springMvc注解之@ResponseBody和@RequestBody
简介
springmvc对json的前后台传输做了很好封装,避免了重复编码的过程,下面来看看常用的@ResponseBody和@RequestBody注解
添加依赖
springmvc对json的处理依赖jackson
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core-asl</artifactId>
<version>1.9.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-mapper-asl</artifactId>
<version>1.9.11</version>
</dependency>
xml配置
<mvc:annotation-driven />//不要忘了命名空间配置
@ResponseBody
如果传输的是单层json对象,我们后台可以直接用 @RequestParam接收
$.ajax({ type : "post", dataType : "json", url : "/testRequestBody", data:{ name:"韦德", age:35 }, success : function(result) { } });
@RequestMapping("/testRequestBody") public String testRequestBody(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> map) { System.out.println(map);// {name=韦德, age=35} return "index"; }
如果传输的是多层嵌套json对象,这个时候会就会出现数据丢失问题
@ResponseBody很好的解决了这个问题,它会把前台传输过来的json转化为后台对应的对象
$.ajax({ type : "post", dataType : "json", url : "/testRequestBody", contentType:"application/json", data:JSON.stringify({ name:"韦德", win:[2006,2012,2013], age:35 }), success : function(result) { } });
@RequestMapping("/testRequestBody") public String testRequestBody(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> map) { System.out.println(map);//{name=韦德, win=[2006, 2012, 2013], age=35} return "index"; }
需要注意的是前台需要指定contentType为"application/json"
同时要把json对象转化为String,否则后台不能识别
@ResponseBody
ajax请求返回json格式,往常我们可以这样做
private void writeJson(HttpServletResponse response, Object object) { String json = JSON.toJSONString(object); response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); response.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter out = null; try { out = response.getWriter(); out.write(json); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (out != null) { out.close(); } } }
这个时候 @ResponseBody就派上用场了,只需要一个注解,全部搞定
$.ajax({ type : "post", dataType : "json", url : "/testResponseBody", success : function(result) { console.info(result); } });
@RequestMapping("/testResponseBody") @ResponseBody public Map<String, Object> testRequestBody() { Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>(); result.put("name", "韦德"); result.put("age", 35); return result; }
前台console输出
{ "age": 35, "name": "韦德" }
总结
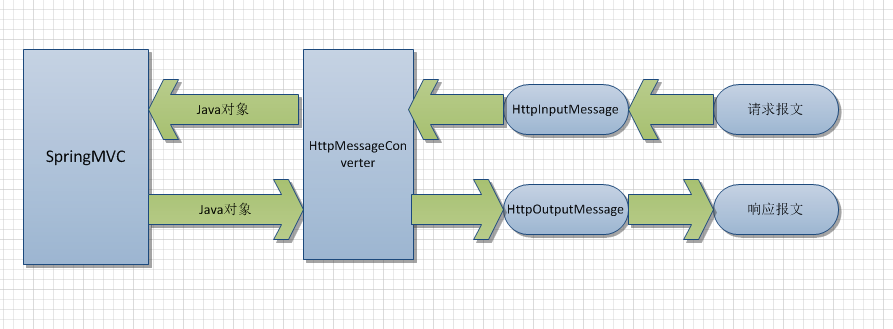
在网上看到很不错的流程图,作为总结吧