C++的SGI版本的STL二级空间配置器实现(基于内存池的实现方式)
C++STL中的空间配置器只有一种,是同过底层的malloc和free实现的,空间配置器中有四种方法:

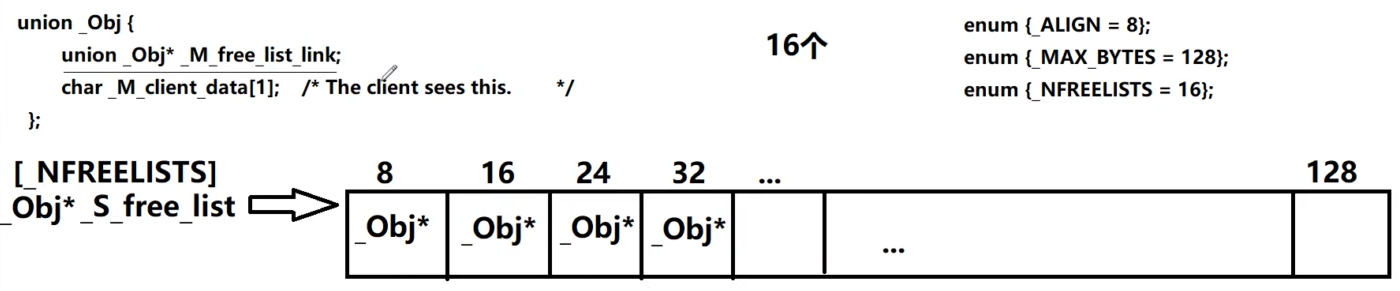
SGI STL中有两种空间配置器,一级allocator是与stl一致的malloc和free的方式,二级allocator是通过内存池的方式实现的。
SGI STL中的vector容器的模板中用到了空间配置器,默认用的是二级allocator。该容器底层存储对象的构造和析构是通过全局的函数模板construct和destroy实现的。这里我们着重研究allocator中的allocate和deallocate方法。
allocate:
// breaks if we make these template class members:
enum {_ALIGN = 8};
enum {_MAX_BYTES = 128};
enum {_NFREELISTS = 16}; // _MAX_BYTES/_ALIGN
/* __n must be > 0 */
//分配大小为__n的内存
static void* allocate(size_t __n)
{
void* __ret = 0;
if (__n > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES) {//如果需要的内存块大小超过最大内存,则按照标准库的方式分配内存
__ret = malloc_alloc::allocate(__n);//调用一级allocator
}
else {
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list//是一个double*的类型,指向数组的位置,解引用之后是数组中元素的值
= _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n);//根据_S_freelist_index(__n)定位数组中chunk块的位置
//_S_free_list就是上图中的数组
// Acquire the lock here with a constructor call.
// This ensures that it is released in exit or during stack
// unwinding.
# ifndef _NOTHREADS
/*REFERENCED*/
_Lock __lock_instance;//上锁
# endif
_Obj* __RESTRICT __result = *__my_free_list;//result是数组中的__Obj*
if (__result == 0)//如果数组中的元素未初始化
__ret = _S_refill(_S_round_up(__n));//构建链表,返回链表的地址
else {//已经初始化
*__my_free_list = __result -> _M_free_list_link;//指向下一个节点
__ret = __result;//返回下一个节点的地址
}
}
return __ret;
};
指针的加法操作注意事项:
指针类型占用的内存多大,其指针加一就会偏移多少字节。举个例子:char类型只占1个字节,那么char* +1就只偏移一个字节,指向下一个内存地址;int类型占4个字节,int* +1就会偏移4个字节,指向4个字节后的内存地址。
_S_refill函数:
/* Returns an object of size __n, and optionally adds to size __n free list.*/
/* We assume that __n is properly aligned. */
/* We hold the allocation lock. */
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
void*
__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_refill(size_t __n)
{
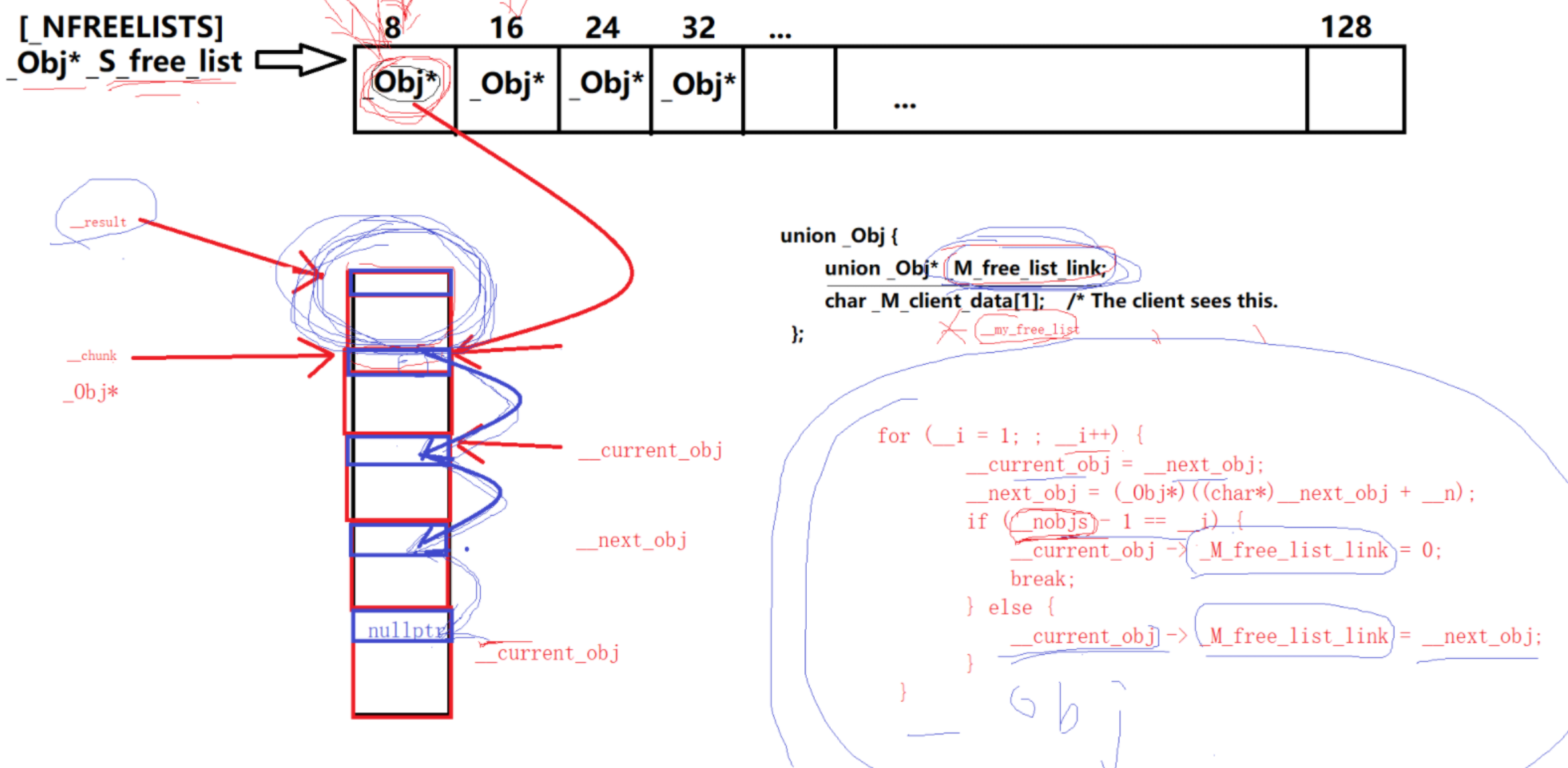
int __nobjs = 20;
