20202315 实验七《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验报告
课程:《程序设计与数据结构》
班级: 2023
姓名: 王梦欣
学号:20202315
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2021年11月4日
必修/选修: 必修
## 1.实验内容
-
定义一个Searching和Sorting类,并在类中实现linearSearch,SelectionSort方法,最后完成测试。
要求不少于10个测试用例,提交测试用例设计情况(正常,异常,边界,正序,逆序),用例数据中要包含自己学号的后四位
提交运行结果图。 -
重构你的代码
把Sorting.java Searching.java放入 cn.edu.besti.cs2023.(姓名首字母+四位学号) 包中(例如:cn.edu.besti.cs1823.G2301)
把测试代码放test包中
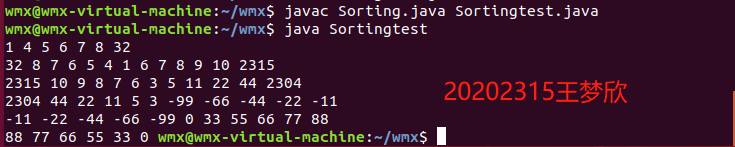
重新编译,运行代码,提交编译,运行的截图(IDEA,命令行两种) -
参考http://www.cnblogs.com/maybe2030/p/4715035.html ,学习各种查找算法并在Searching中补充查找算法并测试
提交运行结果截图 -
实现排序方法等(至少3个)
测试实现的算法(正常,异常,边界)
提交运行结果截图(如果编写多个排序算法,即使其中三个排序程序有瑕疵,也可以酌情得满分) -
编写Android程序对实现各种查找与排序算法进行测试
提交运行结果截图
推送代码到码云(选做,额外加分)
## 2.实验过程与结果
1.定义一个Searching和Sorting类,并在类中实现linearSearch,SelectionSort方法,最后完成测试。
码云链接:https://gitee.com/besti2023javads/wang-mengxin-20202315/blob/master/Searching.java
https://gitee.com/besti2023javads/wang-mengxin-20202315/blob/master/SearchingTest.java
https://gitee.com/besti2023javads/wang-mengxin-20202315/blob/master/Sorting.java
https://gitee.com/besti2023javads/wang-mengxin-20202315/blob/master/SortingTest.java
代码:
//在Searching类中实现linearSearch方法,完成了包括正常情况、异常情况及边界情况在内的测试
//在Sorting类中实现SelectionSort方法,完成了正序选择排序及逆序选择排序
import java.util.Scanner; public class Searching { public void LinearSearch(String a[]){ //实现查找功能 System.out.println("输入你想查找到元素:"); Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); String target=sca.nextLine(); int result =-1; for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ if(a[i].equals(target)){ result=i+1; break; } } //输出查找结果 if(result==-1) System.out.println("您所找的元素"+target+"未找到!"); else System.out.println("您所找的元素"+target+"在第"+result+"位"); } }
public class SearchingTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String a1[]={"1","2","3","4","5","2315"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a1); String a2[]={"5","6","7","8","9","2315"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a2); String a3[]={"11","22","33","44","55","2315"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a3); String a4[]={"-11","-22","33","44","-55","2315"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a4); String a5[]={"wmx","hr","2023","2304","2315"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a5); String a6[]={"wkx","0601","wmx","0912","hr","0403"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a6); String a7[]={"00","99","88","77","66","2315"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a7); String a8[]={"12","23","34","45","56","67"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a8); String a9[]={"5","4","3","2","1","0"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a9); String a10[]={"-66","-88","33","44","-55","2315"}; new Searching().LinearSearch(a10); }
}
public class Sorting { //正序 public void SelectionSort1(int[] a) { int i, j; //选择排序 for (i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { int temp = i; for (j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) { if (a[temp] > a[j]) { temp = j; } } if (temp != i) { swap(a, temp, i); } } for (int t = 0; t < a.length; t++) { System.out.print(a[t] + " "); } System.out.println(""); } //逆序 public void SelectionSort2(int[] a) { int i, j; //选择排序 for (i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { int temp = i; for (j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) { if (a[temp] < a[j]) { temp = j; } } if (temp != i) { swap(a, temp, i); } } for (int t = 0; t < a.length; t++) { System.out.print(a[t] + " "); } System.out.println(""); } public static void swap(int m[], int a, int b){ int temp; //交换 temp=m[a]; m[a]=m[b]; m[b]=temp; } }
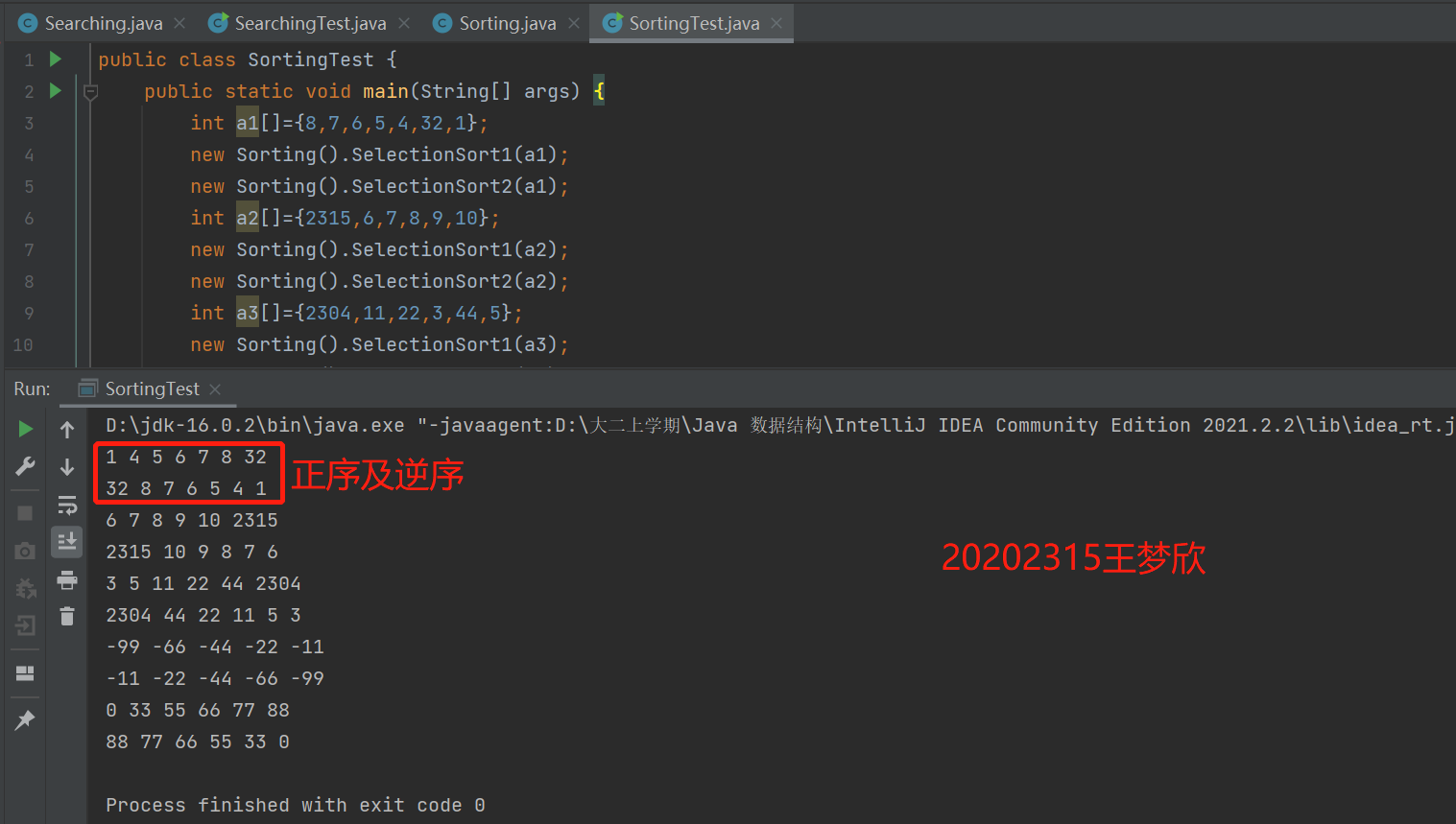
public class SortingTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int a1[]={8,7,6,5,4,32,1}; new Sorting().SelectionSort1(a1); new Sorting().SelectionSort2(a1); int a2[]={2315,6,7,8,9,10}; new Sorting().SelectionSort1(a2); new Sorting().SelectionSort2(a2); int a3[]={2304,11,22,3,44,5}; new Sorting().SelectionSort1(a3); new Sorting().SelectionSort2(a3); int a4[]={-11,-22,-66,-44,-99}; new Sorting().SelectionSort1(a4); new Sorting().SelectionSort2(a4); int a5[]={88,66,55,33,00,77}; new Sorting().SelectionSort1(a5); new Sorting().SelectionSort2(a5); } }
运行结果截图:

2.重构你的代码
把Sorting.java Searching.java放入 cn.edu.besti.cs2023.(姓名首字母+四位学号) 包中(例如:cn.edu.besti.cs1823.G2301)
把测试代码放test包中
重新编译,运行代码,提交编译,运行的截图(IDEA,命令行两种)
重构过程将Searching.java优化,在做出选择之前将原数组输出


3.参考http://www.cnblogs.com/maybe2030/p/4715035.html ,学习各种查找算法并在Searching中补充查找算法并测试
提交运行结果截图
代码:
package cn.edu.besti.cs2023.W2315; import java.util.Scanner; public class Searching { //顺序查找 public void LinearSearch(String a[]){ System.out.println("input what you want to find"); Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); String target=sca.nextLine(); int result =-1; for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ if(a[i].equals(target)){ result=i+1; break; } } if(result==-1) System.out.println("what you find "+target+" don't exist"); else System.out.println("what you