Elastic Stack 入门
我配置的elasticsearch版本是7.0.0,注意事项如下,配置的中文分词器也是7.0.0,踩坑。。。。。。
org.elasticsearch.discovery.MasterNotDiscoveredException异常解决
https://blog.csdn.net/guanking19/article/details/94414811
Elasticsearch 报错-org.elasticsearch.discovery.MasterNotDiscoveredException: null
https://blog.csdn.net/Victory_Lei/article/details/110231689
Elasticsearch的介绍与安装
Elasticsearch的快速入门
Elasticsearch的核心讲解
中文分词
全文搜索
Elasticsearch集群
Java客户端讲解
1、Elastic Stack简介
如果你没有听说过Elastic Stack,那你一定听说过ELK,实际上ELK是三款软件的简称,分别是Elasticsearch、
Logstash、Kibana组成,在发展的过程中,又有新成员Beats的加入,所以就形成了Elastic Stack。所以说,ELK是
旧的称呼,Elastic Stack是新的名字。

全系的Elastic Stack技术栈包括:
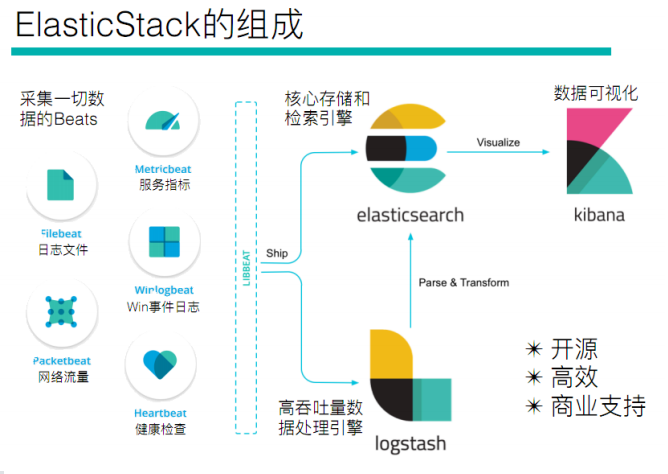
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch 基于java,是个开源分布式搜索引擎,它的特点有:分布式,零配置,自动发现,索引自动分片,索引
副本机制,restful风格接口,多数据源,自动搜索负载等。
Logstash
Logstash 基于java,是一个开源的用于收集,分析和存储日志的工具。
Kibana
Kibana 基于nodejs,也是一个开源和免费的工具,Kibana可以为 Logstash 和 ElasticSearch 提供的日志分析友好的
Web 界面,可以汇总、分析和搜索重要数据日志。
Beats
Beats是elastic公司开源的一款采集系统监控数据的代理agent,是在被监控服务器上以客户端形式运行的数据收集
器的统称,可以直接把数据发送给Elasticsearch或者通过Logstash发送给Elasticsearch,然后进行后续的数据分析活
动。
Beats由如下组成:
Packetbeat:是一个网络数据包分析器,用于监控、收集网络流量信息,Packetbeat嗅探服务器之间的流量,
解析应用层协议,并关联到消息的处理,其支 持ICMP (v4 and v6)、DNS、HTTP、Mysql、PostgreSQL、
Redis、MongoDB、Memcache等协议;
Filebeat:用于监控、收集服务器日志文件,其已取代 logstash forwarder;
Metricbeat:可定期获取外部系统的监控指标信息,其可以监控、收集 Apache、HAProxy、MongoDB
MySQL、Nginx、PostgreSQL、Redis、System、Zookeeper等服务;
Winlogbeat:用于监控、收集Windows系统的日志信息;
2、Elasticsearch
2.1、简介

官网:https://www.elastic.co/cn/products/elasticsearch

2.2、安装
2.2.1、版本说明
Elasticsearch的发展是非常快速的,所以在ES5.0之前,ELK的各个版本都不统一,出现了版本号混乱的状态,所以
从5.0开始,所有Elastic Stack中的项目全部统一版本号。目前最新版本是6.5.4,我们将基于这一版本进行学习。
2.2.2、下载
地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/elasticsearch
或者,使用资料中提供的已下载好的安装包。
2.2.3、单机版安装
#创建elsearch用户,Elasticsearch不支持root用户运行
useradd elsearch
#解压安装包
tar -xvf elasticsearch-6.5.4.tar.gz -C /itcast/es/
#修改配置文件
vim conf/elasticsearch.yml
network.host: 0.0.0.0 #设置ip地址,任意网络均可访问
#说明:在Elasticsearch中如果,network.host不是localhost或者127.0.0.1的话,就会认为是生产环境,
会对环境的要求比较高,我们的测试环境不一定能够满足,一般情况下需要修改2处配置,如下:
#1:修改jvm启动参数
vim conf/jvm.options
-Xms128m #根据自己机器情况修改
-Xmx128m
#2:一个进程在VMAs(虚拟内存区域)创建内存映射最大数量
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.max_map_count=655360
sysctl -p #配置生效
#启动ES服务
su - elsearch
cd bin
./elasticsearch 或 ./elasticsearch -d #后台启动
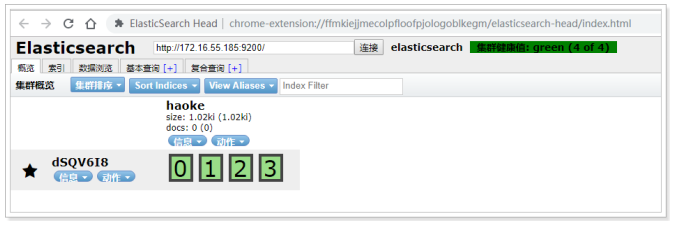
#通过访问进行测试,看到如下信息,就说明ES启动成功了
{
"name": "dSQV6I8",
"cluster_name": "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid": "v5GPTWAtT5emxFdjigFg-w",
"version": {
"number": "6.5.4",
"build_flavor": "default",
"build_type": "tar",
"build_hash": "d2ef93d",
"build_date": "2018-12-17T21:17:40.758843Z",
"build_snapshot": false,
"lucene_version": "7.5.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version": "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version": "5.0.0"
},
"tagline": "You Know, for Search"
}
#停止服务
root@itcast:~# jps
68709 Jps
68072 Elasticsearch
kill 68072 #通过kill结束进程
#启动出错,环境:Centos6
[1]: max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process is too low, increase to at
least [65536]
#解决:切换到root用户,编辑limits.conf 添加类似如下内容
vi /etc/security/limits.conf
添加如下内容:
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 131072
* soft nproc 2048
* hard nproc 4096
[2]: max number of threads [1024] for user [elsearch] is too low, increase to at least
[4096]
#解决:切换到root用户,进入limits.d目录下修改配置文件。
vi /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
#修改如下内容:
* soft nproc 1024
#修改为
* soft nproc 4096
[3]: system call filters failed to install; check the logs and fix your configuration
or disable system call filters at your own risk
#解决:Centos6不支持SecComp,而ES5.2.0默认bootstrap.system_call_filter为true
vim config/elasticsearch.yml
添加:
bootstrap.system_call_filter: false
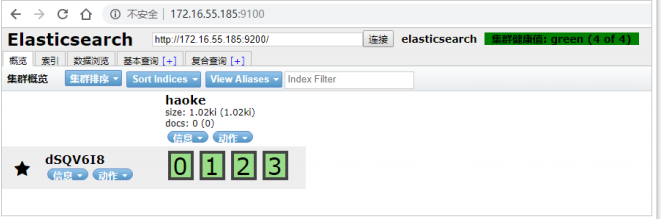
2.2.4、elasticsearch-head
由于ES官方并没有为ES提供界面管理工具,仅仅是提供了后台的服务。elasticsearch-head是一个为ES开发的一个页
面客户端工具,其源码托管于GitHub,地址为:https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head
head提供了4种安装方式:
源码安装,通过npm run start启动(不推荐)
通过docker安装(推荐)
通过chrome插件安装(推荐)
通过ES的plugin方式安装(不推荐)
通过docker安装
#拉取镜像
docker pull mobz/elasticsearch-head:5
#创建容器
docker create --name elasticsearch-head -p 9100:9100 mobz/elasticsearch-head:5
#启动容器
docker start elasticsearch-head
通过浏览器进行访问:
注意:
由于前后端分离开发,所以会存在跨域问题,需要在服务端做CORS的配置,如下:
vim elasticsearch.yml
http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
通过chrome插件的方式安装不存在该问题。
chrome插件的方式安装
打开chrome的应用商店,即可安装https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/elasticsearch-head/ffffmkiejjmec
olpflfloofpjologoblkegm
建议:推荐使用chrome插件的方式安装,如果网络环境不允许,就采用其它方式安装。
2.3、基本概念
索引
索引(index)是Elasticsearch对逻辑数据的逻辑存储,所以它可以分为更小的部分。
可以把索引看成关系型数据库的表,索引的结构是为快速有效的全文索引准备的,特别是它不存储原始值。
Elasticsearch可以把索引存放在一台机器或者分散在多台服务器上,每个索引有一或多个分片(shard),每个
分片可以有多个副本(replica)。
文档
存储在Elasticsearch中的主要实体叫文档(document)。用关系型数据库来类比的话,一个文档相当于数据库
表中的一行记录。
Elasticsearch和MongoDB中的文档类似,都可以有不同的结构,但Elasticsearch的文档中,相同字段必须有相
同类型。
文档由多个字段组成,每个字段可能多次出现在一个文档里,这样的字段叫多值字段(multivalued)。
每个字段的类型,可以是文本、数值、日期等。字段类型也可以是复杂类型,一个字段包含其他子文档或者数
组。
映射
所有文档写进索引之前都会先进行分析,如何将输入的文本分割为词条、哪些词条又会被过滤,这种行为叫做
映射(mapping)。一般由用户自己定义规则。
文档类型
在Elasticsearch中,一个索引对象可以存储很多不同用途的对象。例如,一个博客应用程序可以保存文章和评
论。
每个文档可以有不同的结构。
不同的文档类型不能为相同的属性设置不同的类型。例如,在同一索引中的所有文档类型中,一个叫title的字段
必须具有相同的类型。
2.4、RESTful API
在Elasticsearch中,提供了功能丰富的RESTful API的操作,包括基本的CRUD、创建索引、删除索引等操作。
2.4.1、创建非结构化索引
在Lucene中,创建索引是需要定义字段名称以及字段的类型的,在Elasticsearch中提供了非结构化的索引,就是不
需要创建索引结构,即可写入数据到索引中,实际上在Elasticsearch底层会进行结构化操作,此操作对用户是透明
的。
创建空索引:
PUT /haoke
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "2", #分片数
"number_of_replicas": "0" #副本数
}
}
}
#删除索引
DELETE /haoke
{
"acknowledged": true
}
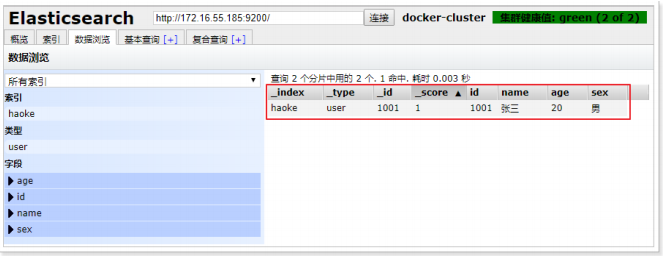
2.4.2、插入数据
URL规则:
POST /{索引}/{类型}/{id}
POST /haoke/user/1001
#数据
{
"id":1001,
"name":"张三",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}
#响应
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1
}
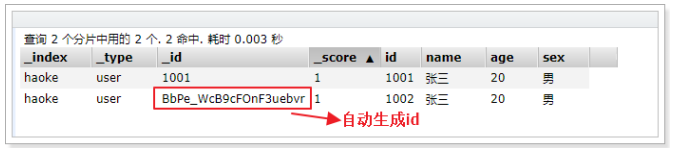
说明:非结构化的索引,不需要事先创建,直接插入数据默认创建索引。
不指定id插入数据:
POST /haoke/user/
{
"id":1002,
"name":"张三",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}
2.4.3、更新数据
在Elasticsearch中,文档数据是不为修改的,但是可以通过覆盖的方式进行更新。
PUT /haoke/user/1001
{
"id":1001,
"name":"张三",
"age":21,
"sex":"女"
}
更新结果如下:
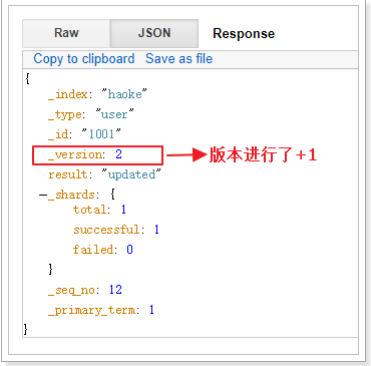
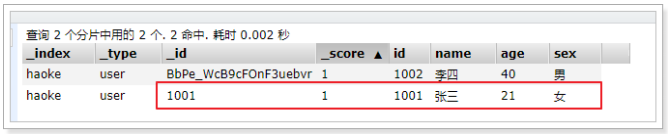
可以看到数据已经被覆盖了。
问题来了,可以局部更新吗? -- 可以的。
前面不是说,文档数据不能更新吗? 其实是这样的:
在内部,依然会查询到这个文档数据,然后进行覆盖操作,步骤如下:
1. 从旧文档中检索JSON
2. 修改它
3. 删除旧文档
4. 索引新文档
示例:
#注意:这里多了_update标识
POST /haoke/user/1001/_update
{
"doc":{
"age":23
}
}
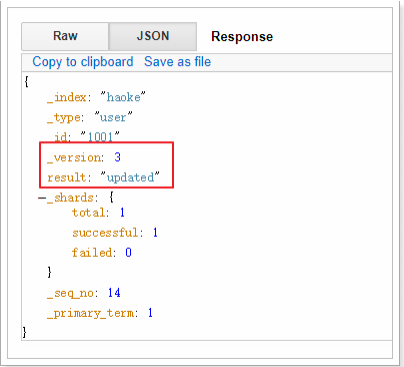
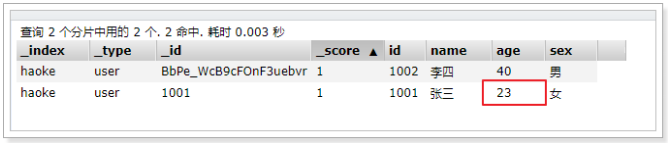
可以看到数据已经被局部更新了。
2.4.4、删除数据
在Elasticsearch中,删除文档数据,只需要发起DELETE请求即可。
DELETE /haoke/user/1001