char* __chunk = _S_chunk_alloc(__n, __nobjs);//分配起始位置的地址
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list;
_Obj* __result;
_Obj* __current_obj;
_Obj* __next_obj;
int __i;
if (1 == __nobjs) return(__chunk);//如果数量为1,直接返回当前块
__my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n);//指向数组块的位置,这里先以 __n=8 为例
/* Build free list in chunk */
__result = (_Obj*)__chunk;//result加一次可以跳到下个节点
*__my_free_list = __next_obj = (_Obj*)(__chunk + __n);//使数组中的第一个元素指向第二个chunk
for (__i = 1; ; __i++) {
__current_obj = __next_obj;
__next_obj = (_Obj*)((char*)__next_obj + __n);//指向下一个节点
if (__nobjs - 1 == __i) {//到链表最后节点
__current_obj -> _M_free_list_link = 0;//使next节点等于nullptr表示最后一个节点
break;
} else {
__current_obj -> _M_free_list_link = __next_obj;
}
}
return(__result);//返回链表首节点地址
}
_S_chunk_alloc(size_t __size, int& __nobjs):
/* We allocate memory in large chunks in order to avoid fragmenting */
/* the malloc heap too much. */
/* We assume that size is properly aligned. */
/* We hold the allocation lock. */
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
char*
__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_chunk_alloc(size_t __size,
int& __nobjs)
{//还是以nobjs为20,size为8来假设
char* __result;
size_t __total_bytes = __size * __nobjs;//160
size_t __bytes_left = _S_end_free - _S_start_free;//0 两者初始化都为0 //第二次_1 __bytes_left=320
if (__bytes_left >= __total_bytes) {//第二次_2 返回开辟的内存
__result = _S_start_free;
_S_start_free += __total_bytes;
return(__result);
} else if (__bytes_left >= __size) {//如果想要申请其他大小的chunk块,可能会调用此方法在上一步申请的备用内存中查找有无可用的内存
__nobjs = (int)(__bytes_left/__size);
__total_bytes = __size * __nobjs;
__result = _S_start_free;
_S_start_free += __total_bytes;
return(__result);
} else {//初始化_1首先进入该分支
size_t __bytes_to_get =
2 * __total_bytes + _S_round_up(_S_heap_size >> 4);//_S_heap_size初始为0,初始化__bytes_to_get=320
// Try to make use of the left-over piece.
if (__bytes_left > 0) {
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list =
