Spring学习笔记(六)——AOP
1.AOP简介
1.1 AOP
Spring 框架的一个关键组件是面向切面的编程(AOP)框架。面向切面的编程需要把程序逻辑分解成不同的部分称为所谓的关注点。跨一个应用程序的多个点的功能被称为横切关注点,这些横切关注点在概念上独立于应用程序的业务逻辑。在软件开发过程中有各种各样的很好的切面的例子,如日志记录、审计、声明式事务、安全性和缓存等。
在 OOP 中,关键单元模块度是类,而在 AOP 中单元模块度是切面。依赖注入帮助你对应用程序对象相互解耦合,AOP 可以帮助你从它们所影响的对象中对横切关注点解耦。AOP 像是编程语言的触发物,如 Perl,.NET,Java 或者其他语言。
Spring AOP 模块提供拦截器来拦截一个应用程序,例如,当执行一个方法时,你可以在方法执行之前或之后添加额外的功能。
1.2 AOP术语
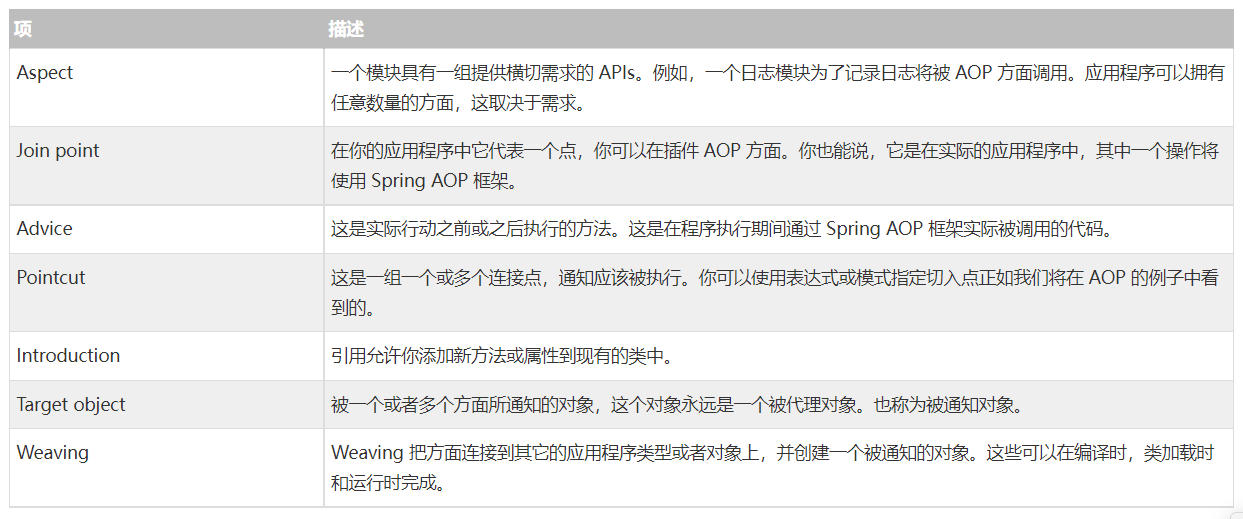
在我们开始使用 AOP 工作之前,让我们熟悉一下 AOP 概念和术语。这些术语并不特定于 Spring,而是与 AOP 有关的。
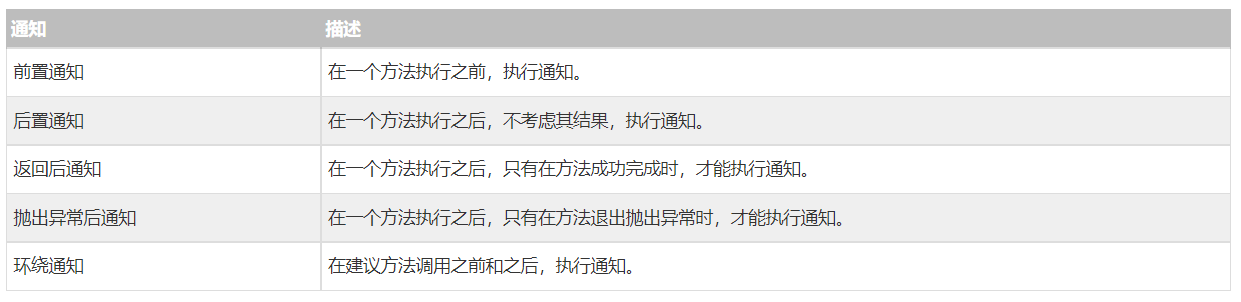
1.3 通知的类型
Spring 方面可以使用下面提到的五种通知工作:
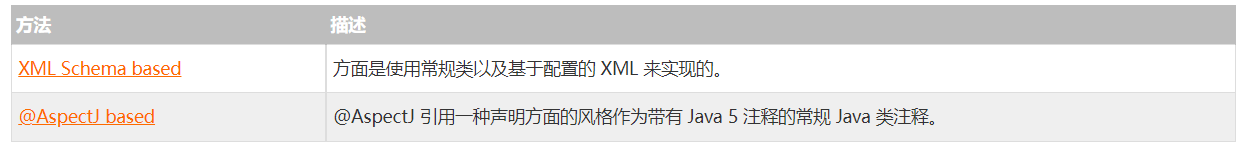
1.4 实现自定义方面
Spring 支持 @AspectJ annotation style 的方法和基于模式的方法来实现自定义方面。这两种方法已经在下面两个子节进行了详细解释。
2. Spring 中基于 AOP 的 XML架构
声明一个Aspect:
一个 aspect 是使用 元素声明的,支持的 bean 是使用 ref 属性引用的,如下所示,这里,“aBean” 将被配置和依赖注入,就像前面的章节中你看到的其他的 Spring bean 一样。
<aop:config> <aop:aspect id="myAspect" ref="aBean"> ... </aop:aspect> </aop:config> <bean id="aBean" class="..."> ... </bean>
声明一个切入点:
一个切入点有助于确定使用不同建议执行的感兴趣的连接点(即方法)。在处理基于配置的 XML 架构时,切入点将会按照如下所示定义。下面的示例定义了一个名为 “businessService” 的切入点,该切入点将与 com.tutorialspoint 包下的 Student 类中的 getName() 方法相匹配,意思是执行这个方法前后会执行这些切入点:
<aop:config> <aop:aspect id="myAspect" ref="aBean"> <aop:pointcut id="businessService" expression="execution(* com.tutorialspoint.Student.getName(..))"/> ... </aop:aspect> </aop:config> <bean id="aBean" class="..."> ... </bean>
声明建议:
你可以在<aop:aspect>中使用<aop:{通知类型名}>元素声明任意五种类型的通知,如下:
<aop:config> <aop:aspect id="myAspect" ref="aBean">
<aop:pointcut id="businessService" expression="execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..))"/>
<!-- a before advice definition --> <aop:before pointcut-ref="businessService" method="doRequiredTask"/>
<!-- an after advice definition --> <aop:after pointcut-ref="businessService" method="doRequiredTask"/>
<!-- an after-returning advice definition --> <!--The doRequiredTask method must have parameter named retVal --> <aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="businessService" returning="retVal" method="doRequiredTask"/>
<!-- an after-throwing advice definition --> <!--The doRequiredTask method must have parameter named ex --> <aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="businessService" throwing="ex" method="doRequiredTask"/>
