Spark算子、累加器、blockmanager
Spark算子
算子分为转换算子(transformation)和行为算子(action)
转换算子:转换算子是懒执行的,需要由Action算子触发执行
行为算子:每个Action算子会触发一个Job
Spark的程序的层级划分:Application --> Job --> Stage --> Task
两者的区分:看算子的返回值是否还是RDD,如果是由一个RDD转换成另一个RDD,则该算子是转换算子
如果由一个RDD得到其他类型(非RDD类型或者没有返回值),则该算子是行为算子

1、map算子
package com.core
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object Demo03map {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf()
conf.setAppName("Demo03map")
conf.setMaster("local")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
/**
* 在使用Spark处理数据时可以大体分为三个步骤:
* 1、加载数据并构建成RDD
* 2、对RDD进行各种各样的转换操作,即调用转换算子
* 3、使用Action算子触发Spark任务的执行
*/
/**
* map算子:转换算子
* 需要接受一个函数f
* 函数f:参数的个数只有一个,类型为RDD中数据的类型 => 返回值类型自己定义
* 可以将函数f作用在RDD中的每一条数据上,需要函数f必须有返回值,最终会得到一个新的RDD
* 传入一条数据得到一条数据
*/
val linesRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/words.txt")
linesRDD.map(line => {
println("执行了map方法")
line
}).foreach(println)
List(1,2,3,4).map(line=>{
println("List的map方法不需要什么Action算子触发")
line
})
while(true){
}
}
}
2、flatmap算子
package com.core
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object Demo04flatMap {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
/**
* flatMap:转换算子
* 同map算子类似,只不过所接受的函数f需要返回一个可以遍历的类型
* 最终会将函数f的返回值进行展开(扁平化处理),得到一个新的RDD
* 传入一条数据 会得到 多条数据
*/
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf()
conf.setAppName("Demo04flatMap")
conf.setMaster("local")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
// 另一种构建RDD的方式:基于Scala本地的集合例如List
val intRDD: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5))
intRDD.foreach(println)
val strRDD: RDD[String] = sc.parallelize(List("java,java,scala", "scala,scala,python", "python,python,python"))
strRDD.flatMap(_.split(",")).foreach(println)
}
}
3、filter算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo05filter { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * filter:转换算子 * 用于过滤数据,需要接受一个函数f * 函数f:参数只有一个,类型为RDD中每一条数据的类型 => 返回值类型必须为Boolean * 最终会基于函数f返回的Boolean值进行过滤,得到一个新的RDD * 如果函数f返回的Boolean为true则保留数据 * 如果函数f返回的Boolean为false则过滤数据 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo05filter") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val seqRDD: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(1 to 100, 4) println(seqRDD.getNumPartitions) // getNumPartitions并不是算子,它只是RDD的一个属性 // seqRDD.foreach(println) // 将奇数过滤出来 seqRDD.filter(i => i % 2 == 1).foreach(println) // 将偶数过滤出来 seqRDD.filter(i => i % 2 == 0).foreach(println) } }
4、sample算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo06sample { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * sample:转换算子 * 用于对数据进行取样 * 总共有三个参数: * withReplacement:有无放回 * fraction:抽样的比例(这个比例并不是精确的,因为抽样是随机的) * seed:随机数种子 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo06sample") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") stuRDD.sample(withReplacement = false, 0.1).foreach(println) // 如果想让每次抽样的数据都一样,则可以将seed进行固定 stuRDD.sample(withReplacement = false, 0.01, 10).foreach(println) } }
5、mapvalues算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo07mapValues { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * mapValues:转换算子 * 同map类似,只不过mapValues需要对KV格式的RDD的Value进行遍历处理 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo07mapValues") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val kvRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = sc.parallelize(List("k1" -> 1, "k2" -> 2, "k3" -> 3)) // 对每个Key对应的Value进行平方 kvRDD.mapValues(i => i * i).foreach(println) // 使用map方法实现 kvRDD.map(kv => (kv._1, kv._2 * kv._2)).foreach(println) } }
6、join算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo08join { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * join:转换算子 * 需要作用在两个KV格式的RDD上,会将相同的Key的数据关联在一起 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo08join") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) // 加载学生数据,并转换成KV格式,以ID作为Key,其他数据作为Value val stuKVRDD: RDD[(String, String)] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt").map(line => { val id: String = line.split(",")(0) // split 指定分割符切分字符串得到Array // mkString 指定拼接符将Array转换成字符串 val values: String = line.split(",").tail.mkString("|")//tail:表示数组除去 head 后的数组 (id, values) }) // 加载分数数据,并转换成KV格式,以ID作为Key,其他数据作为Value val scoKVRDD: RDD[(String, String)] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/score.txt").map(line => { val id: String = line.split(",")(0) val values: String = line.split(",").tail.mkString("|") (id, values) }) // join : 内连接 val joinRDD1: RDD[(String, (String, String))] = stuKVRDD.join(scoKVRDD) // joinRDD1.foreach(println) // stuKVRDD.leftOuterJoin(scoKVRDD).foreach(println) // stuKVRDD.rightOuterJoin(scoKVRDD).foreach(println) stuKVRDD.fullOuterJoin(scoKVRDD).foreach(println) } }
7、union算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo09union { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { // union:转换算子,用于将两个相类型的RDD进行连接 val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo09union") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") val sample01RDD: RDD[String] = stuRDD.sample(withReplacement = false, 0.01, 1) val sample02RDD: RDD[String] = stuRDD.sample(withReplacement = false, 0.01, 1) println(s"sample01RDD的分区数:${sample01RDD.getNumPartitions}") println(s"sample02RDD的分区数:${sample02RDD.getNumPartitions}") // union 操作最终得到的RDD的分区数等于两个RDD分区数之和 println(s"union后的分区数:${sample01RDD.union(sample02RDD).getNumPartitions}") val intRDD: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) // sample01RDD.union(intRDD) // 两个RDD的类型不一致无法进行union // union 等同于SQL中的union all sample01RDD.union(sample02RDD).foreach(println) // 如果要进行去重 即等同于SQL中的union 则可以在 union后再进行distinct sample01RDD.union(sample02RDD).distinct().foreach(println) } }