需要注意的是,result表示已经删除,version也更加了。
如果删除一条不存在的数据,会响应404:
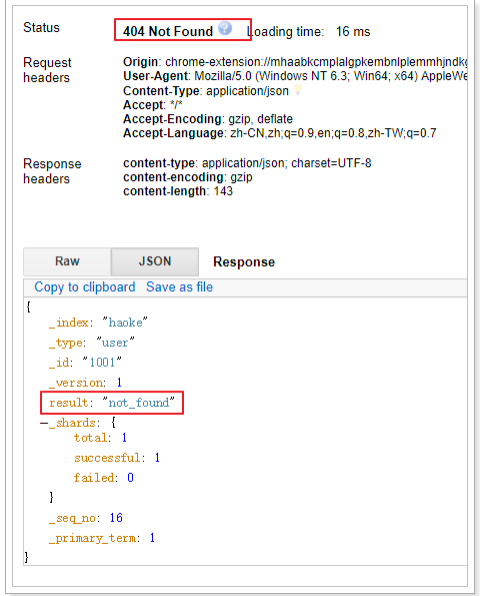
说明:
删除一个文档也不会立即从磁盘上移除,它只是被标记成已删除。Elasticsearch将会在你之后添加更多索引的
时候才会在后台进行删除内容的清理。
2.4.5、搜索数据
根据id搜索数据
GET /haoke/user/BbPe_WcB9cFOnF3uebvr
#返回的数据如下
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "BbPe_WcB9cFOnF3uebvr",
"_version": 8,
"found": true,
"_source": { #原始数据在这里
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 40,
"sex": "男"
}
}
搜索全部数据
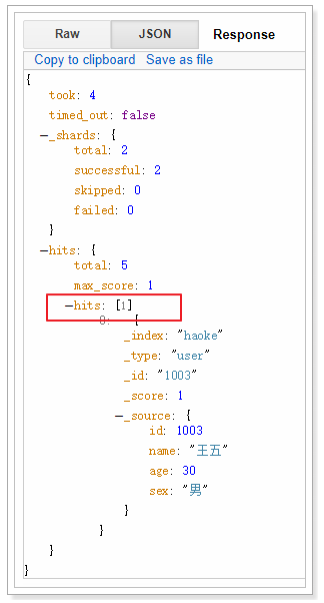
GET /haoke/user/_search
响应:(默认返回10条数据)
{
"took": 26,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 2,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 4,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "BbPe_WcB9cFOnF3uebvr",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 40,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1003",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1003,
"name": "王五",
"age": 30,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1004",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1004,
"name": "赵六",
"age": 30,
"sex": "男"
}
}
]
}
}
关键字搜素数据
#查询年龄等于20的用户
GET /haoke/user/_search?q=age:20
结果:

2.4.6、DSL搜索
Elasticsearch提供丰富且灵活的查询语言叫做DSL查询(Query DSL),它允许你构建更加复杂、强大的查询。
DSL(Domain Specifific Language特定领域语言)以JSON请求体的形式出现。
POST /haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query" : {
"match" : { #match只是查询的一种
"age" : 20
}
}
}
响应数据:

实现:查询年龄大于30岁的男性用户。
现有数据:

POST /haoke/user/_search
#请求数据
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gt": 30
}
}
},
"must": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
}
}
}
}

全文搜索
POST /haoke/user/_search
#请求数据
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三 李四"
}
}
}

2.4.7、高亮显示
POST /haoke/user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三 李四"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"name": {}
}
}
}

2.4.8、聚合
在Elasticsearch中,支持聚合操作,类似SQL中的group by操作。
POST /haoke/user/_search
{
"aggs": {
"all_interests": {
"terms": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}

从结果可以看出,年龄30的有2条数据,20的有一条,40的一条。
3、核心详解
3.1、文档
在Elasticsearch中,文档以JSON格式进行存储,可以是复杂的结构,如:
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1005",
"_version": 1,
"_score": 1,






















"_source": {
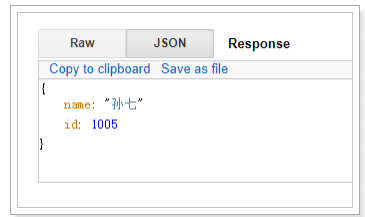
"id": 1005,
"name": "孙七",
"age": 37,
"sex": "女",
"card": {
"card_number": "123456789"
}
}
}
其中,card是一个复杂对象,嵌套的Card对象。
元数据(metadata)
一个文档不只有数据。它还包含了元数据(metadata)——关于文档的信息。三个必须的元数据节点是:

_index
索引(index)类似于关系型数据库里的“数据库”——它是我们存储和索引关联数据的地方。
提示:
事实上,我们的数据被存储和索引在分片(shards)中,索引只是一个把一个或多个分片分组在一起的逻辑空
间。然而,这只是一些内部细节——我们的程序完全不用关心分片。对于我们的程序而言,文档存储在索引
(index)中。剩下的细节由Elasticsearch关心既可。
_type
在应用中,我们使用对象表示一些“事物”,例如一个用户、一篇博客、一个评论,或者一封邮件。每个对象都属于一
个类(class),这个类定义了属性或与对象关联的数据。 user 类的对象可能包含姓名、性别、年龄和Email地址。
在关系型数据库中,我们经常将相同类的对象存储在一个表里,因为它们有着相同的结构。同理,在Elasticsearch
中,我们使用相同类型(type)的文档表示相同的“事物”,因为他们的数据结构也是相同的。
每个类型(type)都有自己的映射(mapping)或者结构定义,就像传统数据库表中的列一样。所有类型下的文档被存储
在同一个索引下,但是类型的映射(mapping)会告诉Elasticsearch不同的文档如何被索引。
_type 的名字可以是大写或小写,不能包含下划线或逗号。我们将使用 blog 做为类型名。
_id
id仅仅是一个字符串,它与 _index 和 _type 组合时,就可以在Elasticsearch中唯一标识一个文档。当创建一个文
档,你可以自定义 _id ,也可以让Elasticsearch帮你自动生成(32位长度)。
3.2、查询响应
3.2.1、pretty
可以在查询url后面添加pretty参数,使得返回的json更易查看。

