Solr
Solr
一、 Solr 介绍
1 全文检索
什么叫做全文检索呢?这要从我们生活中的数据说起。
我们生活中的数据总体分为两种:结构化数据和非结构化数据。
1)结构化数据:指具有固定格式或有限长度的数据,如数据库,元数据等。
2)非结构化数据:指不定长或无固定格式的数据,如邮件,word 文档等。
非结构化数据又一种叫法叫全文数据。
按照数据的分类,搜索也分为两种:
1)对结构化数据的搜索:如对数据库的搜索,用 SQL 语句。
2)对非结构化数据的搜索:如利用 windows 的搜索也可以搜索文件内容,Linux
下的 grep 命令,再如用 Google 和百度可以搜索大量内容数据。
2 Lucene
Lucene 是一个高效的,基于 Java 的全文检索库。
Lucene 是 apache 软件基金会 4 jakarta 项目组的一个子项目,是一个开放源代码的全
文检索引擎工具包,但它不是一个完整的全文检索引擎,而是一个全文检索引擎的架构,
Lucene 的目的是为软件开发人员提供一个简单易用的工具包,以方便的在目标系统中实现
全文检索的功能,或者是以此为基础建立起完整的全文检索引擎。Lucene 是一套用于全文
检索和搜寻的开源程序库,由 Apache 软件基金会支持和提供。Lucene 提供了一个简单却
强大的应用程序接口,能够做全文索引和搜寻。在 Java 开发环境里 Lucene 是一个成熟的
免费开源工具。就其本身而言,Lucene 是当前以及最近几年最受欢迎的免费 Java 信息检
索程序库。
3 Solr 简介
Solr 是基于 Lucene 的面向企业搜索的 web 应用
Solr 是一个独立的企业级搜索应用服务器,它对外提供类似于 Web-service 的 API 接
口。用户可以通过 http 请求,向搜索引擎服务器提交一定格式的 XML 文件,生成索引;也
可以通过 Http Get 操作提出查找请求,并得到 xml/json 格式的返回结果。
Solr 是一个高性能,采用 Java5 开发,基于 Lucene 的全文搜索服务器。同时对其进行
了扩展,提供了比 Lucene 更为丰富的查询语言,同时实现了可配置、可扩展并对查询性能
进行了优化,并且提供了一个完善的功能管理界面,是一款非常优秀的全文检索引擎。
文档通过 Http 利用 XML 加到一个搜索集合中。查询该集合也是通过 http 收到一个
XML/JSON 响应来实现。它的主要特性包括:高效、灵活的缓存功能,垂直搜索功能,高
亮显示搜索结果,通过索引复制来提高可用性,提供一套强大 Data Schema 来定义字段,
类型和设置文本分析,提供基于 Web 的管理界面等。
二、 Solr 单机版安装
1 安装环境
1.1安装 jdk
1.1.1JDK 版本:
jdk-8u11-linux-x64.tar.gz
1.1.2环境变量配置
vim /etc/profile
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
1.2安装 tomcat
1.2.1Tomcat 版本
apache-tomcat-7.0.47.tar.gz
2 安装 Solr
Solr 版本:solr-4.10.3.tgz.tgz
2.1Solr 是由两个部分构成:
1) Solr 的 web 服务
2) Solr 的索引库2.2上传 Solr 压缩包
2.3解压 Solr 压缩包
2.4Solr 的目录介绍
bin:启动 solr 的一些脚本,但是需要依赖 jeety 容器
contrib:存放的是 solr 对第三方插件支持的内容
dist:solr 编译后所产生一些文件夹。War 或者是 jar
example:是 solr 的案例。在该目录下有两个文件夹对于我们来说比较重要。
1) webapps:在该目录中存放了一个 solr 的 war 包。与 dist 目录下的那个 war 文 件是
同一个,只是存放的目录及名称不同而已。
2) solr: 是 solr 的一个标准的索引库示例。
3) lib/ext:该目录下存放的是一些日志处理器的 jar 包。Solr 的 web 服务也要依赖于日志
处理的 jar 包。所以我们在安装 solr 服务时,需要将该目录下的 jar 拷贝
给 solr 服务
2.5安装 Solr 服务
其实安装 solr 服务就是将 solr 的 war 包,拷贝到 tomcat 的 webapps 目录下。
2.6启动 tomcat,解压 war 包
查看 tomcat 的启动日志,查看是否做 war 的解压
tailf logs/catalina.out
2.7添加服务中所依赖的 jar 包
由于我们在解压后的 solr 的项目中,需要依赖一些日志处理的 jar 包。所以我们在添加
依赖的 jar 包时,需要将原来的 war 删除掉。否则 tomcat 再次启动时,会将原来的目录覆盖
掉。那么新添加的 jar 包也就没了。注意:在删除 war 包时,一定要在 tomcat 关闭的状态下
删除 war 包。如果在 tomcat 启动状态下删除 war 包,那么 tomcat 在关闭时会将解压的目录
一并的也删除掉。
把 lib/ext下的jar包拷贝到tomcat中solr的lib下。
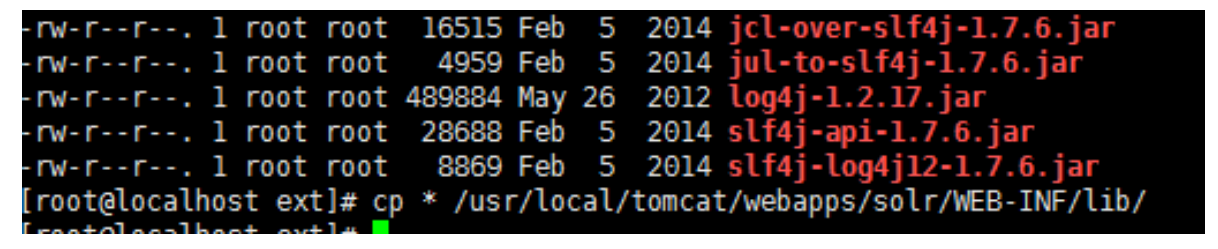
2.8安装 solr 索引库
在 solr 的解压目录的 example 目录下有个 solr 的目录,就是 solr 的一个基本的索引库示
例。
2.9拷贝索引库
将该索引库拷贝到指定目录下(可以是任意目录),虽然具备任意性。但是也不能太随便。
应该放到/usr/local/solrhome。先创建 solrhome 目录
2.10solr 的服务中配置索引库
在 solr 的服务中配置索引库的位置注意:需要配置的路径为索引库的根。可以使用 linux
中的 pwd 命令查看绝对路径。将该路径添加到 solr 服务中的 web.xml 文件中 Solr 服务在启
动时,是通过他的 web.xml 文件中的节点配置获取索引库的绝对位置的。vim web.xml 在
web.xml 中找到<env-entry>.注意:该节点默认是注释状态的,我们需要先去掉注释。然后将
拷贝的索引库的路径添加到该节点的<env-entry-value>节点中
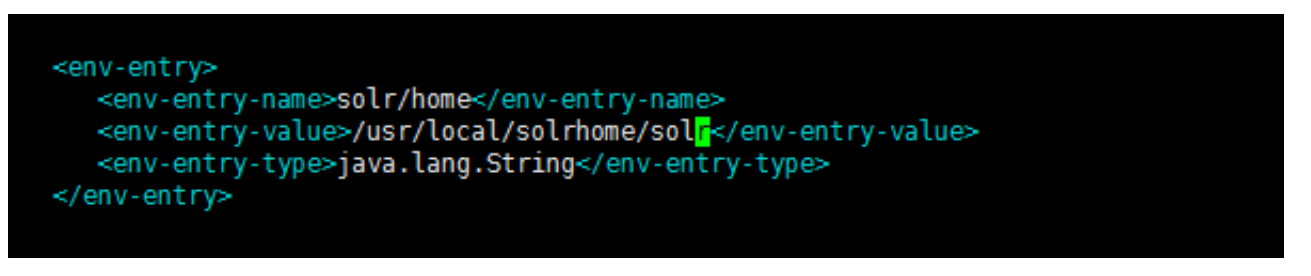
2.11访问 Solr 服务
启动 tomcat 通过 solr 的管理页面可以对 solr 进行操作了。启动 tomcat 后,打开浏览器
输入 solr 的访问 url 就可以访问 solr 服务了
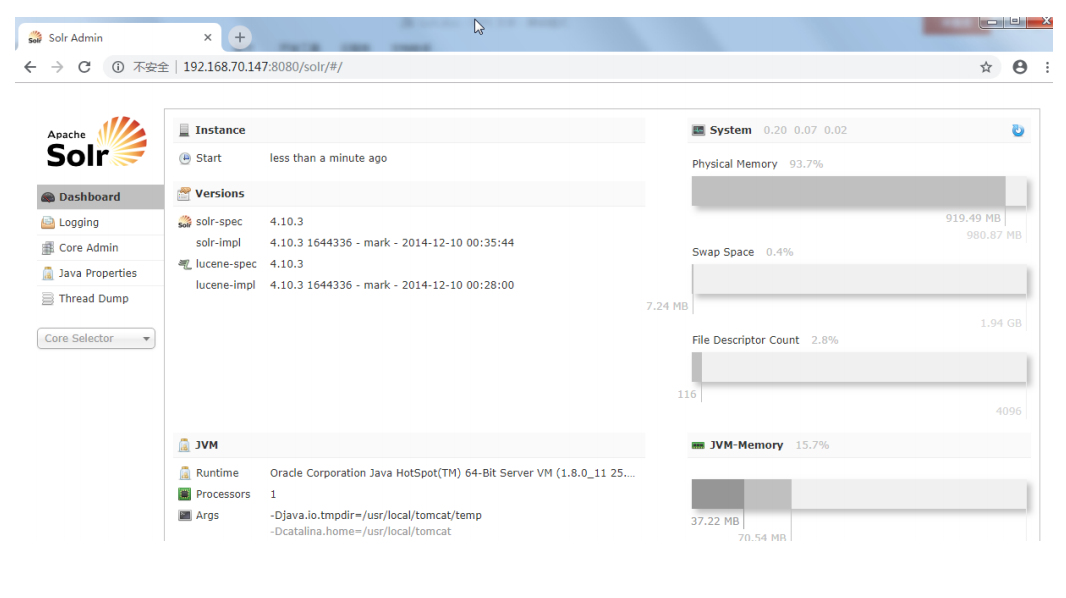
3 Solr 索引库
3.1solr home 目录结构
3.1.1solr.xml 配置 solr 集群
3.1.2collection1(索引库:solr core)
3.1.3core.properties 设置索引库的名称
3.1.4data 存放索引
3.1.5conf 索引库的配置目录
3.1.5.1 schema.xml:配置字段以及字段类型
3.2索引库配置
schema.xml 是用来定义索引数据中的域的,包括域名称,域类型,域是否索引,是否
分词,是否存储等等。
3.2.1如何定义索引库中的 Field
<field>:定义域
<field name="_version_" type="long" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
name:表示域的名称,是强制必须有的属性
type:域类型的名称,与 fieldType 元素的 name 属性值对应,是强制必须有的属性
indexed:是否参与检索。true 即表示需要对该域进行索引。默认值为 false
stored:是否将 field 域中的内容存储到文档域,简单通俗的来说,就是你这一个
field 需不需要被当作查询结果返回。
required:表示这个域是否是必须要在 document 中存在,默认值为 false,如果此配
置项设为 true,则你的 document 中必须要添加此域,否则你创建索引时会抛异常。
3.2.2如何定义索引库中的 FieldType
<fieldType>:定义域的类型
<fieldType name="string" class="solr.StrField" sortMissingLast="true" />
Name:域类型的名称,作为域类型标识符存在,在定义域(Field)时使用的类型
(FieldType)属性就是域类型的名称。
Class:域类型的数据类型,该属性指向的是 solr 中的已定义的类型,或者是用户定
义的类型,域类型中的数据会被初始化成 class 执行类类的对象。sortMissingFirst/sortMissingLast:控制当排序域的值不存在时该文档(Document)
所在队列的位置。true 是则在队头/队尾
3.2.3如何定义索引库中的 CopyField
<copyField>:复制域。可实现更新与查询分离
<copyField source="item_title" dest="item_keywords"/>
Source:源域
Dest:目标域
3.2.4Solr 的索引机制
3.2.4.1 正排索引(正向索引)
正排索引是以文档的 ID 为关键字,索引文档中每个字的位置信息,查找时扫描索引中
每个文档中字的信息直到找出所有包含查询关键字的文档。
但是在查询的时候需对所有的文档进行扫描以确保没有遗漏,这样就使得检索时间大大
延长,检索效率低下。
尽管正排索引的工作原理非常的简单,但是由于其检索效率太低,除非在特定情况下,
否则实用性价值不大。
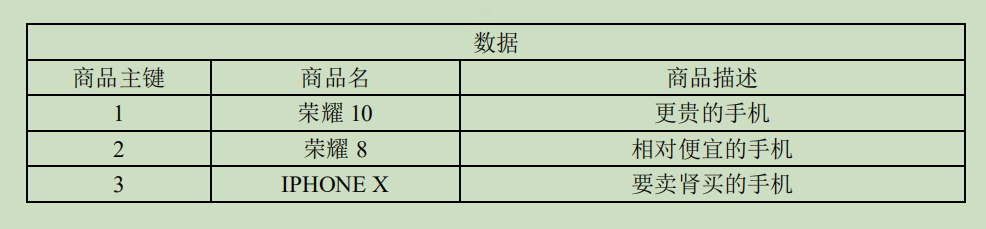
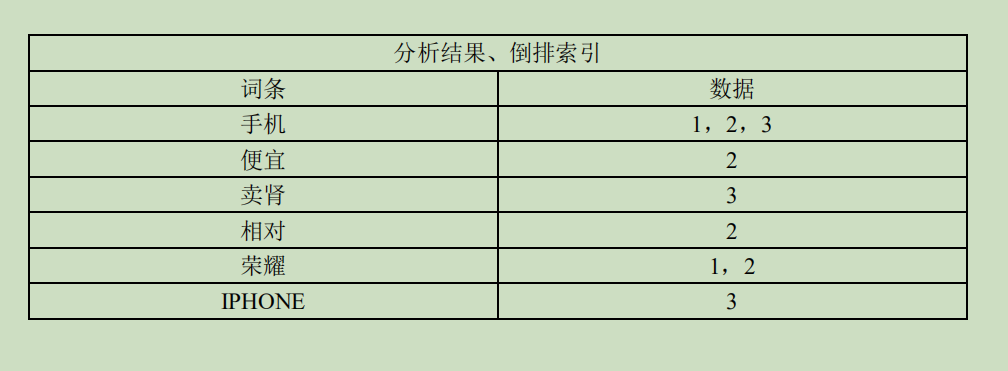
正排索引从文档编号找词

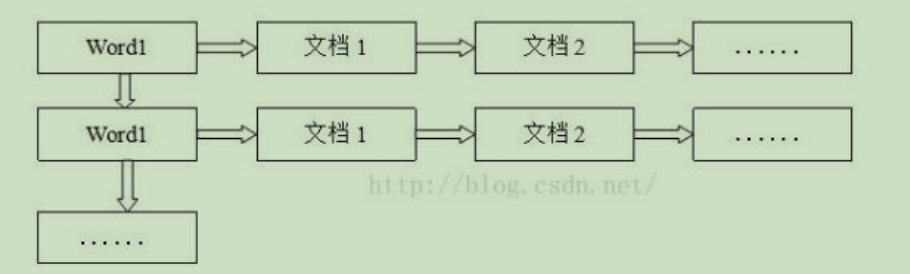
3.2.4.2 倒排索引(反向索引)
对数据进行分析,抽取出数据中的词条,以词条作为 key,对应数据的存储位置作为
value,实现索引的存储。这种索引称为倒排索引。
当 solr 存储文档时,solr 会首先对文档数据进行分词,创建索引库和文档数据库。所谓
的分词是指:将一段字符文本按照一定的规则分成若干个单词。
倒排索引是从词找文档编号
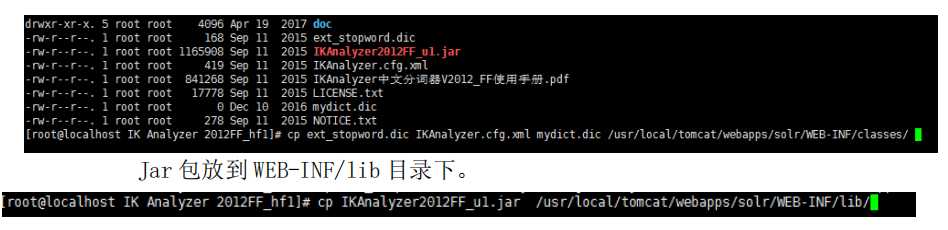
3.2.5配置中文分词器(IK Analyzer)
3.2.5.1 上传中文分词器 jar 包,以及配置文件
3.2.5.2 将中文分词器的配置文件以及 jar包拷贝到 Solr 所对应的目
录下
将配置文件需要放到 classes 目录下。
在 solr 中的 WEB-INF 下时没有 classes 目录的。我们需要先创建一个

3.2.5.3 在 schema.xml 中配置中文分词器

中文分词配置如下:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <!-- This is the Solr schema file. This file should be named "schema.xml" and should be in the conf directory under the solr home (i.e. ./solr/conf/schema.xml by default) or located where the classloader for the Solr webapp can find it. This example schema is the recommended starting point for users. It should be kept correct and concise, usable out-of-the-box. For more information, on how to customize this file, please see http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SchemaXml PERFORMANCE NOTE: this schema includes many optional features and should not be used for benchmarking. To improve performance one could - set stored="false" for all fields possible (esp large fields) when you only need to search on the field but don't need to return the original value. - set indexed="false" if you don't need to search on the field, but only return the field as a result of searching on other indexed fields. - remove all unneeded copyField statements - for best index size and searching performance, set "index" to false for all general text fields, use copyField to copy them to the catchall "text" field, and use that for searching. - For maximum indexing performance, use the ConcurrentUpdateSolrServer java client. - Remember to run the JVM in server mode, and use a higher logging level that avoids logging every request --> <schema name="example" version="1.5"> <!-- attribute "name" is the name of this schema and is only used for display purposes. version="x.y" is Solr's version number for the schema syntax and semantics. It should not normally be changed by applications. 1.0: multiValued attribute did not exist, all fields are multiValued by nature 1.1: multiValued attribute introduced, false by default 1.2: omitTermFreqAndPositions attribute introduced, true by default except for text fields. 1.3: removed optional field compress feature 1.4: autoGeneratePhraseQueries attribute introduced to drive QueryParser behavior when a single string produces multiple tokens. Defaults to off for version >= 1.4 1.5: omitNorms defaults to true for primitive field types (int, float, boolean, string...) --> <!-- Valid attributes for fields: name: mandatory - the name for the field type: mandatory - the name of a field type from the <types> fieldType section indexed: true if this field should be indexed (searchable or sortable) stored: true if this field should be retrievable docValues: true if this field should have doc values. Doc values are useful for faceting, grouping, sorting and function queries. Although not required, doc values will make the index faster to load, more NRT-friendly and more memory-efficient. They however come with some limitations: they are currently only supported by StrField, UUIDField and all Trie*Fields, and depending on the field type, they might require the field to be single-valued, be required or have a default value (check the documentation of the field type you're interested in for more information) multiValued: true if this field may contain multiple values per document omitNorms: (expert) set to true to omit the norms associated with this field (this disables length normalization and index-time boosting for the field, and saves some memory). Only full-text fields or fields that need an index-time boost need norms. Norms are omitted for primitive (non-analyzed) types by default. termVectors: [false] set to true to store the term vector for a given field. When using MoreLikeThis, fields used for similarity should be stored for best performance. termPositions: Store position information with the term vector. This will increase storage costs. termOffsets: Store offset information with the term vector. This will increase storage costs. required: The field is required. It will throw an error if the value does not exist default: a value that should be used if no value is specified when adding a document. --> <!-- field names should consist of alphanumeric or underscore characters only and not start with a digit. This is not currently strictly enforced, but other field names will not have first class support from all components and back compatibility is not guaranteed. Names with both leading and trailing underscores (e.g. _version_) are reserved. --> <!-- If you remove this field, you must _also_ disable the update log in solrconfig.xml or Solr won't start. _version_ and update log are required for SolrCloud --> <field name="_version_" type="long" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <!-- points to the root document of a block of nested documents. Required for nested document support, may be removed otherwise --> <field name="_root_" type="string" indexed="true" stored="false"/> <!-- Only remove the "id" field if you have a very good reason to. While not strictly required, it is highly recommended. A <uniqueKey> is present in almost all Solr installations. See the <uniqueKey> declaration below where <uniqueKey> is set to "id". --> <!--- <field name="id" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" required="true" multiValued="false" /> --> <field name="sku" type="text_en_splitting_tight" indexed="true" stored="true" omitNorms="true"/> <field name="name" type="text_ik" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="manu" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" omitNorms="true"/> <field name="cat" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <field name="features" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <field name="includes" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" termVectors="true" termPositions="true" termOffsets="true" /> <field name="weight" type="float" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="price" type="float" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="popularity" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" /> <field name="inStock" type="boolean" indexed="true" stored="true" /> <field name="store" type="location" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="id" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" required="true" multiValued="false" /> <field name="item_title" type="text_ik" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="item_sell_point" type="text_ik" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="item_price" type="long" indexed="false" stored="true"/> <field name="item_image" type="string" indexed="false" stored="true" /> <field name="item_keywords" type="text_ik" indexed="true" stored="false" multiValued="true"/> <copyField source="item_title" dest="item_keywords"/> <copyField source="item_sell_point" dest="item_keywords"/> <!-- Common metadata fields, named specifically to match up with SolrCell metadata when parsing rich documents such as Word, PDF. Some fields are multiValued only because Tika currently may return multiple values for them. Some metadata is parsed from the documents, but there are some which come from the client context: "content_type": From the HTTP headers of incoming stream "resourcename": From SolrCell request param resource.name --> <field name="title" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <field name="subject" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="description" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="comments" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="author" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="keywords" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="category" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="resourcename" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="url" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="content_type" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <field name="last_modified" type="date" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="links" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <!-- Main body of document extracted by SolrCell. NOTE: This field is not indexed by default, since it is also copied to "text" using copyField below. This is to save space. Use this field for returning and highlighting document content. Use the "text" field to search the content. --> <field name="content" type="text_general" indexed="false" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <!-- catchall field, containing all other searchable text fields (implemented via copyField further on in this schema --> <field name="text" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="false" multiValued="true"/> <!-- catchall text field that indexes tokens both normally and in reverse for efficient leading wildcard queries. --> <field name="text_rev" type="text_general_rev" indexed="true" stored="false" multiValued="true"/> <!-- non-tokenized version of manufacturer to make it easier to sort or group results by manufacturer. copied from "manu" via copyField --> <field name="manu_exact" type="string" indexed="true" stored="false"/> <field name="payloads" type="payloads" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <!-- Some fields such as popularity and manu_exact could be modified to leverage doc values: <field name="popularity" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" docValues="true" /> <field name="manu_exact" type="string" indexed="false" stored="false" docValues="true" /> <field name="cat" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" docValues="true" multiValued="true"/> Although it would make indexing slightly slower and the index bigger, it would also make the index faster to load, more memory-efficient and more NRT-friendly. --> <!-- Dynamic field definitions allow using convention over configuration for fields via the specification of patterns to match field names. EXAMPLE: name="*_i" will match any field ending in _i (like myid_i, z_i) RESTRICTION: the glob-like pattern in the name attribute must have a "*" only at the start or the end. --> <dynamicField name="*_i" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_is" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_s" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" /> <dynamicField name="*_ss" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_l" type="long" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_ls" type="long" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_t" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_txt" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_en" type="text_en" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_b" type="boolean" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_bs" type="boolean" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_f" type="float" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_fs" type="float" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_d" type="double" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_ds" type="double" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <!-- Type used to index the lat and lon components for the "location" FieldType --> <dynamicField name="*_coordinate" type="tdouble" indexed="true" stored="false" /> <dynamicField name="*_dt" type="date" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_dts" type="date" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_p" type="location" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <!-- some trie-coded dynamic fields for faster range queries --> <dynamicField name="*_ti" type="tint" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_tl" type="tlong" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_tf" type="tfloat" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_td" type="tdouble" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_tdt" type="tdate" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="*_c" type="currency" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <dynamicField name="ignored_*" type="ignored" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="attr_*" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/> <dynamicField name="random_*" type="random" /> <!-- uncomment the following to ignore any fields that don't already match an existing field name or dynamic field, rather than reporting them as an error. alternately, change the type="ignored" to some other type e.g. "text" if you want unknown fields indexed and/or stored by default --> <!--dynamicField name="*" type="ignored" multiValued="true" /--> <!-- Field to use to determine and enforce document uniqueness. Unless this field is marked with required="false", it will be a required field --> <uniqueKey>id</uniqueKey> <!-- DEPRECATED: The defaultSearchField is consulted by various query parsers when parsing a query string that isn't explicit about the field. Machine (non-user) generated queries are best made explicit, or they can use the "df" request parameter which takes precedence over this. Note: Un-commenting defaultSearchField will be insufficient if your request handler in solrconfig.xml defines "df", which takes precedence. That would need to be removed. <defaultSearchField>text</defaultSearchField> --> <!-- DEPRECATED: The defaultOperator (AND|OR) is consulted by various query parsers when parsing a query string to determine if a clause of the query should be marked as required or optional, assuming the clause isn't already marked by some operator. The default is OR, which is generally assumed so it is not a good idea to change it globally here. The "q.op" request parameter takes precedence over this. <solrQueryParser defaultOperator="OR"/> --> <!-- copyField commands copy one field to another at the time a document is added to the index. It's used either to index the same field differently, or to add multiple fields to the same field for easier/faster searching. --> <copyField source="cat" dest="text"/> <copyField source="name" dest="text"/> <copyField source="manu" dest="text"/> <copyField source="features" dest="text"/> <copyField source="includes" dest="text"/> <copyField source="manu" dest="manu_exact"/> <!-- Copy the price into a currency enabled field (default USD) --> <copyField source="price" dest="price_c"/> <!-- Text fields from SolrCell to search by default in our catch-all field --> <copyField source="title" dest="text"/> <copyField source="author" dest="text"/> <copyField source="description" dest="text"/> <copyField source="keywords" dest="text"/> <copyField source="content" dest="text"/> <copyField source="content_type" dest="text"/> <copyField source="resourcename" dest="text"/> <copyField source="url" dest="text"/> <!-- Create a string version of author for faceting --> <copyField source="author" dest="author_s"/> <!-- Above, multiple source fields are copied to the [text] field. Another way to map multiple source fields to the same destination field is to use the dynamic field syntax. copyField also supports a maxChars to copy setting. --> <!-- <copyField source="*_t" dest="text" maxChars="3000"/> --> <!-- copy name to alphaNameSort, a field designed for sorting by name --> <!-- <copyField source="name" dest="alphaNameSort"/> --> <!-- field type definitions. The "name" attribute is just a label to be used by field definitions. The "class" attribute and any other attributes determine the real behavior of the fieldType. Class names starting with "solr" refer to java classes in a standard package such as org.apache.solr.analysis --> <!-- The StrField type is not analyzed, but indexed/stored verbatim. It supports doc values but in that case the field needs to be single-valued and either required or have a default value. --> <fieldType name="text_ik" class="solr.TextField"> <analyzer class="org.wltea.analyzer.lucene.IKAnalyzer"/> </fieldType> <fieldType name="string" class="solr.StrField" sortMissingLast="true" /> <!-- boolean type: "true" or "false" --> <fieldType name="boolean" class="solr.BoolField" sortMissingLast="true"/> <!-- sortMissingLast and sortMissingFirst attributes are optional attributes are currently supported on types that are sorted internally as strings and on numeric types. This includes "string","boolean", and, as of 3.5 (and 4.x), int, float, long, date, double, including the "Trie" variants. - If sortMissingLast="true", then a sort on this field will cause documents without the field to come after documents with the field, regardless of the requested sort order (asc or desc). - If sortMissingFirst="true", then a sort on this field will cause documents without the field to come before documents with the field, regardless of the requested sort order. - If sortMissingLast="false" and sortMissingFirst="false" (the default), then default lucene sorting will be used which places docs without the field first in an ascending sort and last in a descending sort. --> <!-- Default numeric field types. For faster range queries, consider the tint/tfloat/tlong/tdouble types. These fields support doc values, but they require the field to be single-valued and either be required or have a default value. --> <fieldType name="int" class="solr.TrieIntField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <fieldType name="float" class="solr.TrieFloatField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <fieldType name="long" class="solr.TrieLongField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <fieldType name="double" class="solr.TrieDoubleField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <!-- Numeric field types that index each value at various levels of precision to accelerate range queries when the number of values between the range endpoints is large. See the javadoc for NumericRangeQuery for internal implementation details. Smaller precisionStep values (specified in bits) will lead to more tokens indexed per value, slightly larger index size, and faster range queries. A precisionStep of 0 disables indexing at different precision levels. --> <fieldType name="tint" class="solr.TrieIntField" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <fieldType name="tfloat" class="solr.TrieFloatField" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <fieldType name="tlong" class="solr.TrieLongField" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <fieldType name="tdouble" class="solr.TrieDoubleField" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <!-- The format for this date field is of the form 1995-12-31T23:59:59Z, and is a more restricted form of the canonical representation of dateTime http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/#dateTime The trailing "Z" designates UTC time and is mandatory. Optional fractional seconds are allowed: 1995-12-31T23:59:59.999Z All other components are mandatory. Expressions can also be used to denote calculations that should be performed relative to "NOW" to determine the value, ie... NOW/HOUR ... Round to the start of the current hour NOW-1DAY ... Exactly 1 day prior to now NOW/DAY+6MONTHS+3DAYS ... 6 months and 3 days in the future from the start of the current day Consult the DateField javadocs for more information. Note: For faster range queries, consider the tdate type --> <fieldType name="date" class="solr.TrieDateField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <!-- A Trie based date field for faster date range queries and date faceting. --> <fieldType name="tdate" class="solr.TrieDateField" precisionStep="6" positionIncrementGap="0"/> <!--Binary data type. The data should be sent/retrieved in as Base64 encoded Strings --> <fieldtype name="binary" class="solr.BinaryField"/> <!-- Note: These should only be used for compatibility with existing indexes (created with lucene or older Solr versions). Use Trie based fields instead. As of Solr 3.5 and 4.x, Trie based fields support sortMissingFirst/Last Plain numeric field types that store and index the text value verbatim (and hence don't correctly support range queries, since the lexicographic ordering isn't equal to the numeric ordering) NOTE: These field types are deprecated will be completely removed in Solr 5.0! --> <!-- <fieldType name="pint" class="solr.IntField"/> <fieldType name="plong" class="solr.LongField"/> <fieldType name="pfloat" class="solr.FloatField"/> <fieldType name="pdouble" class="solr.DoubleField"/> <fieldType name="pdate" class="solr.DateField" sortMissingLast="true"/> --> <!-- The "RandomSortField" is not used to store or search any data. You can declare fields of this type it in your schema to generate pseudo-random orderings of your docs for sorting or function purposes. The ordering is generated based on the field name and the version of the index. As long as the index version remains unchanged, and the same field name is reused, the ordering of the docs will be consistent. If you want different psuedo-random orderings of documents, for the same version of the index, use a dynamicField and change the field name in the request. --> <fieldType name="random" class="solr.RandomSortField" indexed="true" /> <!-- solr.TextField allows the specification of custom text analyzers specified as a tokenizer and a list of token filters. Different analyzers may be specified for indexing and querying. The optional positionIncrementGap puts space between multiple fields of this type on the same document, with the purpose of preventing false phrase matching across fields. For more info on customizing your analyzer chain, please see http://wiki.apache.org/solr/AnalyzersTokenizersTokenFilters --> <!-- One can also specify an existing Analyzer class that has a default constructor via the class attribute on the analyzer element. Example: <fieldType name="text_greek" class="solr.TextField"> <analyzer class="org.apache.lucene.analysis.el.GreekAnalyzer"/> </fieldType> --> <!-- A text field that only splits on whitespace for exact matching of words --> <fieldType name="text_ws" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- A text type for English text where stopwords and synonyms are managed using the REST API --> <fieldType name="managed_en" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.ManagedStopFilterFactory" managed="english" /> <filter class="solr.ManagedSynonymFilterFactory" managed="english" /> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- A general text field that has reasonable, generic cross-language defaults: it tokenizes with StandardTokenizer, removes stop words from case-insensitive "stopwords.txt" (empty by default), and down cases. At query time only, it also applies synonyms. --> <fieldType name="text_general" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer type="index"> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt" /> <!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time <filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/> --> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> <analyzer type="query"> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt" /> <filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- A text field with defaults appropriate for English: it tokenizes with StandardTokenizer, removes English stop words (lang/stopwords_en.txt), down cases, protects words from protwords.txt, and finally applies Porter's stemming. The query time analyzer also applies synonyms from synonyms.txt. --> <fieldType name="text_en" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer type="index"> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time <filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/> --> <!-- Case insensitive stop word removal. --> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_en.txt" /> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.EnglishPossessiveFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/> <!-- Optionally you may want to use this less aggressive stemmer instead of PorterStemFilterFactory: <filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> --> <filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> <analyzer type="query"> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_en.txt" /> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.EnglishPossessiveFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/> <!-- Optionally you may want to use this less aggressive stemmer instead of PorterStemFilterFactory: <filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> --> <filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- A text field with defaults appropriate for English, plus aggressive word-splitting and autophrase features enabled. This field is just like text_en, except it adds WordDelimiterFilter to enable splitting and matching of words on case-change, alpha numeric boundaries, and non-alphanumeric chars. This means certain compound word cases will work, for example query "wi fi" will match document "WiFi" or "wi-fi". --> <fieldType name="text_en_splitting" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" autoGeneratePhraseQueries="true"> <analyzer type="index"> <tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time <filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/> --> <!-- Case insensitive stop word removal. --> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_en.txt" /> <filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="1" generateNumberParts="1" catenateWords="1" catenateNumbers="1" catenateAll="0" splitOnCaseChange="1"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/> <filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> <analyzer type="query"> <tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_en.txt" /> <filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="1" generateNumberParts="1" catenateWords="0" catenateNumbers="0" catenateAll="0" splitOnCaseChange="1"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/> <filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Less flexible matching, but less false matches. Probably not ideal for product names, but may be good for SKUs. Can insert dashes in the wrong place and still match. --> <fieldType name="text_en_splitting_tight" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" autoGeneratePhraseQueries="true"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"/> <filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="0" generateNumberParts="0" catenateWords="1" catenateNumbers="1" catenateAll="0"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/> <filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> <!-- this filter can remove any duplicate tokens that appear at the same position - sometimes possible with WordDelimiterFilter in conjuncton with stemming. --> <filter class="solr.RemoveDuplicatesTokenFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Just like text_general except it reverses the characters of each token, to enable more efficient leading wildcard queries. --> <fieldType name="text_general_rev" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer type="index"> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt" /> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.ReversedWildcardFilterFactory" withOriginal="true" maxPosAsterisk="3" maxPosQuestion="2" maxFractionAsterisk="0.33"/> </analyzer> <analyzer type="query"> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt" /> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- charFilter + WhitespaceTokenizer --> <!-- <fieldType name="text_char_norm" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" > <analyzer> <charFilter class="solr.MappingCharFilterFactory" mapping="mapping-ISOLatin1Accent.txt"/> <tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> --> <!-- This is an example of using the KeywordTokenizer along With various TokenFilterFactories to produce a sortable field that does not include some properties of the source text --> <fieldType name="alphaOnlySort" class="solr.TextField" sortMissingLast="true" omitNorms="true"> <analyzer> <!-- KeywordTokenizer does no actual tokenizing, so the entire input string is preserved as a single token --> <tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- The LowerCase TokenFilter does what you expect, which can be when you want your sorting to be case insensitive --> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory" /> <!-- The TrimFilter removes any leading or trailing whitespace --> <filter class="solr.TrimFilterFactory" /> <!-- The PatternReplaceFilter gives you the flexibility to use Java Regular expression to replace any sequence of characters matching a pattern with an arbitrary replacement string, which may include back references to portions of the original string matched by the pattern. See the Java Regular Expression documentation for more information on pattern and replacement string syntax. http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/regex/package-summary.html --> <filter class="solr.PatternReplaceFilterFactory" pattern="([^a-z])" replacement="" replace="all" /> </analyzer> </fieldType> <fieldtype name="phonetic" stored="false" indexed="true" class="solr.TextField" > <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.DoubleMetaphoneFilterFactory" inject="false"/> </analyzer> </fieldtype> <fieldtype name="payloads" stored="false" indexed="true" class="solr.TextField" > <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- The DelimitedPayloadTokenFilter can put payloads on tokens... for example, a token of "foo|1.4" would be indexed as "foo" with a payload of 1.4f Attributes of the DelimitedPayloadTokenFilterFactory : "delimiter" - a one character delimiter. Default is | (pipe) "encoder" - how to encode the following value into a playload float -> org.apache.lucene.analysis.payloads.FloatEncoder, integer -> o.a.l.a.p.IntegerEncoder identity -> o.a.l.a.p.IdentityEncoder Fully Qualified class name implementing PayloadEncoder, Encoder must have a no arg constructor. --> <filter class="solr.DelimitedPayloadTokenFilterFactory" encoder="float"/> </analyzer> </fieldtype> <!-- lowercases the entire field value, keeping it as a single token. --> <fieldType name="lowercase" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory" /> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Example of using PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory at index time, so queries for paths match documents at that path, or in descendent paths --> <fieldType name="descendent_path" class="solr.TextField"> <analyzer type="index"> <tokenizer class="solr.PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory" delimiter="/" /> </analyzer> <analyzer type="query"> <tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory" /> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Example of using PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory at query time, so queries for paths match documents at that path, or in ancestor paths --> <fieldType name="ancestor_path" class="solr.TextField"> <analyzer type="index"> <tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory" /> </analyzer> <analyzer type="query"> <tokenizer class="solr.PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory" delimiter="/" /> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- since fields of this type are by default not stored or indexed, any data added to them will be ignored outright. --> <fieldtype name="ignored" stored="false" indexed="false" multiValued="true" class="solr.StrField" /> <!-- This point type indexes the coordinates as separate fields (subFields) If subFieldType is defined, it references a type, and a dynamic field definition is created matching *___<typename>. Alternately, if subFieldSuffix is defined, that is used to create the subFields. Example: if subFieldType="double", then the coordinates would be indexed in fields myloc_0___double,myloc_1___double. Example: if subFieldSuffix="_d" then the coordinates would be indexed in fields myloc_0_d,myloc_1_d The subFields are an implementation detail of the fieldType, and end users normally should not need to know about them. --> <fieldType name="point" class="solr.PointType" dimension="2" subFieldSuffix="_d"/> <!-- A specialized field for geospatial search. If indexed, this fieldType must not be multivalued. --> <fieldType name="location" class="solr.LatLonType" subFieldSuffix="_coordinate"/> <!-- An alternative geospatial field type new to Solr 4. It supports multiValued and polygon shapes. For more information about this and other Spatial fields new to Solr 4, see: http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SolrAdaptersForLuceneSpatial4 --> <fieldType name="location_rpt" class="solr.SpatialRecursivePrefixTreeFieldType" geo="true" distErrPct="0.025" maxDistErr="0.000009" units="degrees" /> <!-- Spatial rectangle (bounding box) field. It supports most spatial predicates, and has special relevancy modes: score=overlapRatio|area|area2D (local-param to the query). DocValues is required for relevancy. --> <fieldType name="bbox" class="solr.BBoxField" geo="true" units="degrees" numberType="_bbox_coord" /> <fieldType name="_bbox_coord" class="solr.TrieDoubleField" precisionStep="8" docValues="true" stored="false"/> <!-- Money/currency field type. See http://wiki.apache.org/solr/MoneyFieldType Parameters: defaultCurrency: Specifies the default currency if none specified. Defaults to "USD" precisionStep: Specifies the precisionStep for the TrieLong field used for the amount providerClass: Lets you plug in other exchange provider backend: solr.FileExchangeRateProvider is the default and takes one parameter: currencyConfig: name of an xml file holding exchange rates solr.OpenExchangeRatesOrgProvider uses rates from openexchangerates.org: ratesFileLocation: URL or path to rates JSON file (default latest.json on the web) refreshInterval: Number of minutes between each rates fetch (default: 1440, min: 60) --> <fieldType name="currency" class="solr.CurrencyField" precisionStep="8" defaultCurrency="USD" currencyConfig="currency.xml" /> <!-- some examples for different languages (generally ordered by ISO code) --> <!-- Arabic --> <fieldType name="text_ar" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- for any non-arabic --> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ar.txt" /> <!-- normalizes ﻯ to ﻱ, etc --> <filter class="solr.ArabicNormalizationFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.ArabicStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Bulgarian --> <fieldType name="text_bg" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_bg.txt" /> <filter class="solr.BulgarianStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Catalan --> <fieldType name="text_ca" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- removes l', etc --> <filter class="solr.ElisionFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" articles="lang/contractions_ca.txt"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ca.txt" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Catalan"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- CJK bigram (see text_ja for a Japanese configuration using morphological analysis) --> <fieldType name="text_cjk" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- normalize width before bigram, as e.g. half-width dakuten combine --> <filter class="solr.CJKWidthFilterFactory"/> <!-- for any non-CJK --> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.CJKBigramFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Kurdish --> <fieldType name="text_ckb" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.SoraniNormalizationFilterFactory"/> <!-- for any latin text --> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ckb.txt"/> <filter class="solr.SoraniStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Czech --> <fieldType name="text_cz" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_cz.txt" /> <filter class="solr.CzechStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Danish --> <fieldType name="text_da" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_da.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Danish"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- German --> <fieldType name="text_de" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_de.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.GermanNormalizationFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.GermanLightStemFilterFactory"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.GermanMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> --> <!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="German2"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Greek --> <fieldType name="text_el" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- greek specific lowercase for sigma --> <filter class="solr.GreekLowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="false" words="lang/stopwords_el.txt" /> <filter class="solr.GreekStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Spanish --> <fieldType name="text_es" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_es.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.SpanishLightStemFilterFactory"/> <!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Spanish"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Basque --> <fieldType name="text_eu" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_eu.txt" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Basque"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Persian --> <fieldType name="text_fa" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <!-- for ZWNJ --> <charFilter class="solr.PersianCharFilterFactory"/> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.ArabicNormalizationFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.PersianNormalizationFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_fa.txt" /> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Finnish --> <fieldType name="text_fi" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_fi.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Finnish"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.FinnishLightStemFilterFactory"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- French --> <fieldType name="text_fr" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- removes l', etc --> <filter class="solr.ElisionFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" articles="lang/contractions_fr.txt"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_fr.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.FrenchLightStemFilterFactory"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.FrenchMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> --> <!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="French"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Irish --> <fieldType name="text_ga" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- removes d', etc --> <filter class="solr.ElisionFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" articles="lang/contractions_ga.txt"/> <!-- removes n-, etc. position increments is intentionally false! --> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/hyphenations_ga.txt"/> <filter class="solr.IrishLowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ga.txt"/> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Irish"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Galician --> <fieldType name="text_gl" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_gl.txt" /> <filter class="solr.GalicianStemFilterFactory"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.GalicianMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Hindi --> <fieldType name="text_hi" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <!-- normalizes unicode representation --> <filter class="solr.IndicNormalizationFilterFactory"/> <!-- normalizes variation in spelling --> <filter class="solr.HindiNormalizationFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_hi.txt" /> <filter class="solr.HindiStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Hungarian --> <fieldType name="text_hu" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_hu.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Hungarian"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.HungarianLightStemFilterFactory"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Armenian --> <fieldType name="text_hy" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_hy.txt" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Armenian"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Indonesian --> <fieldType name="text_id" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_id.txt" /> <!-- for a less aggressive approach (only inflectional suffixes), set stemDerivational to false --> <filter class="solr.IndonesianStemFilterFactory" stemDerivational="true"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Italian --> <fieldType name="text_it" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <!-- removes l', etc --> <filter class="solr.ElisionFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" articles="lang/contractions_it.txt"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_it.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.ItalianLightStemFilterFactory"/> <!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Italian"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Japanese using morphological analysis (see text_cjk for a configuration using bigramming) NOTE: If you want to optimize search for precision, use default operator AND in your query parser config with <solrQueryParser defaultOperator="AND"/> further down in this file. Use OR if you would like to optimize for recall (default). --> <fieldType name="text_ja" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" autoGeneratePhraseQueries="false"> <analyzer> <!-- Kuromoji Japanese morphological analyzer/tokenizer (JapaneseTokenizer) Kuromoji has a search mode (default) that does segmentation useful for search. A heuristic is used to segment compounds into its parts and the compound itself is kept as synonym. Valid values for attribute mode are: normal: regular segmentation search: segmentation useful for search with synonyms compounds (default) extended: same as search mode, but unigrams unknown words (experimental) For some applications it might be good to use search mode for indexing and normal mode for queries to reduce recall and prevent parts of compounds from being matched and highlighted. Use <analyzer type="index"> and <analyzer type="query"> for this and mode normal in query. Kuromoji also has a convenient user dictionary feature that allows overriding the statistical model with your own entries for segmentation, part-of-speech tags and readings without a need to specify weights. Notice that user dictionaries have not been subject to extensive testing. User dictionary attributes are: userDictionary: user dictionary filename userDictionaryEncoding: user dictionary encoding (default is UTF-8) See lang/userdict_ja.txt for a sample user dictionary file. Punctuation characters are discarded by default. Use discardPunctuation="false" to keep them. See http://wiki.apache.org/solr/JapaneseLanguageSupport for more on Japanese language support. --> <tokenizer class="solr.JapaneseTokenizerFactory" mode="search"/> <!--<tokenizer class="solr.JapaneseTokenizerFactory" mode="search" userDictionary="lang/userdict_ja.txt"/>--> <!-- Reduces inflected verbs and adjectives to their base/dictionary forms (辞書形) --> <filter class="solr.JapaneseBaseFormFilterFactory"/> <!-- Removes tokens with certain part-of-speech tags --> <filter class="solr.JapanesePartOfSpeechStopFilterFactory" tags="lang/stoptags_ja.txt" /> <!-- Normalizes full-width romaji to half-width and half-width kana to full-width (Unicode NFKC subset) --> <filter class="solr.CJKWidthFilterFactory"/> <!-- Removes common tokens typically not useful for search, but have a negative effect on ranking --> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ja.txt" /> <!-- Normalizes common katakana spelling variations by removing any last long sound character (U+30FC) --> <filter class="solr.JapaneseKatakanaStemFilterFactory" minimumLength="4"/> <!-- Lower-cases romaji characters --> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Latvian --> <fieldType name="text_lv" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_lv.txt" /> <filter class="solr.LatvianStemFilterFactory"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Dutch --> <fieldType name="text_nl" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_nl.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.StemmerOverrideFilterFactory" dictionary="lang/stemdict_nl.txt" ignoreCase="false"/> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Dutch"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Norwegian --> <fieldType name="text_no" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_no.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Norwegian"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.NorwegianLightStemFilterFactory" variant="nb"/> --> <!-- singular/plural: <filter class="solr.NorwegianMinimalStemFilterFactory" variant="nb"/> --> <!-- The "light" and "minimal" stemmers support variants: nb=Bokmål, nn=Nynorsk, no=Both --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Portuguese --> <fieldType name="text_pt" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_pt.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.PortugueseLightStemFilterFactory"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.PortugueseMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> --> <!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Portuguese"/> --> <!-- most aggressive: <filter class="solr.PortugueseStemFilterFactory"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Romanian --> <fieldType name="text_ro" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ro.txt" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Romanian"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Russian --> <fieldType name="text_ru" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ru.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Russian"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.RussianLightStemFilterFactory"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Swedish --> <fieldType name="text_sv" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_sv.txt" format="snowball" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Swedish"/> <!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.SwedishLightStemFilterFactory"/> --> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Thai --> <fieldType name="text_th" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.ThaiTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_th.txt" /> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Turkish --> <fieldType name="text_tr" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100"> <analyzer> <tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/> <filter class="solr.ApostropheFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.TurkishLowerCaseFilterFactory"/> <filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="false" words="lang/stopwords_tr.txt" /> <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Turkish"/> </analyzer> </fieldType> <!-- Similarity is the scoring routine for each document vs. a query. A custom Similarity or SimilarityFactory may be specified here, but the default is fine for most applications. For more info: http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SchemaXml#Similarity --> <!-- <similarity class="com.example.solr.CustomSimilarityFactory"> <str name="paramkey">param value</str> </similarity> --> </schema>
3.2.5.4 测试
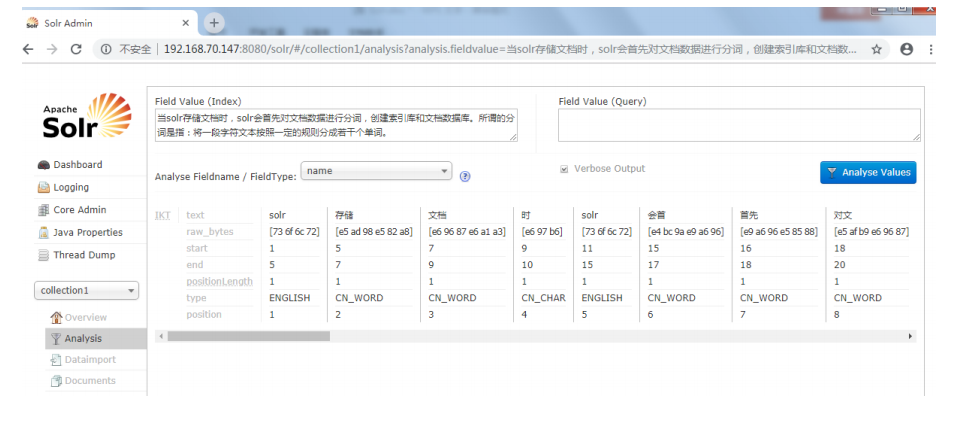
3.3Solr 管理页面操作
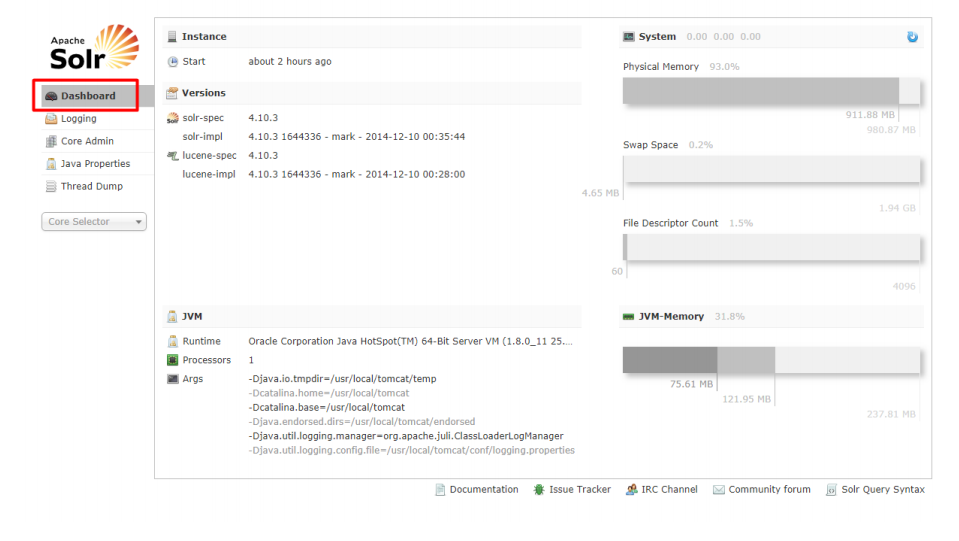
3.3.1Dashboard(仪表盘)
访问 http://localhost:8080/solr 时,出现该主页面,可查看到 solr 运行时间、solr 版本,
系统内存、虚拟机内存的使用情况
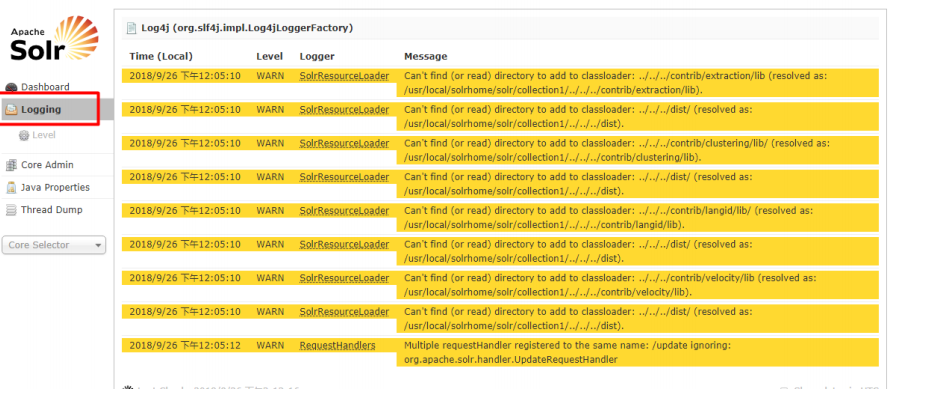
3.3.2Logging(日志)
显示 solr 运行出现的异常或错误
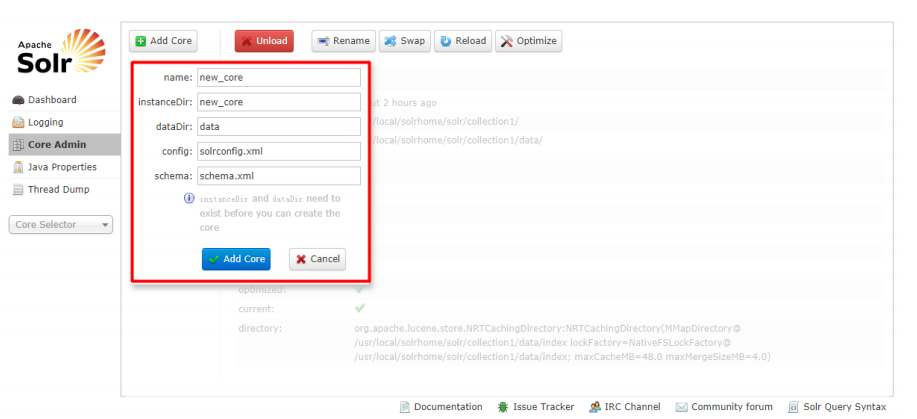
3.3.3Core Admin (core 管理)
主要有 Add Core(添加核心),Unload(卸载核心),Rename(重命名核心),Reload(重
新加载核心),Optimize(优化索引库)
Add Core 是添加 core : 主 要 是 在 instanceDir 对 应 的 文 件 夹 里 生 成 一 个
core.properties 文件

