitionSizes, int p, int myId, int* array) { int* sortedSubList; int* recvDisp, * indexes, * partitionEnds, * subListSizes, totalListSize; indexes = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); partitionEnds = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); indexes[0] = 0; totalListSize = partitionSizes[0]; for (i = 1; i < p; i++) { totalListSize += partitionSizes[i]; indexes[i] = indexes[i - 1] + partitionSizes[i - 1]; partitionEnds[i - 1] = indexes[i]; } partitionEnds[p - 1] = totalListSize; sortedSubList = (int*)malloc(totalListSize * sizeof(int)); subListSizes = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); recvDisp = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); // 归并排序 for (i = 0; i < totalListSize; i++) { int lowest = INT_MAX; int ind = -1; for (j = 0; j < p; j++) { if ((indexes[j] < partitionEnds[j]) && (partitions[indexes[j]] < lowest)) { lowest = partitions[indexes[j]]; ind = j; } } sortedSubList[i] = lowest; indexes[ind] += 1; } // 发送各子列表的大小回根进程中 MPI_Gather(&totalListSize, 1, MPI_INT, subListSizes, 1, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD); // 计算根进程上的相对于recvbuf的偏移量 if (myId == 0) { recvDisp[0] = 0; for (i = 1; i < p; i++) { recvDisp[i] = subListSizes[i - 1] + recvDisp[i - 1]; } } //发送各排好序的子列表回根进程中 MPI_Gatherv(sortedSubList, totalListSize, MPI_INT, array, subListSizes, recvDisp, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD); free(partitionEnds); free(sortedSubList); free(indexes); free(subListSizes); free(recvDisp); return; } //PSRS排序函数,调用了4个过程函数 void p srs_mpi(int* array, int N) { int p, myId, * partitionSizes, * newPartitionSizes, nameLength; int subArraySize, startIndex, endIndex, * pivots, * newPartitions; char processorName[MPI_MAX_PROCESSOR_NAME]; MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &p); MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myId); MPI_Get_processor_name(processorName, &nameLength); printf("Process %d is on %s\n", myId, processorName); pivots = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); partitionSizes = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); newPartitionSizes = (int*)malloc(p * sizeof(int)); for (k = 0; k < p; k++) { partitionSizes[k] = 0; } // 获取起始位置和子数组大小 startIndex = myId * N / p; if (p == (myId + 1)) { endIndex = N; }V else { endIndex = (myId + 1) * N / p; } subArraySize = endIndex - startIndex; MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD); //调用各阶段函数 phase1(array, N, startIndex, subArraySize, pivots, p); if (p > 1) { phase2(array, startIndex, subArraySize, pivots, partitionSizes, p, myId); phase3(array, startIndex, partitionSizes, &newPartitions, newPartitionSizes, p); phase4(newPartitions, newPartitionSizes, p, myId, array); } if (myId == 0) for (k = 0; k < N; k++) { printf("%d ", array[k]); } printf("\n"); if (p > 1) { free(newPartitions); } free(partitionSizes); free(newPartitionSizes); free(pivots); free(array); MPI_Finalize(); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int* array; array = (int*)malloc(N * sizeof(int)); srand(100); for (k = 0; k < N; k++) { array[k] = rand() % 100; } MPI_Init(&argc, &argv); //MPI初始化 psrs_mpi(array, N); //调用PSRS算法进行并行排序 return 0; }
第三部分 实现
3.1 slurm资源调度系统