find "+target+" located at "+result); } //二分查找(折半查找)版本一 public int BinarySearch1(int[] b, int value, int n) { int low,high,mid; low=0; high=n-1; while(low<=high){ mid = (low+high)/2; if(b[mid]==value) return mid; if(b[mid]>value) high=mid-1; if(b[mid]<value) low=mid+1; } return -1; } //二分查找,递归版本 public int BinarySearch2(int [] b, int value, int low, int high){ if (low > high) { return -1; } int mid =low+(high-low)/2; if(b[mid]>value) return BinarySearch2(b,value,low,mid-1); else if(b[mid]<value) return BinarySearch2(b,value,mid+1,high); else return mid; } //插值查找 public int InsertionSearch(int a[],int value,int low,int high){ if(low>=high||a[low]>value||a[high]<value) return -1; int mid = low+(value-a[low])/(a[high]-a[low])*(high-low); if(a[mid]>value) return InsertionSearch(a,value,low,mid-1); else if(a[mid]<value) return InsertionSearch(a,value,mid+1,high); else return mid; } //斐波那契查找(构造一个斐波那契数组) int max_size=20;//斐波那契数组的长度 public void Fibonacci(int []F){ F[0]=0; F[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<max_size;++i){ F[i]=F[i-1]+F[i-2]; } } //定义斐波那契查找法 public int FibonacciSearch(int []a,int n,int key){ int low=0; int high=n-1; int []F=new int[max_size]; Fibonacci(F); //构造一个斐波那契数组F int k=0; while (n>F[k]-1) //计算n位于斐波那契数列的位置 ++k; int []temp; //将数组a扩展到F[k]-1的长度 temp=new int[F[k]-1]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ temp[i]=a[i]; //将C++语言中的memcpy转变为Java语言 } for(int i=n;i<F[k]-1;++i) temp[i]=a[n-1]; while(low<=high){ int mid=low+F[k-1]-1; if(key<temp[mid]){ high=mid-1; k-=1; } else if(key>temp[mid]){ low=mid+1; k-=2; } else{ if(mid<n) return mid; else return n-1; } } return -1; } }
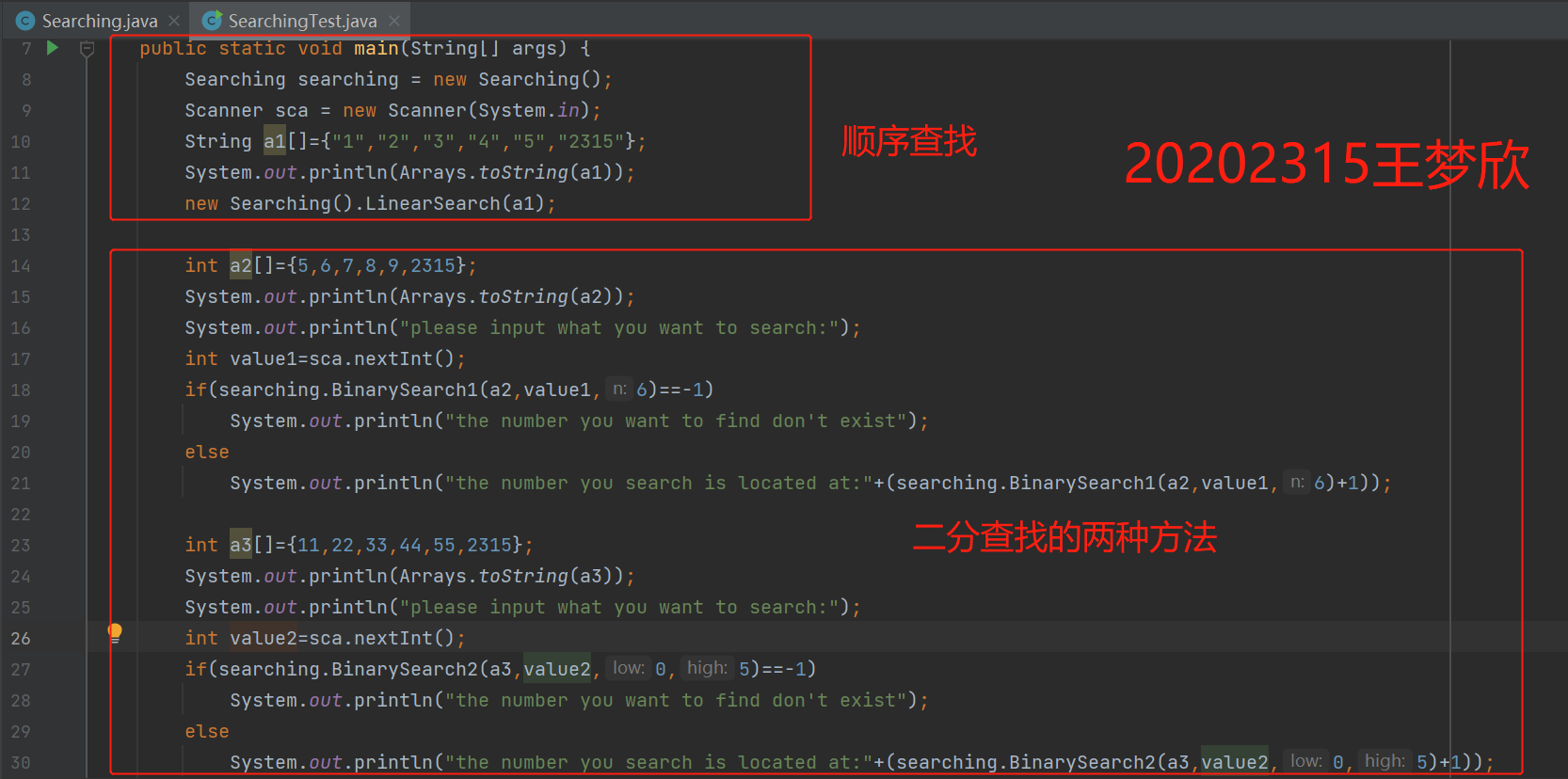
