10.java NIO核心2:通道(Channel)
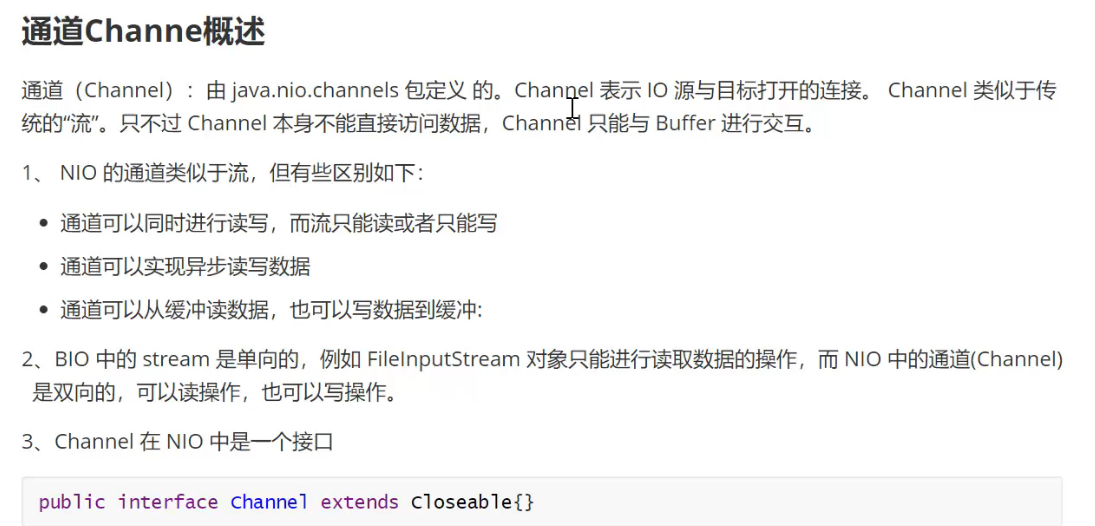
public interface Channel extend Clonseable{}

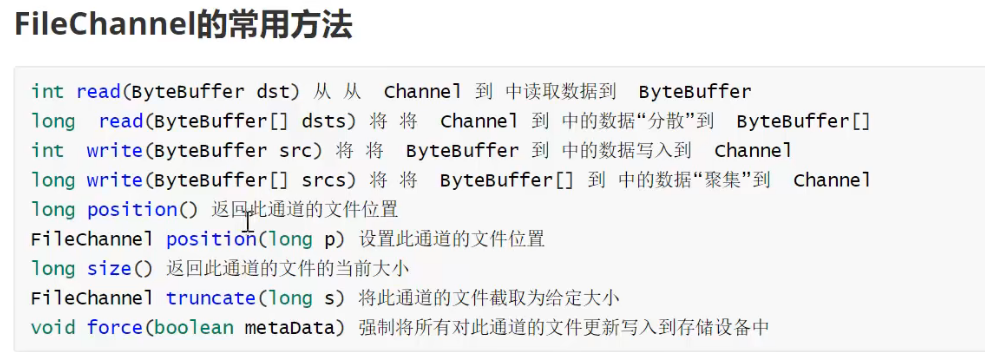 .
.
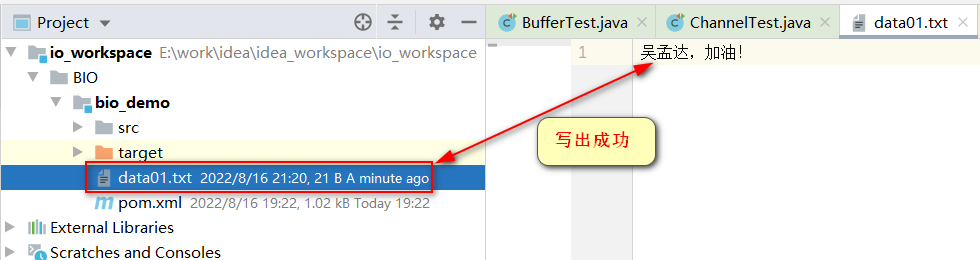
写案例:
@Test
public void write() {
try {
//1.字节输出流到目标文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("data01.txt");
//2.得到字节输出流对应的通道
FileChannel channel=fos.getChannel();
//3.分配缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.put("吴孟达,加油!".getBytes());
//4.把缓冲区切换成写出模式
buffer.flip();
channel.write(buffer);
channel.close();
System.out.println("写数据到文件中!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
读数据:
@Test
public void read(){
try {
//1.获取文件输入流
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("data01.txt");
//2.获取文件输入流对应的文件通道
FileChannel channel = fis.getChannel();
//3.定义一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(11024);
//4.读取数据到缓冲区
channel.read(buffer);
//5.切换读模式,将位置置为0
buffer.flip();
//6.重点:这里使用buffer.remaining去截取buffer中真正有数据的部分,要不输出的是1024个字节内容,后面没有占满也输出
String message=new String(buffer.array(),0,buffer.remaining());
System.out.println(message);//吴孟达,加油!
