c++浅拷贝和深拷贝学习案例
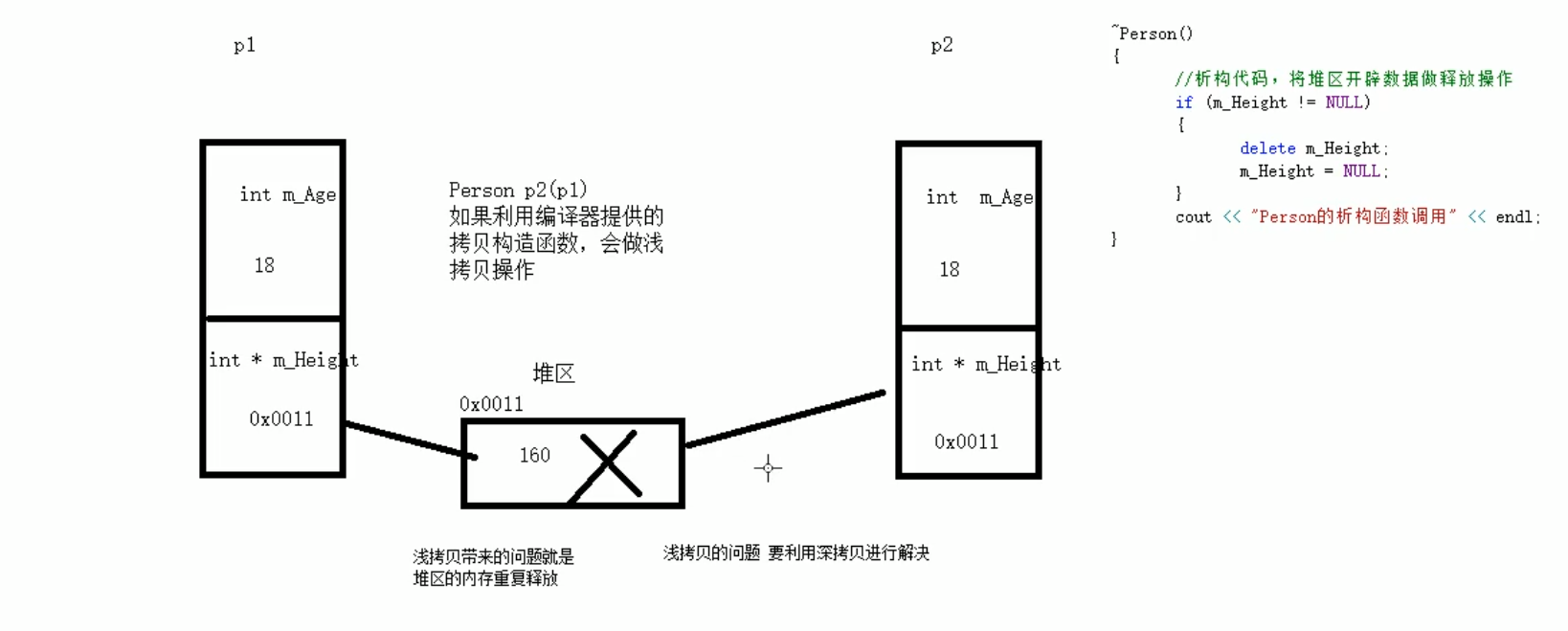
浅拷贝的问题原理:
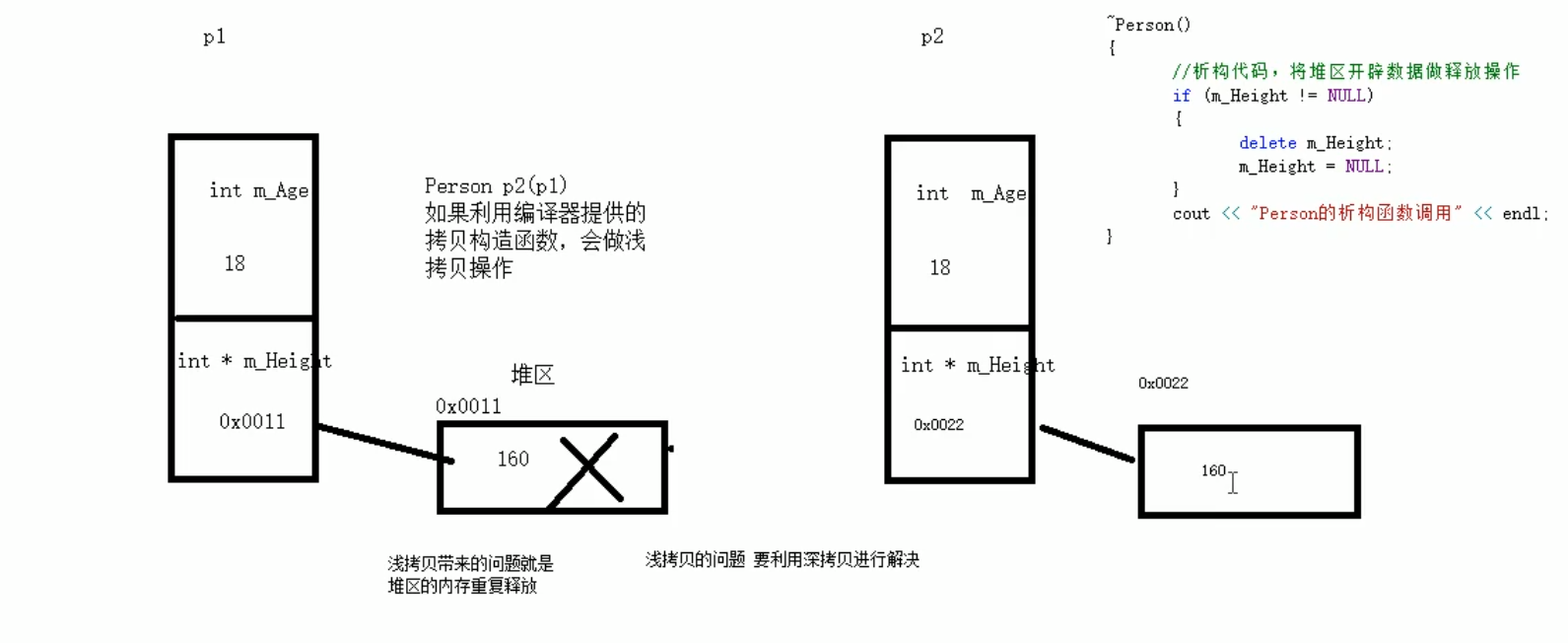
深拷贝的解决方法:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 浅拷贝:简单的赋值拷贝操作(编译器给我们提供的拷贝构造函数就是浅拷贝)
// 存在堆区内存重复释放的问题,因此涉及到堆区内存的时候要用深拷贝
//
// 深拷贝:在堆区重新申请空间,进行拷贝操作
class Person{
public:
Person(){
cout<<"Person的默认构造函数调用"<<endl;
}
Person(int age, int height){
cout<<"Person的有参构造函数调用"<<endl;
m_Age = age;
m_Height = new int(height); // 在堆区创建
}
// 自己实现深拷贝来解决浅拷贝的问题
Person(const Person &p){
cout<<"Person的拷贝构造函数调用"<<endl;
m_Age = p.m_Age;
// m_Height = p.m_Height; // 浅拷贝
m_Height = new int(*p.m_Height); // 深拷贝
}
~Person(){
cout<<"Person的析构函数调用"<<endl;
// 由于在堆区创建的对象需要由程序员手动来释放
// 所以要在析构函数中实现堆区的内存释放操作
if(m_Height != NULL){
delete m_Height;
m_Height = NULL;
}
}
int m_Age;
int *m_Height; // 用指针来指示,因为我们要把这个属性开辟到堆区
};
void test01(){
Person p1(18,160);
cout<<"p1的年龄为:"<< p1.m_Age << ", p1的身高为:" << *p1.m_Height << endl;
Person p2(p1);
cout<<"p2的年龄为:"<< p2.m_Age << ", p2的身高为:" << *p2.m_Height << endl;
}
int main(){
test01();
}
输出结果为: