Java反射详解
反射
反射概念:


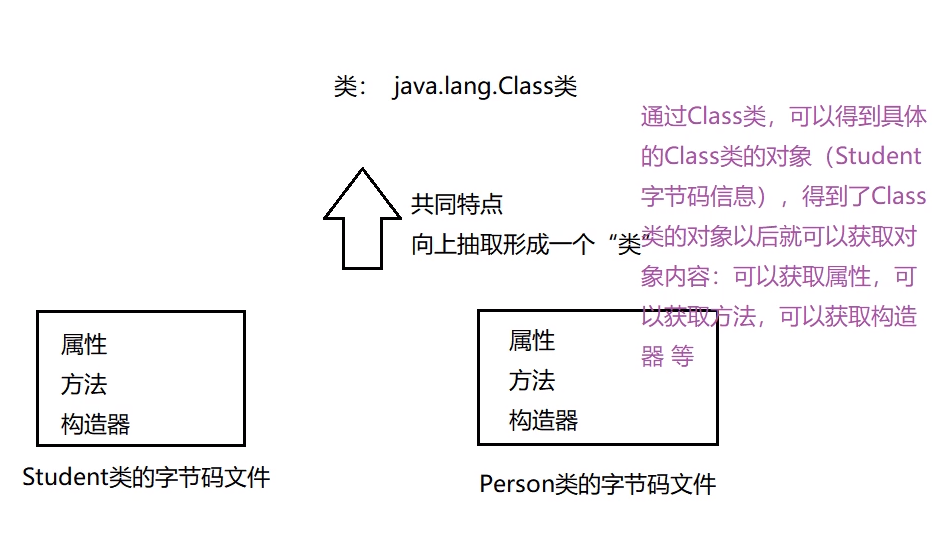
对Class类的理解:
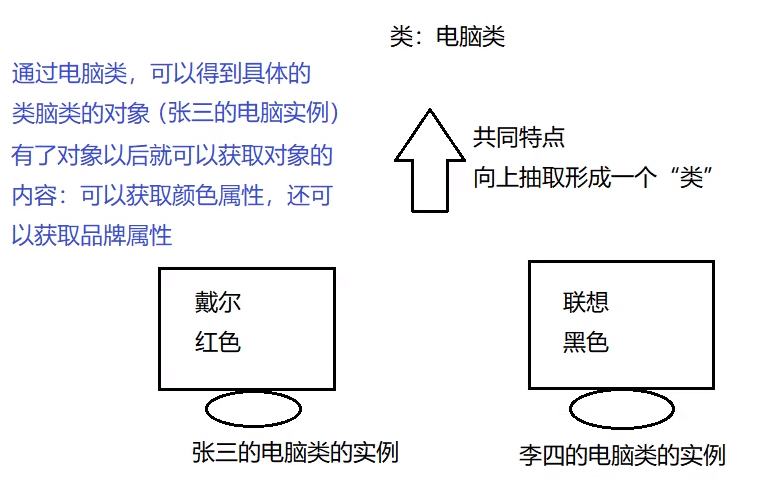
面向对象的思维方式:万事万物皆对象
Class类也就是字节码文件向上抽取形成一个类。
使用反射
首先需要提供一些类:为后面使用反射做好测试环境
一个自定义注解
package com.example.demo1.test02;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
/*
Target定义当前注解能够修饰程序中的那些元素
Retention:定义注解的生命周期
*/
@Target({TYPE, FIELD,METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();
}
一个自定义的接口
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-10:47
*/
public interface MyInterface { //自定义接口
void myMethod();
}
一个Person类
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/18-17:35
*/
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
public class Person implements Serializable {
public String name;
private Integer age;
String sex;
protected List<String> likes;
private void eat() {
System.out.println("Person-eat");
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("Person--sleep");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public List<String> getLikes() {
return likes;
}
public void setLikes(List<String> likes) {
this.likes = likes;
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, String sex, List<String> likes) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.likes = likes;
}
public Person() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", likes=" + likes +
'}';
}
}
一个继承Person的student类
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-10:21
*/
import java.util.List;
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello")
public class Student extends Person implements MyInterface{
private int sno;
double height;
protected double weight;
public double score;
@MyAnnotation(value = "hi method")
public String showInfo() {
return "我是一名学生";
}
public String showInfo(int a,int b) {
return "重载方法-》我是一名学生";
}
private void work(int a) {
System.out.println("找工作称为一只码畜");
}
void happy() {
System.out.println("做人最重要的就是开心");
}
public Student() {
System.out.println("空参构造器");
}
public Student(double height,int sno) {
this.sno = sno;
this.height = height;
}
private Student(int sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
Student(int sno,double weight) {
this.sno = sno;
this.weight = weight;
}
protected Student(int sno,double height,double weight) {
this.sno = sno;
}
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello myMethod")
@Override
public void myMethod() throws RuntimeException {
System.out.println("重写了myMethod方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sno=" + sno +
", height=" + height +
", weight=" + weight +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
获取运行时类的完整结构
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-10:26
*/
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
/*获取字节码信息的四中方式
获取的字节码信息是同一个,因为只有一次类加载
方式1和方式2不常用:原因得到字节码信息的目的就是获取类里面的东西
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//以Person的字节码信息为案例
// 方式1 :通过getClass方法获取
Person p = new Person();
Class c1 = p.getClass();
System.out.println(c1);
// 方式2:通过内置Class属性
Class c2 = Person.class;
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c1==c2);
// 方式3:通过全限定类名,调用Class提供的静态方法
Class c3 = Class.forName("com.example.demo1.test02.Person");
//方式4:(了解)利用类的加载器
ClassLoader loader = Test.class.getClassLoader(); //系统类加载器
System.out.println(loader);
Class c4 = loader.loadClass("com.example.demo1.test02.Person"); //具体对象的字节码信息
}
}
获取字节码信息的方式
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-10:26
*/
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
/*获取字节码信息的四中方式
获取的字节码信息是同一个,因为只有一次类加载
方式1和方式2不常用:原因得到字节码信息的目的就是获取类里面的东西
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//以Person的字节码信息为案例
// 方式1 :通过getClass方法获取
Person p = new Person();
Class c1 = p.getClass();
System.out.println(c1);
// 方式2:通过内置Class属性
Class c2 = Person.class;
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c1==c2);
// 方式3:通过全限定类名,调用Class提供的静态方法
Class c3 = Class.forName("com.example.demo1.test02.Person");
//方式4:(了解)利用类的加载器
ClassLoader loader = Test.class.getClassLoader(); //系统类加载器
System.out.println(loader);
Class c4 = loader.loadClass("com.example.demo1.test02.Person"); //具体对象的字节码信息
}
}
可以作为Class类的实例的种类:
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-10:39
*/
import com.sun.javaws.IconUtil;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.GsonBuilderUtils;
public class Demo {
/*
1.类:外部类,内部类
2.接口
3.注解
4.数组
5.基本数据类型
6.void
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c1 = Person.class;
Class c2 = Comparable.class;
System.out.println(c2);
Class c3 = Override.class;
System.out.println(c3);
int[] arr1 = {1,2,3};
Class c4 = arr1.getClass();
int[] arr2 = {5,6,7};
Class c5 = arr2.getClass();
System.out.println(c5==c4); //同一个维度,同一个类型的数组得到的字节码就是同一个 结果为true
Class c6 = int.class;
System.out.println(c6);
Class c7 = void.class;
System.out.println(c7);
}
}
获取运行时类的反射结构:
获取构造器:
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-11:21
*/
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Test01 {
// 获取字节码信息
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
Class cls = Student.class;
//通过字节码信息可以获取构造器
/*
为什么会是一个数组呢,这个数组是什么?
