mybatis——缓存
前面研究Executor时,里面有一级缓存和二级缓存的使用,这里深入研究一下缓存
一、一级缓存
1、一级缓存初始化
一级缓存指的是在BaseExecutor初始化的时候创建的,是一个PerpetualCache类型的对象.
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { ... this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");//实际就是BaseExecutor.localCache ... } private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ... localCache.putObject(key, list);//实际数据存放在PerpetualCache.cache中这个是一个Map<Object, Object>类型。 ... }
一级缓存的初始化与数据存放比较简单,SqlSessionFactory.openSession()每创建一个Session时就会创建一个Executor,一级缓存存储在BaseExecutor.localCache中
/* org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSessionFromDataSource */ private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
2、总结一下
对应关系:是一个sqlSession对应一个Executor,一个BaseExecutor创建一个一级缓存localCache,然后结合上文的update()、事务提交回退都会清空一级缓存localCache,因此
① 同个session的两次相同查询:mybatis只查询一次数据库
② 同个session的两次不同查询:mybatis查询两次数据库
③ 同个session一个查询、一次更新、然后执行相同查询:mybatis查询两次数据库
④ 同个session一次查询、一次事务提交、然后执行相同查询:mybatis查询两次数据库
⑤ 不同session的两次相同查询:mybatis查询两次数据库
二、二级缓存
1、二级缓存的初始化
二级缓存对应的Configuration.caches是一个Map<String,Cache>类型的对象。Map中的<String,Cache>实例是在解析mapper.xml中的<cache>标签时创建的。即一个mapper.xml对应一个cache。所以尽管mybatis默认的Executor是new CachingExecutor(new SimpleExecutor),但是<mapper>中没加<cache>标签的话,二级缓存默认还是关闭的。
/* org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#newExecutor(org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction, org.apache.ibatis.session.ExecutorType) */ public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) {//默认为true executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
mapper.xml中 <mapper>标签解析+<cache>标签解析
/* org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder#parse */ public void parse() { if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper")); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); bindMapperForNamespace(); } parsePendingResultMaps(); parsePendingCacheRefs(); parsePendingStatements(); } private void configurationElement(XNode context) { try { String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace"); if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) { throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty"); } builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace); cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref")); cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache")); parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap")); resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap")); sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql")); buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e); } } private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL"); Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type); String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU"); Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction); Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval"); Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size"); boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false); boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false); Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props); } } /* org.apache.ibatis.builder.MapperBuilderAssistant#useNewCache */ public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass, Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass, Long flushInterval, Integer size, boolean readWrite, boolean blocking, Properties props) {
//建造器模式创建cache Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace) .implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class)) .addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class)) .clearInterval(flushInterval) .size(size) .readWrite(readWrite) .blocking(blocking) .properties(props) .build(); configuration.addCache(cache); currentCache = cache; return cache; }
2、二级缓存出现的原因
源自官网:在一级缓存中,不同session进行相同SQL查询的时候,是查询两次数据库的。显然这是一种浪费,既然SQL查询相同,就没有必要再次查库了,直接利用缓存数据即可,这种思想就是MyBatis二级缓存的初衷。
另外,Spring和MyBatis整合时,每次查询之后都要进行关闭sqlsession,关闭之后数据被清空。所以MyBatis和Spring整合之后,一级缓存是没有意义的。如果开启二级缓存,关闭sqlsession后,会把该sqlsession一级缓存中的数据添加到mapper namespace的二级缓存中。这样,缓存在sqlsession关闭之后依然存在。
3、二级缓存的使用
<mapper namespace="org.study.mapper.UserMapper"> <!-- 在mapper下加入cache标签 --> <!-- <cache/> -->
由于上面说的spring+mybatis每次查询都会关闭sqlSession,所以一级缓存没有意义,连续两次查询

加上<cache/>后
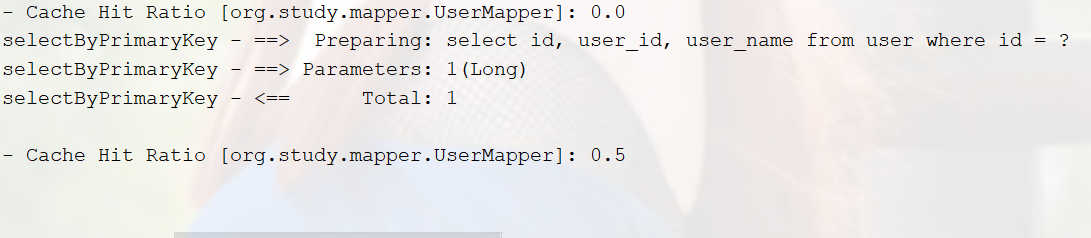
补充一下属性讲解:
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
eviction="LRU":缓存过期置换策略,其实默认的是LRU(LruCache),还有FIFO(FIFOCache)多个装饰者模式的增强PerpetualCache的Cache。

flushInterval="60000":缓存过期时间,装饰者模式,外面加了一层ScheduleCache。控制缓存的有效时间。
size="512":缓存大小,判断Map.size(),不是内存大小是key的个数。
readOnly="true":只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。 因此这些对象不能被修改。这就提供了可观的性能提升。而可读写的缓存会(通过序列化)返回缓存对象的拷贝。速度上会慢一些,但是更安全,因此默认值是 false。
4、总结
① 二级缓存的目的:解决一级缓存不能跨sqlSession的弊病,二级缓存可以跨sqlSession。
② 二级缓存默认是关闭的,默认开启的是CachingExecutor,所以仅需要在mapper.xml中设置<cache/>标签的可以开启二级缓存了。
③ 一级缓存二级缓存的cacheKey相同,但是一级缓存对应一个sqlSession,二级缓存对应一个mapper.xml命名空间(可跨sqlSession)。
④ 写操作都会引起缓存清空。但一级缓存是整体清空,二级缓存清空的是操作的mapper.xml命名空间下对应的缓存,其他命名空间不受影响
⑤ 过期策略。由于最终存储对象都是PerpetualCache中的Map中,所以理论上是都不会过期的。但是一级缓存flush频繁,二级缓存可以通过flushInterval设置过期时间,需要注意的是flushInterval对自定义的Cache不起作用。
⑥ 默认的二级缓存是是JVM层面的缓存,在分布式架构中应用不佳,不能保证缓存数据的一致性。但是可以自定义分布式cache,例如使用redis实现二级缓存。
三、mybatis缓存结构
默认单机:
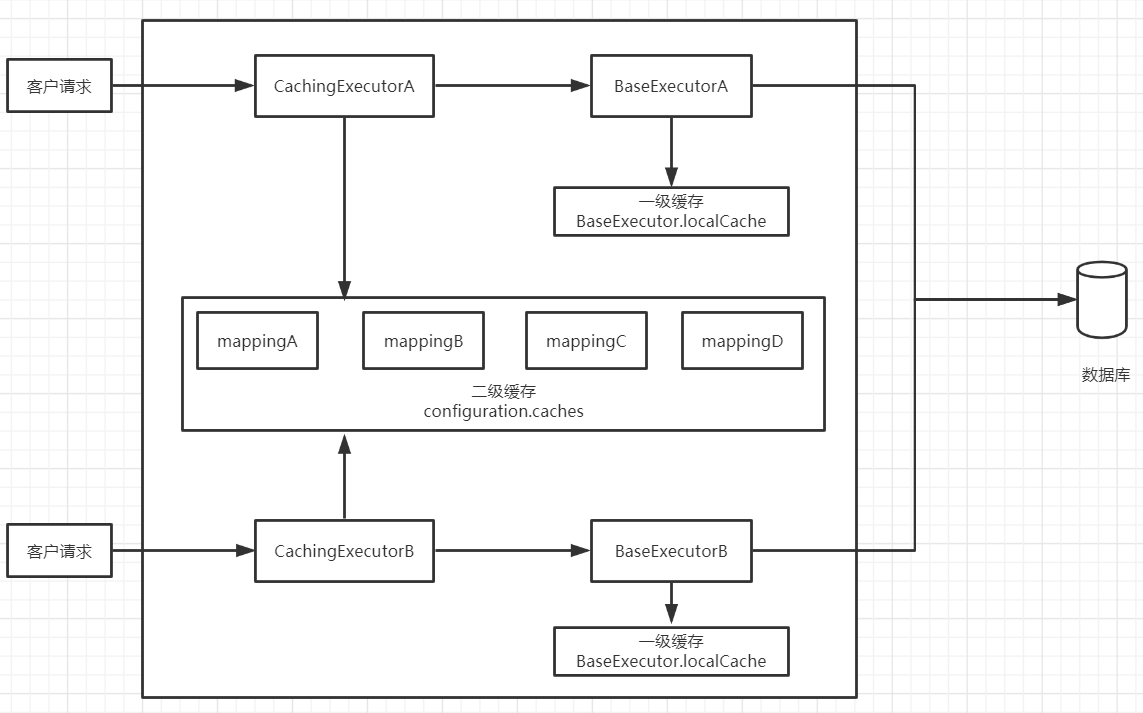
分布式:

四、补充
1、redis实现分布式二级缓存
package org.study.mappercache; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat; import com.google.gson.JsonObject; import com.google.gson.JsonParser; import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import org.study.redis.RedisUtils; import redis.clients.jedis.params.SetParams; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; public class MappedRedisCache implements Cache { /** * redisCache 装饰者模式:增强过期时间控制 */ private Cache cache; public MappedRedisCache(String id){ cache = new RedisCache("mybatis_" + id); } @Override public String getId() { return cache.getId(); } @Override public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { if (key != null && value != null){ //key转hashCode存储 节省空间 RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().set(key.toString().hashCode()+"","1",new SetParams().ex(600)); cache.putObject(key,value); } } @Override public Object getObject(Object key) { if (key == null){ return null; } if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().get(key.toString()))){ RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().set(key.toString().hashCode()+"","1",new SetParams().ex(600)); cache.getObject(key); } cache.removeObject(key); return null; } @Override public Object removeObject(Object key) { if (key == null){ return null; } RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().del(key.toString()); Object obj = cache.getObject(key); cache.removeObject(key); return obj; } @Override public void clear() { Set<String> keySet = RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().hkeys(getId()); if(keySet != null && keySet.size() != 0){ keySet.forEach(key -> RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().del(key)); } cache.clear(); } @Override public int getSize() { return cache.getSize(); } @Override public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() { return cache.getReadWriteLock(); } private class RedisCache implements Cache{ private String id; public RedisCache(String id){ this.id = id; } @Override public String getId() { return id; } @Override public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { if (key != null && value != null){ RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().hset(getId(),key.toString().hashCode()+"",JSONObject.toJSONString(value)); } } @Override public Object getObject(Object key) { if (key != null){ return RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().hget(getId(),key.toString()); } return null; } @Override public Object removeObject(Object key) { if (key != null){ return RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().hdel(getId(),key.toString()); } return null; } @Override public void clear() { RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().del(getId()); } @Override public int getSize() { return RedisUtils.getJedisCluster().hlen(getId()).intValue(); } @Override public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() { return this.lock; } private final ReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); } }



