CSP第31次认证题解 2023.9
A、坐标变换(其一)

样例输入
3 2
10 10
0 0
10 -20
1 -1
0 0
样例输出
21 -11
20 -10
题解
按照题目,一个循环即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 200010
#define ll long long
template <class T>
inline void read(T& a){
T x = 0, s = 1;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)){ if(c == '-') s = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(isdigit(c)){ x = x * 10 + (c ^ '0'); c = getchar(); }
a = x * s;
return ;
}
int n, m;
int dx[N], dy[N];
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
read(dx[i]), read(dy[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
x += dx[j];
y += dy[j];
}
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B、坐标变换(其二)

样例输入
10 5
2 0.59
2 4.956
1 0.997
1 1.364
1 1.242
1 0.82
2 2.824
1 0.716
2 0.178
2 4.094
1 6 -953188 -946637
1 9 969538 848081
4 7 -114758 522223
1 9 -535079 601597
8 8 159430 -511187
样例输出
-1858706.758 -83259.993
-1261428.46 201113.678
-75099.123 -738950.159
-119179.897 -789457.532
114151.88 -366009.892

题解
注意到这两个操作分别可互相叠加。对操作一作前缀积,操作二作前缀和。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 200010
#define ll long long
template <class T>
inline void read(T& a){
T x = 0, s = 1;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)){ if(c == '-') s = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(isdigit(c)){ x = x * 10 + (c ^ '0'); c = getchar(); }
a = x * s;
return ;
}
int n, m;
double opt1[N];
double opt2[N];
double sum1[N], sum2[N];
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int opt; cin >> opt;
if(opt == 1) cin >> opt1[i];
else{
cin >> opt2[i];
opt1[i] = 1;
}
}
sum1[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
sum1[i] = sum1[i-1] * opt1[i];
sum2[i] = sum2[i-1] + opt2[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int l, r;
double x, y;
cin >> l >> r;
cin >> x >> y;
double k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
k1 = sum1[r] / sum1[l-1];
k2 = sum2[r] - sum2[l-1];
double tmp = x;
x = x * cos(k2) - y * sin(k2);
y = tmp * sin(k2) + y * cos(k2);
x *= k1; y *= k1;
printf("%.3lf %.3lf\n", x, y);
}
return 0;
}
C、梯度求解


样例 1
输入:
2 2
x1 x1 x1 * x2 + *
1 2 3
2 3 4
输出:
15
3

样例 2
输入:
3 5
x2 x2 * x2 * 0 + -100000 -100000 * x2 * -
3 100000 100000 100000
2 0 0 0
2 0 -1 0
2 0 1 0
2 0 100000 0
输出:
0
70
73
73
999999867
题解
对表达式建立树,每个节点对其值进行分类。在求导的时候,难点在于乘法,可以发现无论是什么乘法,其实都使用最后一个公式是通用的。
为了方便,我们在求导时,直接在原树的基础上向后增加节点。如果是加法,那么其左右儿子就是原树左右儿子求导后的形态。如果是减法,同理(一定要注意左右顺序!!是谁减谁!!)
在做乘法求导时,直接套用最后那个公式,将当前节点新建成加分节点,左右儿子分别新建为乘法节点。对于左儿子,其左儿子为原树的左儿子求导的结果,右儿子直接接到原树上的右儿子即可,跟线段树合并的做法相同。新建节点的右儿子同理,左儿子直接接到原树的左儿子,右儿子接求导结果返回的新建节点。
建立好新树之后,直接便利一遍带入值即可。(注意负值取模!)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 200010
#define ll long long
#define int long long
template <class T>
inline void read(T& a){
T x = 0, s = 1;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)){ if(c == '-') s = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(isdigit(c)){ x = x * 10 + (c ^ '0'); c = getchar(); }
a = x * s;
return ;
}
int n, m;
struct node{
int isopt, opt; // 1: + 2: - 3: *
int isnum, val; // 数字
int isx, id; // 变量
int lc, rc;
} t[N], pp[N];
stack <int> stac;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int did;
int variable[N]; // 变量的值
#define lson t[u].lc
#define rson t[u].rc
int id = n;
int dfs(int now, int k){ // 返回以当前节点为根的求导后的新节点的编号
if(t[now].isopt == 1){
id++;
t[id].isopt = 1;
t[id].opt = t[now].opt;
int u = id;
if(t[u].opt == 1 || t[u].opt == 2){
t[u].lc = dfs(t[now].lc, k);
t[u].rc = dfs(t[now].rc, k);
}
else{
t[u].opt = 1;
t[u].lc = ++id;
t[lson].isopt = 1;
t[lson].opt = 3;
t[lson].lc = dfs(t[now].lc, k);
t[lson].rc = t[now].rc;
t[u].rc = ++id;
t[rson].isopt = 1;
t[rson].opt = 3;
t[rson].lc = t[now].lc;
t[rson].rc = dfs(t[now].rc, k);
}
return u;
}
else if(t[now].isnum == 1){
id++;
t[id].isnum = 1;
t[id].val = 0;
return id;
}
else{
id++;
t[id].isnum = 1;
if(t[now].id == k){
t[id].val = 1;
}
else{
t[id].val = 0;
}
return id;
}
return 0;
}
int dfs2(int now){
if(t[now].isopt == 1){
if(t[now].opt == 1) {
int tmp = (dfs2(t[now].lc) + dfs2(t[now].rc)) % mod;
while(tmp < 0)
tmp += mod;
return tmp;
}
if(t[now].opt == 2) {
int tmp = (dfs2(t[now].rc) - dfs2(t[now].lc)) % mod;
while(tmp < 0)
tmp += mod;
return tmp;
}
if(t[now].opt == 3) {
int tmp = dfs2(t[now].lc) * dfs2(t[now].rc);
while(tmp < 0)
tmp += mod;
return tmp % mod;
}
}
else if(t[now].isnum == 1){
return t[now].val;
}
else{
return variable[t[now].id] % mod;
}
return 0;
}
signed main(){
cin >> n >> m;
char ch = getchar();
string tmp;
getline(cin, tmp);
int p = 0;
int i = 0;
while(p < tmp.length()){
string s;
int q = p;
while(tmp[q] != ' ' && q < tmp.length()){
s.push_back(tmp[q]);
q++;
}
p = q + 1;
i++;
if(s[0] == '+' || (s[0] == '-' && s.length() == 1) || s[0] == '*'){
t[i].isopt = 1;
if(s[0] == '+') t[i].opt = 1;
if(s[0] == '-') t[i].opt = 2;
if(s[0] == '*') t[i].opt = 3;
t[i].lc = stac.top(); stac.pop();
t[i].rc = stac.top(); stac.pop();
stac.push(i);
}
else if(isdigit(s[0])){
t[i].isnum = 1;
int x = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
x = x * 10 + (s[i] - '0');
t[i].val = x;
stac.push(i);
}
else if(s[0] == '-'){
int x = 0;
t[i].isnum = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++)
x = x * 10 + (s[i] - '0');
t[i].val = x * (-1);
stac.push(i);
}
else{
t[i].isx = 1;
int num = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++)
num = num * 10 + (s[i] - '0');
t[i].id = num;
stac.push(i);
}
pp[i] = t[i]; // 存档
}
p = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
cin >> did;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cin >> variable[j], t[i] = pp[i];
id = p;
dfs(p, did);
cout << dfs2(p + 1) % mod << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D、阴阳龙

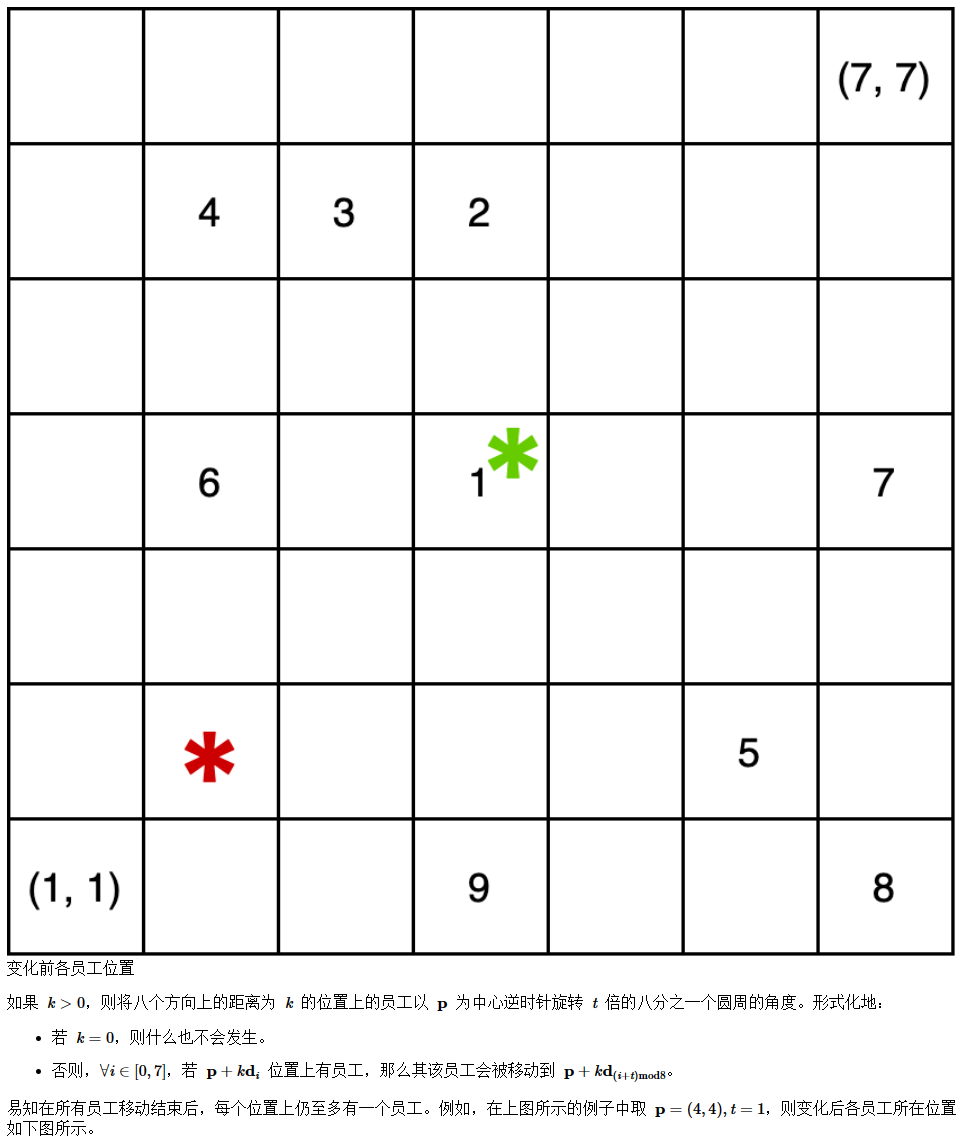
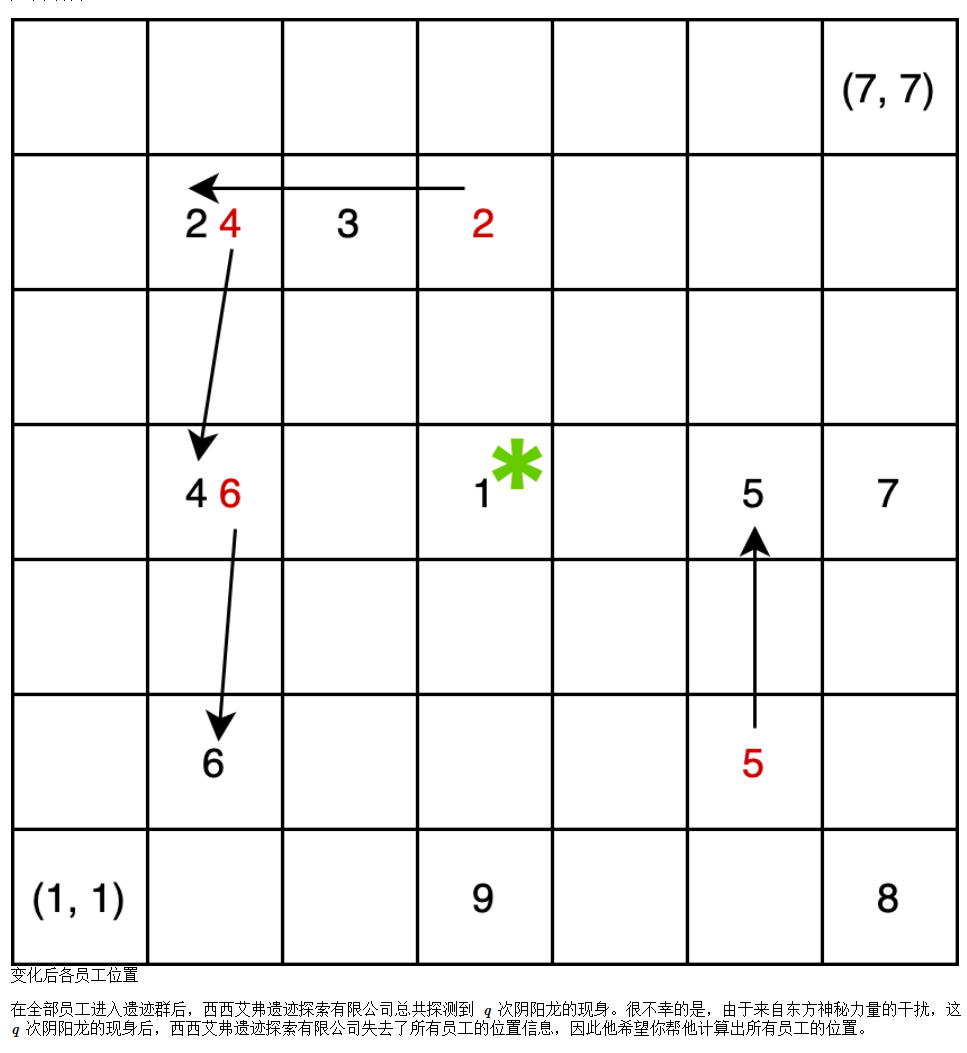

