RNN和LSTM
一、RNN
全称为Recurrent Neural Network,意为循环神经网络,用于处理序列数据。
序列数据是指在不同时间点上收集到的数据,反映了某一事物、现象等随时间的变化状态或程度。即数据之间有联系。
RNN的特点:1,,层间神经元也有连接(主要为隐层);2,共享参数
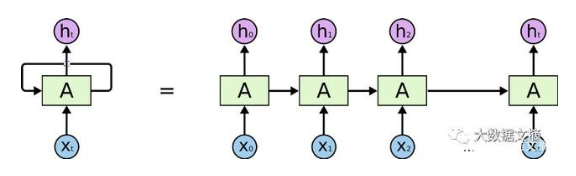
其结构如上图所示,数据为顺序处理,在处理长序列数据时,极易导致梯度消失问题。
二、LSTM
LSTM为长短期记忆,是一种变种的RNN,在RNN的基础上引入了细胞状态,根据细胞状态可决定哪些状态应该保留下来,哪些状态应该被遗忘。
LSTM可一定程度上解决梯度消失问题。
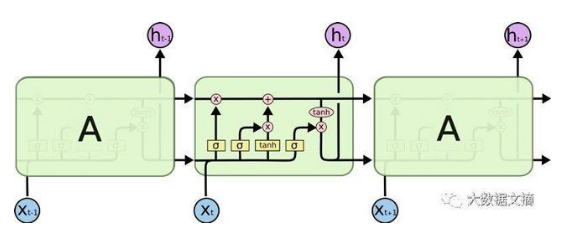
由上图可知,在RNN的基础上,增加了一路输入和输出,增加的这一路就是细胞状态。
由上一时刻的输出和当前时刻的输入,经过sigmod函数之后,趋近于0被遗忘的多,趋近于1被遗忘的少。
由上一时刻的输出和当前时刻的输入,经过sigmod函数之后,决定哪些内容应该被记住,被记住的内容并不是上一时刻的输出和当前时刻的输入,而是需要经过tanh函数。
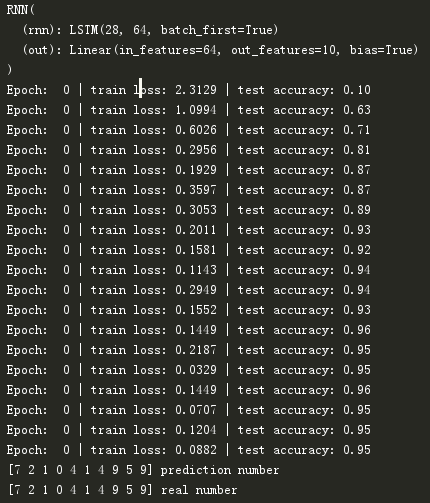
程序:应用LSTM训练mnist数据集
import os import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.utils.data as Data from torch.autograd import Variable import torchvision.datasets as dsets import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import torchvision.transforms as transforms # torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible # Hyper Parameters EPOCH = 1 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch BATCH_SIZE = 64 LR = 0.01 # learning rate DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False #已下载好数据集,就设置为False,否则为TRUE TIME_STEP=28 #可理解为输入图像维度 INPUT_SIZE=28 # Mnist digits dataset if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'): # not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True train_data = dsets.MNIST( root='./mnist/', train=True, # this is training data transform=transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to # torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0] download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST, ) # plot one example # print(train_data.train_data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28) # print(train_data.train_labels.size()) # (60000) # plt.imshow(train_data.train_data[0].numpy(), cmap='gray') # plt.title('%i' % train_data.train_labels[0]) # plt.show() # Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28) train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True) # pick 2000 samples to speed up testing test_data = dsets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False,transform=transforms.ToTensor()) test_x = test_data.test_data.type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000]/255. # shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1) test_y = test_data.test_labels.numpy()[:2000] class RNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(RNN, self).__init__() self.rnn = nn.LSTM( input_size=INPUT_SIZE, hidden_size=64, num_layers=1, batch_first=True ) self.out=nn.Linear(64,10) def forward(self,x): r_out,(h_n,h_c)=self.rnn(x,None) out=self.out(r_out[:,-1,:]) #数据格式为[batch,time_step,input],因此输出参考的是最后时刻的数据 return out rnn=RNN() print(rnn) # net architecture optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted for epoch in range(EPOCH): for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader): # gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader b_x=Variable(x.view(-1,28,28)) b_y=Variable(y) output = rnn(b_x) # cnn output loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients optimizer.step() # apply gradients if step % 50 == 0: test_output = rnn(test_x) pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy().squeeze() accuracy =float((pred_y==test_y).astype(int).sum())/float(test_y.size) print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss: %.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), '| test accuracy: %.2f' % accuracy) # print 10 predictions from test data test_output = rnn(test_x[:10].view(-1,28,28)) pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy().squeeze() print(pred_y, 'prediction number') print(test_y[:10], 'real number')
运行结果为: