线程池(ThreadPool)
线程池(ThreadPool)
一、简介
前面介绍了平时用到的大多数的多线程的例子,但在实际开发中使用的线程往往是大量的和更为复杂的,这时,每次都创建线程、启动线程。从性能上来讲,这样做并不理想(因为每使用一个线程就要创建一个,需要占用系统开销);从操作上来讲,每次都要启动,比较麻烦。为此引入的线程池的概念。
好处:
1.减少在创建和销毁线程上所花的时间以及系统资源的开销
2.如不使用线程池,有可能造成系统创建大量线程而导致消耗完系统内存以及”过度切换”。
在什么情况下使用线程池?
1.单个任务处理的时间比较短
2.需要处理的任务的数量大
线程池最多管理线程数量=“处理器数 * 250”。也就是说,如果您的机器为2个2核CPU,那么CLR线程池的容量默认上限便是1000。通过线程池创建的线程默认为后台线程,优先级默认为Normal。
二、代码
案例一:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(ThreadMethod1), new object()); //参数可选 Console.ReadKey(); } public static void ThreadMethod1(object val) { for (int i = 0; i <= 10000; i++) { if (i % 1000 == 0) { if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(Thread.CurrentThread.Name) ) { Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Thred_" + i; } Console.WriteLine("循環{0}次的線程的線程名稱為:{1}",i,Thread.CurrentThread.Name); } } } }
运行结果:

案例二:
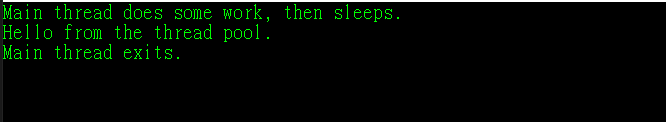
class Program { public static void Main() { // Queue the task. ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(ThreadProc); Console.WriteLine("Main thread does some work, then sleeps."); Thread.Sleep(1000); Console.WriteLine("Main thread exits."); Console.ReadKey(); } // This thread procedure performs the task. static void ThreadProc(Object stateInfo) { // No state object was passed to QueueUserWorkItem, so stateInfo is null. Console.WriteLine("Hello from the thread pool."); } }
运行结果:
本文来自博客园,作者:码农阿亮,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wml-it/p/14822883.html
技术的发展日新月异,随着时间推移,无法保证本博客所有内容的正确性。如有误导,请大家见谅,欢迎评论区指正!
开源库地址,欢迎点亮:
GitHub:https://github.com/ITMingliang
Gitee: https://gitee.com/mingliang_it
GitLab: https://gitlab.com/ITMingliang
建群声明: 本着技术在于分享,方便大家交流学习的初心,特此建立【编程内功修炼交流群】,为大家答疑解惑。热烈欢迎各位爱交流学习的程序员进群,也希望进群的大佬能不吝分享自己遇到的技术问题和学习心得!进群方式:扫码关注公众号,后台回复【进群】。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号