ELK 安装部署实战 (最新6.4.0版本)
一、实战背景
根据公司平台的发展速度,对于ELK日志分析日益迫切。主要的需求有:
1.用户行为分析
2.运营活动点击率分析
作为上述2点需求,安装最新版本6.4.0是非常有必要的,大家可根据本人之前博文ELK实战得知,之前ELK本人主要采用5.5.2 版本,
但是根据平台发展,5.5.2的功能不能完全满足我们的需求,所以现在博主与大家一起来对 6.4.0 (目前最新稳定版)版本进行安装部署。
二、ELK安装部署开始
大家安装部署之前,可先参考官方文档进行部署。(官方参考文档地址可点击一下超链接)
注:Elasticsearch 6.4.0 默认安装了x-pack 安全插件,该插件授权 30天试用。(如过期,则自行选择购买,或者破解,本方案不提供破解方案)
Elasticsearch 6.4.0 Kibana 6.4.0 Logstash 6.4.0 Filebeat 6.4.0
1、安装 Elasticsearch
1.1、下载安装Elasticsearch 6.4.0
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.4.0.tar.gz wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.4.0.tar.gz.sha512
# 当shasum命令不存在时,可执行命令安装 yum install perl-Digest-SHA shasum -a 512 -c elasticsearch-6.4.0.tar.gz.sha512
tar -xzf elasticsearch-6.4.0.tar.gz cd elasticsearch-6.4.0/
2.1、配置Elasticsearch 集群
2.1.1 配置服务器hosts
由于模拟生产环境,提升计算能力,跨主机集群配置为优选
#1.配置集群之前先配置每台节点主机hosts,下图以测试环境为例:
配置 es-node1 和 es-node2 两台主机名称, es-node1为本机主机 ,如若增加主机节点,可配置es-node3 …,elasticsearch可配置上千节点作为集群服务节点。
vi /etc/hosts 192.168.30.21 es-node1 192.168.30.22 es-node2 192.168.30.23 es-node3
2.1.2 配置Elasticsearch
A.配置es-node1节点集群配置,如下配置 node.master:true 表示为主节点,node.data:true 表示主节点也作为数据节点
vi config/elasticsearch.yml cluster.name: my_es_cluster node.name: es-node1
path.data: /data/elk/es/data
path.logs: /data/elk/es/logs
http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*" node.master: true node.data: true
# 配置白名单 0.0.0.0表示其他机器都可访问
network.host: 0.0.0.0
transport.tcp.port: 9300
# tcp 传输压缩
transport.tcp.compress: true
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["es-node1","es-node2","es-node3"]
B.配置es-node2节点集群配置
vi config/elasticsearch.yml cluster.name: my_es_cluster node.name: es-node2
path.data: /data/elk/es/data
path.logs: /data/elk/es/logs
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
node.master: false
node.data: true
# 配置白名单 0.0.0.0表示其他机器都可访问
network.host: 0.0.0.0
transport.tcp.port: 9300
# tcp 传输压缩
transport.tcp.compress: true
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["es-node1","es-node2","es-node3"]
C.配置es-node3节点集群配置
vi config/elasticsearch.yml cluster.name: my_es_cluster node.name: es-node3
path.data: /data/elk/es/data
path.logs: /data/elk/es/logs
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
node.master: false
node.data: true
# 配置白名单 0.0.0.0表示其他机器都可访问
network.host: 0.0.0.0
transport.tcp.port: 9300
# tcp 传输压缩
transport.tcp.compress: true
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["es-node1","es-node2","es-node3"]
2.1.3 启动elasticsearch
A.启动elasticsearch服务之前,需先配置es用户组和es用户(由于es安全因素)
groupadd es #增加es组 useradd es –g es –p pwd #增加es用户并附加到es组 chown -R es:es elasticsearch-6.4.0 #分配es的目录访问权限 su –es #切换es用户
B.启动命令
/tools/elk/elasticsearch-6.4.0 ./bin/elasticsearch
C.第一次启动将遇到问题
ERROR: [2] bootstrap checks failed
[1]: max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process is too low, increase to at least [65536]
#切换到root用户修改 vi /etc/security/limits.conf #在最后面追加 es hard nofile 65536 es soft nofile 65536 #修改后重新登录es账号,使用命令查看上面设置是否成功,结果为65536则成功 ulimit -Hn
[2]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
#切换到root用户 vi /etc/sysctl.conf #在最后追加 vm.max_map_count=262144 #使用 sysctl -p 查看修改结果 sysctl -p
D.解决以上问题,则先启动 数据节点,最后启动主节点
/tools/elk/elasticsearch-6.4.0 ./bin/elasticsearch
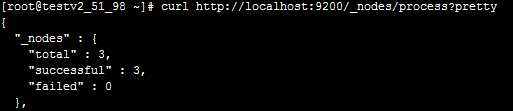
F.当所有节点启动成功后,在主节点服务器执行以下curl命令,如下图所示,标识Elasticsearch集群启动成功。
curl http://localhost:9200/_nodes/process?pretty
2、安装 Kibana
2.1 下载安装Kibana
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-6.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-6.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.sha512
shasum -a 512 kibana-6.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.sha512
tar -xzf kibana-6.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
mv kibana-6.4.0-linux-x86_64/ kibana-6.4.0
cd kibana-6.4.0/
2.2 配置kibana
vi ./config/kibana.yml server.host: "192.168.30.21"
2.3 启动kibana
./bin/kibana
2.4 访问kibana,如下图所示,表示启动成功
http://192.168.30.21:5601
3、安装 Logstash 与 Filebeat
3.1 下载安装Logstash和Filebeat
# Logstash
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-6.4.0.tar.gz
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-6.4.0.tar.gz.sha512
shasum -a 512 logstash-6.4.0.tar.gz.sha512
tar -xzf logstash-6.4.0.tar.gz
cd logstash-6.4.0
# Filebeat
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-6.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-6.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.sha512
shasum -a 512 filebeat-6.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.sha512
tar -xzf filebeat-6.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
mv filebeat-6.4.0-linux-x86_64 filebeat-6.4.0
cd filebeat-6.4.0
3.2 配置Logstash、Filebeat (最新版与5.5.2版本有差异,最新版引入module的概念,具体查看官方文档)
官方参考地址:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/6.4/advanced-pipeline.html
Filebeat + Kafka + Logstash方案地址(可参考): https://www.cnblogs.com/woodylau/p/9488339.html
在本篇博文,将仅说明 Logstash与Filebeat的交互,采集日志,该交互参考了以上官方文档。采集nginx日志。
# Filebeat.yml filebeat.prospectors: - type: log paths: - /path/to/file/logstash-tutorial.log
multiline.pattern: ^\[
multiline.negate: true
multiline.match: after output.logstash: hosts: ["localhost:5044"]
# Logstash-test.yml
cd logstash-6.4.0
vi logstash_test.conf
input { beats { port => "5044" } } filter { grok { match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}"} } geoip { source => "clientip" } } output { elasticsearch { hosts => [ "localhost:9200" ] } }
3.3 启动Logstash、Filebeat
#后台启动 filebeat nohup ./filebeat -c ./filebeat.yml & #启动Logstash nohup ./bin/logstash -f logstash-test.conf &