8、groupBy算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo10groupBy { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * groupBy:按照某个字段进行分组 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo10groupBy") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") // 统计班级人数 stuRDD.groupBy(s => s.split(",")(4)).map(kv => s"${kv._1},${kv._2.size}").foreach(println) } }
9、groupByKey算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo11groupByKey { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * groupByKey:转换算子,需要作用在KV格式的RDD上 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo11groupByKey") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") // 使用groupByKey统计班级人数 // 将学生数据变成KV格式的RDD,以班级作为Key,1作为Value val clazzKVRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = stuRDD.map(s => (s.split(",")(4), 1)) val grpRDD: RDD[(String, Iterable[Int])] = clazzKVRDD.groupByKey() grpRDD.map(kv => s"${kv._1},${kv._2.size}").foreach(println) } }
10、reduceByKey算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD object Demo12reduceByKey { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * reduceByKey:转换算子,需要作用在KV格式的RDD上,不仅能实现分组,还能实现聚合 * 需要接受一个函数f * 函数f:两个参数,参数的类型同RDD的Value的类型一致,最终需要返回同RDD的Value的类型一致值 * 实际上函数f可以看成一个聚合函数 * 常见的聚合函数(操作):max、min、sum、count、avg * reduceByKey可以实现Map端的预聚合,类似MR中的Combiner * 并不是所有的操作都能使用预聚合,例如avg就无法实现 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo11groupByKey") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") // 使用reduceByKey统计班级人数 // 将学生数据变成KV格式的RDD,以班级作为Key,1作为Value val clazzKVRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = stuRDD.map(s => (s.split(",")(4), 1)) clazzKVRDD.reduceByKey((i1: Int, i2: Int) => i1 + i2).foreach(println) // 简写形式 clazzKVRDD.reduceByKey((i1, i2) => i1 + i2).foreach(println) clazzKVRDD.reduceByKey(_ + _).foreach(println) } }
reduceByKey和groupByKey的区别
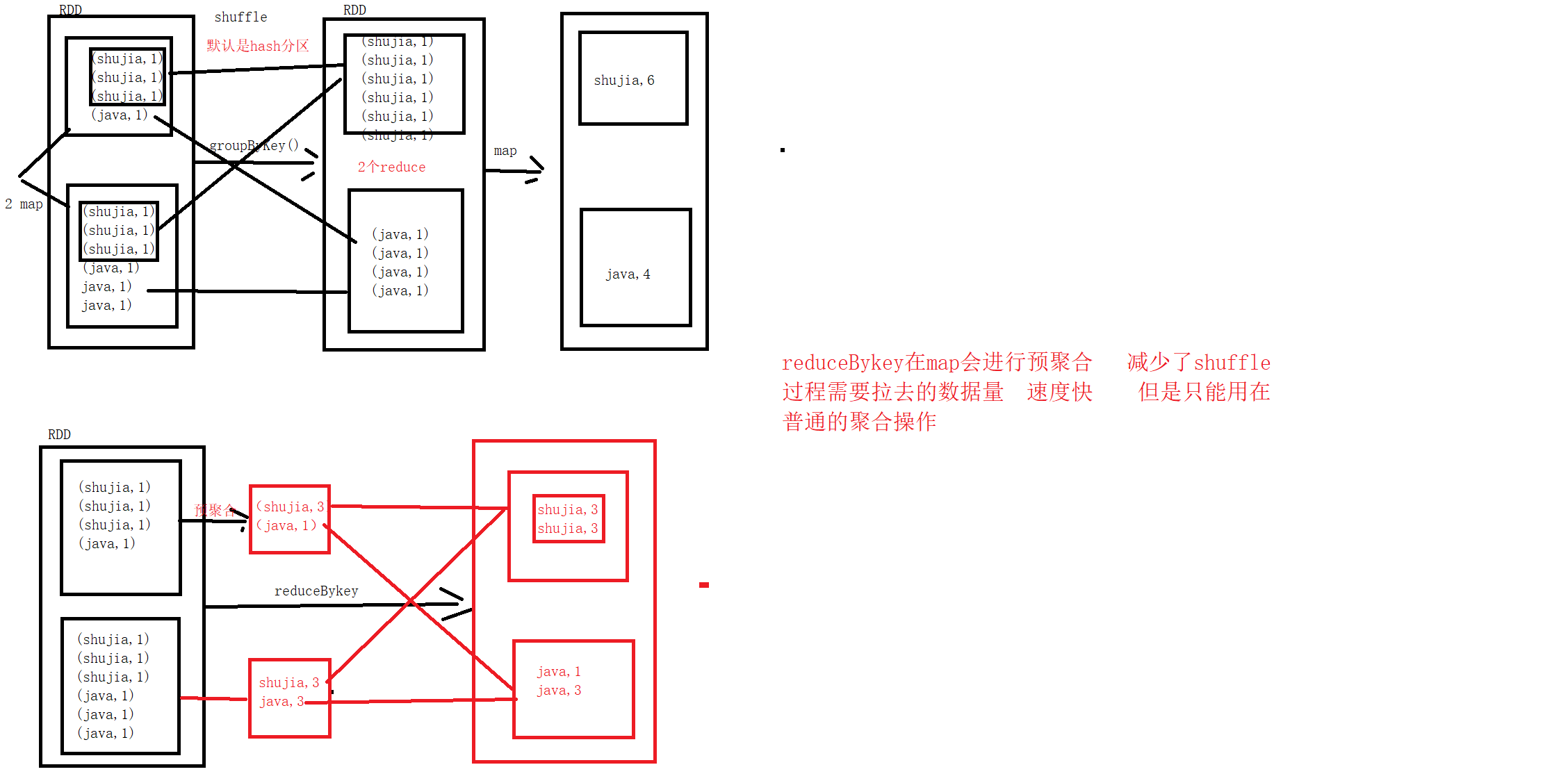
11、aggregateByKey算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD object Demo13aggregateByKey { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * aggregateByKey:转换算子,可以实现将多个聚合方式放在一起实现,并且也能对Map进行预聚合 * 可以弥补reduceByKey无法实现avg操作 * */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo13aggregateByKey") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") val ageKVRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = stuRDD.map(s => (s.split(",")(4), s.split(",")(2).toInt)) val clazzCntKVRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = stuRDD.map(s => (s.split(",")(4), 1)) // 统计每个班级年龄之和 val ageSumRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = ageKVRDD.reduceByKey(_ + _) // 统计每个班级人数 val clazzCntRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = clazzCntKVRDD.reduceByKey(_ + _) // 统计每个班级的平均年龄 ageSumRDD.join(clazzCntRDD).map { case (clazz: String, (ageSum: Int, cnt: Int)) => (clazz, ageSum.toDouble / cnt) }.foreach(println) /** * zeroValue:初始化的值,类型自定义,可以是数据容器 * seqOp:在组内(每个分区内部即每个Map任务)进行的操作,相当是Map端的预聚合操作 * combOp:在组之间(每个Reduce任务之间)进行的操作,相当于就是最终每个Reduce的操作 */ // 使用aggregateByKey统计班级年龄之和 ageKVRDD.aggregateByKey(0)((age1: Int, age2: Int) => { age1 + age2 // 预聚合 }, (map1AgeSum: Int, map2AgeSum: Int) => { map1AgeSum + map2AgeSum // 聚合 }).foreach(println) // 使用aggregateByKey统计班级人数 clazzCntKVRDD.aggregateByKey(0)((c1: Int, c2: Int) => { c1 + 1 // 预聚合 }, (map1Cnt: Int, map2Cnt: Int) => { map1Cnt + map2Cnt // 聚合 }).foreach(println) // 使用aggregateByKey统计班级的平均年龄 ageKVRDD.aggregateByKey((0, 0))((t2: (Int, Int), age: Int) => { val mapAgeSum: Int = t2._1 + age val mapCnt: Int = t2._2 + 1 (mapAgeSum, mapCnt) }, (map1U: (Int, Int), map2U: (Int, Int)) => { val ageSum: Int = map1U._1 + map2U._1 val cnt: Int = map1U._2 + map2U._2 (ageSum, cnt) }).map { case (clazz: String, (sumAge: Int, cnt: Int)) => (clazz, sumAge.toDouble / cnt) }.foreach(println) } }
12、cartesian算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo14cartesian { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * cartesian:转换算子,可以对两个RDD做笛卡尔积 * * 当数据重复时 很容易触发笛卡尔积 造成数据的膨胀 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo14cartesian") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val idNameKVRDD: RDD[(String, String)] = sc.parallelize(List(("001", "zs"), ("002", "ls"), ("003", "ww"))) val genderAgeKVRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = sc.parallelize(List(("男", 25), ("女", 20), ("男", 22))) idNameKVRDD.cartesian(genderAgeKVRDD).foreach(println) } }
13、soreBy算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo15sortBy { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * sortBy:转换算子 可以指定一个字段进行排序 默认升序 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo15sortBy") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val intRDD: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(List(1, 3, 6, 5, 2, 4, 6, 8, 9, 7)) intRDD.sortBy(i => i).foreach(println) // 升序 intRDD.sortBy(i => -i).foreach(println) // 降序 intRDD.sortBy(i => i, ascending = false).foreach(println) // 降序 val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") // 按照年龄进行降序 stuRDD.sortBy(s => -s.split(",")(2).toInt).foreach(println) } }
14、Action算子(行动算子)
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import java.sql.{Connection, DriverManager, PreparedStatement} object Demo16Action { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * 常见的Action算子:foreach、take、collect、count、reduce、save相关 * 每个Action算子都会触发一个job * */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo16Action") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") /** * foreach:对每条数据进行处理,跟map算子的区别在于,foreach算子没有返回值 */ stuRDD.foreach(println) // 将stuRDD中的每条数据保存到MySQL中 /** * 建表语句: * CREATE TABLE `stu_rdd` ( * `id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, * `name` char(5) DEFAULT NULL, * `age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, * `gender` char(2) DEFAULT NULL, * `clazz` char(4) DEFAULT NULL, * PRIMARY KEY (`id`) * ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; */ // 每一条数据都会创建一次连接,频繁地创建销毁连接效率太低,不合适 // stuRDD.foreach(line => { // val splits: Array[String] = line.split(",") // // 1、建立连接 // val conn: Connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://master:3306/bigdata19?useSSL=false", "root", "123456") // println("建立了一次连接") // // 2、创建prepareStatement // val pSt: PreparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement("insert into stu_rdd(id,name,age,gender,clazz) values(?,?,?,?,?)") // // // 3、传入参数 // pSt.setInt(1, splits(0).toInt) // pSt.setString(2, splits(1)) // pSt.setInt(3, splits(2).toInt) // pSt.setString(4, splits(3)) // pSt.setString(5, splits(4)) // // // 4、执行SQL // pSt.execute() // // // 5、关闭连接 // conn.close() // // }) /** * take : Action算子,可以将指定条数的数据转换成Scala中的Array * */ // 这里的foreach是Array的方法,不是算子 stuRDD.take(5).foreach(println) /** * collect : Action算子,可以将RDD中所有的数据转换成Scala中的Array */ // 这里的foreach是Array的方法,不是算子 stuRDD.collect().foreach(println) /** * count : Action算子,统计RDD中数据的条数 */ println(stuRDD.count()) /** * reduce : Action算子,将所有的数据作为一组进行聚合操作 */ // 统计所有学生的年龄之和 println(stuRDD.map(_.split(",")(2).toInt).reduce(_ + _)) /** * save相关: * saveAsTextFile、saveAsObjectFile */ } }
15、SparkPi算子
package com.core //计算π的值 import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import scala.util.Random object Demo17SparkPi { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * 通过Spark代码实现PI的计算 */ // 生成随机数 for (elem <- 1 to 10) { println(Random.nextDouble()*2-1,Random.nextDouble()*2-1) } val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo17SparkPi") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val seqRDD: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(1 to 1000) seqRDD.map(i=>{ (Random.nextDouble()*2-1,Random.nextDouble()*2-1) }).foreach(println) } }
16、foreachPartition算子
package com.core import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import java.sql.{Connection, DriverManager, PreparedStatement} object Demo19foreachPartition { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo19foreachPartition") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("Spark/data/students.txt") /** * Spark代码虽然在编程时看起来是一个完整的程序就一个部分 * 而且在IDEA中也不会报错,也能正常package,一运行时才会报错 * 原因: * Spark代码是分为两个部分: * 1、算子外部:Driver端 * 2、算子内部:以Task的形式发送到Executor中去执行 * * 连接是不能够被序列化的,Driver端和Executor属于不同的JVM进程,甚至在不同的节点上, * 所以在算子外部创建的连接不能够在算子内部使用 */ // // 1、建立连接 // val conn: Connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://master:3306/bigdata19?useSSL=false", "root", "123456") // println("建立了一次连接") // // 