霍夫变换原理
---恢复内容开始---
注意事项:
1.由霍夫变换产生的线条的长度是无限的。
2.霍夫变换可很好的解决遮挡问题。(边缘检测无法还原物体完整轮廓)
一.原理
坐标变换
将笛卡尔坐标系下的直线方程转化为极坐标系下的直线方程。
直角坐标表达式(又称为斜截式):
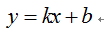
k---斜率;b---y轴截距
极坐标系下的表达式(又称为法线式):
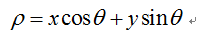
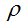 ---直线到原点的距离;
---直线到原点的距离; 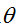 ---直线与x轴的夹角
---直线与x轴的夹角
因此笛卡尔坐标系下的一个点,转化到极坐标系下为一条直线;而笛卡尔坐标系下的一条正弦曲线,转换至极坐标系下为众多曲线的交点
因此把笛卡尔坐标系下直线的问题转化为求极坐标系下交点的问题。
二.程序
2.1 算法流程
1.将图像转化为灰度图,边缘检测,转化为二值化边缘图像
2.对图像进行霍夫变换
3.先使用峰值检测函数,找到大于阈值的霍夫变换单元
4.将上诉识别出的一组侯选峰,需确定与其相关的起始点和终止点。
5.绘图
2.1按照霍夫变换的原理,其计算过程大致如下:
import numpy as np import cv2 def hough_detectline(img): thetas=np.deg2rad(np.arange(0,180)) #角度变弧度 row,cols=img.shape diag_len=np.ceil(np.sqrt(row**2+cols**2)) #np.ceil朝正无穷方向取整 rhos=np.linspace(-(diag_len),diag_len,int(2*diag_len)) #np.linspace生成等差数列 #默认为50,第三个参数为元素个数,本程序中生成int(2*diag_len)个元素 cos_t=np.cos(thetas) sin_t=np.sin(thetas) num_theta=len(thetas) #投票 vote=np.zeros(int(2*diag_len),num_theta,dtype=np.uint64) y_inx,x_inx=np.nonzero(img) #返回img数组中不为0的元素的下标,数组可以为布尔值 for i in range(len(x_inx)): x=x_inx[i] y=y_inx[i] for j in range(num_theta): rho=round(x*cos_t[j]+y*sin_t[j])+diag_len #round为返回四舍五入值 if isinstance(rho,int): #如果rho是int类型,则 vote[rho,j]+=1 else: vote[int(rho),j]+=1 return vote,rhos,thetas image=np.zeros((500,500)) image[10:100,10:100]=np.eye(90) accumulator,rhos,thetas=hough_detectline(image) idx=np.argmax(accumulator) #返回最大值的索引,即得票最多 rho=rhos[int(idx/accumulator.shape[1])] theta=thetas[idx%accumulator.shape[1]] k=-np.cos(theta)/np.sin(theta) b=rho/np.sin(theta) x=np.float32(np.arange(1,150,2)) y=np.float32(k*x+b) cv2.imshow("original",image) cv2.waitKey(0) for i in range(len(x)-1): cv2.circle(image,x[i],y[i],5,(255,0,0),1) #画圆 cv2.imshow("hough",image) cv2.waitKey(0) print("rho={0:.2f},theta={1:.0f}".format(rho,np.rad2deg(theta)))
该段程序按照霍夫变换规则写,重在理解各种索引与元素之间的关系。(程序未跑成功,先记录下来,待深入理解后思考其存在的问题)
霍夫变换存在函数,该函数存在于skimage库中,tranform模块内,函数为hough_line(img),该函数返回三个值,霍夫变换累加器值、theta和distance,即夹角和距离。
2.2利用skimage库中,tranform模块内,函数为hough_line(img)寻找并绘制直线
import skimage.transform as st import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 构建测试图片 image = np.zeros((100, 100)) #背景图 idx = np.arange(25, 75) #25-74序列 image[idx[::-1], idx] = 255 # 线条\ image[idx, idx] = 255 # 线条/ # hough线变换 h, theta, d = st.hough_line(image) #生成一个一行三列的窗口(可显示三张图片). fig, (ax0, ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(8, 6)) plt.tight_layout() #显示原始图片 ax0.imshow(image, plt.cm.gray) ax0.set_title('Input image') ax0.set_axis_off() #显示hough变换所得数据 ax1.imshow(np.log(1 + h)) ax1.set_title('Hough transform') ax1.set_xlabel('Angles (degrees)') ax1.set_ylabel('Distance (pixels)') ax1.axis('image') #显示检测出的线条 ax2.imshow(image, 'gray') row1, col1 = image.shape for _, angle, dist in zip(*st.hough_line_peaks(h, theta, d)): y0 = (dist - 0 * np.cos(angle)) / np.sin(angle) y1 = (dist - col1 * np.cos(angle)) / np.sin(angle) ax2.plot((0, col1), (y0, y1), '-r') ax2.axis((0, col1, row1, 0)) ax2.set_title('Detected lines') ax2.set_axis_off() plt.show()
利用cv2库中函数cv2.HoughLines()函数检测直线
import cv2 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from numpy import * img=cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\Jimmy\Desktop\qi3.jpg") plt.subplot(121) plt.imshow(img) plt.title('input') gray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) edges=cv2.Canny(gray,50,100,apertureSize=3) lines=cv2.HoughLines(edges,1,np.pi/180,150,5) lines1=lines[:,0,:] #3维化为2维 for rho,theta in lines1[:]: a=np.cos(theta) b=np.sin(theta) x0=a*rho y0=b*rho x1=int(x0+1000*(-b)) y1=int(y0+1000*(a)) x2=int(x0-1000*(-b)) y2=int(y0-1000*(a)) cv2.line(img,(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(0,255,0),5) plt.subplot(122) plt.imshow(img) plt.title('output') plt.show()
该函数返回值为直线的rho和theta
利用优化霍夫变换函数cv2.HoughLinesP()做直线检测
import cv2 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from numpy import * img=cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\Jimmy\Desktop\qi3.jpg") plt.subplot(121) plt.imshow(img) plt.title('input') gray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) edges=cv2.Canny(gray,50,100,apertureSize=3) lines=cv2.HoughLinesP(edges,1,np.pi/180,150,minLineLength=60,maxLineGap=10) lines1=lines[:,0,:] #3维化为2维 for x1,y1,x2,y2 in lines1[:]: cv2.line(img,(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(0,255,0),5) plt.subplot(122) plt.imshow(img) plt.title('output') plt.show()
该函数直接返回直线的起始点坐标。
2.2 霍夫变换提取圆
采用cv2.HoughCircles()函数
输入参数为(image,method,dp,min_dist,param1,param2,minRadius,maxRadius)
image为需要进行霍夫变换的图像
method:为检测方法,一般用CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT,即霍夫梯度法
dp:为检测内侧圆心的累加器图像的分辨率与输入图像之比的倒数。若为1,即累加器和输入图像具有相同的分辨率;若为2,则累加器有输入图像一半的宽度和高度。
min_dist:两个圆之间圆心的最小距离。防止重复画一个圆
param1:默认值100,为传递给canny边缘检测算子的高阈值,低阈值为其一半
param2:默认值100,表示在检测阶段圆心的累加器阈值,它越小,表示可以检测到更多不存在的圆,它越大,表示能检测出来的圆越完美。
minRadius:默认值0,圆半径的最小值
maxRadius:默认值0,圆半径的最大值。
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import cv2 img=cv2.imread(r"F:\pycharm\test\iterable\filr\water1.jpg") cv2.imshow('image',img) #灰度化 gray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) cv2.imshow('gray',gray) print(gray.shape) circles=cv2.HoughCircles(gray,cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1,100,param1=100,param2=31,minRadius=10,maxRadius=100) #查看返回值类型 print(circles) circles=np.uint16(np.around(circles)) for i in circles[0,:]: cv2.circle(img,(i[0],i[1]),i[2],(0,0,255),2) # cv2.circle(gray, (i[0], i[1], i[2]), (0, 0, 255), 2) cv2.imshow('detected circle',gray) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行上述代码,可在图中绘出圆。
2.3在视频中检测圆
import cv2 from numpy import * cap=cv2.VideoCapture(r'F:\pycharm\test\iterable\filr\FLIR0563.mp4') # fps=cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) fps=10 size = (int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))) fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('M', 'P', '4', '2') outVideo = cv2.VideoWriter('F:\\pycharm\\test\\iterable\\filr\\out_new2.avi', fourcc, fps, size) while(1): ret, img = cap.read() gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 灰度图像 circles1=cv2.HoughCircles(gray,cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1,100,param1=100,param2=31,minRadius=10,maxRadius=100) try: circles = circles1[0, :, :] except TypeError: continue # print("NULL") else: circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles)) # 四舍五入 for i in circles[:]: cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), i[2], (0, 255, 0), 2) # 画圆 # cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), 2, color=[0, 255, 0], thickness=2) # 画圆心 outVideo.write(img) # cv2.imshow('cap', img) # if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xff == ord('q'): # break # cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3卡尔坐标系下圆的方程:
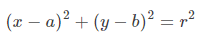
由于参数增加,计算复杂度增加
计算步骤:
1.创建累加器空间(提取圆需要3维累加器),初始化累加器
2.对图像中的每个边缘点检测,将可能是同一个圆的值累加
3.搜索局部最大值,检测圆