name:给 core 起的名字;
instanceDir:与我们在配置 solr 到 tomcat 里时的 solr_home 里新建的 core
文件夹名一致;
dataDir:确认 Add Core 时,会在 new_core 目录下生成名为 data 的文件夹
config:new_core 下的 conf 下的 config 配置文件(solrconfig.xml)
schema: new_core 下的 conf 下的 schema 文件(schema.xml)
3.3.4Java Properties
可查看到 java 相关的一些属性的信息

3.3.5Thread Dump
查看每个线程的详细信息,以及状态信息
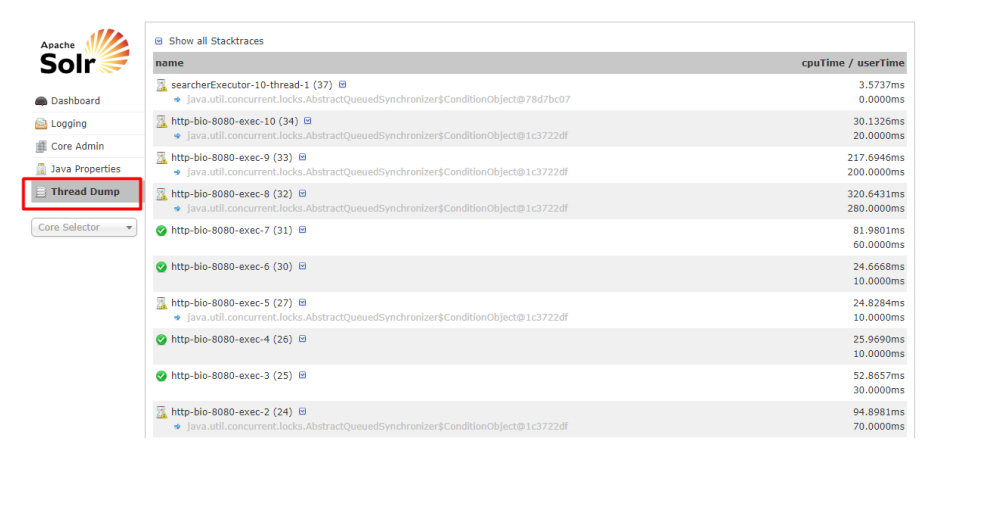
3.3.6Core Selecter(core 选择器)