2、创建prepareStatement // val pSt: PreparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement("insert into stu_rdd(id,name,age,gender,clazz) values(?,?,?,?,?)") // // stuRDD.foreach(line => { // val splits: Array[String] = line.split(",") // // // 3、传入参数 // pSt.setInt(1, splits(0).toInt) // pSt.setString(2, splits(1)) // pSt.setInt(3, splits(2).toInt) // pSt.setString(4, splits(3)) // pSt.setString(5, splits(4)) // // // 4、执行SQL // pSt.execute() // // // 5、关闭连接 // conn.close() // // }) // 连接建立的次数过多 ---> 减少连接建立的次数 // foreachPartition 对每个分区进行一次操作 stuRDD.foreachPartition(iter => { // 对每个分区进行操作 // 1、建立连接,每个分区建立一次连接 val conn: Connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://master:3306/bigdata19?useSSL=false", "root", "123456") println("建立了一次连接") // 2、创建prepareStatement val pSt: PreparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement("insert into stu_rdd(id,name,age,gender,clazz) values(?,?,?,?,?)") // 对分区内的每条数据进行处理 iter.foreach(line => { val splits: Array[String] = line.split(",") // 3、传入参数 pSt.setInt(1, splits(0).toInt) pSt.setString(2, splits(1)) pSt.setInt(3, splits(2).toInt) pSt.setString(4, splits(3)) pSt.setString(5, splits(4)) // 4、将构建好的每个pSt放入一个Batch批次中 pSt.addBatch() }) // 5、执行批量插入 pSt.executeBatch() // 6、关闭连接 conn.close() }) } }
17、mapPartitions
package com.core import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import java.sql.{Connection, DriverManager, PreparedStatement, ResultSet} import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer object Demo20mapPartitions { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * 如何选择foreachPartition/mapPartitions? * 当需要同外部系统建立连接时: * 如果需要从外部获取数据并进行后续操作-->mapPartitions * 如果只是想将数据保存到外部系统-->foreachPartition */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo20mapPartitions") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") val stuSampleRDD: RDD[String] = stuRDD.sample(withReplacement = false, fraction = 0.01, 1) /** * 1500100110,牛晨朗,22,男,文科六班 * 1500100137,宣向山,22,女,理科四班 * 1500100196,汤浩博,21,男,文科三班 * 1500100231,桂痴安,22,女,文科三班 * 1500100283,侯千风,24,女,文科三班 * 1500100456,鄂运凯,24,男,文科一班 * 1500100483,邵海阳,21,男,理科六班 * 1500100721,钱泽雨,23,男,理科三班 * 1500100783,弓浩言,21,男,理科四班 * 1500100944,查振国,22,男,理科四班 * 1500100972,王昂杰,23,男,理科二班 * 使用JDBC的方式从MySQL获取每个学生每门科目的成绩,最后计算总分 */ stuSampleRDD.flatMap(line => { val id: String = line.split(",")(0) // 1、建立连接 val conn: Connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://master:3306/bigdata19?useSSL=false", "root", "123456") println("建立了一次连接") // 2、创建prepareStatement val pSt: PreparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement("select student_id,score from score where student_id=?") // 3、设置参数 pSt.setString(1, id) // 4、执行查询 val rs: ResultSet = pSt.executeQuery() // 5、从ResultSet中提取查询结果 val stuScoreLB: ListBuffer[String] = ListBuffer[String]() while (rs.next()) { val score: Int = rs.getInt("score") stuScoreLB.append(line + "," + score) } stuScoreLB }).map(line => { val splits: Array[String] = line.split(",") (s"${splits(0)},${splits(1)}", splits(5).toInt) }) .reduceByKey(_ + _) .foreach(println) // 使用mapPartitions进行优化,减少建立连接的次数,做到每个Partition公用一个连接 stuSampleRDD.mapPartitions(iter => { // 1、建立连接 val conn: Connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://master:3306/bigdata19?useSSL=false", "root", "123456") println("建立了一次连接conn") // 2、创建prepareStatement val pSt: PreparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement("select student_id,score from score where student_id=?") // 对分区内部的每一条数据进行操作 iter.flatMap(line => { val id: String = line.split(",")(0) // 3、设置参数 pSt.setString(1, id) // 4、执行查询 val rs: ResultSet = pSt.executeQuery() // 5、从ResultSet中提取查询结果 val stuScoreLB: ListBuffer[String] = ListBuffer[String]() while (rs.next()) { val score: Int = rs.getInt("score") stuScoreLB.append(line + "," + score) } stuScoreLB }) }).map(line => { val splits: Array[String] = line.split(",") (s"${splits(0)},${splits(1)}", splits(5).toInt) }) .reduceByKey(_ + _) .foreach(println) } }
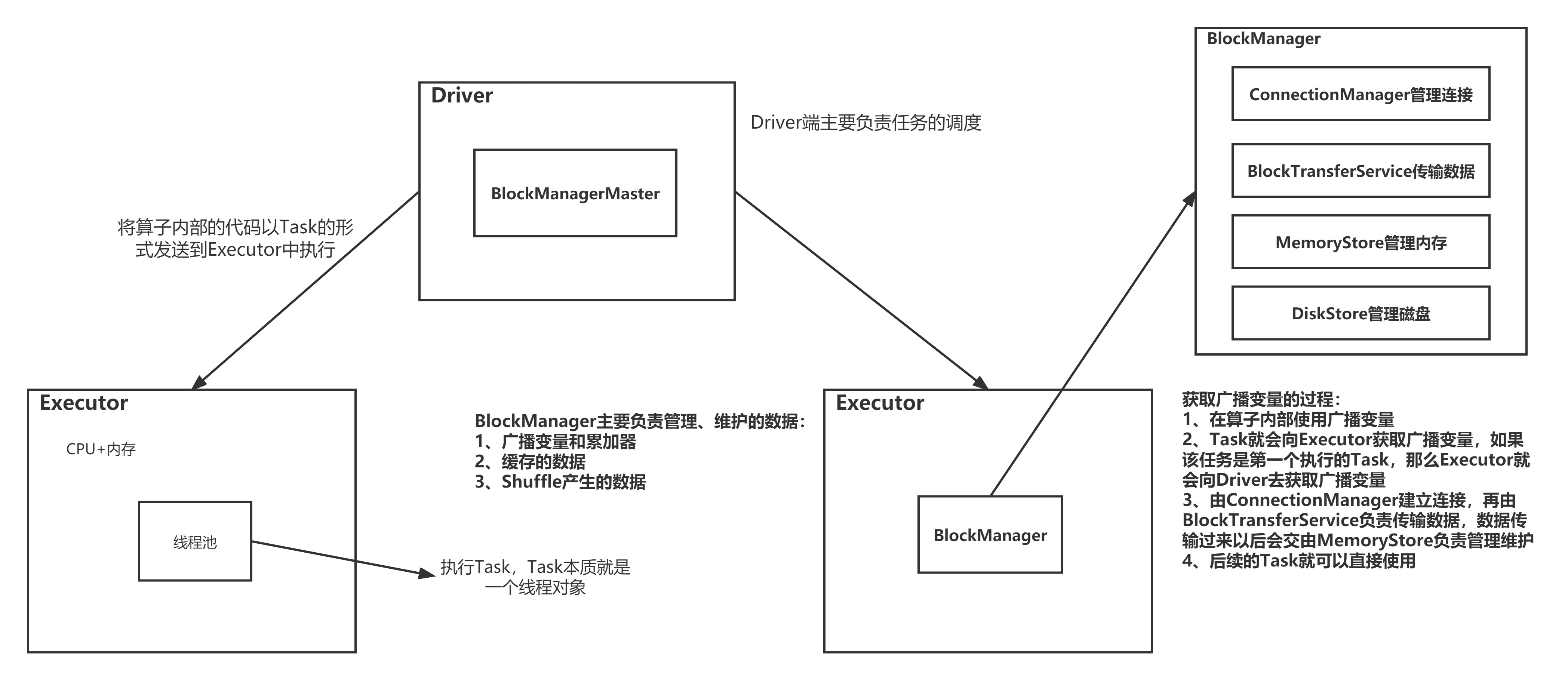
18、broadcast
package com.core import org.apache.spark.broadcast.Broadcast import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD object Demo21broadcast { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo21broadcast") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") val scoRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/score.txt") // 构建KV格式的RDD val stuKVRDD: RDD[(String, String)] = stuRDD.map(line => (line.split(",")(0), line)) val scoKVRDD: RDD[(String, String)] = scoRDD.map(line => (line.split(",")(0), line)) /** * 直接关联是Reduce Join效率比较低 * 当大表关联小表的时,可以将小表的数据广播给每个Executor,实现MapJoin */ // stuKVRDD.join(scoKVRDD).foreach(println) // 将stuKVRDD转成本地集合再进行广播 val stuKVRDDMap: Map[String, String] = stuKVRDD.collect().toMap // 在算子外部通过sc进行广播 val stuKVRDDMapBro: Broadcast[Map[String, String]] = sc.broadcast(stuKVRDDMap) // 处理大表的数据 scoKVRDD.map(kv => { /** * 当大表的数据量比较大的时候-->切片的数量很多-->Task的数量很多 * 如果直接在算子内部使用算子外部的变量,会导致算子外部的变量复制的次数等于Task的次数 * 又因为Task最终是在每个Executor中执行的,所以可以将变量广播到每个Executor中 * 当Task执行时 只需要向Executor获取数据即可 * * 前提条件: * Executor的数量 << Task的数量 */ // 通过广播变量的方式获取外部的数据 val map: Map[String, String] = stuKVRDDMapBro.value val stuInfo: String = map.getOrElse(kv._1, "") (kv, stuInfo) }).foreach(println) while (true) { } } }
19、cache
package com.core import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel object Demo22cache { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * cache:缓存 * 当一个RDD被使用多次的时候 可以进行缓存 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo22cache") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") val stu2RDD: RDD[String] = stuRDD.map(line => { println("执行了map方法") line }) // 对多次使用的RDD进行缓存 // stu2RDD.cache() // 默认将数据缓存到内存中 // 如果内存不够,容易造成OOM // 需要考虑缓存的策略 // 如果内存足够 --> cache --> MEMORY_ONLY // 如果内存不够 --> persist --> MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER (尽可能将数据放入内存) stu2RDD.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER) // 统计班级人数 stu2RDD.map(line => (line.split(",")(4), 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _).foreach(println) // 统计性别人数 stu2RDD.map(line => (line.split(",")(3), 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _).foreach(println) // 用完记得释放缓存 stu2RDD.unpersist() } }
20、checkPoint
package com.core import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD object Demo23checkPoint { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * checkPoint 检查点 * 使用前需要先设置一个checkPoint的目录 * 主要用于SparkStreaming中做高可靠,保证程序在失败后恢复时不会处理大量的数据 * 类似 VMWare 比如 每隔一个阶段拍一次快照 * 如果虚拟机某个时间点出现了意外,可以通过最新的快照恢复 * */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo23checkPoint") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) sc.setCheckpointDir("bigdata19-spark/data/ck") val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt") val stu2RDD: RDD[String] = stuRDD.map(line => { println("执行了map方法") line }) //在checkPoint之前做一次cache
stu2RDD.cache()
// 在进行checkPoint操作时,需要额外启动一个Job将数据写入到高可靠的文件系统中(HDFS) stu2RDD.checkpoint() // 统计班级人数 stu2RDD.map(line => (line.split(",")(4), 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _).foreach(println) // 统计性别人数 stu2RDD.map(line => (line.split(",")(3), 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _).foreach(println) // 统计年龄分布人数 stu2RDD.map(line => (line.split(",")(2), 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _).foreach(println) } }
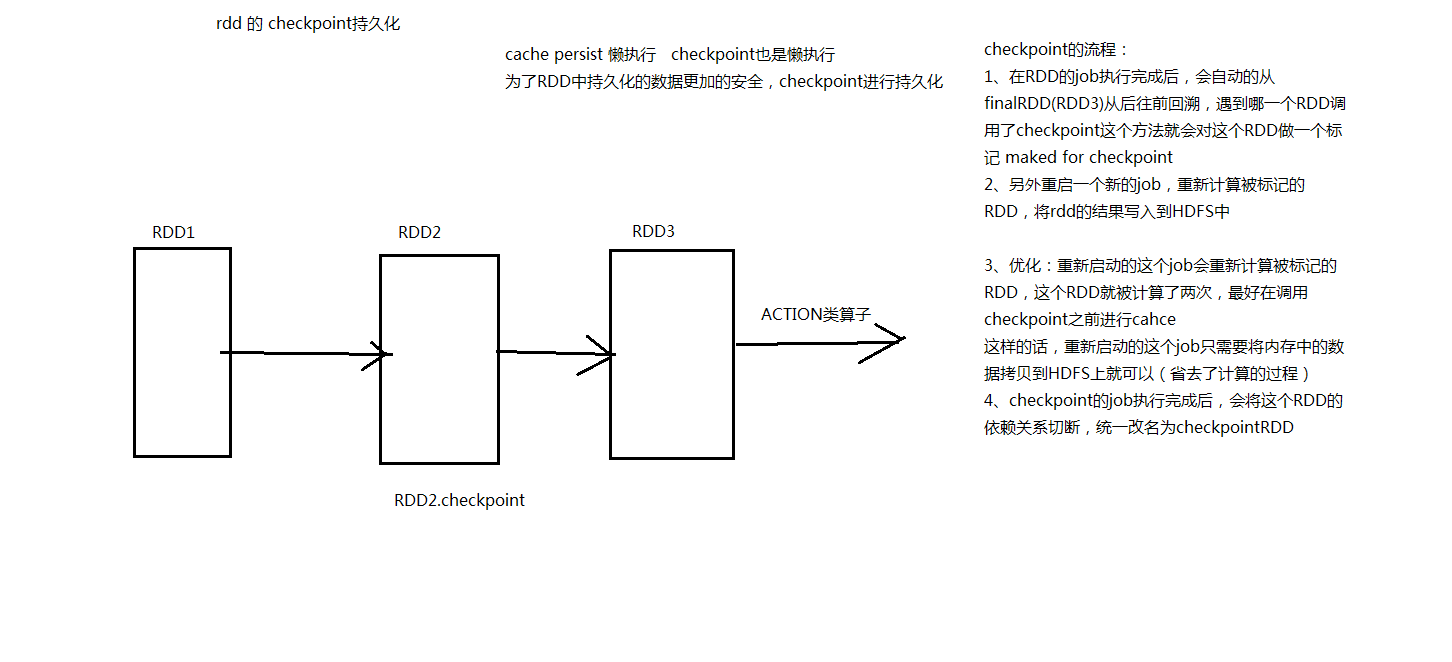
cache保存到内存或者是executor的磁盘上;checkPoint保存在HDFS
21、累加器
package com.core import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.util.LongAccumulator import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Demo24acc { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * 累加器 */ val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf() conf.setAppName("Demo24acc") conf.setMaster("local") val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf) var i: Int = 0 // 当某些情况下 想在算子内部对算子外部的变量进行操作时 需要使用累加器 // 在Driver端创建一个累加器 val longAcc: LongAccumulator = sc.longAccumulator val stuRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("bigdata19-spark/data/students.txt", minPartitions = 2).sample(withReplacement = false, fraction = 0.01, seed = 10) // 在算子内部对算子外部的变量进行累加 stuRDD.map(line=>{ // 在算子内部使用算子外部变量时,外部的变量会以副本的形式跟着Task发送到Executor中去执行 // 在算子内部操作其实是外部变量的副本 i=i+1 println("i的值为:"+i) //使用累加器 longAcc.add(1) println("累加器的值为:"+longAcc.value) line }).foreach(println) println("i的值为:"+i) //在Driver端汇总 println("累加器的值为:"+longAcc.value) } }
spark运行架构