3.2.2、指定响应字段
在响应的数据中,如果我们不需要全部的字段,可以指定某些需要的字段进行返回。
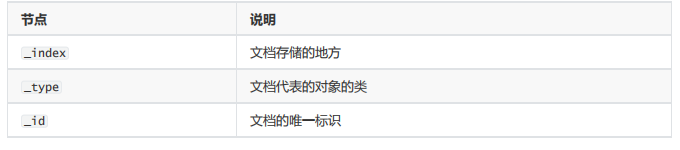
GET /haoke/user/1005?_source=id,name
#响应
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1005",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "孙七",
"id": 1005
}
}
如不需要返回元数据,仅仅返回原始数据,可以这样:
GET /haoke/user/1005/_source

还可以这样:
GET /haoke/user/1005/_source?_source=id,name

3.3、判断文档是否存在
如果我们只需要判断文档是否存在,而不是查询文档内容,那么可以这样:
HEAD /haoke/user/1005

HEAD /haoke/user/1006

当然,这只表示你在查询的那一刻文档不存在,但并不表示几毫秒后依旧不存在。另一个进程在这期间可能创
建新文档。
3.4、批量操作
有些情况下可以通过批量操作以减少网络请求。如:批量查询、批量插入数据。
3.4.1、批量查询
POST /haoke/user/_mget
{
"ids" : [ "1001", "1003" ]
}
结果:

如果,某一条数据不存在,不影响整体响应,需要通过found的值进行判断是否查询到数据。
POST /haoke/user/_mget
{
"ids" : [ "1001", "1006" ]
}
结果:

3.4.2、_bulk操作
在Elasticsearch中,支持批量的插入、修改、删除操作,都是通过_bulk的api完成的。
请求格式如下:(请求格式不同寻常)
{ action: { metadata }}\n
{ request body }\n
{ action: { metadata }}\n
{ request body }\n
...
批量插入数据:
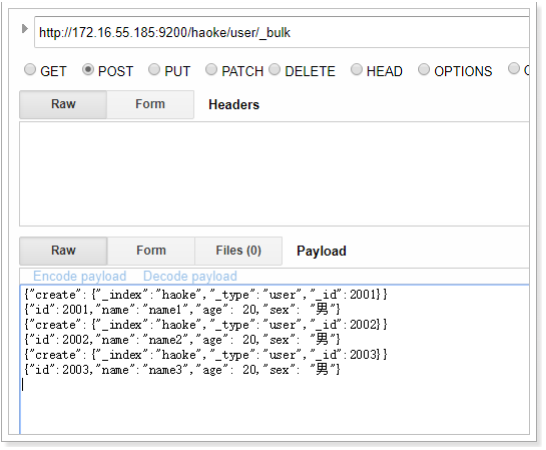
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"id":2001,"name":"name1","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"id":2002,"name":"name2","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
{"id":2003,"name":"name3","age": 20,"sex": "男"}

响应结果:
{
"took": 17,
"errors": false,
"items": [
{
"create": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2001",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 24,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
},
{
"create": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2002",
_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
},
{
"create": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2003",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
}
]
}
批量删除:
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
由于delete没有请求体,所以,action的下一行直接就是下一个action。

{
"took": 3,
"errors": false,
"items": [
{
"delete": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2001",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 25,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
},
{
"delete": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2002",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 2,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
},
{
"delete": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2003",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 3,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
}
]
}
其他操作就类似了。
一次请求多少性能最高?
整个批量请求需要被加载到接受我们请求节点的内存里,所以请求越大,给其它请求可用的内存就越小。有一
个最佳的bulk请求大小。超过这个大小,性能不再提升而且可能降低。
最佳大小,当然并不是一个固定的数字。它完全取决于你的硬件、你文档的大小和复杂度以及索引和搜索的负
载。
幸运的是,这个最佳点(sweetspot)还是容易找到的:试着批量索引标准的文档,随着大小的增长,当性能开始
降低,说明你每个批次的大小太大了。开始的数量可以在1000~5000个文档之间,如果你的文档非常大,可以
使用较小的批次。
通常着眼于你请求批次的物理大小是非常有用的。一千个1kB的文档和一千个1MB的文档大不相同。一个好的
批次最好保持在5-15MB大小间。
3.5、分页
和SQL使用 LIMIT 关键字返回只有一页的结果一样,Elasticsearch接受 from 和 size 参数:
size: 结果数,默认10
from: 跳过开始的结果数,默认0
如果你想每页显示5个结果,页码从1到3,那请求如下:
GET /_search?size=5
GET /_search?size=5&from=5
GET /_search?size=5&from=10
应该当心分页太深或者一次请求太多的结果。结果在返回前会被排序。但是记住一个搜索请求常常涉及多个分
片。每个分片生成自己排好序的结果,它们接着需要集中起来排序以确保整体排序正确。
GET /haoke/user/_search?size=1&from=2

在集群系统中深度分页
为了理解为什么深度分页是有问题的,让我们假设在一个有5个主分片的索引中搜索。当我们请求结果的第一
页(结果1到10)时,每个分片产生自己最顶端10个结果然后返回它们给请求节点(requesting node),它再
排序这所有的50个结果以选出顶端的10个结果。
现在假设我们请求第1000页——结果10001到10010。工作方式都相同,不同的是每个分片都必须产生顶端的
10010个结果。然后请求节点排序这50050个结果并丢弃50040个!
你可以看到在分布式系统中,排序结果的花费随着分页的深入而成倍增长。这也是为什么网络搜索引擎中任何
语句不能返回多于1000个结果的原因。
3.6、映射
前面我们创建的索引以及插入数据,都是由Elasticsearch进行自动判断类型,有些时候我们是需要进行明确字段类型
的,否则,自动判断的类型和实际需求是不相符的。
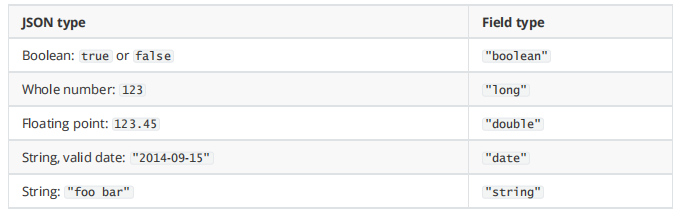
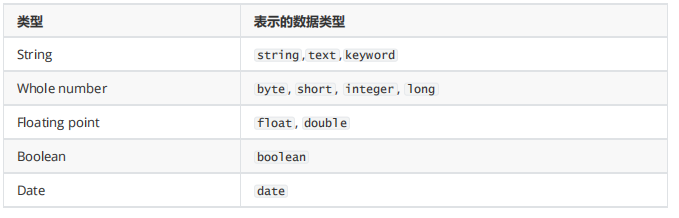
自动判断的规则如下:

Elasticsearch中支持的类型如下:

string类型在ElasticSearch 旧版本中使用较多,从ElasticSearch 5.x开始不再支持string,由text和
keyword类型替代。
text 类型,当一个字段是要被全文搜索的,比如Email内容、产品描述,应该使用text类型。设置text类型
以后,字段内容会被分析,在生成倒排索引以前,字符串会被分析器分成一个一个词项。text类型的字段
不用于排序,很少用于聚合。
keyword类型适用于索引结构化的字段,比如email地址、主机名、状态码和标签。如果字段需要进行过
滤(比如查找已发布博客中status属性为published的文章)、排序、聚合。keyword类型的字段只能通过精
确值搜索到
创建明确类型的索引:
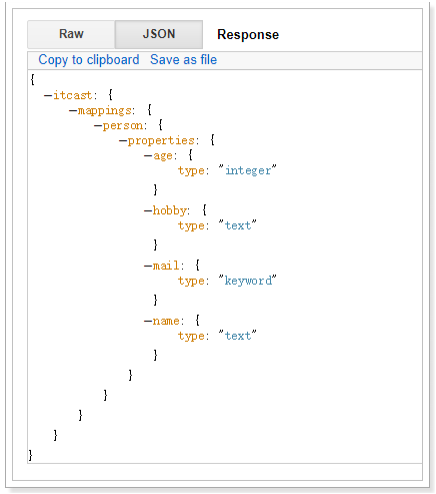
PUT /itcast
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "2",
"number_of_replicas": "0"
}
},
"mappings": {
"person": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"mail": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"hobby": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
查看映射:
GET /itcast/_mapping

插入数据:
POST /itcast/_bulk
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"张三","age": 20,"mail": "111@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"李四","age": 21,"mail": "222@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球、篮球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"王五","age": 22,"mail": "333@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听音乐"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"赵六","age": 23,"mail": "444@qq.com","hobby":"跑步、游泳"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"孙七","age": 24,"mail": "555@qq.com","hobby":"听音乐、看电影"}

测试搜索:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query" : {
"match" : {
"hobby" : "音乐"
}
}
}

3.7、结构化查询
3.7.1、term查询
term 主要用于精确匹配哪些值,比如数字,日期,布尔值或 not_analyzed 的字符串(未经分析的文本数据类型):
{ "term": { "age": 26 }}
{ "term": { "date": "2014-09-01" }}
{ "term": { "public": true }}
{ "term": { "tag": "full_text" }}
示例:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query" : {
"term" : {
"age" : 20
}
}
}

3.7.2、terms查询
terms 跟 term 有点类似,但 terms 允许指定多个匹配条件。 如果某个字段指定了多个值,那么文档需要一起去
做匹配:
{
"terms": {
"tag": [ "search", "full_text", "nosql" ]
}
}
示例:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query" : {
"terms" : {
"age" : [20,21]
}
}
}

3.7.3、range查询
range 过滤允许我们按照指定范围查找一批数据:
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 20,
"lt": 30
}
}
}
范围操作符包含:
gt :: 大于
gte :: 大于等于
lt :: 小于
lte :: 小于等于
示例
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 20,
"lte": 22
}
}
}
}

3.7.4、exists 查询
exists 查询可以用于查找文档中是否包含指定字段或没有某个字段,类似于SQL语句中的 IS_NULL 条件
{
"exists": {
"field": "title"
}
}
这两个查询只是针对已经查出一批数据来,但是想区分出某个字段是否存在的时候使用。
示例:
POST /haoke/user/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": { #必须包含
"field": "card"
}
}
}

3.6.5、match查询
match 查询是一个标准查询,不管你需要全文本查询还是精确查询基本上都要用到它。
如果你使用 match 查询一个全文本字段,它会在真正查询之前用分析器先分析 match 一下查询字符:
{
"match": {
"tweet": "About Search"
}
}
如果用 match 下指定了一个确切值,在遇到数字,日期,布尔值或者 not_analyzed 的字符串时,它将为你搜索你
给定的值:
{ "match": { "age": 26 }}
{ "match": { "date": "2014-09-01" }}
{ "match": { "public": true }}
{ "match": { "tag": "full_text" }}
3.7.6、bool查询
bool 查询可以用来合并多个条件查询结果的布尔逻辑,它包含一下操作符:
must :: 多个查询条件的完全匹配,相当于 and 。
must_not :: 多个查询条件的相反匹配,相当于 not 。
should :: 至少有一个查询条件匹配, 相当于 or 。
这些参数可以分别继承一个查询条件或者一个查询条件的数组:
{
"bool": {
"must": { "term": { "folder": "inbox" }},
"must_not": { "term": { "tag": "spam" }},
"should": [
{ "term": { "starred": true }},
{ "term": { "unread": true }}
]
}
}
3.8、过滤查询
前面讲过结构化查询,Elasticsearch也支持过滤查询,如term、range、match等。
示例:查询年龄为20岁的用户。
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"age": 20
}
}
}
}
}

查询和过滤的对比
查询语句会询问每个文档的字段值与特定值的匹配程度如何。
一条查询语句会计算每个文档与查询语句的相关性,会给出一个相关性评分 _score,并且 按照相关性对匹
配到的文档进行排序。 这种评分方式非常适用于一个没有完全配置结果的全文本搜索。
一个简单的文档列表,快速匹配运算并存入内存是十分方便的, 每个文档仅需要1个字节。这些缓存的过滤结果
集与后续请求的结合使用是非常高效的。
查询语句不仅要查找相匹配的文档,还需要计算每个文档的相关性,所以一般来说查询语句要比 过滤语句更耗
时,并且查询结果也不可缓存。
建议:
做精确匹配搜索时,最好用过滤语句,因为过滤语句可以缓存数据。
4、中文分词
4.1、什么是分词
分词就是指将一个文本转化成一系列单词的过程,也叫文本分析,在Elasticsearch中称之为Analysis。
举例:我是中国人 --> 我/是/中国人
4.2、分词api
指定分词器进行分词
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer":"standard",
"text":"hello world"
}
结果:

在结果中不仅可以看出分词的结果,还返回了该词在文本中的位置。
指定索引分词
POST /itcast/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"field": "hobby",
"text": "听音乐"
}

4.4、中文分词
中文分词的难点在于,在汉语中没有明显的词汇分界点,如在英语中,空格可以作为分隔符,如果分隔不正确就会造
成歧义。
如:
我/爱/炒肉丝
我/爱/炒/肉丝
常用中文分词器,IK、jieba、THULAC等,推荐使用IK分词器。
IK Analyzer是一个开源的,基于java语言开发的轻量级的中文分词工具包。从2006年12月推出1.0版开始,
IKAnalyzer已经推出了3个大版本。最初,它是以开源项目Luence为应用主体的,结合词典分词和文法分析算
法的中文分词组件。新版本的IK Analyzer 3.0则发展为面向Java的公用分词组件,独立于Lucene项目,同时提
供了对Lucene的默认优化实现。
采用了特有的“正向迭代最细粒度切分算法“,具有80万字/秒的高速处理能力 采用了多子处理器分析模式,支
持:英文字母(IP地址、Email、URL)、数字(日期,常用中文数量词,罗马数字,科学计数法),中文词汇
(姓名、地名处理)等分词处理。 优化的词典存储,更小的内存占用。
IK分词器 Elasticsearch插件地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
#安装方法:将下载到的elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip解压到/elasticsearch/plugins/ik目录下
即可。
mkdir es/plugins/ik
cp elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip ./es/plugins/ik
#解压
unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip
#重启
./bin/elasticsearch
测试:
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "我是中国人"
}
结果:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "我",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 1,
"type": "CN_CHAR",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "是",
"start_offset": 1,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "CN_CHAR",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "中国人",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 5,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "中国",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 4,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 3
},
{
"token": "国人",
"start_offset": 3,
"end_offset": 5,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 4
}
]
}
可以看到,已经对中文进行了分词。
5、全文搜索
全文搜索两个最重要的方面是:
相关性(Relevance) 它是评价查询与其结果间的相关程度,并根据这种相关程度对结果排名的一种能力,这
种计算方式可以是 TF/IDF 方法、地理位置邻近、模糊相似,或其他的某些算法。
分词(Analysis) 它是将文本块转换为有区别的、规范化的 token 的一个过程,目的是为了创建倒排索引以及
查询倒排索引。
5.1、构造数据
PUT /itcast
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "1",
"number_of_replicas": "0"
}
},
"mappings": {
"person": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"mail": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"hobby": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}
POST http://172.16.55.185:9200/itcast/_bulk
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"张三","age": 20,"mail": "111@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"李四","age": 21,"mail": "222@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球、篮球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"王五","age": 22,"mail": "333@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听音乐"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"赵六","age": 23,"mail": "444@qq.com","hobby":"跑步、游泳、篮球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"孙七","age": 24,"mail": "555@qq.com","hobby":"听音乐、看电影、羽毛球"}

5.2、单词搜索
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 9,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 0.6841192,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "itcast",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "Uv0cDWgBR-bSw8-LpdkZ",
"_score": 0.6841192,
"_source": {
"name": "王五",
"age": 22,
"mail": "333@qq.com",
"hobby": "羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听音乐"
},
"highlight": {
"hobby": [
"羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听<em>音乐</em>"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "itcast",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "VP0cDWgBR-bSw8-LpdkZ",
"_score": 0.6841192,
"_source": {
"name": "孙七",
"age": 24,
"mail": "555@qq.com",
"hobby": "听音乐、看电影、羽毛球"
},
"highlight": {
"hobby": [
"听<em>音乐</em>、看电影、羽毛球"
]
}
}
]
}
}
过程说明:
1. 检查字段类型
爱好 hobby 字段是一个 text 类型( 指定了IK分词器),这意味着查询字符串本身也应该被分词。
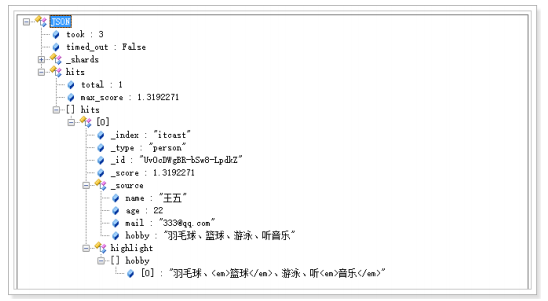
2. 分析查询字符串 。
将查询的字符串 “音乐” 传入IK分词器中,输出的结果是单个项 音乐。因为只有一个单词项,所以 match 查询执
行的是单个底层 term 查询。
3. 查找匹配文档 。
用 term 查询在倒排索引中查找 “音乐” 然后获取一组包含该项的文档,本例的结果是文档:3 、5 。
4. 为每个文档评分 。
用 term 查询计算每个文档相关度评分 _score ,这是种将 词频(term frequency,即词 “音乐” 在相关文档的
hobby 字段中出现的频率)和 反向文档频率(inverse document frequency,即词 “音乐” 在所有文档的
hobby 字段中出现的频率),以及字段的长度(即字段越短相关度越高)相结合的计算方式。
5.3、多词搜索
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐 篮球"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 3,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 4,
"max_score": 1.3192271,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "itcast",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "Uv0cDWgBR-bSw8-LpdkZ",
"_score": 1.3192271,
"_source": {
"name": "王五",
"age": 22,
"mail": "333@qq.com",
"hobby": "羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听音乐"
},
"highlight": {
"hobby": [
"羽毛球、<em>篮球</em>、游泳、听<em>音乐</em>"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "itcast",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "VP0cDWgBR-bSw8-LpdkZ",
"_score": 0.81652206,
"_source": {
"name": "孙七",
"age": 24,
"mail": "555@qq.com",
"hobby": "听音乐、看电影、羽毛球"
},
"highlight": {
"hobby": [
"听<em>音乐</em>、看电影、羽毛球"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "itcast",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "Vf0gDWgBR-bSw8-LOdm_",
"_score": 0.6987338,
"_source": {
"name": "赵六",
"age": 23,
"mail": "444@qq.com",
"hobby": "跑步、游泳、篮球"
},
"highlight": {
"hobby": [
"跑步、游泳、<em>篮球</em>"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "itcast",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "Uf0cDWgBR-bSw8-LpdkZ",
"_score": 0.50270504,
"_source": {
"name": "李四",
"age": 21,
"mail": "222@qq.com",
"hobby": "羽毛球、乒乓球、足球、篮球"
},
"highlight": {
"hobby": [
"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球、<em>篮球</em>"
]
}
}
]
}
}
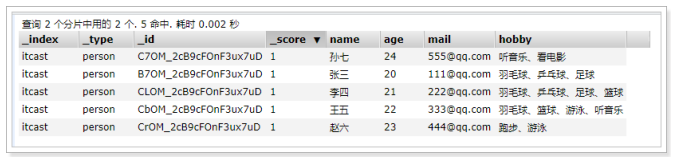
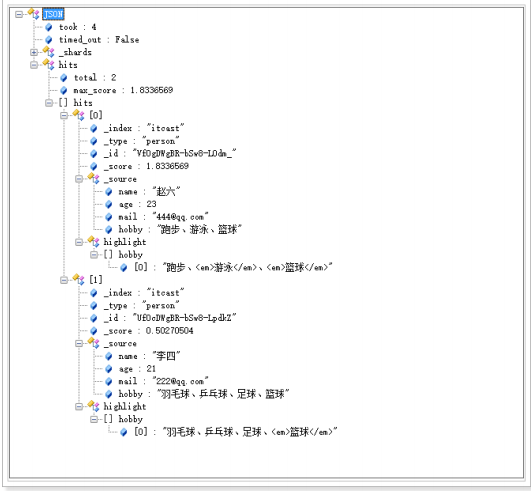
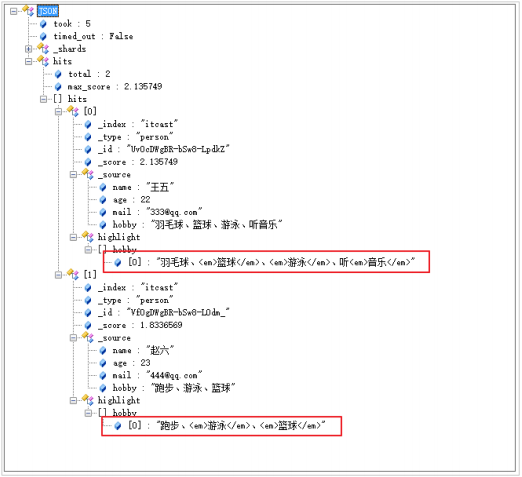
可以看到,包含了“音乐”、“篮球”的数据都已经被搜索到了。
可是,搜索的结果并不符合我们的预期,因为我们想搜索的是既包含“音乐”又包含“篮球”的用户,显然结果返回
的“或”的关系。
在Elasticsearch中,可以指定词之间的逻辑关系,如下
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":{
"query":"音乐 篮球",
"operator":"and"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
结果:

可以看到结果符合预期。
前面我们测试了“OR” 和 “AND”搜索,这是两个极端,其实在实际场景中,并不会选取这2个极端,更有可能是选取这
种,或者说,只需要符合一定的相似度就可以查询到数据,在Elasticsearch中也支持这样的查询,通过
minimum_should_match来指定匹配度,如:70%;
示例:
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":{
"query":"游泳 羽毛球",
"minimum_should_match":"80%"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
#结果:省略显示
"hits": {
"total": 4, #相似度为80%的情况下,查询到4条数据
"max_score": 1.621458,
"hits": [
.........
}
#设置40%进行测试:
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":{
"query":"游泳 羽毛球",
"minimum_should_match":"40%"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
#结果:
"hits": {
"total": 5, #相似度为40%的情况下,查询到5条数据
"max_score": 1.621458,
"hits": [
........
}
相似度应该多少合适,需要在实际的需求中进行反复测试,才可得到合理的值。
5.4、组合搜索
在搜索时,也可以使用过滤器中讲过的bool组合查询,示例:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":{
"match":{
"hobby":"篮球"
}
},
"must_not":{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐"
}
},
"should":[
{
"match": {
"hobby":"游泳"
}
}
]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
上面搜索的意思是:
搜索结果中必须包含篮球,不能包含音乐,如果包含了游泳,那么它的相似度更高。
结果:

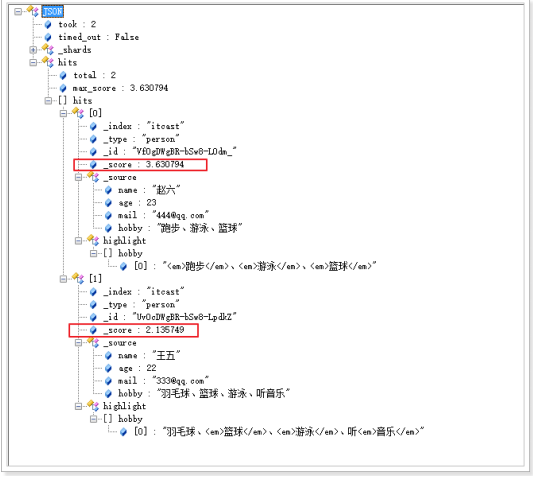
评分的计算规则
bool 查询会为每个文档计算相关度评分 _score , 再将所有匹配的 must 和 should 语句的分数 _score 求和,
最后除以 must 和 should 语句的总数。
must_not 语句不会影响评分; 它的作用只是将不相关的文档排除。
默认情况下,should中的内容不是必须匹配的,如果查询语句中没有must,那么就会至少匹配其中一个。当然了,
也可以通过minimum_should_match参数进行控制,该值可以是数字也可以的百分比。
示例:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"should":[
{
"match": {
"hobby":"游泳"
}
},
{
"match": {
"hobby":"篮球"
}
},
{
"match": {
"hobby":"音乐"
}
}
],
"minimum_should_match":2
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
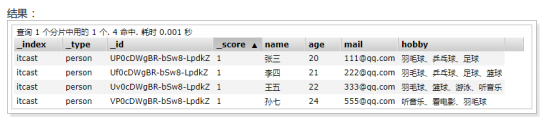
minimum_should_match为2,意思是should中的三个词,至少要满足2个。
结果:

5.5、权重
有些时候,我们可能需要对某些词增加权重来影响该条数据的得分。如下:
搜索关键字为“游泳篮球”,如果结果中包含了“音乐”权重为10,包含了“跑步”权重为2。
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "游泳篮球",
"operator": "and"
}
}
},
"should": [
{
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "音乐",
"boost": 10
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "跑步",
"boost": 2
}
}
}
]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
结果:

如果不设置权重的查询结果是这样:

6、Elasticsearch集群
6.1、集群节点
ELasticsearch的集群是由多个节点组成的,通过cluster.name设置集群名称,并且用于区分其它的集群,每个节点
通过node.name指定节点的名称。
在Elasticsearch中,节点的类型主要有4种:
master节点
配置文件中node.master属性为true(默认为true),就有资格被选为master节点。
master节点用于控制整个集群的操作。比如创建或删除索引,管理其它非master节点等。
data节点
配置文件中node.data属性为true(默认为true),就有资格被设置成data节点。
data节点主要用于执行数据相关的操作。比如文档的CRUD。
客户端节点
配置文件中node.master属性和node.data属性均为false。
该节点不能作为master节点,也不能作为data节点。
可以作为客户端节点,用于响应用户的请求,把请求转发到其他节点
部落节点
当一个节点配置tribe.*的时候,它是一个特殊的客户端,它可以连接多个集群,在所有连接的集群上执行
搜索和其他操作。
6.2、搭建集群
#启动3个虚拟机,分别在3台虚拟机上部署安装Elasticsearch
mkdir /itcast/es-cluster
#分发到其它机器
scp -r es-cluster elsearch@192.168.40.134:/itcast
#node01的配置:
cluster.name: es-itcast-cluster
node.name: node01
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.40.133","192.168.40.134","192.168.40.135"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
#node02的配置:
cluster.name: es-itcast-cluster
node.name: node02
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.40.133","192.168.40.134","192.168.40.135"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
#node03的配置:
cluster.name: es-itcast-cluster
node.name: node02
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.40.133","192.168.40.134","192.168.40.135"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
#分别启动3个节点
./elasticsearch
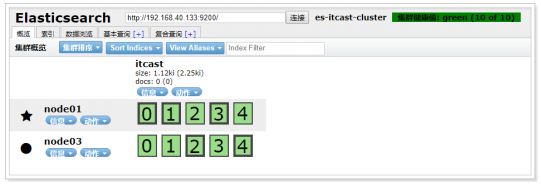
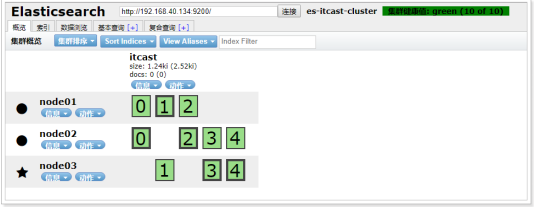
查看集群:

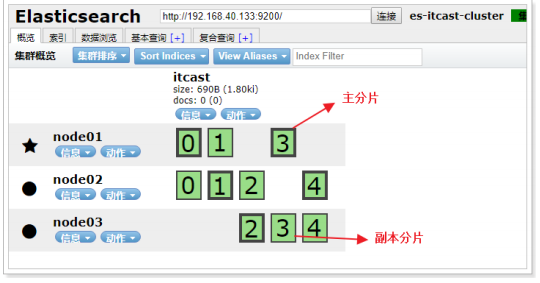
创建索引:

查询集群状态:/_cluster/health
响应:
{
cluster_name: "es-itcast-cluster"
status: "green"
timed_out: false
number_of_nodes: 3
number_of_data_nodes: 3
active_primary_shards: 5
active_shards: 10
relocating_shards: 0
initializing_shards: 0
unassigned_shards: 0
delayed_unassigned_shards: 0
number_of_pending_tasks: 0
number_of_in_flight_fetch: 0
task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis: 0
active_shards_percent_as_number: 100
}
集群状态的三种颜色:

6.3、分片和副本
为了将数据添加到Elasticsearch,我们需要索引(index)——一个存储关联数据的地方。实际上,索引只是一个用来
指向一个或多个分片(shards)的“逻辑命名空间(logical namespace)”.
一个分片(shard)是一个最小级别“工作单元(worker unit)”,它只是保存了索引中所有数据的一部分。
我们需要知道是分片就是一个Lucene实例,并且它本身就是一个完整的搜索引擎。应用程序不会和它直接通
信。
分片可以是主分片(primary shard)或者是复制分片(replica shard)。
索引中的每个文档属于一个单独的主分片,所以主分片的数量决定了索引最多能存储多少数据。
复制分片只是主分片的一个副本,它可以防止硬件故障导致的数据丢失,同时可以提供读请求,比如搜索或者
从别的shard取回文档。
当索引创建完成的时候,主分片的数量就固定了,但是复制分片的数量可以随时调整。
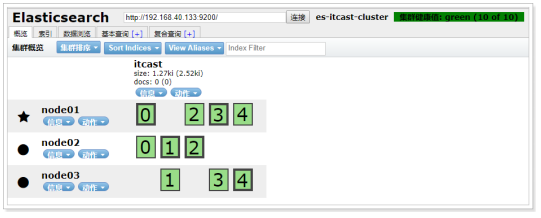
6.4、故障转移
6.4.1、将data节点停止
这里选择将node02停止:

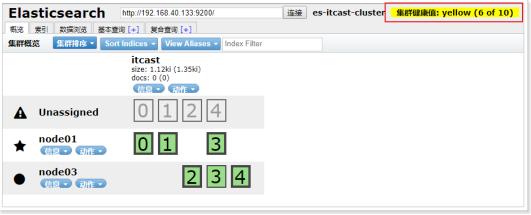
说明:
当前集群状态为黄色,表示主节点可用,副本节点不完全可用
过一段时间观察,发现节点列表中看不到node02,副本节点分配到了node01和node03,集群状态恢复到绿色。

将node02恢复:
./node02/bin/elasticsearch

可以看到,node02恢复后,重新加入了集群,并且重新分配了节点信息。
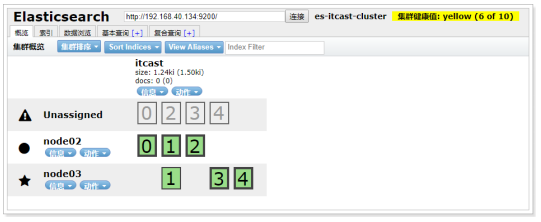
6.4.2、将master节点停止
接下来,测试将node01停止,也就是将主节点停止