<!-- an around advice definition --> <aop:around pointcut-ref="businessService" method="doRequiredTask"/>
... </aop:aspect> </aop:config> <bean id="aBean" class="..."> ... </bean>
你可以对不同的建议使用相同的 doRequiredTask 或者不同的方法。这些方法将会作为 aspect 模块的一部分来定义。
下边给出一个示例理解用法:
这里是 Logging.java 文件的内容。这实际上是 aspect 模块的一个示例,它定义了在各个点调用的方法。
public class Logging { /** * This is the method which I would like to execute * before a selected method execution. */ public void beforeAdvice(){ System.out.println("Going to setup student profile."); } /** * This is the method which I would like to execute * after a selected method execution. */ public void afterAdvice(){ System.out.println("Student profile has been setup."); } /** * This is the method which I would like to execute * when any method returns. */ public void afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal){ System.out.println("Returning:" + retVal.toString() ); } /** * This is the method which I would like to execute * if there is an exception raised. */ public void AfterThrowingAdvice(IllegalArgumentException ex){ System.out.println("There has been an exception: " + ex.toString()); } }
下面是 Student.java 文件的内容:
public class Student { private Integer age; private String name; public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Integer getAge() { System.out.println("Age : " + age ); return age; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { System.out.println("Name : " + name ); return name; } public void printThrowException(){ System.out.println("Exception raised"); throw new IllegalArgumentException(); } }
下面是 MainApp.java 文件的内容:
public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student"); student.getName(); student.getAge(); student.printThrowException(); } }
下面是配置文件 Beans.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd ">
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="log" ref="logging">
<aop:pointcut id="selectAll"
expression="execution(* com.tutorialspoint.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="selectAll" method="beforeAdvice"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref="selectAll" method="afterAdvice"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="selectAll"