_S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__bytes_left);
((_Obj*)_S_start_free) -> _M_free_list_link = *__my_free_list;
*__my_free_list = (_Obj*)_S_start_free;
}
_S_start_free = (char*)malloc(__bytes_to_get);//初始化_2跳到这一步
if (0 == _S_start_free) {//如果开辟内存失败
size_t __i;
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list;
_Obj* __p;
// Try to make do with what we have. That can't
// hurt. We do not try smaller requests, since that tends
// to result in disaster on multi-process machines.
for (__i = __size;
__i <= (size_t) _MAX_BYTES;
__i += (size_t) _ALIGN) {
__my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__i);
__p = *__my_free_list;
if (0 != __p) {
*__my_free_list = __p -> _M_free_list_link;
_S_start_free = (char*)__p;
_S_end_free = _S_start_free + __i;
return(_S_chunk_alloc(__size, __nobjs));
// Any leftover piece will eventually make it to the
// right free list.
}
}
_S_end_free = 0; // In case of exception.
_S_start_free = (char*)malloc_alloc::allocate(__bytes_to_get);
// This should either throw an
// exception or remedy the situation. Thus we assume it
// succeeded.
}
_S_heap_size += __bytes_to_get;//初始化_3 _S_heap_size=320
_S_end_free = _S_start_free + __bytes_to_get;//_S_end_free是 char*类型,开辟一块320字节的内存块
return(_S_chunk_alloc(__size, __nobjs));//初始化_4 递归调用自己
}
}
deallocate
/* __p may not be 0 */
static void deallocate(void* __p, size_t __n)
{
if (__n > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES)//如果大于_MAX_BYTES,就用标准库的方法来
malloc_alloc::deallocate(__p, __n);
else {
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list
= _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n);//取数组中的元素
_Obj* __q = (_Obj*)__p;
// acquire lock
# ifndef _NOTHREADS
/*REFERENCED*/
_Lock __lock_instance;
# endif /* _NOTHREADS */
__q -> _M_free_list_link = *__my_free_list;
*__my_free_list = __q;//回收原来数组Obj*指向的内存
// lock is released here
}
}






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!