dataframe转化(二)之 apply(),transform(),agg() 的用法和区别
用法介绍
transform用法
pandas.Series.transform

Call func on self producing a Series with transformed values. Produced Series will have same axis length as self. Parameters funcfunction, str, list or dict Function to use for transforming the data. If a function, must either work when passed a Series or when passed to Series.apply. Accepted combinations are: function string function name list of functions and/or function names, e.g. [np.exp. 'sqrt'] dict of axis labels -> functions, function names or list of such. axis{0 or ‘index’} Parameter needed for compatibility with DataFrame. *args Positional arguments to pass to func. **kwargs Keyword arguments to pass to func. Returns Series A Series that must have the same length as self. Raises ValueErrorIf the returned Series has a different length than self.
agg用法
pandas.Series.agg

Series.agg(self, func, axis=0, *args, **kwargs)[source] Aggregate using one or more operations over the specified axis. New in version 0.20.0. Parameters funcfunction, str, list or dict Function to use for aggregating the data. If a function, must either work when passed a Series or when passed to Series.apply. Accepted combinations are: function string function name list of functions and/or function names, e.g. [np.sum, 'mean'] dict of axis labels -> functions, function names or list of such. axis{0 or ‘index’} Parameter needed for compatibility with DataFrame. *args Positional arguments to pass to func. **kwargs Keyword arguments to pass to func. Returns scalar, Series or DataFrame The return can be: scalar : when Series.agg is called with single function Series : when DataFrame.agg is called with a single function DataFrame : when DataFrame.agg is called with several functions Return scalar, Series or DataFrame.
pandas.DataFrame.agg

DataFrame.agg(self, func, axis=0, *args, **kwargs)[source] Aggregate using one or more operations over the specified axis. Parameters funcfunction, str, list or dict Function to use for aggregating the data. If a function, must either work when passed a DataFrame or when passed to DataFrame.apply. Accepted combinations are: function string function name list of functions and/or function names, e.g. [np.sum, 'mean'] dict of axis labels -> functions, function names or list of such. axis{0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’}, default 0 If 0 or ‘index’: apply function to each column. If 1 or ‘columns’: apply function to each row. *args Positional arguments to pass to func. **kwargs Keyword arguments to pass to func. Returns scalar, Series or DataFrame The return can be: scalar : when Series.agg is called with single function Series : when DataFrame.agg is called with a single function DataFrame : when DataFrame.agg is called with several functions Return scalar, Series or DataFrame. The aggregation operations are always performed over an axis, either the index (default) or the column axis. This behavior is different from numpy aggregation functions (mean, median, prod, sum, std, var), where the default is to compute the aggregation of the flattened array, e.g., numpy.mean(arr_2d) as opposed to numpy.mean(arr_2d, axis=0). agg is an alias for aggregate. Use the alias.
案例:

df = pd.DataFrame({'A': range(3), 'B': range(1, 4)})
df
A B
0 0 1
1 1 2
2 2 3
df.transform(lambda x: x + 1)
A B
0 1 2
1 2 3
2 3 4
异同点
apply() 与transform() agg()的异同点:
同:
- pandas.core.groupby.GroupBy
- pandas.DataFrame
- pandas.Series
类的对象都可以调用如上方法
异:
1.apply()里面可以跟自定义的函数,包括简单的求和函数以及复杂的特征间的差值函数等,但是agg()做不到
2.agg() / transform()方法可以反射调用(str调用)‘sum‘、'max'、'min'、'count‘等方法,形如agg('sum')。apply不能直接使用,而可以用自定义函数+列特征的方法调用。
3.transform() 里面不能跟自定义的特征交互函数,因为transform是真针对每一元素(即每一列特征操作)进行计算
性能比较
分别计算在同样简单需求下各组合方法的计算时长
数据源是最近kaggle比赛:
# Correct data types for "sell_prices.csv" priceDTypes = {"store_id": "category", "item_id": "category", "wm_yr_wk": "int16", "sell_price":"float32"} # Read csv file prices = pd.read_csv("./sell_prices.csv", dtype = priceDTypes) prices.head()

len(prices)

2.1 transform() 方法+自定义函数

prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x:x.min()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x:x.max()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x:x.sum()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x:x.count()) len(prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x:x.mean()))

2.2 transform() 方法+python内置方法

prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform('min') prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform('max') prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform('sum') prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform('count') len(prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].transform('mean'))

2.3 apply() 方法+自定义函数

prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].apply(lambda x:x.min()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].apply(lambda x:x.max()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].apply(lambda x:x.sum()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].apply(lambda x:x.count()) len(prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].apply(lambda x:x.mean()))

2.4 agg() 方法+自定义函数

prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg(lambda x:x.min()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg(lambda x:x.max()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg(lambda x:x.sum()) prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg(lambda x:x.count()) len(prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg(lambda x:x.mean()))
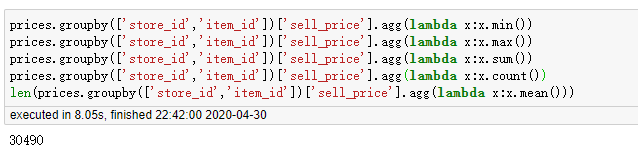
2.5 agg() 方法+python内置方法

prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg('min') prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg('max') prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg('sum') prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg('count') len(prices.groupby(['store_id','item_id'])['sell_price'].agg('mean'))
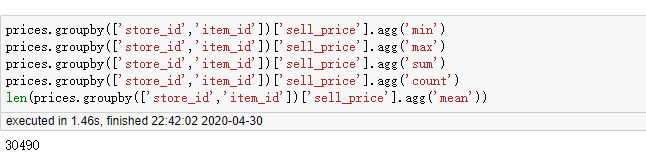
2.6 结论
agg()+python内置方法的计算速度最快,其次是transform()+python内置方法。而 transform() 方法+自定义函数 的组合方法最慢,需要避免使用!
python自带的stats统计模块在pandas结构中的计算也非常慢,也需要避免使用!
转化差异
agg运算groupby的数据完直接赋给原生df数据某字段报错
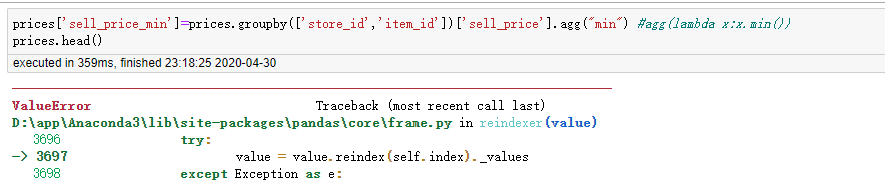
apply运算groupby的数据完直接赋给原生df数据某字段报错
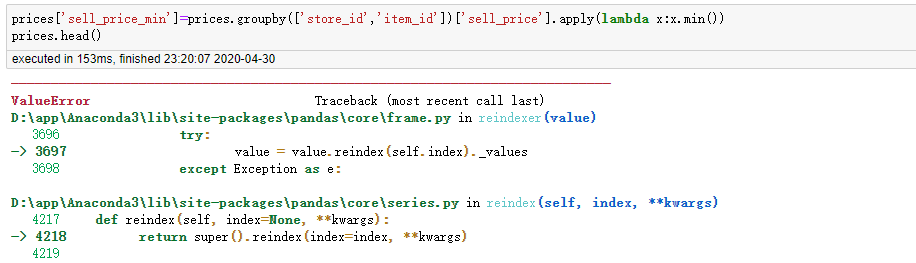
transform运算groupby的数据完直接赋给原生df数据某字段就不会报错
大多数人都以为是才智成就了科学家,他们错了,是品格。---爱因斯坦



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号