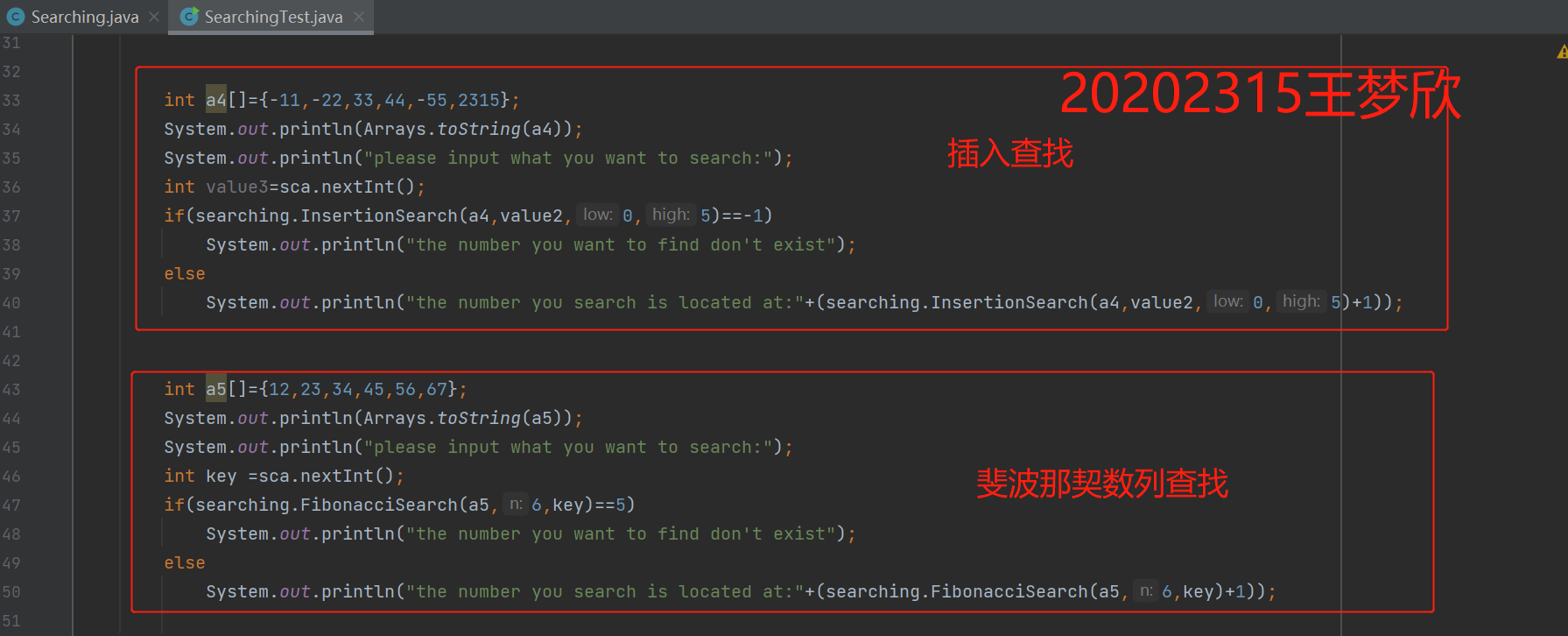
package cn.edu.besti.cs2023.W2315; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; public class SearchingTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Searching searching = new Searching(); Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); String a1[]={"1","2","3","4","5","2315"}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a1)); new Searching().LinearSearch(a1); int a2[]={5,6,7,8,9,2315}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a2)); System.out.println("please input what you want to search:"); int value1=sca.nextInt(); if(searching.BinarySearch1(a2,value1,6)==-1) System.out.println("the number you want to find don't exist"); else System.out.println("the number you search is located at:"+(searching.BinarySearch1(a2,value1,6)+1)); int a3[]={11,22,33,44,55,2315}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a3)); System.out.println("please input what you want to search:"); int value2=sca.nextInt(); if(searching.BinarySearch2(a3,value2,0,5)==-1) System.out.println("the number you want to find don't exist"); else System.out.println("the number you search is located at:"+(searching.BinarySearch2(a3,value2,0,5)+1)); int a4[]={-11,-22,33,44,-55,2315}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a4)); System.out.println("please input what you want to search:"); int value3=sca.nextInt(); if(searching.InsertionSearch(a4,value2,0,5)==-1) System.out.println("the number you want to find don't exist"); else System.out.println("the number you search is located at:"+(searching.InsertionSearch(a4,value2,0,5)+1)); int a5[]={12,23,34,45,56,67}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a5)); System.out.println("please