returning="retVal"
method="afterReturningAdvice"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="selectAll"
throwing="ex"
method="afterThrowingAdvice"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<!-- Definition for student bean -->
<bean id="student" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Zara" />
<property name="age" value="11"/>
</bean>
<!-- Definition for logging aspect -->
<bean id="logging" class="com.tutorialspoint.Logging"/>
</beans>
说明:
<aop:aspect id="log" ref="logging">中是把带有各个点调用方法的bean注入到这个aspect中去。
<aop:pointcut id="selectAll" expression="execution(* com.tutorialspoint.*.*(..))"/>这里的expression属性指的是有哪个或者哪些方法在执行的各个点会调用这些方法。
一旦你已经完成的创建了源文件和 bean 配置文件,让我们运行一下应用程序。如果你的应用程序一切都正常的话,这将会输出以下消息:
Going to setup student profile.
Name : Zara
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:Zara
Going to setup student profile.
Age : 11
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:11
Going to setup student profile.
Exception raised
Student profile has been setup.
There has been an exception: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
.....
other exception content
让我们来解释一下上面定义的在 com.tutorialspoint 中 选择所有方法的 。让我们假设一下,你想要在一个特殊的方法之前或者之后执行你的建议,你可以通过替换使用真实类和方法名称的切入点定义中的星号(*)来定义你的切入点来缩短你的执行。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd "> <aop:config> <aop:aspect id="log" ref="logging"> <aop:pointcut id="selectAll" expression="execution(* com.tutorialspoint.Student.getName(..))"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="selectAll" method="beforeAdvice"/> <aop:after pointcut-ref="selectAll" method="afterAdvice"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> <!-- Definition for student bean --> <bean id="student" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student"> <property name="name" value="Zara" /> <property name="age" value="11"/> </bean> <!-- Definition for logging aspect --> <bean id="logging" class="com.tutorialspoint.Logging"/> </beans>
如果你想要执行通过这些更改之后的示例应用程序,这将会输出以下消息:
Going to setup student profile.
Name : Zara
Student profile has been setup.
Age : 11
Exception raised
.....