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
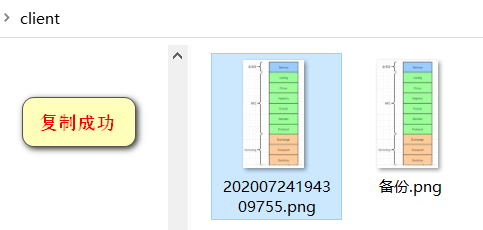
}3.使用Buffer完成文件复制
@Test
public void copy() {
try {
//原文件
File srcFile = new File("C:\\Users\\24459\\Desktop\\client\\20200724194309755.png");
//复制后的目标文件
File destFile = new File("C:\\Users\\24459\\Desktop\\client\\备份.png");
//定义文件输入流
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
//定义文件输出流
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//文件输入通道
FileChannel isChannel = is.getChannel();
//文件输出通道
FileChannel osChannel = os.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (true) {
//重点:每次进来都得先请缓存
buffer.clear();
//将数据读到缓冲区
int flag = isChannel.read(buffer);
//当读取完了就退出!
if (flag==-1){
break;
}
//重置位置开始写
buffer.flip();
osChannel.write(buffer);
}
isChannel.close();
osChannel.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
案例4:分散(Scatter)和聚集(Gather)
分散读取(Scatter):实指将Channel通道中的数据读入到缓冲区中
聚集写入(Gathering):实指将多个buffer中的数据聚集到Channel
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
//1.定义文件输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("data01.txt");
//2.定义文件输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("data02.txt");
//3.定义第一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
//4.定义第二个缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//5.获取输入流通道
FileChannel fisChannel = fis.getChannel();
//6.获取输出流通道
FileChannel fosChannel = fos.getChannel();
ByteBuffer[] buffers={buffer1,buffer2};
fisChannel.read(buffers);
//7.查看每个缓冲区是否可以渠道数据
for (ByteBuffer buffer:buffers){
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(),0,buffer.remaining()));
}
//6.聚集到写通道里
fosChannel.write(buffers);
fisChannel.close();
fosChannel.close();
System.out.println("文件复制结束...");
}
输出:
吴�
��达,加油!
文件复制结束... 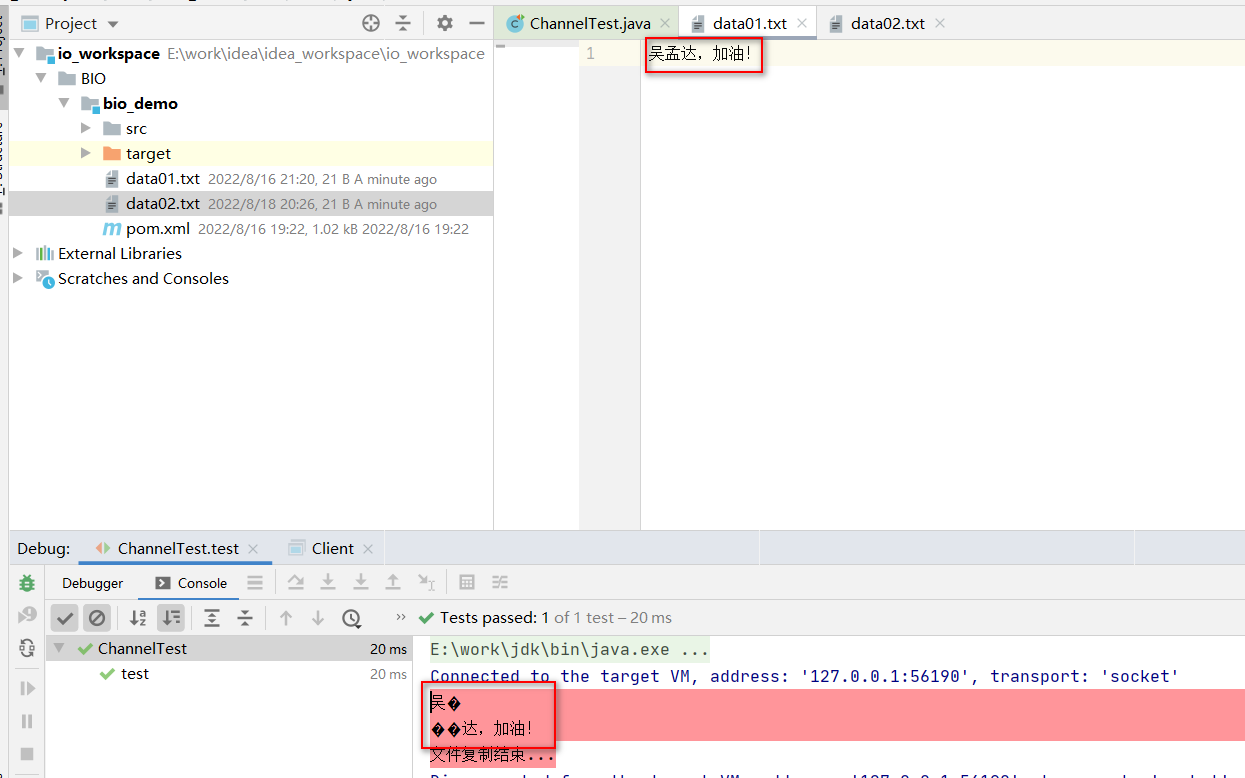
结论:发现分散的两个bytebuffer里面是分散的数据!
案例5:NIO下的FileChannel的transferFrom和transferTo。
@Test
public void test02() throws Exception {
//1.定义文件输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("data01.txt");
FileChannel fisChannel = fis.getChannel();
//2.定义文件输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("data03.txt");
FileChannel fosChannel = fos.getChannel();
//3.复制数据
fisChannel.transferTo(fisChannel.position(),fisChannel.size(),fosChannel);
//fosChannel.transferFrom(fisChannel,fisChannel.position(),fisChannel.size());
fisChannel.close();
fosChannel.close();
System.out.println("复制完成");
}
也可以完成文件的复制!