input what you want to search:"); int key =sca.nextInt(); if(searching.FibonacciSearch(a5,6,key)==5) System.out.println("the number you want to find don't exist"); else System.out.println("the number you search is located at:"+(searching.FibonacciSearch(a5,6,key)+1)); } }
运行结果截图:

4.实现排序方法等(至少3个)
测试实现的算法(正常,异常,边界),提交运行结果截图
这里我实现了选择排序、冒泡排序、插入排序及希尔排序,并实现了选择排序的正序及逆序。
代码:
package cn.edu.besti.cs2023.W2315; import java.util.Arrays; public class Sorting { //选择排序1(正序) public void SelectionSort1(int[] a) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { int temp = i; for (j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) { if (a[temp] > a[j]) { temp = j; } } if (temp != i) { swap(a, temp, i); } } System.out.print("Selection Sort1:"); for (int t = 0; t < a.length; t++) { System.out.print(a[t] + " "); } System.out.println(""); } //选择排序2(逆序) public void SelectionSort2(int[] a) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { int temp = i; for (j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) { if (a[temp] < a[j]) { temp = j; } } if (temp != i) { swap(a, temp, i); } } System.out.print("Selection Sort2:"); for (int t = 0; t < a.length; t++) { System.out.print(a[t] + " "); } System.out.println(""); } public static void swap(int m[], int a, int b){ int temp; temp=m[a]; m[a]=m[b]; m[b]=temp; } //冒泡排序 public void BubbleSort(int a[]){ for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ int min = a[i]; int index = i; //默认第一个是最小的并记录最小的下标 for(int j=i+1;j<a.length;j++){ if(min>a[j]){ min=a[j]; index=j; } } //值交换 int temp=a[i]; a[i]=min; a[index]=temp; } System.out.println("Bubble Sort:"+Arrays.toString(a)); } //插入排序 public void InsertSort(int