附近的人位置距离计算方法
附近的人的位置用经纬度表示,然后通过两点的经纬度计算距离。根据网上的推荐,最终采用geohash。
geohash的实现java版:

1 import java.util.BitSet; 2 import java.util.HashMap; 3 import java.util.Map; 4 5 import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils; 6 7 public class Geohash { 8 9 private static int numbits = 6 * 5; 10 final static char[] digits = { '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', 11 '9', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'j', 'k', 'm', 'n', 'p', 12 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z' }; 13 14 final static HashMap<Character, Integer> lookup = new HashMap<Character, Integer>(); 15 static { 16 int i = 0; 17 for (char c : digits) 18 lookup.put(c, i++); 19 20 } 21 22 public Geohash() { 23 setMap(); 24 } 25 26 public double[] decode(String geohash) { 27 StringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder(); 28 for (char c : geohash.toCharArray()) { 29 30 int i = lookup.get(c) + 32; 31 buffer.append(Integer.toString(i, 2).substring(1)); 32 } 33 34 BitSet lonset = new BitSet(); 35 BitSet latset = new BitSet(); 36 37 // even bits 38 int j = 0; 39 for (int i = 0; i < numbits * 2; i += 2) { 40 boolean isSet = false; 41 if (i < buffer.length()) 42 isSet = buffer.charAt(i) == '1'; 43 lonset.set(j++, isSet); 44 } 45 46 // odd bits 47 j = 0; 48 for (int i = 1; i < numbits * 2; i += 2) { 49 boolean isSet = false; 50 if (i < buffer.length()) 51 isSet = buffer.charAt(i) == '1'; 52 latset.set(j++, isSet); 53 } 54 55 double lon = decode(lonset, -180, 180); 56 double lat = decode(latset, -90, 90); 57 58 return new double[] { lat, lon }; 59 } 60 61 private double decode(BitSet bs, double floor, double ceiling) { 62 double mid = 0; 63 for (int i = 0; i < bs.length(); i++) { 64 mid = (floor + ceiling) / 2; 65 if (bs.get(i)) 66 floor = mid; 67 else 68 ceiling = mid; 69 } 70 return mid; 71 } 72 73 public String encode(String lat, String lon) { 74 75 return encode(Double.parseDouble(lat), Double.parseDouble(lon)); 76 77 } 78 79 public String encode(double lat, double lon) { 80 BitSet latbits = getBits(lat, -90, 90); 81 BitSet lonbits = getBits(lon, -180, 180); 82 StringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder(); 83 for (int i = 0; i < numbits; i++) { 84 buffer.append((lonbits.get(i)) ? '1' : '0'); 85 buffer.append((latbits.get(i)) ? '1' : '0'); 86 } 87 return base32(Long.parseLong(buffer.toString(), 2)); 88 } 89 90 private BitSet getBits(double lat, double floor, double ceiling) { 91 BitSet buffer = new BitSet(numbits); 92 for (int i = 0; i < numbits; i++) { 93 double mid = (floor + ceiling) / 2; 94 if (lat >= mid) { 95 buffer.set(i); 96 floor = mid; 97 } else { 98 ceiling = mid; 99 } 100 } 101 return buffer; 102 } 103 104 public static String base32(long i) { 105 char[] buf = new char[65]; 106 int charPos = 64; 107 boolean negative = (i < 0); 108 if (!negative) 109 i = -i; 110 while (i <= -32) { 111 buf[charPos--] = digits[(int) (-(i % 32))]; 112 i /= 32; 113 } 114 buf[charPos] = digits[(int) (-i)]; 115 116 if (negative) 117 buf[--charPos] = '-'; 118 return new String(buf, charPos, (65 - charPos)); 119 } 120 121 /*********************** 获取九个的矩形编码 ****************************************/ 122 public static String BASE32 = "0123456789bcdefghjkmnpqrstuvwxyz"; 123 public static Map<String, String> BORDERS = new HashMap<String, String>(); 124 public static Map<String, String> NEIGHBORS = new HashMap<String, String>(); 125 126 public static void setMap() { 127 NEIGHBORS.put("right:even", "bc01fg45238967deuvhjyznpkmstqrwx"); 128 NEIGHBORS.put("left:even", "238967debc01fg45kmstqrwxuvhjyznp"); 129 NEIGHBORS.put("top:even", "p0r21436x8zb9dcf5h7kjnmqesgutwvy"); 130 NEIGHBORS.put("bottom:even", "14365h7k9dcfesgujnmqp0r2twvyx8zb"); 131 132 NEIGHBORS.put("right:odd", "p0r21436x8zb9dcf5h7kjnmqesgutwvy"); 133 NEIGHBORS.put("left:odd", "14365h7k9dcfesgujnmqp0r2twvyx8zb"); 134 NEIGHBORS.put("top:odd", "bc01fg45238967deuvhjyznpkmstqrwx"); 135 NEIGHBORS.put("bottom:odd", "238967debc01fg45kmstqrwxuvhjyznp"); 136 137 BORDERS.put("right:even", "bcfguvyz"); 138 BORDERS.put("left:even", "0145hjnp"); 139 BORDERS.put("top:even", "prxz"); 140 BORDERS.put("bottom:even", "028b"); 141 142 BORDERS.put("right:odd", "prxz"); 143 BORDERS.put("left:odd", "028b"); 144 BORDERS.put("top:odd", "bcfguvyz"); 145 BORDERS.put("bottom:odd", "0145hjnp"); 146 147 } 148 149 /** 150 * 获取九个点的矩形编码 151 * 152 * @param geohash 153 * @return 154 */ 155 public String[] getGeoHashExpand(String geohash) { 156 try { 157 String geohashTop = calculateAdjacent(geohash, "top"); 158 String geohashBottom = calculateAdjacent(geohash, "bottom"); 159 String geohashRight = calculateAdjacent(geohash, "right"); 160 String geohashLeft = calculateAdjacent(geohash, "left"); 161 String geohashTopLeft = calculateAdjacent(geohashLeft, "top"); 162 String geohashTopRight = calculateAdjacent(geohashRight, "top"); 163 String geohashBottomRight = calculateAdjacent(geohashRight, 164 "bottom"); 165 String geohashBottomLeft = calculateAdjacent(geohashLeft, "bottom"); 166 String[] expand = { geohash, geohashTop, geohashBottom, 167 geohashRight, geohashLeft, geohashTopLeft, geohashTopRight, 