将每个构造器向上抽取形成一个大类,构造器类
*/
Constructor[] constructors = cls.getConstructors(); //只能获取当前运行时类被public修饰的构造器
for(Constructor c : constructors) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
Constructor[] c2 = cls.getDeclaredConstructors(); //获取的是所有的构造器
for(Constructor c:c2) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
//获取指定的构造器
Constructor con1 = cls.getConstructor(); //获取的是空构造器
System.out.println(con1);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
// 得到两个参数的有参构造器
Constructor con2 = cls.getConstructor(double.class,int.class);
System.out.println(con2);
System.out.println("-------------------------");
//得到一个参数的有参构造器,并且是private修饰的
Constructor con3 = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);
System.out.println(con3);
// 有了构造器之后就可以创建对象了
Object o1 = con1.newInstance();
System.out.println(o1);
Object o2 = con2.newInstance(15.5, 18);
System.out.println(o2);
}
}
获取属性和对属性进行赋值:
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-11:53
*/
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Class cls = Student.class;
//获取public属性
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();
for(Field f : fields) {
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println("---------------------");
//获取运行时类的所有属性
Field[] declaredFields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field f : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(f);
}
//获取指定的属性
Field score = cls.getField("score");
System.out.println(score);
//获取指定的属性
Field sno = cls.getDeclaredField("sno");
System.out.println(sno);
//获取修饰符
int modifiers = sno.getModifiers(); //底层每一个书对应一个修饰符 Modifier
System.out.println( Modifier.toString(modifiers));
//获取属性的数据类型
Class type = sno.getType();
System.out.println(type.getName());
//获取属性的名字
String name = sno.getName();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
// 给属性赋值
/*
给属性设置值必须要有对象
*/
Field scp = cls.getField("score");
Object obj = cls.newInstance();
score.set(obj,18);
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
获取方法和调用方法:
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-17:08
*/
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
//获取字节码信息
Class cls = Student.class;
//获取方法,会获取运行时类的方法以及父类中的所有方法
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
for(Method m:methods) {
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//获取到的是Sutdent中的所有方法,获取不到父类
Method[] declaredConstructor= cls.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m:declaredConstructor) {
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//获取指定的方法
Method showInfo = cls.getMethod("showInfo");
System.out.println(showInfo);
Method showInfo1 = cls.getMethod("showInfo", int.class, int.class);
System.out.println(showInfo1);
Method work = cls.getDeclaredMethod("work",int.class);
System.out.println(work);
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//获取方法的具体结构
System.out.println(work.getName());
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(work.getModifiers()));
//返回值
System.out.println(work.getReturnType());
// 参数列表 返回的是一个数组
Class[] parameterTypes = work.getParameterTypes();
for(Class c : parameterTypes) {
System.out.println(c);
}
// 获取注解和异常
Method myMethod = cls.getMethod("myMethod");
Annotation[] annotations = myMethod.getDeclaredAnnotations();
for(Annotation a:annotations) { //获取的注解是运行时期的注解
System.out.println(a);
}
System.out.println("------------------异常");
//获取异常
Class[] types = myMethod.getExceptionTypes();
for(Class c:types) {
System.out.println(c);
}
// 调用方法
Object o = cls.newInstance();
myMethod.invoke(o); //调用o对象的myMethod方法
System.out.println(showInfo.invoke(o));
}
}
获取类的接口,所在包,注解
package com.example.demo1.test02;/*
*@author wupeng
*@time 2021/6/19-17:40
*/
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
public class Tets04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class cls = Student.class;
//获取接口
Class[] inter = cls.getInterfaces();
for(Class i:inter) {
System.out.println(i);
}
//得到父类的接口
Class superclass = cls.getSuperclass();
Class[] interfaces = superclass.getInterfaces();
for (Class i:interfaces) {
System.out.println(i);
}
//获取运行时类所在的包
Package aPackage = cls.getPackage();
System.out.println(aPackage);
System.out.println(aPackage.getName());
//获取运行类的注解
Annotation[] annotations = cls.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation a:annotations) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
关于反射的面试题:
1.反射的应用场景
反射是框架设计的灵魂,平时模块化的开发,通过反射调用对应的字节码;动态代理设计模式也采用了反射机制日常使用的spring框架也大量使用到了反射。
举例:
1.我们在使用JDBC连接数据库使用Class.forName()通过反射加载数据库的驱动程序;
2.Spring框架也用到了很多反射机制,xml配置模式。Spring通过XML配置模式装载Bean的过程:
1.将程序内所有XML或Properties配置文件加载入内存中·;
2.Java类里面解析XML或properties里面的内容,得到的对应实体类的字节码字符串以及相关的属性信息。
3.使用反射机制,根据这个字符串获得某个类的Class实例。
4.动态配置实例的属性
2.反射是否破坏了面向对象的封装性?
封装是为了提高代码的安全性,
反射目的就是为了动态性,
反射有反射的意义,
封装有封装的意义。
封装性是指对外隐藏对象的属性和实现细节,仅对外提供公共的访问方式。反射是通过对象找到类,既然找到类了,那么我们就可以得到这个类的成员结构了,例如这个类的属性和方法,即使是private的也能得到,你想,现在这个类我都得到了,那么这个类中的所以东西我肯定是都得到了,我现在只是得到了这个类的成员,并没有说是在外部访问这个类的private的东西。这并没有破坏面向对象的封装性



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号