从源码看java中Integer的缓存问题
在开始详细的说明问题之前,我们先看一段代码
1 public static void compare1(){ 2 Integer i1 = 127, i2 = 127, i3 = 128, i4 = 128; 3 System.out.println(i1 == i2); 4 System.out.println(i1.equals(i2)); 5 System.out.println(i3 == i4); 6 System.out.println(i3.equals(i4)); 7 }
这段代码输出的结果是什么呢?
答案是:
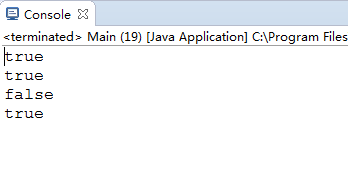
是不是感到奇怪呢?为什么127的时候==是true,128的时候就变成了false?其实要回答这个问题不难。
Integer在赋值的时候会发生自动装箱操作,调用Integer的valueOf方法,那么我们看一下java的源码(1.8):
1 /** 2 * Returns an {@code Integer} instance representing the specified 3 * {@code int} value. If a new {@code Integer} instance is not 4 * required, this method should generally be used in preference to 5 * the constructor {@link #Integer(int)}, as this method is likely 6 * to yield significantly better space and time performance by 7 * caching frequently requested values. 8 * 9 * This method will always cache values in the range -128 to 127, 10 * inclusive, and may cache other values outside of this range. 11 * 12 * @param i an {@code int} value. 13 * @return an {@code Integer} instance representing {@code i}. 14 * @since 1.5 15 */ 16 public static Integer valueOf(int i) { 17 if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) 18 return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; 19 return new Integer(i); 20 }
这里根据源码可以看出,在传入的i值在IntegerCache.low和IntegerCache.high之间的时候,会返回IntegerCache.cache数组里面的数,不在这个范围才会new一个Integer对象。接下来我们看一下IntegerCache数组的初始化情况:
1 /** 2 * Cache to support the object identity semantics of autoboxing for values between 3 * -128 and 127 (inclusive) as required by JLS. 4 * 5 * The cache is initialized on first usage. The size of the cache 6 * may be controlled by the {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size>} option. 7 * During VM initialization, java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high property 8 * may be set and saved in the private system properties in the 9 * sun.misc.VM class. 10 */ 11 12 private static class IntegerCache { 13 static final int low = -128; 14 static final int high; 15 static final Integer cache[]; 16 17 static { 18 // high value may be configured by property 19 int h = 127; 20 String integerCacheHighPropValue = 21 sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"); 22 if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) { 23 try { 24 int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue); 25 i = Math.max(i, 127); 26 // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE 27 h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1); 28 } catch( NumberFormatException nfe) { 29 // If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it. 30 } 31 } 32 high = h; 33 34 cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1]; 35 int j = low; 36 for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++) 37 cache[k] = new Integer(j++); 38 39 // range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7) 40 assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; 41 } 42 43 private IntegerCache() {} 44 }
我们看到IntegerCache的low定义为-128,high默认定义为127.但是high是可以配置的,如果没有配置才是127.我们不去看配置的情况,因为java默认是没有配置的。看一下cache数组,长度为high-low+1,从-128开始到127,存在cache数组内。
从上面的代码中可以看出,java在申请一个大于-128小于127的数时,其实是从cache中直接取出来用的,如果不在这个范围则是new了一个Integer对象。
对于==,他比较的是地址。对于int来说比较的是值。
对于equals,比较的是内容(要看equals的具体实现)。看一下Integer里面的实现:
1 /** 2 * Compares this object to the specified object. The result is 3 * {@code true} if and only if the argument is not 4 * {@code null} and is an {@code Integer} object that 5 * contains the same {@code int} value as this object. 6 * 7 * @param obj the object to compare with. 8 * @return {@code true} if the objects are the same; 9 * {@code false} otherwise. 10 */ 11 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 12 if (obj instanceof Integer) { 13 return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue(); 14 } 15 return false; 16 }
它比较的确实是值的大小。
因此i1==i2和i1.equals(i2)都是true
i3==i4为false
i3.equals(i4)为true。