#SBATCH -o PSRS.log #SBATCH -e PSRS.err #SBATCH --output=PSRS.out #SBATCH -N 2 -n 32 #SBATCH --partition=ty_public echo Time is `date` echo Directory is $PWD echo This job runs on the following nodes: echo $SLURM_JOB_NODELIST echo This job has allocated $SLURM_JOB_CPUS_PER_NODE cpu cores. # load the environment module purge #clean the environment module load compiler/intel/2017.5.239 module load mpi/hpcx/2.7.4/intel-2017.5.239 module load compiler/devtoolset/7.3.1 export I_MPI_PMI_LIBRARY=/opt/gridview/slurm/lib/libpmi.so mpicc -g -pthread -o PSRS PSRS.cpp MPIRUN=mpirun #Intel mpi and Open MPI #MPIRUN=mpiexec #MPICH MPIOPT="-env I_MPI_FABRICS shm:ofa" #Intel MPI 2018 #MPIOPT="-env I_MPI_FABRICS shm:ofi" #Intel MPI 2019 #MPIOPT="-\-mca plm_rsh_agent ssh -\-mca btl self,openib,sm" #Open MPI #MPIOPT="-iface ib0" #MPICH3 MPIOPT= $MPIRUN $MPIOPT ./PSRS
3.2 作业提交及其结果
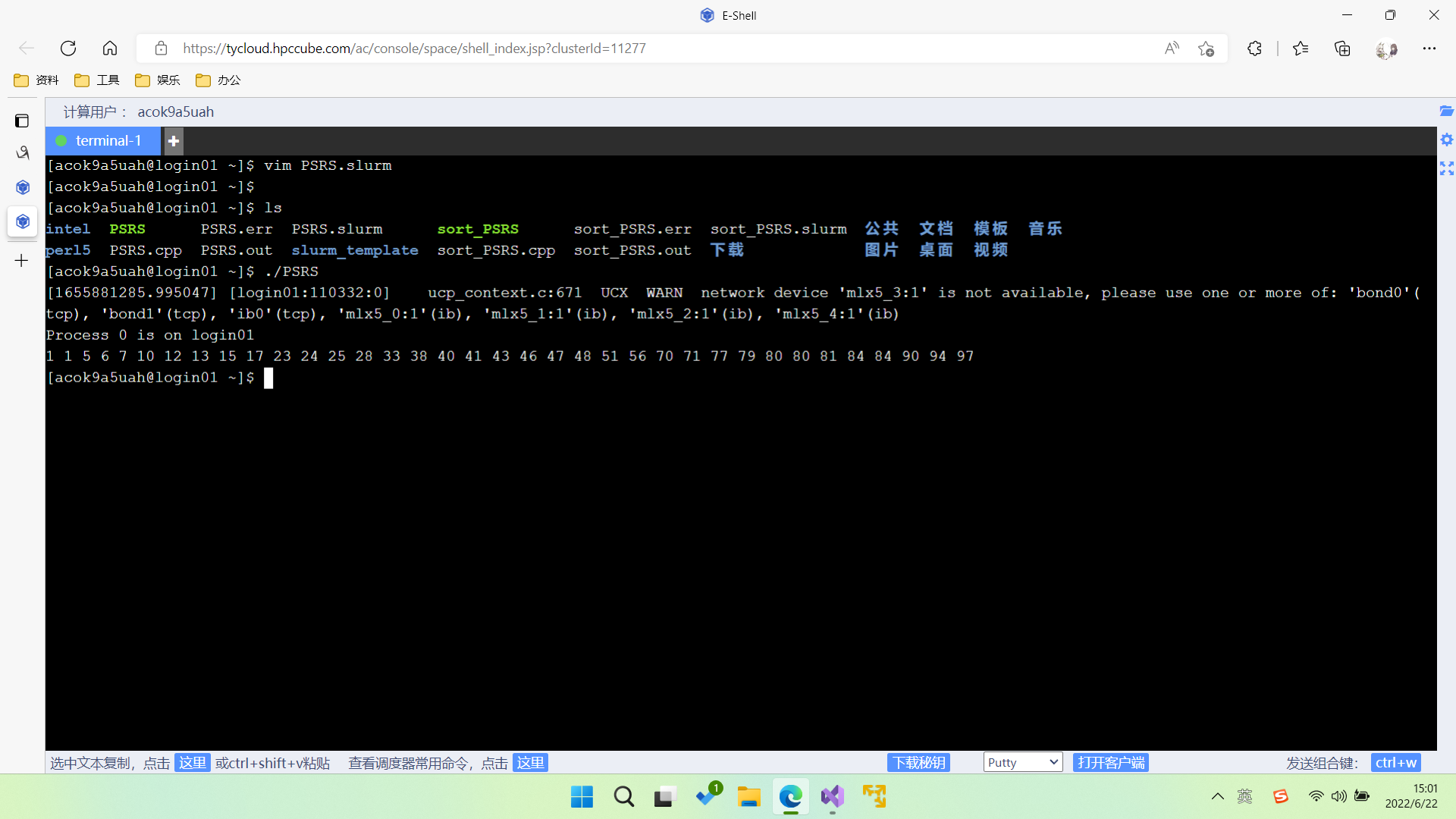
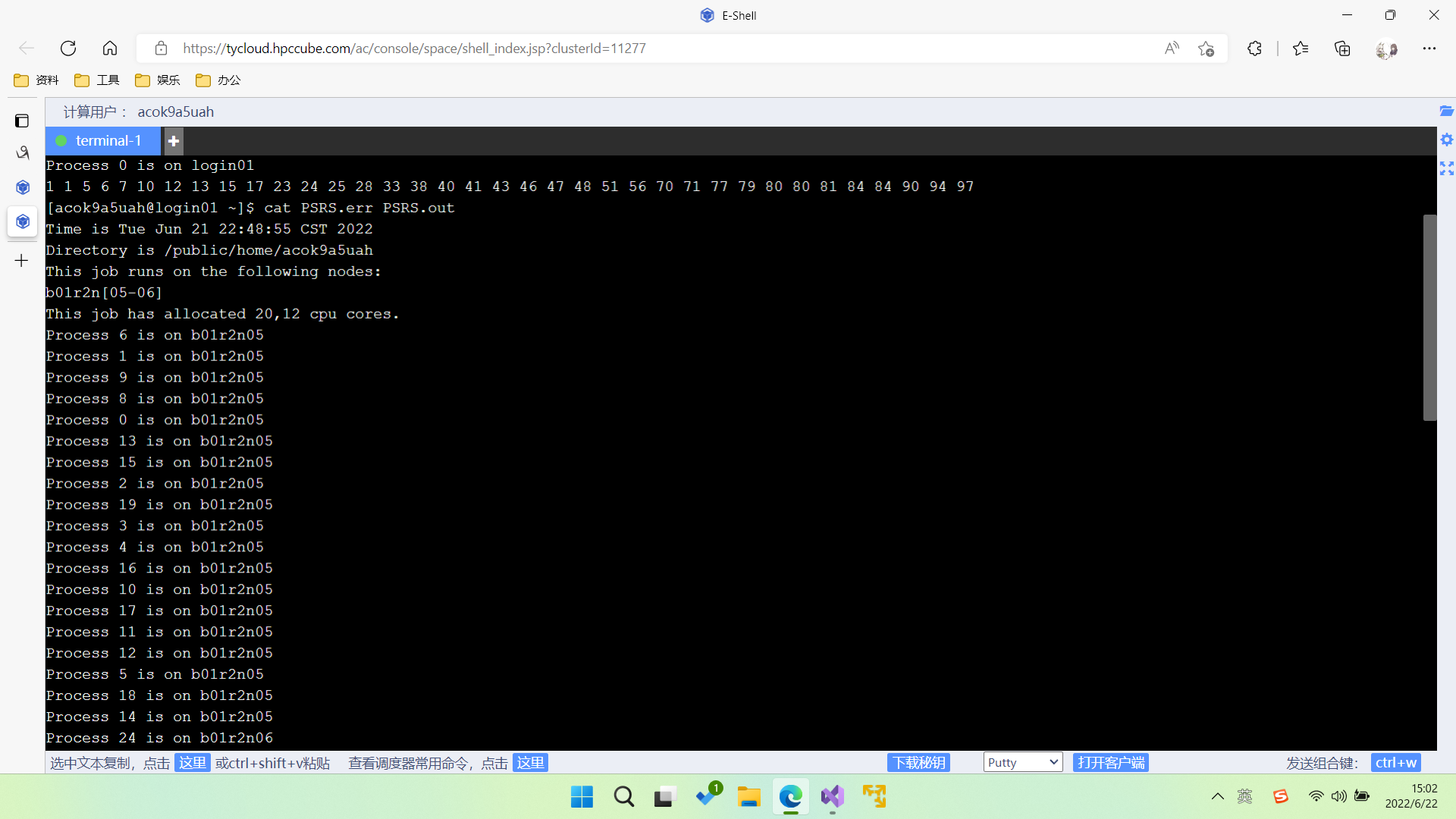
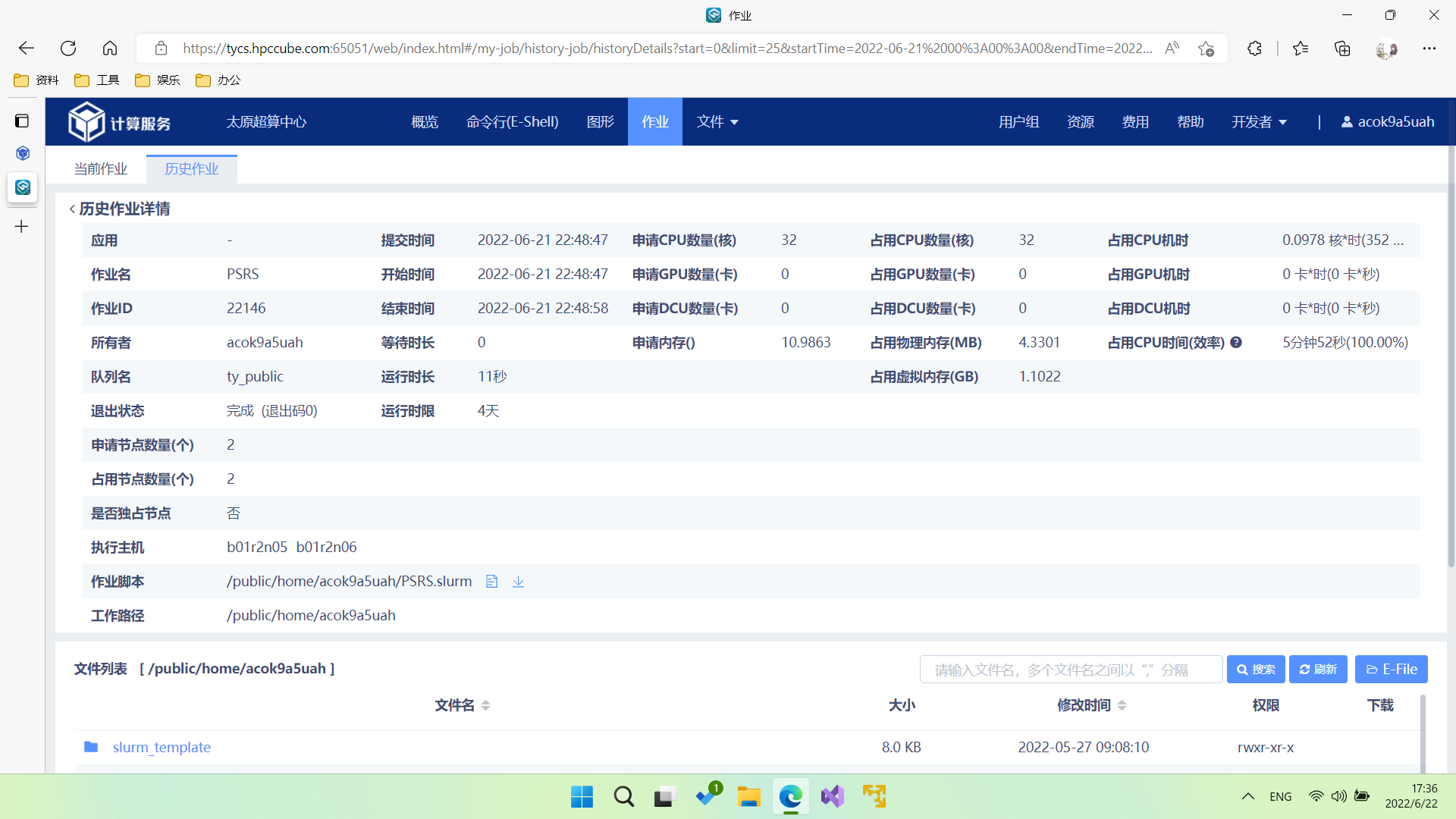
3.3 实验过程分析
本实验经历了一下几个过程
3.4 实验讨论
在实验开始阶段,主要问题停留在mpi编程上,主要通过bilibili的网课进行解决。后来mpi代码一直不能进行提交,我使用老师给的模板和学长给的中科大模板,进行修改终于使得代码能够提交到高算平台。我发现我的代码一直报错,我并不会制造数据,测试自己的代码正确性,就直接去掉了本应该设计的数据读入部分,转而使用给定数字,虽然这可能会使得代码的泛用性降低,但是却使得编程和测试难度下降。
3.5 实验不足及其算法缺陷
3.5.1 实验不足
1.未使用大量数据进行测试。
2.未设计数据快速读取部分。
3.5.2 算法缺陷
在进行主元划分时时可能会引起不均匀性,即位于某两个主元之间的元素可能要多一些(多于个)。我们可以证明,在算法中进行到第六步全局交换时,可能会有某一个处理器中数据达到个;这样引起的直接后果是处理器负载不均匀,那么在归并排序中可能会引起排序时间的不均匀。
3.5.3 未知错误
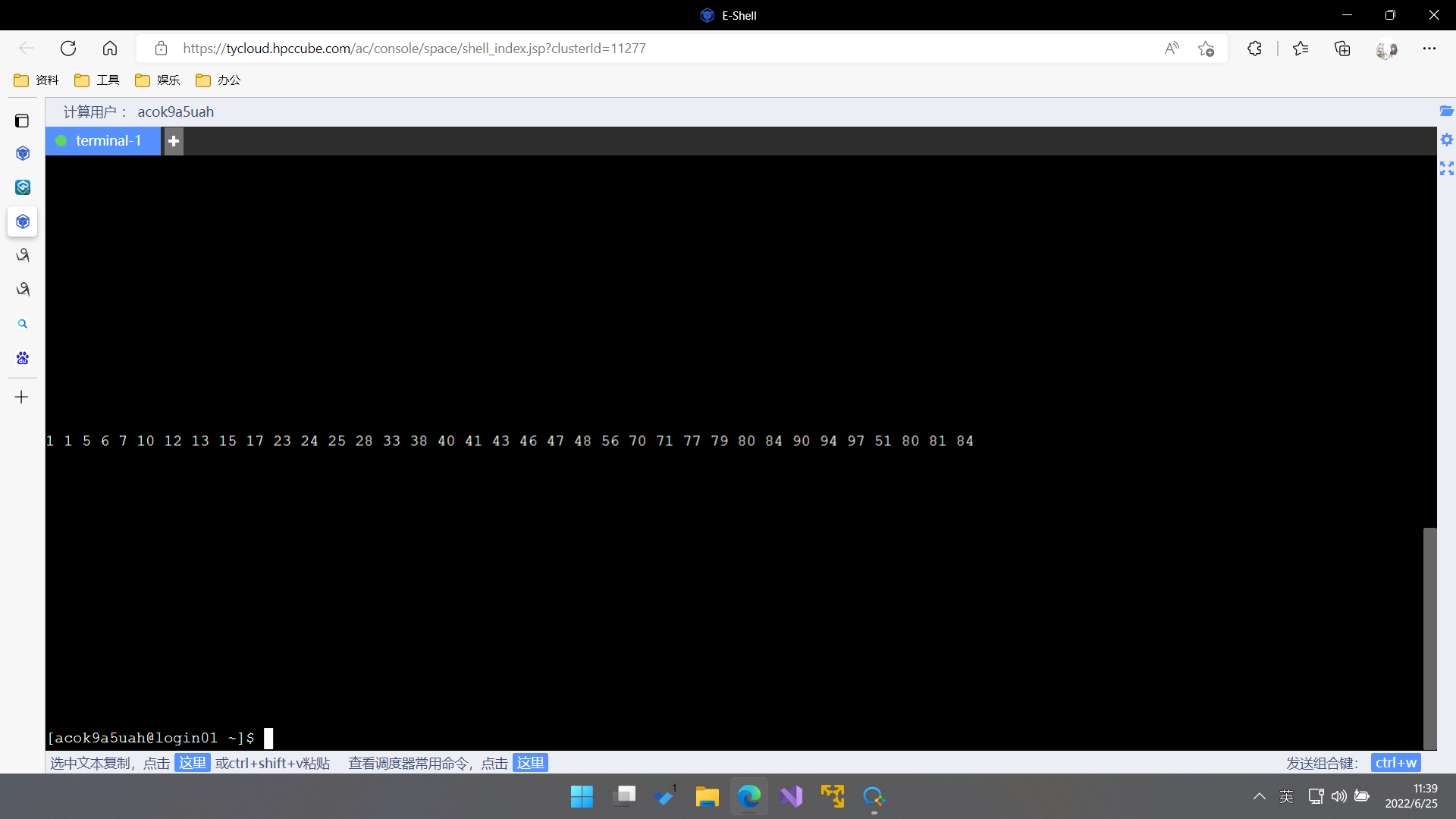
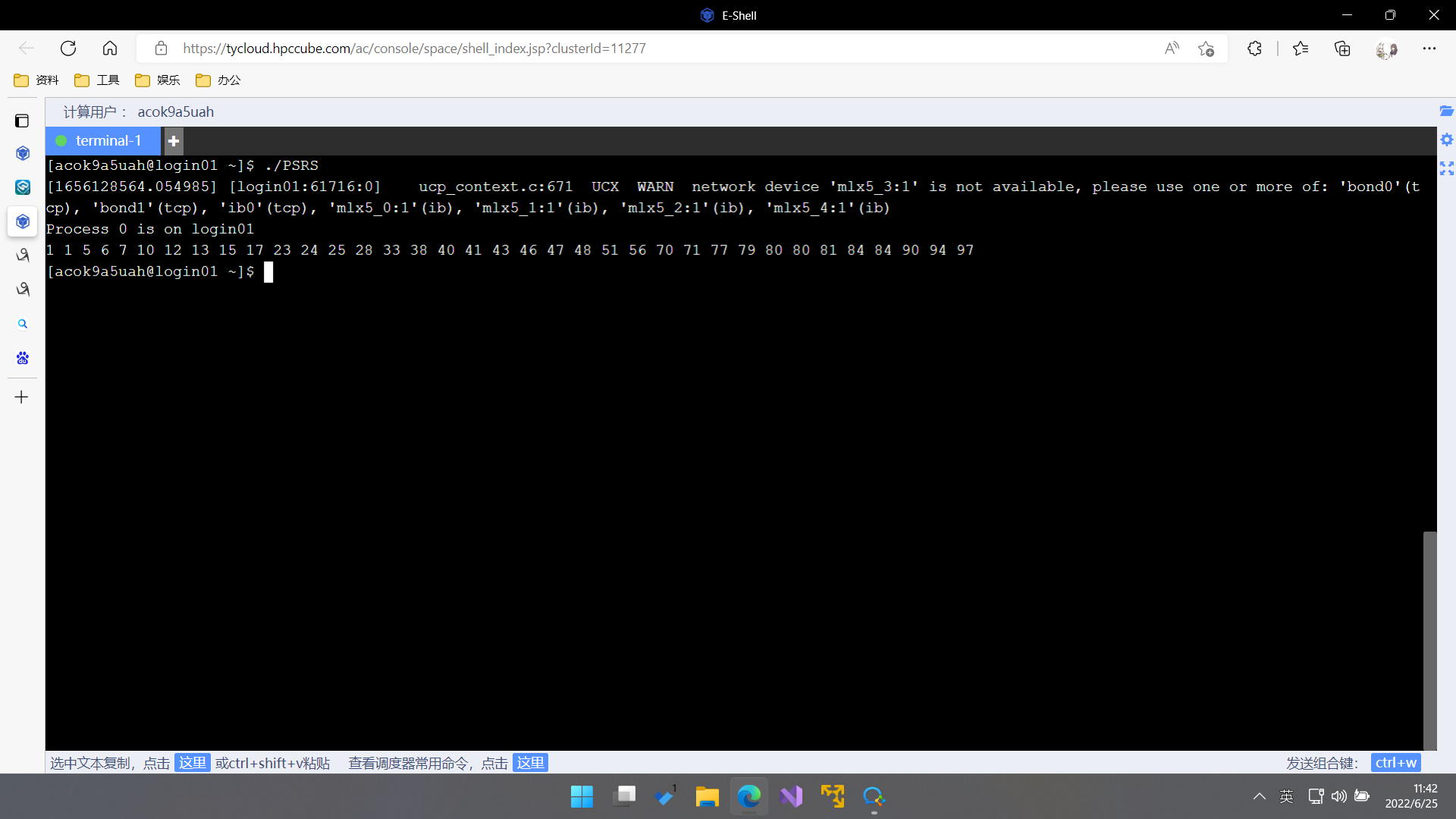
编译后cat PSRS.out文件的输出,可以发现有一组数据虽然局部有序但未实现归并排序。
使用./PSRS输出,结果正常
再次提交编译,问题依旧存在。







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结