168 geohashBottomRight, geohashBottomLeft }; 169 return expand; 170 } catch (Exception e) { 171 return null; 172 } 173 } 174 175 /** 176 * 分别计算每个点的矩形编码 177 * 178 * @param srcHash 179 * @param dir 180 * @return 181 */ 182 public static String calculateAdjacent(String srcHash, String dir) { 183 srcHash = srcHash.toLowerCase(); 184 char lastChr = srcHash.charAt(srcHash.length() - 1); 185 int a = srcHash.length() % 2; 186 String type = (a > 0) ? "odd" : "even"; 187 String base = srcHash.substring(0, srcHash.length() - 1); 188 if (BORDERS.get(dir + ":" + type).indexOf(lastChr) != -1) { 189 base = calculateAdjacent(base, dir); 190 } 191 base = base 192 + BASE32.toCharArray()[(NEIGHBORS.get(dir + ":" + type) 193 .indexOf(lastChr))]; 194 return base; 195 } 196 197 // @Deprecated 198 // public static void expandLngLat(String geohash, int len){ 199 // boolean is_even = true; 200 // double[] lat = new double[3]; 201 // double[] lon = new double[3]; 202 // lat[0] = -90.0; 203 // lat[1] = 90.0; 204 // lon[0] = -180.0; 205 // lon[1] = 180.0; 206 // double lat_err = 90.0; 207 // double lon_err = 180.0; 208 // char[] geohashChar = geohash.toCharArray(); 209 // // String[] BITS = {"16", "8", "4", "2", "1"}; 210 // int[] BITS = {16, 8, 4, 2, 1}; 211 // for (int i = 0; i < geohashChar.length; i++) { 212 // char c = geohashChar[i]; 213 // int cd = BASE32.indexOf(c); 214 // for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { 215 // int mask = BITS[j]; 216 // if (is_even) { 217 // lon_err /= 2; 218 // refine_interval(lon, cd, mask); 219 // } else { 220 // lat_err /= 2; 221 // refine_interval(lat, cd, mask); 222 // } 223 // is_even = !is_even; 224 // } 225 // } 226 // lat[2] = (lat[0] + lat[1])/2; 227 // //1:[38.8970947265625, 38.902587890625, 38.89984130859375] 228 // //1: 38.8970947265625, 38.902587890625, 38.89984130859375 229 // //2:[38.902587890625, 38.9080810546875, 38.90533447265625] 230 // //2: 38.902587890625, 38.9080810546875, 38.90533447265625 231 // lon[2] = (lon[0] + lon[1])/2; 232 // //1:[-77.047119140625, -77.0361328125, -77.0416259765625] 233 // //1: -77.047119140625, -77.0361328125, -77.0416259765625 234 // //2:[-77.047119140625, -77.0361328125, -77.0416259765625] 235 // //2: -77.047119140625, -77.0361328125, -77.0416259765625 236 // 237 // String topLeft = lat[0]+","+lon[0]; 238 // String topRight = lat[0]+","+lon[1]; 239 // 240 // String bottomleft = lat[1]+","+lon[0]; 241 // String bottoomRight = lat[1]+","+lon[1]; 242 // String centerPoint = (lat[0]+lat[1])/2+","+(lon[0]+lon[1])/2; 243 // 244 // String centerTop = lat[0]+","+(lon[0]+lon[1])/2; 245 // String centerBottom = lat[1]+","+(lon[0]+lon[1])/2; 246 // 247 // String centerLeft = (lat[0]+lat[1])/2+","+lon[0]; 248 // String centerRight = (lat[0]+lat[1])/2+","+lon[1]; 249 // // System.out.println("topLeft:["+topLeft+"] geoHash:"+g.encode(lat[0], 250 // lon[0])); 251 // // System.out.println("topRight:["+topRight+"] geoHash:"+g.encode(lat[0], 252 // lon[1])); 253 // // 254 // System.out.println("bottomleft:["+bottomleft+"] geoHash:"+g.encode(lat[1], 255 // lon[0])); 256 // // 257 // System.out.println("bottoomRight:["+bottoomRight+"] geoHash:"+g.encode(lat[1], 258 // lon[1])); 259 // // 260 // System.out.println("centerPoint:["+centerPoint+"] geoHash:"+g.encode((lat[0]+lat[1])/2, 261 // (lon[0]+lon[1])/2)); 262 // // 263 // System.out.println("centerTop:["+centerTop+"] geoHash:"+g.encode(lat[0], 264 // (lon[0]+lon[1])/2)); 265 // // 266 // System.out.println("centerBottom:["+centerBottom+"] geoHash:"+g.encode(lat[1], 267 // (lon[0]+lon[1])/2)); 268 // // 269 // System.out.println("centerLeft:["+centerLeft+"] geoHash:"+g.encode((lat[0]+lat[1])/2, 270 // lon[0])); 271 // // 272 // System.out.println("centerRight:["+centerRight+"] geoHash:"+g.encode((lat[0]+lat[1])/2, 273 // lon[1])); 274 // 275 // } 276 // 277 // @Deprecated 278 // public static void refine_interval(double[] interval, int cd, int mask){ 279 // if ((cd & mask)>0){ 280 // interval[0] = (interval[0] + interval[1])/2; 281 // }else{ 282 // interval[1] = (interval[0] + interval[1])/2; 283 // } 284 // } 285 // 286 287 // **************************************************************************************************************** 288 289 private static final double EARTH_RADIUS = 6371;// 赤道半径(单位m) 290 291 /** 292 * 转化为弧度(rad) 293 * */ 294 private static double rad(double d) { 295 return d * Math.PI / 180.0; 296 } 297 298 /** 299 * 基于googleMap中的算法得到两经纬度之间的距离,计算精度与谷歌地图的距离精度差不多,相差范围在0.2米以下 300 * 301 * @param lon1 302 * 第一点的精度 303 * @param lat1 304 * 第一点的纬度 305 * @param lon2 306 * 第二点的精度 307 * @param lat2 308 * 第二点的纬度 309 * @return 返回的距离,单位m 310 * */ 311 public double getDistance(double lon1, double lat1, double lon2, 312 double lat2) { 313 double radLat1 = rad(lat1); 314 double radLat2 = rad(lat2); 315 double a = radLat1 - radLat2; 316 double b = rad(lon1) - rad(lon2); 317 double s = 2 * Math.asin(Math.sqrt(Math.pow(Math.sin(a / 2), 2) 318 + Math.cos(radLat1) * Math.cos(radLat2) 319 * Math.pow(Math.sin(b / 2), 2))); 320 s = s * EARTH_RADIUS; 321 s = Math.round(s * 1000)/1000.0; 