到底什么是多态?
“多态性”(polymorphism)一词意味着具有多种形式。 简单来说,我们可以将多态性定义为消息以多种形式展示的能力。
多态性的一个真实例子是一个人可以同时具有不同的特征。 男人同时是父亲、丈夫和雇员。 所以同一个人在不同的情况下会表现出不同的行为。 这称为多态性。 多态性被认为是面向对象编程的重要特征之一。
多态性的类型
- 编译时的多态性
- 运行时的多态性
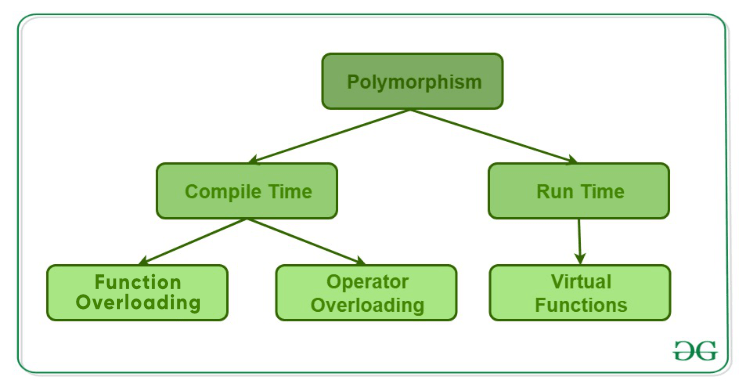
1.编译时多态性
这种类型的多态性是通过函数重载或运算符重载来实现的。
A. 函数重载
当有多个同名但参数不同的函数时,这些函数被称为 重载, 因此这被称为函数重载。 来重载函数 可以通过更改参数数量 或/和 更改参数类型 。 简单来说,它是面向对象编程的一个特点,当许多任务列在一个函数名称下时,它提供许多具有相同名称但不同参数的函数。 某些 函数重载规则,重载函数时应遵循
下面是显示函数重载或编译时多态性的 C++ 程序:
// C++ program to demonstrate // function overloading or // Compile-time Polymorphism #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Geeks { public: // Function with 1 int parameter void func(int x) { cout << "value of x is " << x << endl; } // Function with same name but // 1 double parameter void func(double x) { cout << "value of x is " << x << endl; } // Function with same name and // 2 int parameters void func(int x, int y) { cout << "value of x and y is " << x << ", " << y << endl; } }; // Driver code int main() { Geeks obj1; // Function being called depends // on the parameters passed // func() is called with int value obj1.func(7); // func() is called with double value obj1.func(9.132); // func() is called with 2 int values obj1.func(85, 64); return 0; }
输出
value of x is 7 value of x is 9.132 value of x and y is 85, 64
解释: 在上面的例子中,一个名为 function func() 的函数在三种不同的情况下表现不同,这是多态性的一个特性。
B. 运算符重载
C++ 能够为运算符提供对数据类型的特殊含义,这种能力称为运算符重载。 例如,我们可以使用字符串类的加法运算符 (+) 来连接两个字符串。 我们知道这个运算符的任务是将两个操作数相加。 因此,单个运算符“+”,当放在整数操作数之间时,将它们相加,当放在字符串操作数之间时,将它们连接起来。
下面是演示运算符重载的 C++ 程序:
// C++ program to demonstrate // Operator Overloading or // Compile-Time Polymorphism #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Complex { private: int real, imag; public: Complex(int r = 0, int i = 0) { real = r; imag = i; } // This is automatically called // when '+' is used with between // two Complex objects Complex operator+(Complex const& obj) { Complex res; res.real = real + obj.real; res.imag = imag + obj.imag; return res; } void print() { cout << real << " + i" << imag << endl; } }; // Driver code int main() { Complex c1(10, 5), c2(2, 4); // An example call to "operator+" Complex c3 = c1 + c2; c3.print(); }
输出
12 + i9
解释: 在上面的例子中,运算符'+'被重载了。 通常,此运算符用于将两个数(整数或浮点数)相加,但此处使该运算符执行两个虚数或复数的相加。
2. 运行时多态性
这种类型的多态性是通过 Function Overriding 实现的。 后期绑定和动态多态是运行时多态的其他名称。 函数调用在运行时 多态性 中在运行时解析。 相反,对于编译时多态性,编译器在运行时推导后确定将哪个函数调用绑定到对象。
A. 函数覆盖
当派生类具有基类的成员函数之一的定义时,就会发生函数覆盖。 据说该基本功能已被覆盖。

下面是演示函数覆盖的 C++ 程序:
// C++ program for function overriding #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class base { public: virtual void print() { cout << "print base class" << endl; } void show() { cout << "show base class" << endl; } }; class derived : public base { public: // print () is already virtual function in // derived class, we could also declared as // virtual void print () explicitly void print() { cout << "print derived class" << endl; } void show() { cout << "show derived class" << endl; } }; // Driver code int main() { base* bptr; derived d; bptr = &d; // 虚函数绑定在 // 运行时 (Runtime polymorphism) bptr->print(); // 非虚函数绑定在 // 编译时 bptr->show(); return 0; }
输出
print derived class show base class
虚函数
一个虚函数是 在基类中使用关键字virtual声明并在派生类中重新定义(Overridden)的成员函数。
关于虚函数的一些要点:
*虚函数本质上是动态的。 *插入关键字“ virtual ”来定义的,并且总是用基类声明并在子类中被覆盖 它们是通过在基类中 *在运行时调用虚函数
下面是演示虚函数的C++程序:
// C++ Program to demonstrate // the Virtual Function #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Declaring a Base class class GFG_Base { public: // virtual function virtual void display() { cout << "Called virtual Base Class function" << "\n\n"; } void print() { cout << "Called GFG_Base print function" << "\n\n"; } }; // Declaring a Child Class class GFG_Child : public GFG_Base { public: void display() { cout << "Called GFG_Child Display Function" << "\n\n"; } void print() { cout << "Called GFG_Child print Function" << "\n\n"; } }; // Driver code int main() { // Create a reference of class GFG_Base GFG_Base* base; GFG_Child child; base = &child; // This will call the virtual function base->GFG_Base::display(); // this will call the non-virtual function base->print(); }
输出
Called virtual Base Class function Called GFG_Base print function




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律