从结果中可以看出,集群对master进行了重新选举,选择node03为master。并且集群状态变成黄色。
等待一段时间后,集群状态从黄色变为了绿色:

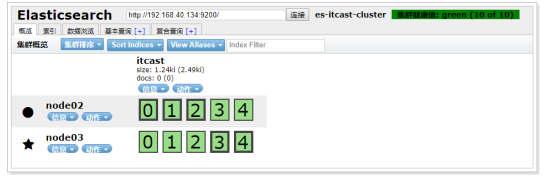
恢复node01节点:
./node01/bin/elasticsearch
重启之后,发现node01可以正常加入到集群中,集群状态依然为绿色:

特别说明:
如果在配置文件中discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes设置的不是N/2+1时,会出现脑裂问题,之前宕机
的主节点恢复后不会加入到集群。

6.5、分布式文档
6.5.1、路由
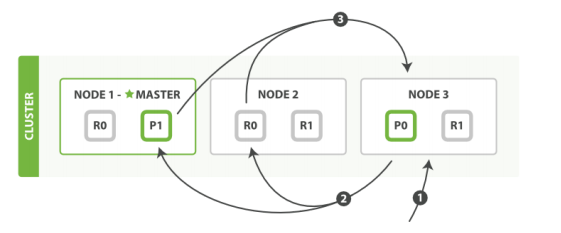
首先,来看个问题:

如图所示:当我们想一个集群保存文档时,文档该存储到哪个节点呢? 是随机吗? 是轮询吗?
实际上,在ELasticsearch中,会采用计算的方式来确定存储到哪个节点,计算公式如下:
shard = hash(routing) % number_of_primary_shards
routing值是一个任意字符串,它默认是_id但也可以自定义。
这个routing字符串通过哈希函数生成一个数字,然后除以主切片的数量得到一个余数(remainder),余数
的范围永远是0到number_of_primary_shards - 1,这个数字就是特定文档所在的分片。
这就是为什么创建了主分片后,不能修改的原因。
6.5.2、文档的写操作
新建、索引和删除请求都是写(write)操作,它们必须在主分片上成功完成才能复制到相关的复制分片上。

下面我们罗列在主分片和复制分片上成功新建、索引或删除一个文档必要的顺序步骤:
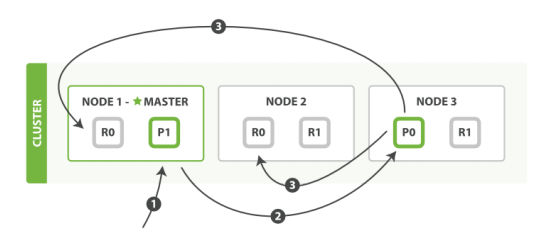
1. 客户端给 Node 1 发送新建、索引或删除请求。
2. 节点使用文档的 _id 确定文档属于分片 0 。它转发请求到 Node 3 ,分片 0 位于这个节点上。
3. Node 3 在主分片上执行请求,如果成功,它转发请求到相应的位于 Node 1 和 Node 2 的复制节点上。当所有
的复制节点报告成功, Node 3 报告成功到请求的节点,请求的节点再报告给客户端。
客户端接收到成功响应的时候,文档的修改已经被应用于主分片和所有的复制分片。你的修改生效了。
6.5.3、搜索文档(单个文档)
文档能够从主分片或任意一个复制分片被检索。

下面我们罗列在主分片或复制分片上检索一个文档必要的顺序步骤:
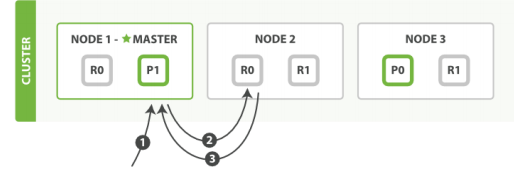
1. 客户端给 Node 1 发送get请求。
2. 节点使用文档的 _id 确定文档属于分片 0 。分片 0 对应的复制分片在三个节点上都有。此时,它转发请求到
Node 2 。
3. Node 2 返回文档(document)给 Node 1 然后返回给客户端。
对于读请求,为了平衡负载,请求节点会为每个请求选择不同的分片——它会循环所有分片副本。
可能的情况是,一个被索引的文档已经存在于主分片上却还没来得及同步到复制分片上。这时复制分片会报告文档未
找到,主分片会成功返回文档。一旦索引请求成功返回给用户,文档则在主分片和复制分片都是可用的。
6.5.4、全文搜索
对于全文搜索而言,文档可能分散在各个节点上,那么在分布式的情况下,如何搜索文档呢?
搜索,分为2个阶段,搜索(query)+取回(fetch)。
搜索(query)

查询阶段包含以下三步:
1. 客户端发送一个 search(搜索) 请求给 Node 3 , Node 3 创建了一个长度为 from+size 的空优先级队
2. Node 3 转发这个搜索请求到索引中每个分片的原本或副本。每个分片在本地执行这个查询并且结果将结果到
一个大小为 from+size 的有序本地优先队列里去。
3. 每个分片返回document的ID和它优先队列里的所有document的排序值给协调节点 Node 3 。 Node 3 把这些
值合并到自己的优先队列里产生全局排序结果。

分发阶段由以下步骤构成:
1. 协调节点辨别出哪个document需要取回,并且向相关分片发出 GET 请求。
2. 每个分片加载document并且根据需要丰富(enrich)它们,然后再将document返回协调节点。
3. 一旦所有的document都被取回,协调节点会将结果返回给客户端。
7、Java客户端
在Elasticsearch中,为java提供了2种客户端,一种是REST风格的客户端,另一种是Java API的客户端。

7.1、REST客户端
Elasticsearch提供了2种REST客户端,一种是低级客户端,一种是高级客户端。
Java Low Level REST Client:官方提供的低级客户端。该客户端通过http来连接Elasticsearch集群。用户在使
用该客户端时需要将请求数据手动拼接成Elasticsearch所需JSON格式进行发送,收到响应时同样也需要将返回
的JSON数据手动封装成对象。虽然麻烦,不过该客户端兼容所有的Elasticsearch版本。
Java High Level REST Client:官方提供的高级客户端。该客户端基于低级客户端实现,它提供了很多便捷的
API来解决低级客户端需要手动转换数据格式的问题
7.2、构造数据
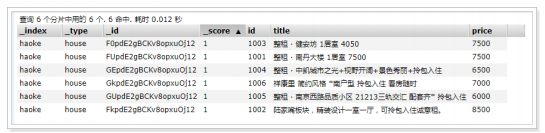
POST /haoke/house/_bulk
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1001","title":"整租 · 南丹大楼 1居室 7500","price":"7500"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1002","title":"陆家嘴板块,精装设计一室一厅,可拎包入住诚意租。","price":"8500"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1003","title":"整租 · 健安坊 1居室 4050","price":"7500"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1004","title":"整租 · 中凯城市之光+视野开阔+景色秀丽+拎包入住","price":"6500"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1005","title":"整租 · 南京西路品质小区 21213三轨交汇 配套齐* 拎包入住","price":"6000"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1006","title":"祥康里 简约风格 *南户型 拎包入住 看房随时","price":"7000"}

7.3、REST低级客户端
7.3.1、创建工程
创建工程itcast-elasticsearch:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cn.itcast.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>itcast-elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
<version>6.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- java编译插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
7.3.2、编写测试用例
package com.wq.test_spring_security.es; /** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * User:wq * Date:2022/10/26 * Time: 14:29 * Description: No Description */ import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import org.apache.http.HttpHost; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import org.elasticsearch.client.*; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class TestESREST { private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper(); private RestClient restClient; @Before public void init() { RestClientBuilder restClientBuilder = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("10.25.20.222", 9200, "http")); restClientBuilder.setFailureListener(new RestClient.FailureListener() { @Override public void onFailure(Node node) { System.out.println("出错了 -> " + node); } }); this.restClient = restClientBuilder.build(); } @After public void after() throws IOException { restClient.close(); } // 查询集群状态 @Test public void testGetInfo() throws IOException { Request request = new Request("GET", "/_cluster/state"); request.addParameter("pretty","true"); Response response = this.restClient.performRequest(request); System.out.println(response.getStatusLine()); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); } // 新增数据 @Test public void testCreateData() throws IOException { Request request = new Request("POST", "/haoke/house"); Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>(); data.put("id","2001"); data.put("title","张江高科"); data.put("price","3500"); request.setJsonEntity(MAPPER.writeValueAsString(data)); Response response = this.restClient.performRequest(request); System.out.println(response.getStatusLine()); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); } // 根据id查询数据 @Test public void testQueryData() throws IOException { Request request = new Request("GET", "/haoke/house/G0pfE2gBCKv8opxuRz1y"); Response response = this.restClient.performRequest(request); System.out.println(response.getStatusLine()); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); } // 搜索数据 @Test public void testSearchData() throws IOException { Request request = new Request("POST", "/haoke/house/_search"); String searchJson = "{\"query\": {\"match\": {\"title\": \"拎包入住\"}}}"; request.setJsonEntity(searchJson); request.addParameter("pretty","true"); Response response = this.restClient.performRequest(request); System.out.println(response.getStatusLine()); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); } }
从使用中,可以看出,基本和我们使用RESTful api使用几乎是一致的。
7.4、REST高级客户端
7.4.1、引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>6.5.4</version>
</dependency>
7.4.2、编写测试用例
package com.wq.test_spring_security.es; /** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * User:wq * Date:2022/10/26 * Time: 14:36 * Description: No Description */ import org.apache.http.HttpHost; import org.elasticsearch.action.ActionListener; import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteResponse; import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse; import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse; import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse; import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateResponse; import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions; import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient; import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder; import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient; import org.elasticsearch.common.Strings; import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue; import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders; import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHit; import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHits; import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder; import org.elasticsearch.search.fetch.subphase.FetchSourceContext; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class TestRestHighLevel { private RestHighLevelClient client; @Before public void init() { RestClientBuilder restClientBuilder = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("10.25.20.222", 9200, "http")); this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(restClientBuilder); } @After public void after() throws Exception { this.client.close(); } /** * 新增文档,同步操作 * * @throws Exception */ @Test public void testCreate() throws Exception { Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>(); data.put("id", "2002"); data.put("title", "南京西路 拎包入住 一室一厅"); data.put("price", "4500"); IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("haoke", "house") .source(data); IndexResponse indexResponse = this.client.index(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("id->" + indexResponse.getId()); System.out.println("index->" + indexResponse.getIndex()); System.out.println("type->" + indexResponse.getType()); System.out.println("version->" + indexResponse.getVersion()); System.out.println("result->" + indexResponse.getResult()); System.out.println("shardInfo->" + indexResponse.getShardInfo()); } /** * 新增文档,异步操作 * * @throws Exception */ @Test public void testCreateAsync() throws Exception { Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>(); data.put("id", "2003"); data.put("title", "南京东路 最新房源 二室一厅"); data.put("price", "5500"); IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("haoke", "house") .source(data); this.client.indexAsync(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT, new ActionListener<IndexResponse>() { @Override public void onResponse(IndexResponse indexResponse) { System.out.println("id->" + indexResponse.getId()); System.out.println("index->" + indexResponse.getIndex()); System.out.println("type->" + indexResponse.getType()); System.out.println("version->" + indexResponse.getVersion()); System.out.println("result->" + indexResponse.getResult()); System.out.println("shardInfo->" + indexResponse.getShardInfo()); } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { System.out.println(e); } }); System.out.println("ok"); Thread.sleep(20000); } @Test public void testQuery() throws Exception { GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("haoke", "house", "GkpdE2gBCKv8opxuOj12"); // 指定返回的字段 String[] includes = new String[]{"title", "id"}; String[] excludes = Strings.EMPTY_ARRAY; FetchSourceContext fetchSourceContext = new FetchSourceContext(true, includes, excludes); getRequest.fetchSourceContext(fetchSourceContext); GetResponse response = this.client.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("数据 -> " + response.getSource()); } /** * 判断是否存在 * * @throws Exception */ @Test public void testExists() throws Exception { GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("haoke", "house", "GkpdE2gBCKv8opxuOj12"); // 不返回的字段 getRequest.fetchSourceContext(new FetchSourceContext(false)); boolean exists = this.client.exists(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("exists -> " + exists); } /** * 删除数据 * * @throws Exception */ @Test public void testDelete() throws Exception { DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("haoke", "house", "GkpdE2gBCKv8opxuOj12"); DeleteResponse response = this.client.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(response.status());// OK or NOT_FOUND } /** * 更新数据 * * @throws Exception */ @Test public void testUpdate() throws Exception { UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("haoke", "house", "G0pfE2gBCKv8opxuRz1y"); Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>(); data.put("title", "张江高科2"); data.put("price", "5000"); updateRequest.doc(data); UpdateResponse response = this.client.update(updateRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("version -> " + response.getVersion()); } /** * 测试搜索 * * @throws Exception */ @Test public void testSearch() throws Exception { SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("haoke"); searchRequest.types("house"); SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "拎包入住")); sourceBuilder.from(0); sourceBuilder.size(5); sourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder); SearchResponse search = this.client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("搜索到 " + search.getHits().totalHits + " 条数据."); SearchHits hits = search.getHits(); for (SearchHit hit : hits) { System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString()); } } }
课程介绍
Nginx日志分析系统
Filebeat入门学习
Metricbeat入门学习
Kibana入门学习
Logstash入门学习
综合练习
1、Nginx日志分析系统
1.1、项目需求
Nginx是一款非常优秀的web服务器,往往nginx服务会作为项目的访问入口,那么,nginx的性能保障就变得非常重
要了,如果nginx的运行出现了问题就会对项目有较大的影响,所以,我们需要对nginx的运行有监控措施,实时掌握
nginx的运行情况,那就需要收集nginx的运行指标和分析nginx的运行日志了。
1.2、业务流程
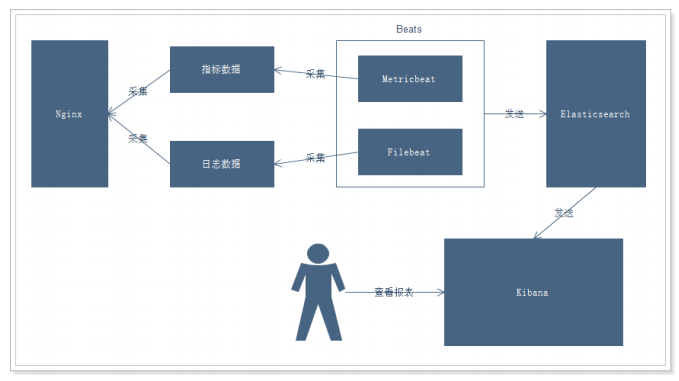
说明:
通过Beats采集Nginx的指标数据和日志数据
Beats采集到数据后发送到Elasticsearch中
Kibana读取数据进行分析
用户通过Kibana进行查看分析报表
2、部署安装Nginx
tar -xvf nginx-1.11.6.tar.gz
yum -y install pcre-devel zlib-devel
./configure
make install
#启动
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
./nginx
#通过浏览器访问页面并且查看日志
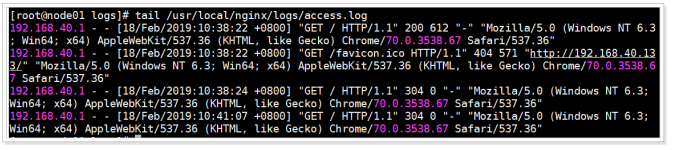
#访问地址:http://192.168.40.133/
tail -f /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log

3、Beats 简介

官网:https://www.elastic.co/cn/products/beats

Beats系列产品:

4、Filebeat

4.1、架构
用于监控、收集服务器日志文件.

4.2、部署与运行
下载(或使用资料中提供的安装包,版本为:fifilebeat-6.5.4):https://www.elastic.co/downloads/beats
mkdir /itcast/beats
tar -xvf filebeat-6.5.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
cd filebeat-6.5.4-linux-x86_64
#创建如下配置文件 itcast.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: stdin
enabled: true
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
output.console:
pretty: true
enable: true
#启动filebeat
./filebeat -e -c itcast.yml
#输入hello运行结果如下:
hello
{
"@timestamp": "2019-01-12T12:50:03.585Z",
"@metadata": { #元数据信息
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "doc",
"version": "6.5.4"
},
"source": "",
"offset": 0,
"message": "hello", #输入的内容
"prospector": { #标准输入勘探器
"type": "stdin"
},
"input": { #控制台标准输入
"type": "stdin"
},
"beat": { #beat版本以及主机信息
"name": "itcast01",
"hostname": "itcast01",
"version": "6.5.4"
},
"host": {
"name": "itcast01"
}
}
4.3、读取文件
#配置读取文件项 itcast-log.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /itcast/beats/logs/*.log
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
output.console:
pretty: true
enable: true
#启动filebeat
./filebeat -e -c itcast-log.yml
#/haoke/beats/logs下创建a.log文件,并输入如下内容
hello
world
#观察filebeat输出
{
"@timestamp": "2019-01-12T14:16:10.192Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "doc",
"version": "6.5.4"
},
"host": {
"name": "itcast01"
},
"source": "/haoke/beats/logs/a.log",
"offset": 0,
"message": "hello",
"prospector": {
"type": "log"
},
"input": {
"type": "log"
},
"beat": {
"version": "6.5.4",
"name": "itcast01",
"hostname": "itcast01"
}
}
{
"@timestamp": "2019-01-12T14:16:10.192Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "doc",
"version": "6.5.4"
},
"prospector": {
"type": "log"
},
"input": {
"type": "log"
},
"beat": {
"version": "6.5.4",
"name": "itcast01",
"hostname": "itcast01"
},
"host": {
"name": "itcast01"
},
"source": "/haoke/beats/logs/a.log",
"offset": 6,
"message": "world"
}
可以看出,已经检测到日志文件有更新,立刻就会读取到更新的内容,并且输出到控制台。
4.4、自定义字段
#配置读取文件项 itcast-log.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /itcast/beats/logs/*.log
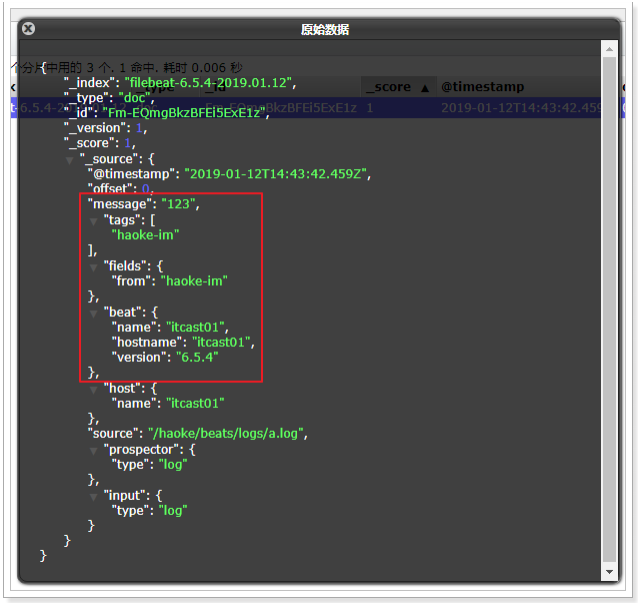
tags: ["web"] #添加自定义tag,便于后续的处理
fields: #添加自定义字段
from: itcast-im
fields_under_root: true #true为添加到根节点,false为添加到子节点中
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
output.console:
pretty: true
enable: true
#启动filebeat
./filebeat -e -c itcast-log.yml
#/haoke/beats/logs下创建a.log文件,并输入如下内容
123
#执行效果
{
"@timestamp": "2019-01-12T14:37:19.845Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "doc",
"version": "6.5.4"
},
"offset": 0,
"tags": [
"haoke-im"
],
"prospector": {
"type": "log"
},
"beat": {
"name": "itcast01",
"hostname": "itcast01",
"version": "6.5.4"
},
"host": {
"name": "itcast01"
},
"source": "/itcast/beats/logs/a.log",
"message": "123",
"input": {
"type": "log"
},
"from": "haoke-im"
}
4.5、输出到Elasticsearch
# itcast-log.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /itcast/beats/logs/*.log
tags: ["haoke-im"]
fields:
from: haoke-im
fields_under_root: false
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3 #指定索引的分区数
output.elasticsearch: #指定ES的配置
hosts: ["192.168.1.7:9200","192.168.1.7:9201","192.168.1.7:9202"]
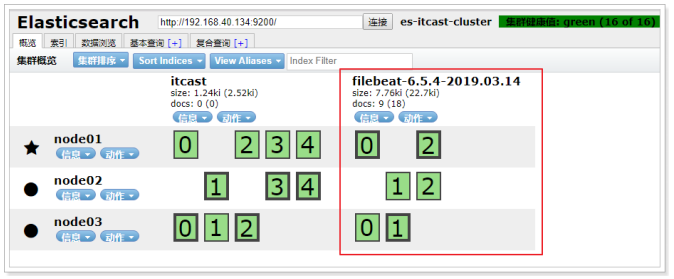
在日志文件中输入新的内容进行测试:

查看数据:

4.6、Filebeat工作原理
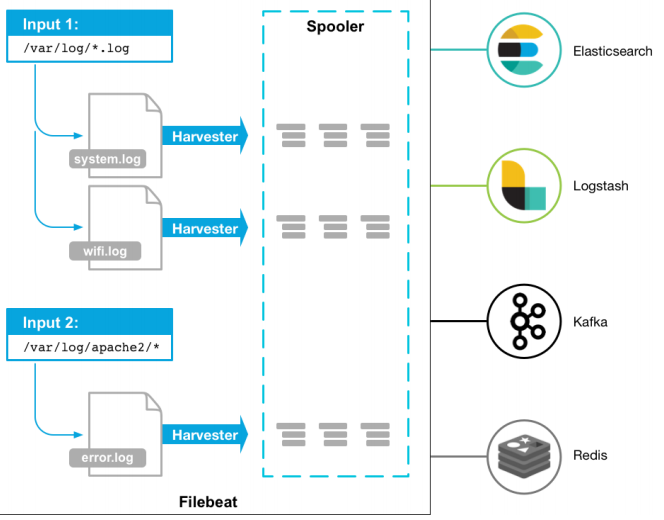
Filebeat由两个主要组件组成:prospector 和 harvester。
harvester:
负责读取单个文件的内容。
如果文件在读取时被删除或重命名,Filebeat将继续读取文件。
prospector
prospector 负责管理harvester并找到所有要读取的文件来源。
如果输入类型为日志,则查找器将查找路径匹配的所有文件,并为每个文件启动一个harvester。
Filebeat目前支持两种prospector类型:log和stdin。
Filebeat如何保持文件的状态
Filebeat 保存每个文件的状态并经常将状态刷新到磁盘上的注册文件中。
该状态用于记住harvester正在读取的最后偏移量,并确保发送所有日志行。
如果输出(例如Elasticsearch或Logstash)无法访问,Filebeat会跟踪最后发送的行,并在输出再次可用
时继续读取文件
在Filebeat运行时,每个prospector内存中也会保存的文件状态信息,当重新启动Filebeat时,将使用注册
文件的数据来重建文件状态,Filebeat将每个harvester在从保存的最后偏移量继续读取。
文件状态记录在data/registry文件中。
启动命令:
4.7、读取Nginx日志文件
./filebeat -e -c itcast.yml
./filebeat -e -c itcast.yml -d "publish"
#参数说明
-e: 输出到标准输出,默认输出到syslog和logs下
-c: 指定配置文件
-d: 输出debug信息
#测试: ./filebeat -e -c itcast-log.yml -d "publish"
DEBUG [publish] pipeline/processor.go:308 Publish event: {
"@timestamp": "2019-01-12T15:03:50.820Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "doc",
"version": "6.5.4"
},
"offset": 0,
"tags": [
"haoke-im"
],
"input": {
"type": "log"
},
"prospector": {
"type": "log"
},
"beat": {
"name": "itcast01",
"hostname": "itcast01",
"version": "6.5.4"
},
"source": "/haoke/beats/logs/a.log",
"fields": {
"from": "haoke-im"
},
"host": {
"name": "itcast01"
},
"message": "456"
}
4.7、读取Nginx日志文件
# itcast-nginx.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /usr/local/nginx/logs/*.log
tags: ["nginx"]
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3 #指定索引的分区数
output.elasticsearch: #指定ES的配置
hosts: ["192.168.40.133:9200","192.168.40.134:9200","192.168.40.135:9200"]
#启动
./filebeat -e -c itcast-nginx.yml

启动后,可以在Elasticsearch中看到索引以及查看数据:


可以看到,在message中已经获取到了nginx的日志,但是,内容并没有经过处理,只是读取到原数据,那么对于我
们后期的操作是不利的,有办法解决吗?
4.7、Module
前面要想实现日志数据的读取以及处理都是自己手动配置的,其实,在Filebeat中,有大量的Module,可以简化我
们的配置,直接就可以使用,如下:
./filebeat modules list
Enabled:
Disabled:
apache2
auditd
elasticsearch
haproxy
icinga
iis
kafka
kibana
logstash
mongodb
mysql
nginx
osquery
postgresql
redis
suricata
system
traefik
可以看到,内置了很多的module,但是都没有启用,如果需要启用需要进行enable操作:
./filebeat modules enable nginx #启动
./filebeat modules disable nginx #禁用
Enabled:
nginx
Disabled:
apache2
auditd
elasticsearch
haproxy
icinga
iis
kafka
kibana
logstash
mongodb
mysql
redis
osquery
postgresql
suricata
system
traefik
可以发现,nginx的module已经被启用。
4.7.1、nginx module 配置
- module: nginx
# Access logs
access:
enabled: true
var.paths: ["/usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log*"]
# Set custom paths for the log files. If left empty,
# Filebeat will choose the paths depending on your OS.
#var.paths:
# Error logs
error:
enabled: true
var.paths: ["/usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log*"]
# Set custom paths for the log files. If left empty,
# Filebeat will choose the paths depending on your OS.
#var.paths:
4.7.2、配置fifilebeat
#vim itcast-nginx.yml
filebeat.inputs:
#- type: log
# enabled: true
# paths:
# - /usr/local/nginx/logs/*.log
# tags: ["nginx"]
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["192.168.40.133:9200","192.168.40.134:9200","192.168.40.135:9200"]
filebeat.config.modules:
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: false
4.7.3、测试
./filebeat -e -c itcast-nginx.yml
#启动会出错,如下
ERROR fileset/factory.go:142 Error loading pipeline: Error loading pipeline for
fileset nginx/access: This module requires the following Elasticsearch plugins:
ingest-user-agent, ingest-geoip. You can install them by running the following
commands on all the Elasticsearch nodes:
sudo bin/elasticsearch-plugin install ingest-user-agent
sudo bin/elasticsearch-plugin install ingest-geoip
#解决:需要在Elasticsearch中安装ingest-user-agent、ingest-geoip插件
#在资料中可以找到,ingest-user-agent.tar、ingest-geoip.tar、ingest-geoip-conf.tar 3个文件
#其中,ingest-user-agent.tar、ingest-geoip.tar解压到plugins下
#ingest-geoip-conf.tar解压到config下
#问题解决。

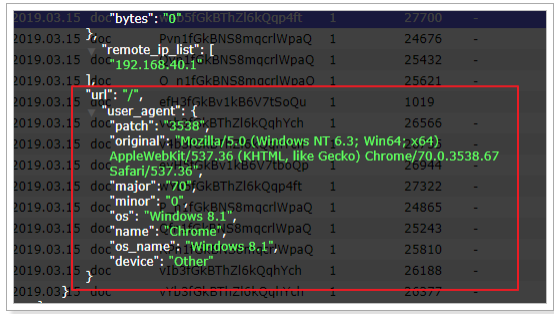
测试发现,数据已经写入到了Elasticsearch中,并且拿到的数据更加明确了

当然了,其他的Module的用法参加官方文档:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/fifilebeat/current/fifilebeat-modules.html

5、Metricbeat
定期收集操作系统或应用服务的指标数据
存储到Elasticsearch中,进行实时分析
5.1、Metricbeat组成
Metricbeat有2部分组成,一部分是Module,另一部分为Metricset。
Module
收集的对象,如:mysql、redis、nginx、操作系统等;
Metricset
收集指标的集合,如:cpu、memory、network等;
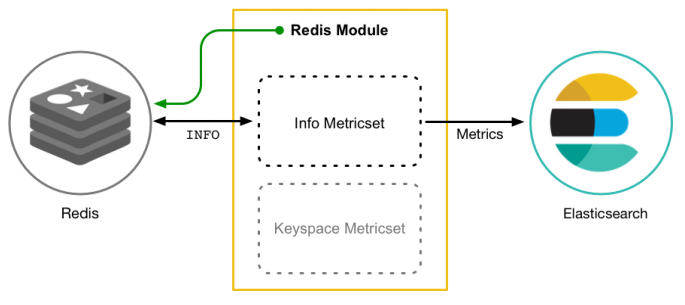
以Redis Module为例:

5.2、部署与收集系统指标
tar -xvf metricbeat-6.5.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
cd metricbeat-6.5.4-linux-x86_64
vim metricbeat.yml
metricbeat.config.modules:
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: false
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 1
index.codec: best_compression
setup.kibana:
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["192.168.40.133:9200","192.168.40.134:9200","192.168.40.135:9200"]
processors:
- add_host_metadata: ~
- add_cloud_metadata: ~
#启动
./metricbeat -e
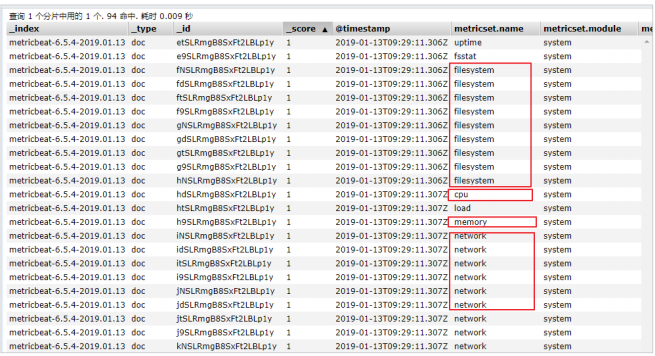
在ELasticsearch中可以看到,系统的一些指标数据已经写入进去了:

system module配置:
root@itcast01:modules.d# cat system.yml
# Module: system
# Docs: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/6.5/metricbeat-module-
system.html
- module: system
period: 10s
metricsets:
- cpu
- load
- memory
- network
- process
- process_summary
#- core
#- diskio
#- socket
process.include_top_n:
by_cpu: 5 # include top 5 processes by CPU
by_memory: 5 # include top 5 processes by memory
- module: system
period: 1m
metricsets:
- filesystem
- fsstat
processors:
- drop_event.when.regexp:
system.filesystem.mount_point: '^/(sys|cgroup|proc|dev|etc|host|lib)($|/)'
- module: system
period: 15m
metricsets:
- uptime
#- module: system
# period: 5m
# metricsets:
# - raid
# raid.mount_point: '/'
