如何用gcc/g++编译生成so链接库,以及how to use .so
说明:
文件目录:my
文件: foo.h num.cpp size.cpp name.cpp main.cpp
准备文件:
foo.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
#ifndef _MY_FOO_H#define _MY_FOO_H#define u_int unsigned int#include<malloc.h>class mysql{ public : char *file_name; u_int file_size; int num; public : void init_size(u_int size); u_int get_size(); char *get_name(); void init_name(char* name); void init_num(int n); int get_num(); void add(int n); void del(int n); ~mysql() { free(file_name); }}; |
num.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
#include"foo.h"#include<iostream>using namespace std;void mysql::init_num(int n){ this->num = n;}int mysql::get_num(){ return this->num;} |
size.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
#include"foo.h"void mysql::init_size(u_int size) { this->file_size = size;}u_int mysql::get_size(){ return this->file_size;} |
name.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#include"foo.h"#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#include<malloc.h>void mysql::init_name(char * name) { if( ( sizeof(name) + 1 ) > this->file_size) { printf("the length of name is too long\n"); return ; } this->file_name = (char *)calloc(1,sizeof(name)+1); strcpy(this->file_name, name);}char* mysql::get_name(){ return this->file_name;} |
main.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#include"foo.h"#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ mysql *my = new mysql(); my->init_num(4); int num = my->get_num(); cout << "num is " << num << endl; my->init_size(100); u_int size = my->get_size(); cout << "file_size is " << size << endl; my->init_name( (char*)("MYSQL") ); cout << my->get_name() << endl; return 0; } |
编译生成so文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
libnum.so$ g++ num.cpp -fPIC -shared -o libnum.solibsize.so$ g++ size.cpp -fPIC -shared -o libsize.solibname.so$ g++ name.cpp -fPIC -shared -o libname.so$ ls |
说明
-fPIC:表示编译为位置独立的代码,不用此选项的话编译后的代码是位置相关的所以动态载入时是通过代码拷贝的方式来满足不同进程的需要,而不能达到真正代码段共享的目的。
-L.:表示要连接的库在当前目录中
-lxxx:编译器查找动态连接库时有隐含的命名规则,即在给出的名字前面加上lib,后面加上.so来确定库的名称libxxx.so
生成可执行文件
$ g++ main.cpp -L. -lnum -lname -lsize -o main然后就有可执行文件,但是好像不给力,没法运行。因为没有修改,LD_LIBRARY_PATH,这个环境变量指示动态连接器可以装载动态库的路径。
加上 export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:. 然后执行ldd
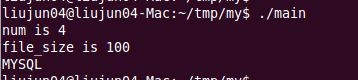
然后运行./main,终于出现结果了





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号