other exception content
3. Spring 中基于 AOP 的 @AspectJ
这次我们先来看一个示例,然后再来看一下两种方式的区别。
这里是 Logging.java 文件的内容。这实际上是 aspect 模块的一个示例,它定义了在各个点调用的方法。
@Aspect public class Logging { /** Following is the definition for a pointcut to select * all the methods available. So advice will be called * for all the methods. */ @Pointcut("execution(* com.tutorialspoint.*.*(..))") private void selectAll(){} /** * This is the method which I would like to execute * before a selected method execution. */ @Before("selectAll()") public void beforeAdvice(){ System.out.println("Going to setup student profile."); } /** * This is the method which I would like to execute * after a selected method execution. */ @After("selectAll()") public void afterAdvice(){ System.out.println("Student profile has been setup."); } /** * This is the method which I would like to execute * when any method returns. */ @AfterReturning(pointcut = "selectAll()", returning="retVal") public void afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal){ System.out.println("Returning:" + retVal.toString() ); } /** * This is the method which I would like to execute * if there is an exception raised by any method. */ @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "selectAll()", throwing = "ex") public void AfterThrowingAdvice(IllegalArgumentException ex){ System.out.println("There has been an exception: " + ex.toString()); } }
下面是 Student.java 文件的内容:
public class Student { private Integer age; private String name; public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Integer getAge() { System.out.println("Age : " + age ); return age; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { System.out.println("Name : " + name ); return name; } public void printThrowException(){ System.out.println("Exception raised"); throw new IllegalArgumentException(); } }
下面是 MainApp.java 文件的内容:
public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student"); student.getName(); student.getAge(); student.printThrowException(); } }
下面是配置文件 Beans.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd "> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <!-- Definition for student bean --> <bean id="student" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student"> <property name="name" value="Zara" /> <property name="age" value="11"/> </bean> <!-- Definition for logging aspect --> <bean id="logging" class="com.tutorialspoint.Logging"/> </beans>
一旦你已经完成的创建了源文件和 bean 配置文件,让我们运行一下应用程序。如果你的应用程序一切都正常的话,这将会输出以下消息:
Going to setup student profile.
Name : Zara
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:Zara
Going to setup student profile.
Age : 11
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:11
Going to setup student profile.
Exception raised
Student profile has been setup.
There has been an exception: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
.....
other exception content
现在我们来分析一下基于@AspectJ注解的实现与基于xml实现的区别。
如何支持@AspectJ:
@AspectJ 作为通过 Java 5 注释注释的普通的 Java 类,它指的是声明 aspects 的一种风格。通过在你的基于架构的 XML 配置文件中包含以下元素,@AspectJ 支持是可用的。
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
声明一个aspect:
Aspects 类和其他任何正常的 bean 一样,除了它们将会用 @AspectJ 注释之外,它和其他类一样可能有方法和字段,如下所示:
package org.xyz; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; @Aspect public class AspectModule { }
它们将在 XML 中按照如下进行配置,就和其他任何 bean 一样:
<bean id="myAspect" class="org.xyz.AspectModule"> <!-- configure properties of aspect here as normal --> </bean>
声明一个切入点
一个切入点有助于确定使用不同建议执行的感兴趣的连接点(即方法)。在处理基于配置的 XML 架构时,切入点的声明有两个部分:
-
一个切入点表达式决定了我们感兴趣的哪个方法会真正被执行。
- 一个切入点标签包含一个名称和任意数量的参数。方法的真正内容是不相干的,并且实际上它应该是空的。
下面的示例一中定义了一个名为 ‘businessService’ 的切入点,该切入点将与 com.xyz.myapp.service 包下的类中可用的每一个方法相匹配:
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; @Pointcut("execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..))") // expression private void businessService() {} // signature
下面的示例二中定义了一个名为 ‘getname’ 的切入点,该切入点将与 com.tutorialspoint 包下的 Student 类中的 getName() 方法相匹配:
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; @Pointcut("execution(* com.tutorialspoint.Student.getName(..))") private void getname() {}
声明建议
你可以使用 @{ADVICE-NAME} 注释声明五个建议中的任意一个,如下所示。这假设你已经定义了一个切入点标签方法 businessService():
@Before("businessService()")
public void doBeforeTask(){
...
}
@After("businessService()")
public void doAfterTask(){
...
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "businessService()", returning="retVal")
public void doAfterReturnningTask(Object retVal){
// you can intercept retVal here.
...
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "businessService()", throwing="ex")
public void doAfterThrowingTask(Exception ex){
// you can intercept thrown exception here.
...
}
@Around("businessService()")
public void doAroundTask(){
...
}
你可以为任意一个建议定义你的切入点内联。下面是在建议之前定义内联切入点的一个示例:
@Before("execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..))")
public doBeforeTask(){
...
}