3.3.6.1 overview(概览)
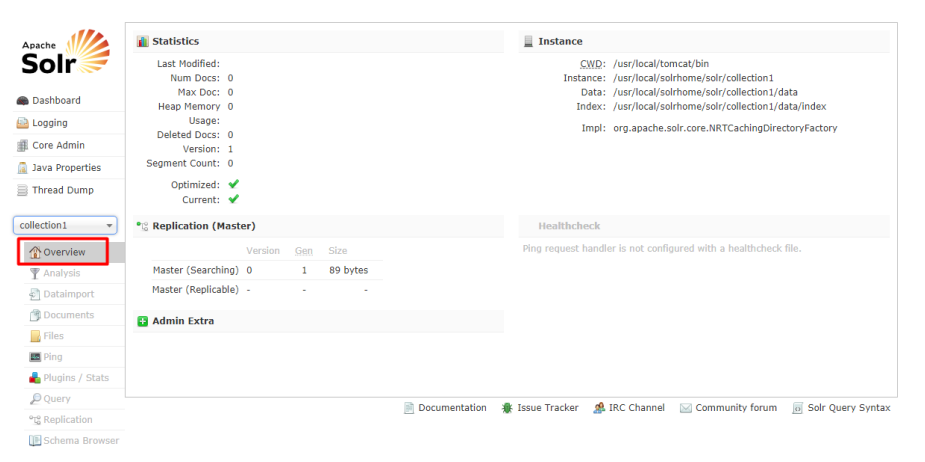
包含基本统计如当前文档数;和实例信息如当前核心的配置目录
3.3.6.2 Analysis(分析)
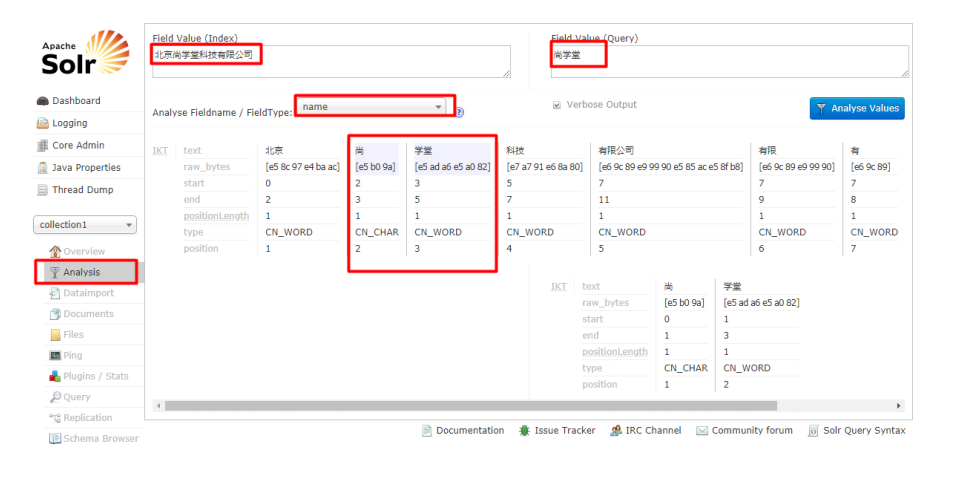
检验分词效果
3.3.6.3 Dataimport(导入数据)
3.3.6.4 Documents
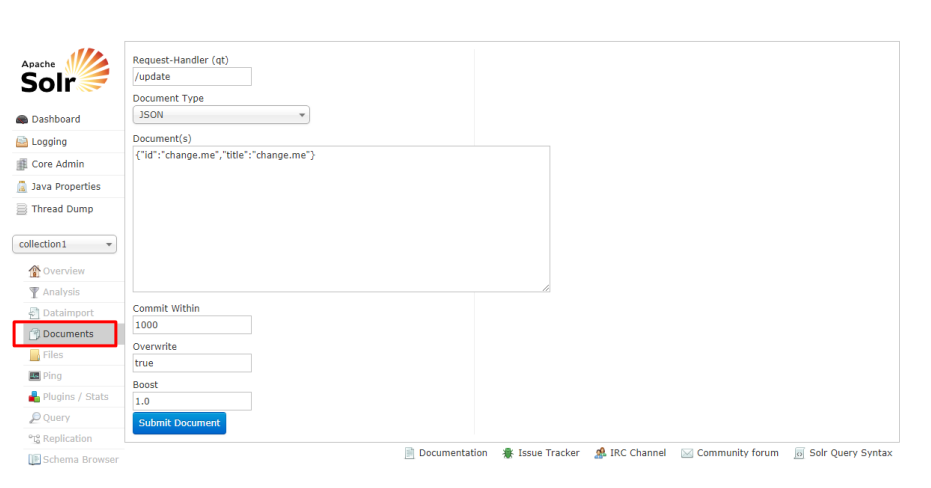
Documents (索引文档)索引的相关操作,如:增加,修改,删除等
在如下页面,选择/update ,文档格式选择 json ,然后 submit 提交。这样 索引就增
加上了。修改与增加一样,都是/update ,删除为/delete 。 成功之后,我们去 query 里查询数据
就能查到我们刚添加的数据.
3.3.6.5 Files 文件夹
solr_home 下的 core 下的 conf 下的相关文件,可单击查看里面的内容
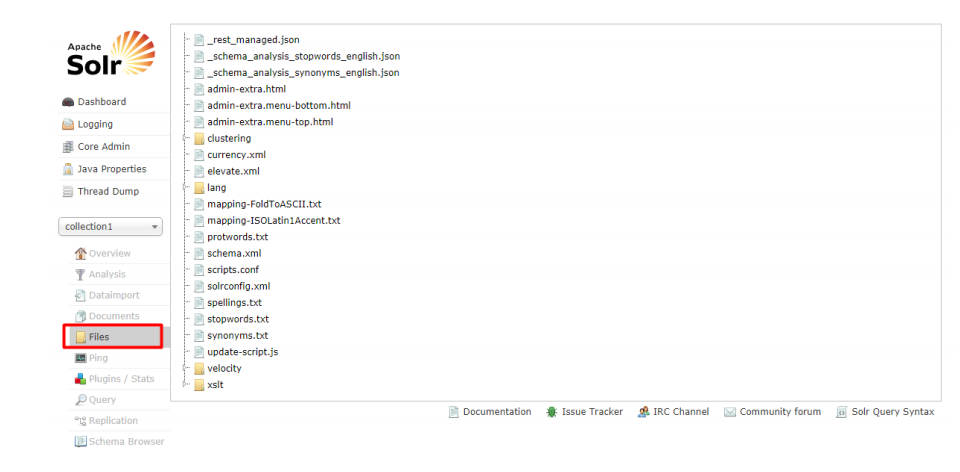
3.3.6.6 Ping
查看当前核心库还是否工作的以及响应时间