322 return s; 323 } 324 325 /* 326 * 永相逢超市 108.83457500177 34.256981052624 wqj6us6cmkj5bbfj6qdg s6q08ubhhuq7 327 */ 328 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 329 330 // 东四站 灯市口站 331 double lon1 = 116.4174628300; 332 double lat1 = 39.9243669400; 333 double lon2 = 116.4177739600; 334 double lat2 = 39.9171260300; 335 double dist; 336 String geocode; 337 338 Geohash geohash = new Geohash(); 339 dist = geohash.getDistance(lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2); 340 System.out.println("两点相距:" + dist + " km"); 341 342 geocode = geohash.encode(lat1, lon1); 343 System.out.println("当前位置编码:" + geocode); 344 double[] decode = new Geohash().decode(geocode); 345 for (double d : decode) { 346 System.out.println(d); 347 } 348 349 geocode = geohash.encode(lat2, lon2); 350 System.out.println("远方位置编码:" + geocode); 351 decode = new Geohash().decode(geocode); 352 for (double d : decode) { 353 System.out.println(d); 354 } 355 356 /* 获取的geohash多少位,位数越长,精度越准 */ 357 int geohashLen = 5; 358 359 /* 获取中心点的geohash */ 360 String code = geohash.encode(lat1, lon1).substring(0, geohashLen); 361 362 /* 获取所有的矩形geohash, 一共是九个 ,包含中心点,打印顺序请参考图2 */ 363 String[] result = geohash.getGeoHashExpand(code); 364 for (String string : result) { 365 System.out.println(string); 366 } 367 368 } 369 370 }
原理看起来很容易懂的样子,就是分区编码。但仔细一想却不是那么简单。算法设计,编码设计,为什么相似等等,现在只会痛恨当时为啥不好好学数学。
那么,只要在上传位置信息的时候计算geohash,然后根据geohash的精度前缀进行匹配查询就可以搜索附近的人。但有两个问题。
问题1:
计算的附近的概念不精准,仅仅只是一个区域,在边界问题上需要考虑。距离相近的在边界位置geohash显示却在两块区域。因此引入周围8个区域来精算中间一个区域的位置。这样做会把中间区域周围的包含,但最大范围无法估量。因为周围8块所代表的的精度算法,仅仅是该区域内的,而不是包含所有。就是说,假如中间区域精度1km以内,我需要将周围的区域加上才能把全部1km以内的位置包含。如下图所示:
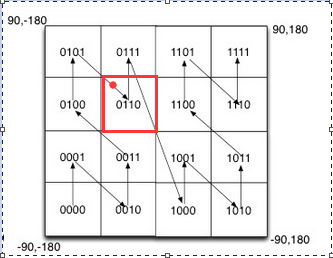

我按照0110的编码匹配,只能得到红色区域内的位置。倘若客户站在区域中心,那么正好该区域的精度就是距离客户的最大距离。但是,在其他区域的客户,比如红点。记红点为A点,A点距离最近的除了0110还包括另外三个区域的点。这样,若仅仅只按中心区域0110搜索附近的人反而不是正确的。于是引入周围8个区域的点。这样,可以把0110区域的人的附近的点全部包含。
距离:
记一个geohash的精度(区域的边长)为len,记最大距离为可以搜索到的最远的附近的位置,记最小距离为该距离内的所有位置必然包含在内。比如最小距离为d,则方圆为d的距离内的所有点都包含。
位于中心区域0110的人最大附近距离为:两个对角线b=2√2len。最小距离为:a=len
再次重申:可以肯定搜索到一个精度内的所有人,但还可以包含附近大于一个精度达部分人。
问题2:
距离需要进行2次计算。若有排序概念还需要排序。
我的抉择:
我选择了匹配前6位,测试距离大概1km以内。然后面临另一个问题:分页。
分页:
客户端滚动加载,我一次查完9个区域内所有点,然后根据时间排序。选取该时间之前的n条记录。第一页就是前n条。第一页最后一条的时间为t1,第二页就是t1时间往前的的n条,以此类推。那么,问题来了。假如第一页花费时间t,在这段时间内,本来第二页的数据位置信息更新(每次更新后时间改变);然后查询第二页的时候,变动的数据不包含在内了。也就是说,遗漏了变化的点。
在我看来,位置信息可以延时,但不要遗漏。因为喜欢查看附近的人的位置通常是实时改变的,而我们遗漏的恰恰就是互相有需求的双方。所以,要一次查询一个很大范围内的数据。
办法:
我一次将9个区域的点全部取出,然后缓存。由于geohash区域内的人共享一个查询,因此将geohash的前缀作为key来缓存该区域附近的点。那么,其他该区域的人也可以使用本次查询的结果。
用java做分页处理。
第一次请求,所有数据缓存。然后取出前n个,如果排序,则排序后的前n个。缓存信息不可以改变。第二次请求,计算缓存的索引n开始的n个。....
缺点:
我需要每次都计算距离,排序。
思考:
我想要第一次计算完之后缓存数据,然后第二次直接取出想要的部分。进而省略每次的计算。接着,问题来了。
第一次数据库的查询数据缓存,标记为key_all;客户a通过缓存计算距离,排序,放入缓存,标记为key_a;显然,两个缓存有大量的重复数据。如果仅仅是标记索引,那计算结果的部分无法保存,所以需要复制而后修改,而后存储。虽然省略了部分计算,但加大了内存需求。
对于时间和空间的问题,我们再来看需求。需求是附近的人,而我查看附近的人的翻页频率并不高,也就是说每次计算的次数很少。那我可以不用为了减少部分计算而加大存储。因为加大存储需要空间加倍,而减少计算影响不大。所以放弃每人都缓存数据。采用每次翻页时计算需要的数据。
然后,面临两个问题。
第一个:ehcache读取后的数据,被计算修改后缓存相应改变,因为对象引用相同。
然后我花了两天看反射和序列化,最后采用序列化来复制缓存对象。成功后又觉得不对,缓存显然是有序列化的,我干嘛重复加工,找到配置,copyOnRead="true" copyOnWrite="true"。解决。
第二个:排序和分页的计算方法。
客户分页的时候也会传新的位置过来,位置必然发生改变。那么按照上次分页计算的距离就不能使用了。
也就是说,我需要用户只传递一次位置,只在第一页请求的时候传递位置,往后的页码忽略其位置。因此,还需要保存第一次请求的位置。首先我要区分第一次和其他。根据现有标记无法区分,因为是按照时间排序的。所以不能区分,也就不能忽略。也就是,用户每次请求传递位置和时间。查询该位置附近该时间之前的n条记录。
finally:缓存边界
缓存是有时间限制的,如果用户第一页查询完后,第二页缓存更新,第二页就不能和第一页衔接了。
所以,为了逻辑上还是拓扑上啥的,严谨不漏。我不能接着查询第二页了。也就是读取缓存的时候,策略需要改变。若缓存不在,重新缓存数据,并查询第一页,告诉客户端刷新页面而不是请求第二页。缺点是若用户第二页是缓存结束前访问的就只能刷新,用户体验不好。所以还是不提示了?我不是产品,但严谨的态度来说,我悄悄更新?也就是第二页数据若缓存不在,我就接着查询缓存第一页作为第二页给客户端。又想多了,我不是根据页码分页的,而是根据时间分页的。那么缓存更新的时候需不需要限制时间呢。我需要按时间排序,而且需要全部数据缓存。所以不能限制时间。这样,取出新缓存的数据中,前n条,忽视时间。当缓存存在而不更新的时候才按照时间取下一组数据。客户端虽然会发现和第一页一样的数据,但时间不一样了。为了避免缓存边界的发生,我或许应该延长缓存时间。
算法遗漏:
假设默认第一次搜索是geohash匹配前6位,1km以内。设计一共2页,翻到第三页的时候就要加载更大范围内的。所以匹配前5位,这样,问题出现了。
重新匹配前5位的时候包含了之前查过的前6位的数据。
我当然可以对比数组,取消已经显示的,或者在查询匹配的时候就直接去除(比如java 8中的stream)。但这样查询语句就变的复杂。比如我的坐标是&lat=39.9346650000&lon=116.3951690000,对应的geohash是:wx4g0tukk10e。第一次匹配前6位的sql:
1 SELECT id, lat, lon, geohash, updatetime FROM user_location 2 WHERE 1=1 3 and ( 4 geohash like 'wx4g0t%' or geohash like 'wx4g0w%' or geohash like 'wx4g0s%' 5 or geohash like 'wx4g0v%' or geohash like 'wx4g0m%' or geohash like 'wx4g0q%' 6 or geohash like 'wx4g0y%' or geohash like 'wx4g0u%' or geohash like 'wx4g0k%')
匹配前5位并去除前6位的

1 SELECT id, lat, lon, geohash, updatetime FROM user_location 2 WHERE 1=1 3 and ( 4 geohash like 'wx4g0%' or geohash like 'wx4g2%' or geohash like 'wx4fb%' 5 or geohash like 'wx4g1%' or geohash like 'wx4ep%' or geohash like 'wx4er%' 6 or geohash like 'wx4g3%' or geohash like 'wx4fc%' or geohash like 'wx4dz%') 7 and( 8 geohash not like 'wx4g0t%' or geohash not like 'wx4g0w%' or geohash not like 'wx4g0s%' 9 or geohash not like 'wx4g0v%' or geohash not like 'wx4g0m%' or geohash not like 'wx4g0q%' 10 or geohash not like 'wx4g0y%' or geohash not like 'wx4g0u%' or geohash not like 'wx4g0k%' 11 )
这在数据层次一次性搜索增加了比较次数num*6倍。而事实上,我想做缓存的话,key=6和key=5的缓存存在被包含与包含的关系。理想的状态应该是:key=5的所有数据缓存,key=6的缓存持有key=5的缓存。这是一个对我来说复杂的缓存了。我也发现了,当我自习研究某项技术的时候什么都不会,换句话说自己就是代码搬运工而已。
现在的做法是直接缓存数据。以后升级redis了再考虑别的。
关注我的公众号




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号