a[]){ for(int i=1;i<a.length;i++){ //外层循环,从第二个开始比较 for(int j=i;j>0;j--){ //内层循环 if(a[j]<a[j-1]){ int temp= a[j-1]; a[j-1]=a[j]; a[j]=temp; }else{ break; } } } System.out.println("Insert Sort:"+Arrays.toString(a)); } //希尔排序(插入排序变种版) public void ShellSort(int a[]){ for(int i=a.length/2;i>0;i/=2){ //i层循环控制步长 for(int j=i;j<a.length;j++){ //j控制无序端的起始位置 for(int k=j;k>0 && k-i>=0;k-=i){ if(a[k]<a[k-i]){ int temp = a[k-i]; a[k-i]=a[k]; a[k]=temp; }else{ break; } } } } System.out.println("Shell Sort:"+Arrays.toString(a)); } }
package cn.edu.besti.cs2023.W2315; public class SortingTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int a1[]={8,7,6,5,4,32,1}; new Sorting().SelectionSort1(a1); new Sorting().SelectionSort2(a1); int a2[]={2315,6,7,8,9,10}; new Sorting().SelectionSort1(a2); new Sorting().SelectionSort2(a2); int a3[]={2304,11,22,3,44,5}; new Sorting().BubbleSort(a3); int a4[]={-11,-22,-66,-44,-99}; new Sorting().InsertSort(a4); int a5[]={88,66,55,33,00,77}; new Sorting().ShellSort(a5); } }
运行结果截图:

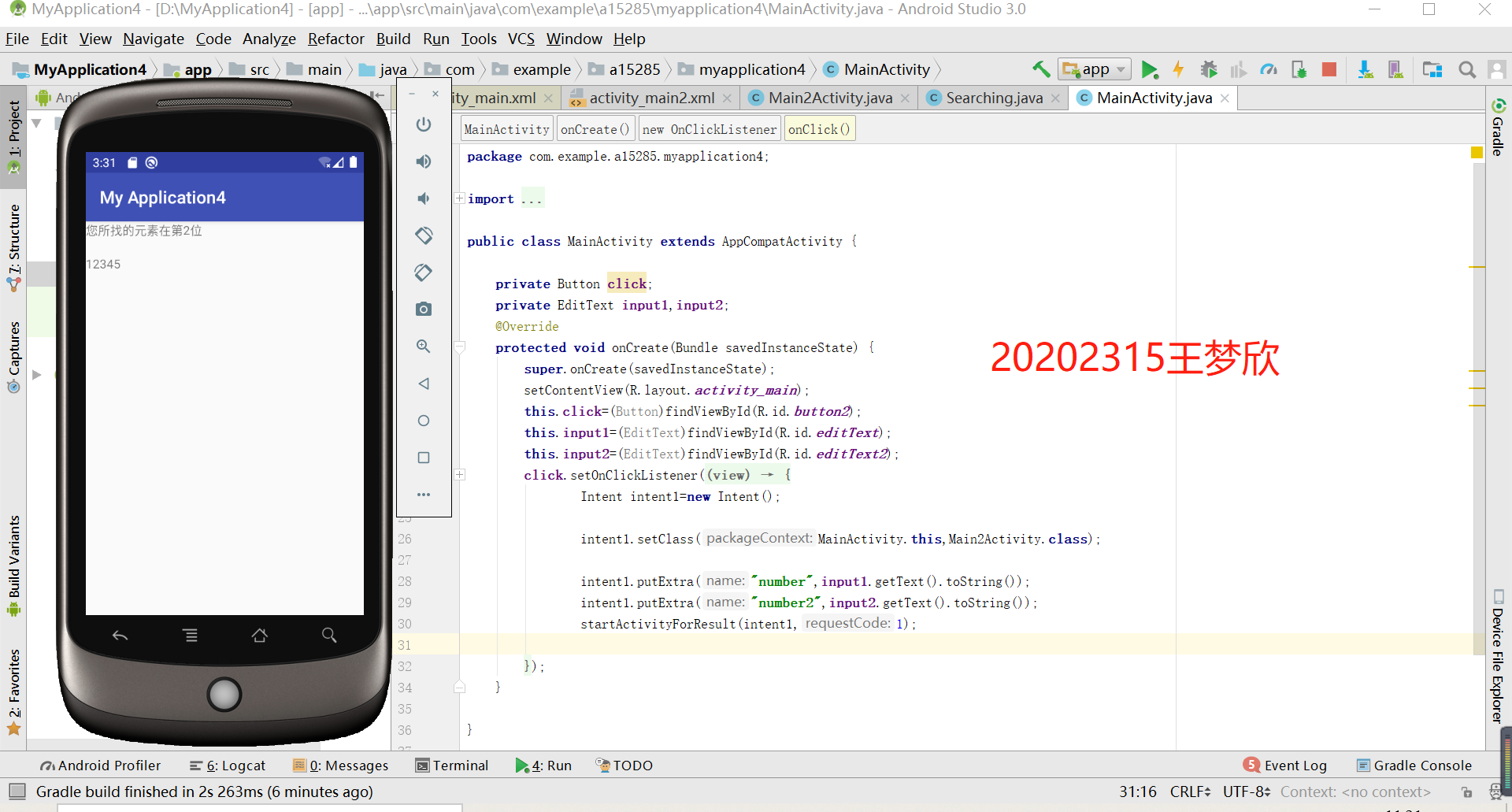
5.编写Android程序对实现各种查找与排序算法进行测试
提交运行结果截图
推送代码到码云(选做,额外加分)
码云链接:https://gitee.com/besti2023javads/wang-mengxin-20202315/blob/master/MainActivity.java
https://gitee.com/besti2023javads/wang-mengxin-20202315/blob/master/Main2Activity.java

## 3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:定义方法的过程中始终出现public int 与public void报错的问题。
- 问题1解决方案:参考了其他人的代码,发现针对于if语句,int定义的方法必须有返回值,所以必须有else,不能只是用if及else if
- 问题2:插入查找及二分法查找中的递归查找,一开始运行异常情况一直报错
- 问题2解决方案:由于使用if及else if在方法内部组成了循环,所以应该在一开始将异常情况加以表示,方便循环跳出,也方便区分返回值。
## 其他(感悟、思考等)
C++跟Java语言真的很像很像,除了那些函数库,类之外的不同,在语句上差别很小,实验中第三个给的网址上程序全部都是C++语言编写的,稍加修改就可以敲到Java里面。调用其他类的方法之前切记将该类初始化。