3.3.6.7 Plugins /stats
Solr 自带的一些插件以及我们安装的插件的信息以及统计

3.3.6.8 Query(查询页面)
查询的结果要显示哪个字段,就得将 schema.xml 文件配置字段时的 stored 属性设为 true

Request-Handler(qt): 请求处理器
q: 查询字符串(必须的)。:表示查询所有;keyword:尚学堂 表示按关键字“尚学堂”
查询
fq: filter query 过滤查询。使用 Filter Query 可以充分利用 Filter Query Cache,提高检索
性能。作用:在 q 查询符合结果中同时是 fq 查询符合的(类似求交集),例如:
q=mm&fq=date_time:[20081001 TO 20091031],找关键字 mm,并且 date_time 是 20081001
到 20091031 之间的。
sort: 排序。格式如下:字段名 排序方式;如 id desc 表示按 id 字段降序排列查询结果。
start,rows:表示查回结果从第几条数据开始显示,共显示多少条。
fl: field list。指定查询结果返回哪些字段。多个时以空格“ ”或逗号“,”分隔。不指
定时,默认全返回。
df: default field 默认的查询字段,一般默认指定。
Raw Query Parameters: 原始查询参数的
wt: write type。指定查询输出结果格式,我们常用的有 json 格式与 xml 格式。在
solrconfig.xml 中定义了查询输出格式:xml、json、python、ruby、php、csv。
indent: 返回的结果是否缩进,默认关闭,用 indent=true | on 开启,一般调试
json,php,phps,ruby 输出才有必要用这个参数。
debugQuery: 设置返回结果是否显示 Debug 信息。
dismax:
edismax:
hl: high light 高亮。hl=true 表示启用高亮
hl.fl : 用空格或逗号隔开的字段列表(指定高亮的字段)。要启用某个字段的
highlight 功能,就得保证该字段在 schema 中是 stored。
hl.simple.pre: 设置高亮显示的 html 标记的开始标记
hl.simple.post:设置高亮显示的 html 标记的结束标记
hl.requireFieldMatch: 如果置为 true,除非该字段的查询结果不为空才会被高亮。它
的默认值是 false,意味 着它可能匹配某个字段却高亮一个不同的字段。如果 hl.fl 使用了通
配符,那么就要启用该参数。尽管如此,如果你的查询是 all 字段(可能是使用 copy-field 指
令),那么还是把它设为 false,这样搜索结果能表明哪个字段的查询文本未被找到
hl.usePhraseHighlighter:如果一个查询中含有短语(引号框起来的)那么会保证一
定要完全匹配短语的才会被高亮。
hl.highlightMultiTerm:如果使用通配符和模糊搜索,那么会确保与通配符匹配的
term 会高亮。默认为 false,同时 hl.usePhraseHighlighter 要为 true。
facet:分组统计,在搜索关键字的同时,能够按照 Facet 的字段进行分组并统计。
facet.query:Facet Query 利用类似于 filter query 的语法提供了更为灵活的 Facet.通
过 facet.query 参数,可以对任意字段进行筛选。
facet.field:需要分组统计的字段,可以多个。
facet.prefix: 表示 Facet 字段值的前缀。比如 facet.field=cpu&facet.prefix=Intel,
那么对 cpu 字段进行 Facet 查询,返回的 cpu 都是以 Intel 开头的, AMD 开头的 cpu 型号将
不会被统计在内。
spatial:
spellcheck: 拼写检查。
3.3.6.9 Replication
显示你当前 Core 的副本,并提供 disable/enable 功能
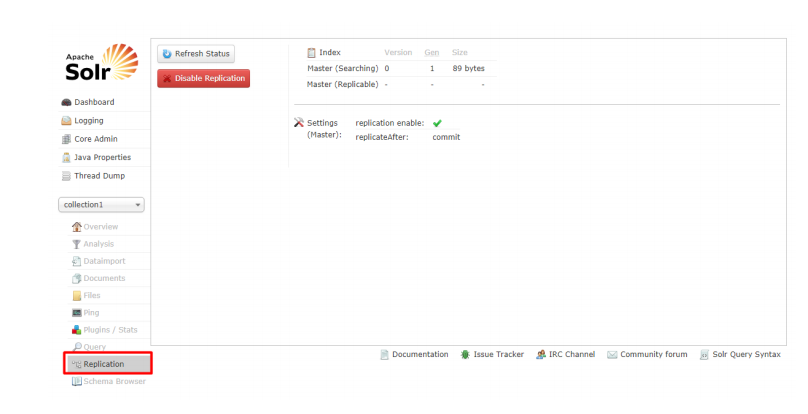
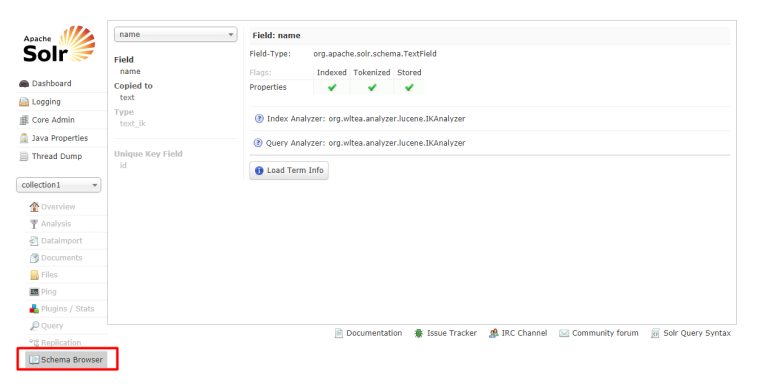
3.3.6.10 Schema
展示该 Core 的 shema.xml 文件中的内容
三、 在索引库中定义业务字段
1 表结构
CREATE TABLE `tb_item` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品 id,同时也是商品编号', `title` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品标题', `sell_point` varchar(500) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品卖点', `price` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品价格,单位为:分', `num` int(10) NOT NULL COMMENT '库存数量', `barcode` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品条形码', `image` varchar(500) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品图片',
`cid` bigint(10) NOT NULL COMMENT '所属类目,叶子类目',
`status` tinyint(4) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '商品状态,1-正常,2-下架,
3-删除',
`created` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`updated` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `cid` (`cid`),
KEY `status` (`status`),
KEY `updated` (`updated`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='商品表';
2 定义域
<field name="id" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" required="true" multiValued="false" /> <field name="item_title" type="text_ik" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="item_sell_point" type="text_ik" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="item_price" type="long" indexed="false" stored="true"/> <field name="item_image" type="string" indexed="false" stored="true" />
3 定义默认检索域
<field name="item_keywords" type="text_ik" indexed="true" stored="false" multiValued="true"/> <copyField source="item_title" dest="item_keywords"/> <copyField source="item_sell_point" dest="item_keywords"/>
四、 SolrJ 的使用
1 什么是 SolrJ
solrJ 是访问 Solr 服务的 JAVA 客户端,提供索引和搜索的请求方法,SolrJ 通常嵌入在
业务系统中,通过 solrJ 的 API 接口操作 Solr 服务。
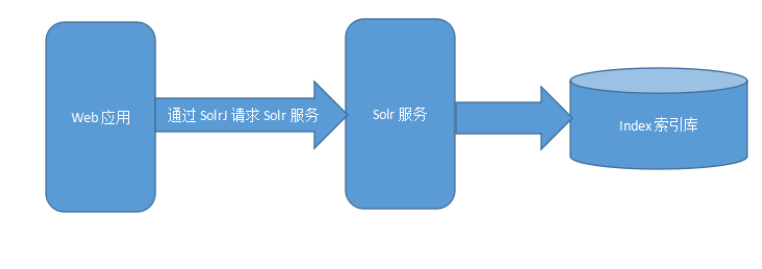
2 测试 SolrJ
2.1创建项目
2.2修改 POM 文件添加 SolrJ 坐标
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instan ce" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/P OM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>solrJDemo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.solr</groupId> <artifactId>solr-solrj</artifactId> <version>4.10.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2.3向索引库中添加文档
/** * 向索引库中添加文档 * @throws Exception * @throws SolrServerException */ public static void solrInsert() throws Exception{ //创建一个 solrj 的链接对象 SolrServer server = new HttpSolrServer("http://192.168.70.147:8080/solr"); //创建一个 Solr 的文档对象 SolrInputDocument docu = new SolrInputDocument(); //向文档对象中添加需要插入到索引库的内容 docu.addField("id", "OldLu"); docu.addField("item_title", "老好了"); docu.addField("item_price",1000); //将文档插入到 solr 的索引库中 server.add(docu); //事务的提交 server.commit(); }
2.4删除索引库文档
/** * 删除索引库中的文档 * @throws Exception * @throws SolrServerException */ public static void solrDelete() throws Exception{ //创建一个 solrj 的链接对象 SolrServer server = new HttpSolrServer("http://192.168.70.147:8080/solr"); //给定删除条件 //1.根据主键删除 //server.deleteById("test"); //2.根据查询删除 server.deleteByQuery("*:*"); server.commit(); }
2.5查询索引库中的文档

/** * 查询索引库 * @throws Exception */ public static void solrSearch() throws Exception{ //创建一个 solrj 的链接对象 SolrServer server = new HttpSolrServer("http://192.168.70.147:8080/solr"); //创建查询条件 SolrQuery query = new SolrQuery(); query.setQuery("老好了 0"); query.set("df", "item_keywords"); //设置分页 query.setStart(0); query.setRows(10); //执行查询 //QueryResponse:封装查询的结果集 QueryResponse res = server.query(query); SoloDocumentList docu =res.getResults(); //list.getNumFound() 数据总条数 System.out.println("总条数: "+docu.getNumFound()); for(SolrDocument var :docu){ System.out.println(var.get("item_title")); System.out.println(var.get("item_price")); } }
五、 Solr 集群(SolrCloud)
1 什么是 SolrCloud
SolrCloud(solr 云)是 Solr 提供的分布式搜索方案,当你需要大规模,容错,分布
式索引和检索能力时使用 SolrCloud。当一个系统的索引数据量少的时候是不需要使用
SolrCloud 的,当索引量很大,搜索请求并发很高,这时需要使用 SolrCloud 来满足这些
需求。
SolrCloud 是基于 Solr 和 Zookeeper 的分布式搜索方案,它的主要思想是使用
Zookeeper 作为集群的配置信息中心。
它有几个特色功能:
1)集中式的配置信息
2)自动容错
3)近实时搜索
4)查询时自动负载均衡2 Solr 集群结构图
2 Solr 集群结构图

3 Solr 集群搭建设计
本次集群采用伪集群的方式进行安装,如果是真正的生产环境,建议搭建真实集群。
SolrCloud 结构图如下:

4 安装 Solr 集群环境
4.1需求:
1) 在 192.168.70.147 环境中安装 zookeeper 集群(已安装)
2) 创建 4 个 tomcat 实例,修改其端口为 8080-8083
3) 使用已安装好的单机版 solr 作为集群的节点使用
4.2创建 solrcloud 目录
mkdir solrcloud
4.3安装 Zookeeper 集群
略.......
4.4安装
4 个 tomcat 实例并将 tomcat 与索引库拷贝到 solrCloud
目录中

4.5修改 tomcat 端口
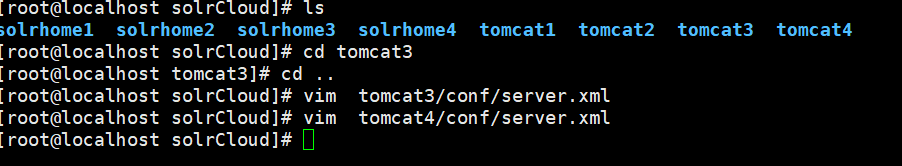

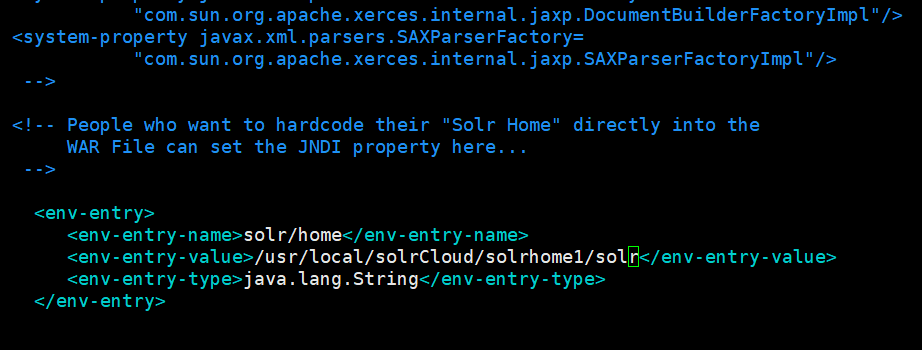
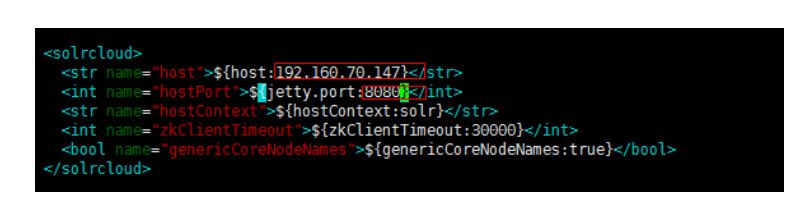
4.6修改 solr 服务中指向 solr 索引库的路径
/usr/local/solrCloud/tomcat1/webapps/solr/WEB-INF/web.xml
5 创建集群
5.1上传索引库配置文件
把 solrhome 中的配置文件上传到 zookeeper 集群。使用 zookeeper 的客户端上传
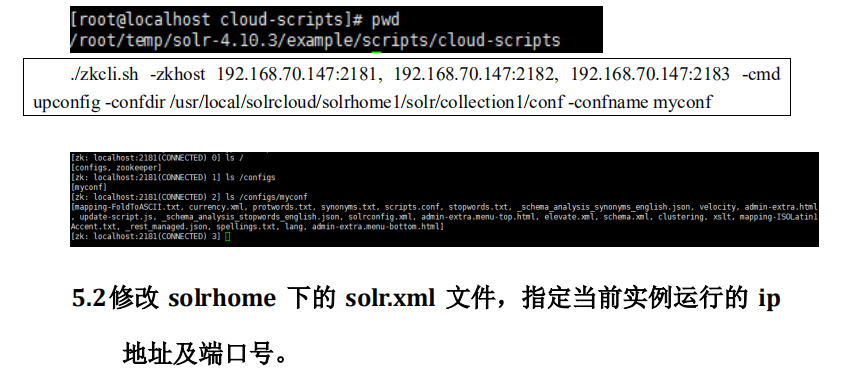
5.3修改每一台 solr 的 tomcat 的 bin 目录下 catalina.sh 文件中
加入 DzkHost 指定 zookeeper 服务器地址
JAVA_OPTS="-DzkHost=192.168.70.147:2181,192.168.70.147:2182,192.168.70.14
7:2183"
(可以使用 vim 的查找功能查找到 JAVA_OPTS 的定义的位置,然后添加)
注意不能含有空格
5.4启动 tomcat