样例
3 3 9 1
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
2 2 1
20
题解
思路其实并不难,就是用\(map + set\) 把行、列、左对角线以及右对角线全部存起来,然后使用\(lower\)_\(bound\)进行查找就行。但是实现细节比较多,很容易写挂。一定要想好再开始写。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 100010
#define ll long long
#define int long long
template <class T>
inline void read(T& a){
T x = 0, s = 1;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)){ if(c == '-') s = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(isdigit(c)){ x = x * 10 + (c ^ '0'); c = getchar(); }
a = x * s;
return ;
}
int n, m, p, q;
int nn;
struct Point{
int x, y;
int id;
} P[N];
map <int, set<pair<int, int> > > s1, s2, s3, s4; // 水平, 竖直,对角1,对角2
vector <Point> G;
vector <Point> chosen; // 选中的点
int x, y, t;
int get_d(int sx, int sy){
if(sx > x && sy > y) return 1;
if(sx == x && sy > y) return 2;
if(sx < x && sy > y) return 3;
if(sx < x && sy == y) return 4;
if(sx < x && sy < y) return 5;
if(sx == x && sy < y) return 6;
if(sx > x && sy < y) return 7;
if(sx > x && sy == y) return 0;
}
void find_point(set <pair<int, int>> &s, int d){
if(d == 1){
auto it = s.lower_bound(make_pair(y, 1e9));
if(it != s.end()) G.push_back(P[(*it).second]);
if(it != s.begin()){
it--;
if((*it).first == y){
if(it != s.begin()){
it--;
G.push_back(P[(*it).second]);
}
}
else G.push_back(P[(*it).second]);
}
}
else{
auto it = s.lower_bound(make_pair(x, 1e9));
if(it != s.end()) G.push_back(P[(*it).second]);
if(it != s.begin()){
it--;
if((*it).first == x){
if(it != s.begin()){
it--;
G.push_back(P[(*it).second]);
}
}
else G.push_back(P[(*it).second]);
}
}
return ;
}
void del(Point t){
int x = t.x, y = t.y, id = t.id;
s1[x].erase(make_pair(y, id));
s2[y].erase(make_pair(x, id));
s3[x + y].erase(make_pair(x, id));
s4[nn - x + y].erase(make_pair(x, id));
return ;
}
signed main(){
//freopen("hh.txt", "r", stdin);
read(n), read(m), read(p), read(q);
nn = max(n, m);
for(int i = 1; i <= p; i++){
int xx, yy;
read(xx), read(yy); // 转化
P[i].x = xx, P[i].y = yy, P[i].id = i;
s1[xx].insert(make_pair(yy, i));
s2[yy].insert(make_pair(xx, i));
s3[xx + yy].insert(make_pair(xx, i));
s4[nn - xx + yy].insert(make_pair(xx, i));
}
while(q--){
G.clear();
read(x), read(y), read(t);
find_point(s1[x], 1);
find_point(s2[y], 2);
find_point(s3[x + y], 3);
find_point(s4[nn - x + y], 4);
sort(G.begin(), G.end(), [](Point a, Point b) -> bool {
return max(abs(a.x - x), abs(a.y - y)) < max(abs(b.x - x), abs(b.y - y));
}) ;
int mind1 = min(x - 1, min(y - 1, min(n - x, m - y)));
int mind2 = max(abs(x - G[0].x), abs(y - G[0].y));
if(mind1 < mind2) continue;
chosen.clear();
for(auto it : G){
int d = max(abs(x - it.x), abs(y - it.y));
if(d == mind2){
del(it);
chosen.push_back(it);
}
}
for(auto it : chosen){
int d = get_d(it.x, it.y);
int tod = (d + t) % 8;
int nx, ny;
if(tod == 1) nx = x + mind2, ny = y + mind2;
if(tod == 2) nx = x, ny = y + mind2;
if(tod == 3) nx = x - mind2, ny = y + mind2;
if(tod == 4) nx = x - mind2, ny = y;
if(tod == 5) nx = x - mind2, ny = y - mind2;
if(tod == 6) nx = x, ny = y - mind2;
if(tod == 7) nx = x + mind2, ny = y - mind2;
if(tod == 0) nx = x + mind2, ny = y;
P[it.id].x = nx, P[it.id].y = ny;
s1[nx].insert(make_pair(ny, it.id));
s2[ny].insert(make_pair(nx, it.id));
s3[nx + ny].insert(make_pair(nx, it.id));
s4[nn - nx + ny].insert(make_pair(nx, it.id));
}
}
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= p; i++){
ans ^= ((1ll) * i * P[i].x + P[i].y);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}