5.5创建新的逻辑索引库并分片
创建一个新的 collection,并分两片,每片是一主一备。
使用以下命令创建:
http://192.168.70.147:8080/solr/admin/collections?action=CREATE&name=collec
tion2&numShards=2&replicationFactor=2
5.6删除原来的逻辑索引库
http://192.168.70.147:8080/solr/admin/collections?action=DELETE&name=collec
tion1
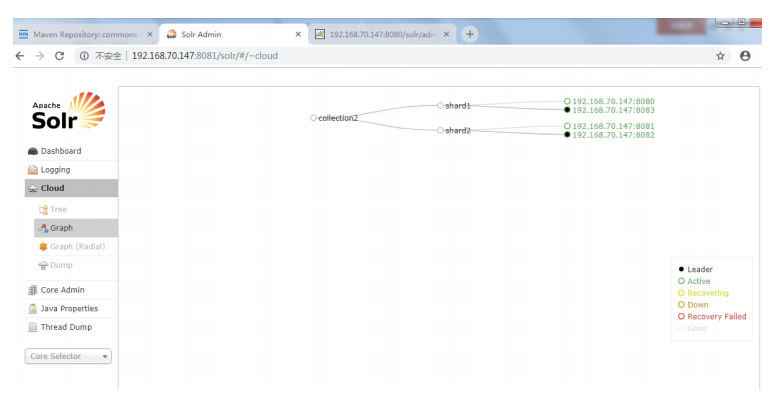
5.7测试 SolrJ 操作 Solr 集群
5.7.1在集群中添加文档

/** * 向集群的索引库中添加文档 */ public static void solrCloudInsert()throws Exception{ //zookeeper 地址 String zkHost = "192.168.70.147:2181,192.168.70.147:2182,192.168.7 0.147:2183"; //创建 solrCloud 对象 CloudSolrServer cloud = new CloudSolrServer(zkHost); //给定索引库 cloud.setDefaultCollection("collection2"); //创建 solr 文档对象 SolrInputDocument docu = new SolrInputDocument(); docu.addField("id", "OldLu"); docu.addField("item_title", "老好了"); docu.addField("item_price",1000); cloud.add(docu); cloud.commit(); cloud.shutdown(); }
5.7.2删除集群中的文档
/** * 删除集群中的文档 */ public static void solrCloudDel()throws Exception{ //zookeeper 地址 String zkHost = "192.168.70.147:2181,192.168.70.147:2182,192.168.7 0.147:2183"; //创建 solrCloud 对象 CloudSolrServer cloud = new CloudSolrServer(zkHost); cloud.setDefaultCollection("collection2"); cloud.deleteByQuery("*:*"); cloud.commit(); cloud.shutdown(); }
5.7.3查询集群中的文档

/** * 查询集群中的文档 */ public static void solrCloudSearch()throws Exception{ //zookeeper 地址 String zkHost = "192.168.70.147:2181,192.168.70.147:2182,192.168.7 0.147:2183"; //创建 solrCloud 对象 CloudSolrServer cloud = new CloudSolrServer(zkHost); cloud.setDefaultCollection("collection2"); //常见查询对象 SolrQuery query = new SolrQuery(); query.setQuery("老好了"); query.set("df", "item_keywords"); query.setStart(0); query.setRows(10); //开始查询 QueryResponse res = cloud.query(query); list = res.getResults(); System.out.println("总条数: "+list.getNumFound()); for var:list){ System.out.println(var.get("item_title")); System.out.println(var.get("item_price")); } }
六、 Solr 实战案例
1 案例需求:
1) 使用技术 springMVC+Spring+Mybatis+solrJ
2) 将 mysql 中的 tb_item 表中的部分业务数据导入到 solr 的索引库中
3) 提供一个搜索页面,在搜索页面中完成数据搜索
2 创建实战项目
2.1创建项目

2.2修改 POM 文件添加依赖

<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instan ce" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4. 0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>parent</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>solrDemo2</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.solr</groupId> <artifactId>solr-solrj</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 单元测试 --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 日志处理 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- MySql --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 连接池 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- JSP 相关 --> <dependency> <groupId>jstl</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.xml</include> <include>**/*.properties</include> </includes> </resource> </resources> <!-- tomcat 插件,由于子项目不一定每个都是 web 项目,所以该插件只是声明,并未开启 --> <plugins> <!-- 配置 Tomcat 插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <path>/</path> <port>8080</port> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
2.3框架整合
2.4测试整合
3 Spring 整合 SolrJ
3.1创建 application-solrj.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans " xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-i nstance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org /schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/sch ema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframewor k.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring -beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-m vc-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spri ng-context.xsd"> <!-- 整合单机版 Solr --> <!-- <bean id="httpSolrServer" class="org.apache.solr.client.solrj.impl.HttpSolrS erver"> <constructor-arg name="baseURL"> <value>${SOLR_SERVICE_URL}</value> </constructor-arg> </bean> --> <!-- 整合 solr 集群 --> <bean class="org.apache.solr.client.solrj.impl.CloudSolr Server"><constructor-arg name="zkHost"> <value>${SOLR_CLOUD_SERVICE_URL}</value> </constructor-arg> <property name="defaultCollection"> <value>${DEFAULT_COLLECTION}</value> </property> </bean> </beans>
3.2编写测试代码

/** * 测试 Spring 整合 SolrCloud */ @Test public void solrCloudTest()throws Exception{ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/a pplication*"); CloudSolrServer cloud = ac.getBean(CloudSolrServer.class); SolrInputDocument docu = new SolrInputDocument(); //向文档对象中添加需要插入到索引库的内容 docu.addField("id", "OldLu"); docu.addField("item_title", "老好了"); docu.addField("item_price",1000); //将文档插入到 solr 的索引库中 cloud.add(docu); cloud.commit(); cloud.shutdown(); }
4 将 tb_item 表中的数据导入到 Solr 的索引库中
4.1创建导入数据 Service

@Service public class ImportItemServiceImpl implements ImportItemService { @Autowired private ItemMapper itemMapper; @Autowired private CloudSolrServer cloudServer; /** * 导入数据 */ @Override public void importItem() { try{ //查询数据库中的数据 List<TbItem> list = this.itemMapper.findAll(); List<SolrInputDocument> result = new ArrayList<>(); //模型转换 for(TbItem item:list){ SolrInputDocument docu = new SolrInputDocument(); docu.setField("id", item.getId()+""); docu.setField("item_title", item.getTitle()); docu.setField("item_sell_point", item.getSell_Point()); docu.setField("item_price", item.getPrice()); docu.setField("item_image", item.getImage()); result.add(docu); } this.cloudServer.add(result); this.cloudServer.commit(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4.2创建导入数据 Controller

/** * 处理导入数据的 Controller * @author Administrator * */ @Controller @RequestMapping("/import") public class ImportDataController { @Autowired private ImportItemService importItemService; @RequestMapping("/importData") public String importData(){ this.importItemService.importItem(); return "ok"; } }
4.3测试
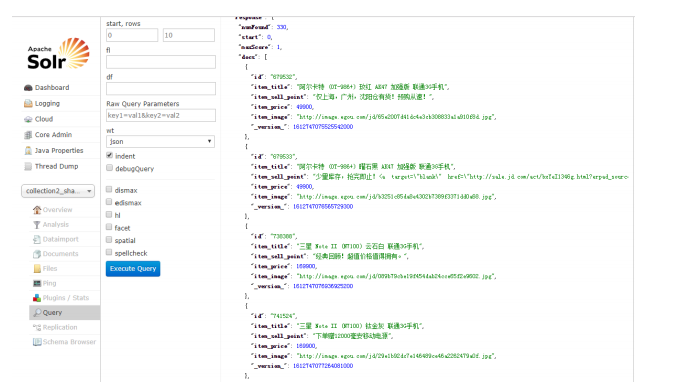
5 实现搜索业务
5.1创建搜索页面

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="/search/searchItem" method="post"> <input type="text" name="query"/> <input type="submit" value="Search"/> </form> </body> </html>
5.2创建 SolrDao

/** * 查询 solr * @author Administrator * */ @Repository public class SolrDaoImpl implements SolrDao { @Autowired private CloudSolrServer cloudSolrServer; @Override public PageResult searchItem(SolrQuery solrQuery)throws Exception { QueryResponse res = this.cloudSolrServer.query(solrQuery); SolrDocumentList list = res.getResults(); //处理结果集 PageResult page = new PageResult(); //总条数 page.setTotalNum(list.getNumFound()); List<TbItem> items = new ArrayList<>(); //取高亮信息 Map<String,Map<String, List<String>> > hl = res.getHighlighting(); //模型转换 for(SolrDocument var :list){ TbItem item = new TbItem(); item.setId(Long.parseLong((String)var.get("id") )); item.setImage((String)var.get("item_image")); item.setSell_Point((String)var.get("item_sell_p oint")); item.setPrice(Long.parseLong((String)var.get("i tem_price"))); List<String> h = hl.get(var.get("id")).get("item_tile"); String title = ""; if(h != null && h.size() > 0){ title = h.get((0)); }else{ title= (String)var.get("item_title"); } item.setTitle(title); items.add(item); } page.setResult(items); return page; } }
5.3创建搜索 Service

/** * 完成 solr 搜索业务 * @author Administrator * */ @Service public class SearchItemServiceImpl implements SearchItemService { @Autowired private SolrDao solrDao; @Override public PageResult searchItem(String query, Integer page, Integer rows)throws Exception { //创建查询条件 SolrQuery solrQuery = new SolrQuery(); //添加查询条件 solrQuery.setQuery(query); //默认域 solrQuery.set("df", "item_keywords"); //设置分页 solrQuery.setStart((page-1)*rows); solrQuery.setRows(rows); //设置高亮 solrQuery.setHighlight(true); solrQuery.addHighlightField("item_title"); //设置高亮样式 solrQuery.setHighlightSimplePre("<em style='color:red;'>"); solrQuery.setHighlightSimplePost("</em>"); //调用 SolrDao PageResult result = this.solrDao.searchItem(solrQuery); //补齐数据 //当前页 result.setPageIndex(page); //总页数 Long total = result.getTotalNum()/rows; if(result.getTotalNum() % rows > 0){ total++; } result.setTotalPage(total); return result; } }
5.4创建搜索 Controller

/** * 处理商品搜索 Controller * @author Administrator * */ @Controller @RequestMapping("/search") public class SearchController { @Autowired private SearchItemService searchItemService; /** * 商品搜索 */ @RequestMapping("/searchItem") public String searchItem(String query,@RequestParam(value="page",defaultValue=" 1")Integer page, @RequestParam(value="rows",defaultValue="20")In teger rows,Model model){ try{ PageResult result = this.searchItemService.searchItem(query, page, rows); model.addAttribute("result", result); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return "showItem"; } }
5.5创建展示搜索结果页面

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <span>当前页:${result.pageIndex }</span> <span>总页数:${result.totalPage }</span> <span>总条数:${result.totalNum }</span> <table align="center" border="1"> <c:forEach items="${result.result }" var="item"><tr><td>${item.id }</td> <td>${item.title }</td> <td>${item.sell_Point }</td> <td>${item.price }</td> <td>${item.image }</td> </tr> </c:forEach> </table> </body> </html>
5.6测试

删除节点:https://blog.csdn.net/fellhair/article/details/82429100
删除solr集群某个分支的一个节点
http://10.100.10.130:6060/solr/admin/collections?action=DELETEREPLICA&collection=bjsxt&shard=shard1&replica=core_node6
删除solr集群
http://10.100.10.130:6060/solr/admin/collections?action=DELETE&name=solrCore
个人学习笔记,记录日常学习,便于查阅及加深,仅为方便个人使用。



