27.指标监控功能
1.springboot Actuator
简介:
未来每个微服务在云上部署以后,我们都会对其进行监控、追踪、审计、控制等。springboot就抽取了Actuator场景,使得每个微服务能快速的引用即可获得生产级别的应用监控
简单实用步骤:
1.引入依赖:
<!--引入监控功能-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>
2.将监控节点以web形式暴露出来,即可以通过http请求获取到
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: true #默认开启所有的监控断点
web:
exposure:
include: '*' #以web形式的去暴露所有的监控断点
3.请求:参考地址为https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/actuator.html#actuator
此时就可以请求获取到所有的监控节点信息
1.监控bean的信息
http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans
2.只需要改actuator路径上的后缀就可以获取到各种监控信息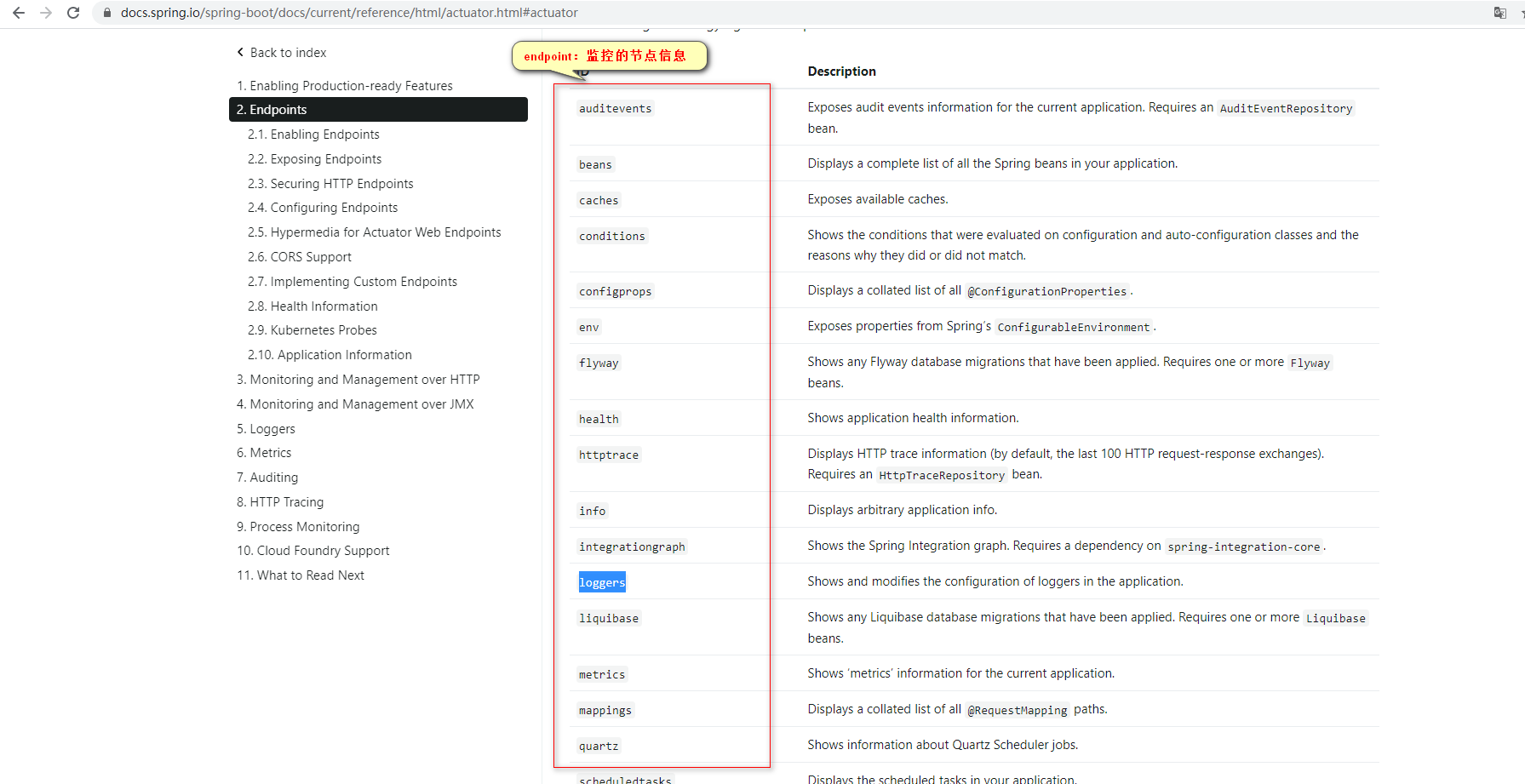

2.Actuator Endpoint(Actuator常用的监控断点)
|
ID
|
Description
|
|
auditevents
|
Exposes audit events information for the current application. Requires an AuditEventRepository bean.
|
|
beans
|
Displays a complete list of all the Spring beans in your application.
|
|
caches
|
Exposes available caches.
|
|
conditions
|
Shows the conditions that were evaluated on configuration and auto-configuration classes and the reasons why they did or did not match.
|
|
configprops
|
Displays a collated list of all @ConfigurationProperties.
|
|
env
|
Exposes properties from Spring’s ConfigurableEnvironment.
|
|
flyway
|
Shows any Flyway database migrations that have been applied. Requires one or more Flyway beans.
|
|
health(健康监控)
|
Shows application health information.
|
|
httptrace
|
Displays HTTP trace information (by default, the last 100 HTTP request-response exchanges). Requires an HttpTraceRepository bean.
|
|
info
|
Displays arbitrary application info.
|
|
integrationgraph
|
Shows the Spring Integration graph. Requires a dependency on spring-integration-core.
|
|
loggers(日志监控)
|
Shows and modifies the configuration of loggers in the application.
|
|
liquibase
|
Shows any Liquibase database migrations that have been applied. Requires one or more Liquibase beans.
|
|
metrics(运行时指标:例如磁盘,cpu占用率等)
|
Shows ‘metrics’ information for the current application.
|
|
mappings
|
Displays a collated list of all @RequestMapping paths.
|
|
quartz
|
Shows information about Quartz Scheduler jobs.
|
|
scheduledtasks
|
Displays the scheduled tasks in your application.
|
|
sessions
|
Allows retrieval and deletion of user sessions from a Spring Session-backed session store. Requires a Servlet-based web application using Spring Session.
|
|
shutdown
|
Lets the application be gracefully shutdown. Disabled by default.
|
|
startup
|
Shows the startup steps data collected by the ApplicationStartup. Requires the SpringApplication to be configured with a BufferingApplicationStartup.
|
|
threaddump
|
Performs a thread dump.
|
2.1监控监控(health)
用法示例:
以健康监控为例:
1.当配置文件中配置的是:配置的是整个的endpoints(所有端点)监控,并没有具体哪个端点时
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: true #默认开启所有的监控断点
web:
exposure:
include: '*' #以web形式的去暴露所有的监控断点
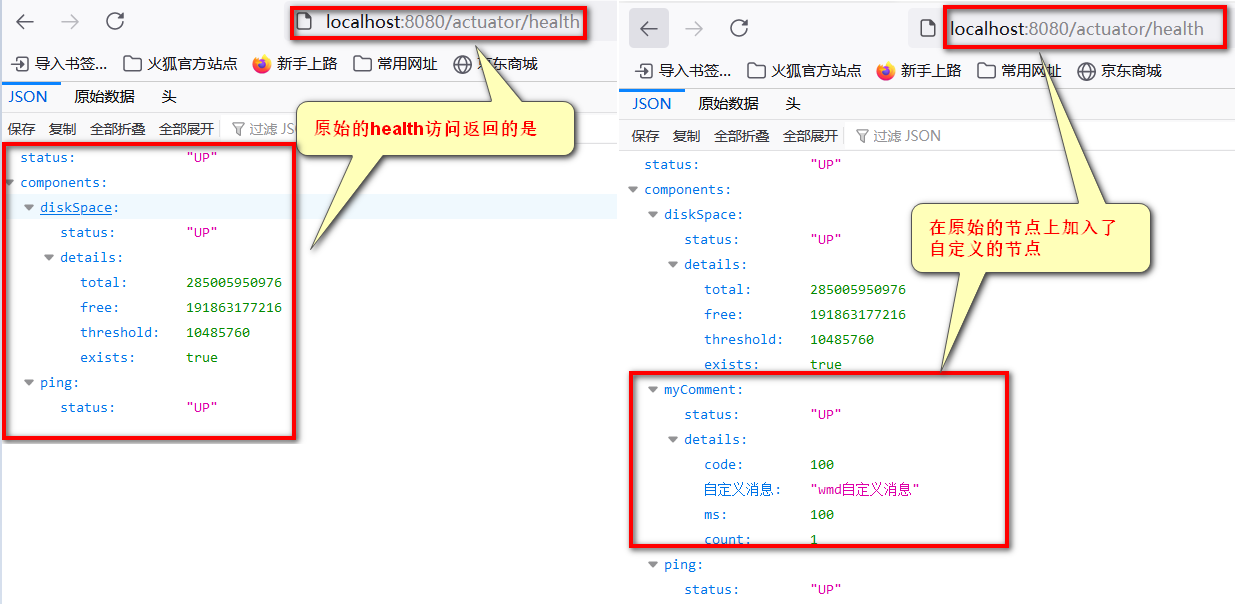
路径访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
页面输出:只有简单的整体状态,并没有具体的细节
{"status":"UP"}
2.在配置文件中具体配置helth节点:
配置文件中写法:
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: true #默认开启所有的监控断点
web:
exposure:
include: '*' #以web形式的去暴露所有的监控断点
endpoint: #具体端点里的详细配置
health:
show-details: always #health端点的展示细节,默认是never
路径访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
页面输出:
{
#整体状态监控
"status":"UP",
#监控的详细信息
"components":{
#1.数据库监控:使用的是isValid方法判断数据库是否可用
"db":{
"status":"UP",
"details":{
"database":"MySQL",
"validationQuery":"isValid()"
}
},
#2.磁盘监控:分为整体,空闲,已用
"diskSpace":{
"status":"UP",
"details":{
"total":68249812992,
"free":59284303872,
"threshold":10485760,
"exists":true
}
},
#3.ping:判断程序是否可以对外访问
"ping":{
"status":"UP"
}
}
}
结论:
整体的健康状态是依据里面的各项状态,有一项状态为down,则整体的状态就为down2.2运行时指标监控(Metrics Endpoint)
提供详细的、层级的、空间指标信息,这些信息可以被push(主动推送)或者(被动获取)方式获得
1.通过Metric对接多种监控系统
2.简化核心Metric开发
3.添加自定义的Metrics或者扩展已有的Metrics
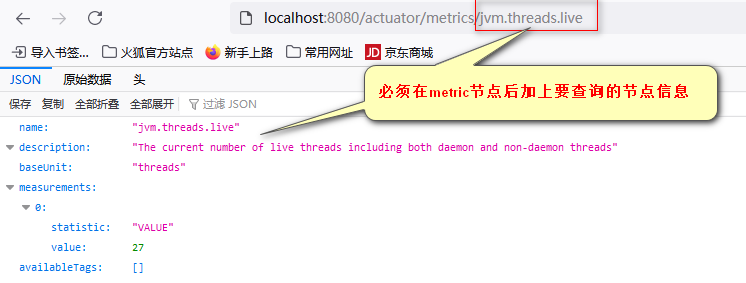
3.定制Endpoint
3.1定制health信息
步骤:
1.编写类继承于AbstractHealthIndicator(定制health的检查)
代码如下:
//加载到容器中
@Component
//注意点1:类名必须是HealthIndicator结束
public class MyCommentHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
/**
* 真实的检查方法
* @param builder
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
//mongdb模拟:获取连接开始测试
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
//模拟检查完成
if(1==1){
//1.第一种写法
//builder.up();
builder.status(Status.UP);
map.put("count",1);
map.put("ms",100);
map.put("自定义消息","wmd自定义消息");
}else {
builder.status(Status.OUT_OF_SERVICE);
map.put("er","连接超时");
map.put("ms","3000");
}
builder.withDetail("code",100).withDetails(map);
}
}
如何展示固定节点
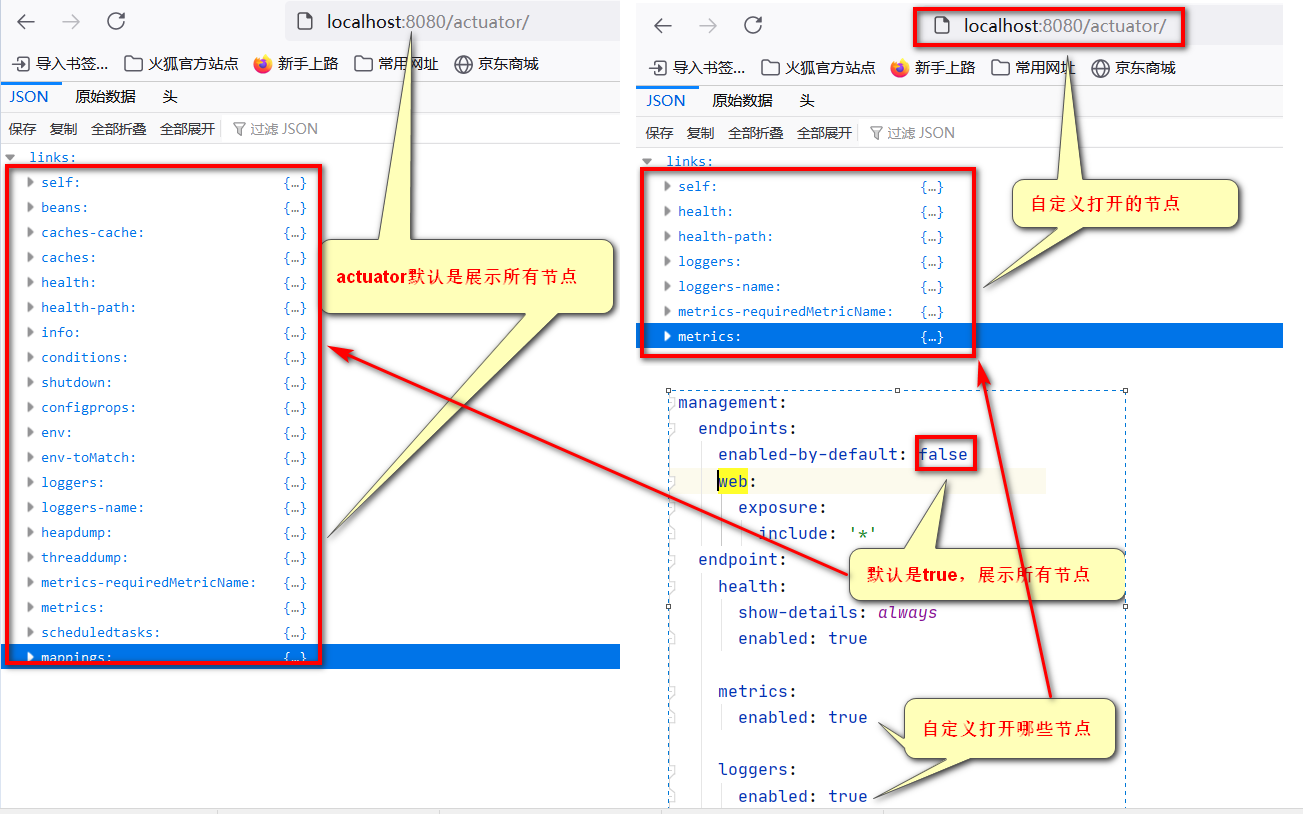
management:
endpoints:
#改为false,默认是true,打开所有节点
enabled-by-default: false
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
enabled: true
#分开打开某些节点
metrics:
enabled: true
#打开logger的节点
loggers:
enabled: true3.2定制info信息
定制info可以有两种办法:
1.配置文件的形式进行配置
2.代码的形式进行配置
1.配置文件形式:注意目录层级很重要
management:
endpoints:
#注意点:1.关闭了默认的展示所有的节点,改为手动打开固定节点
enabled-by-default: false
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
enabled: true
metrics:
enabled: true
loggers:
enabled: true
#注意点2:打开指定的节点
info:
enabled: true
#注意点3:info节点的层级和management层级一样,下面是自定义的目录层级
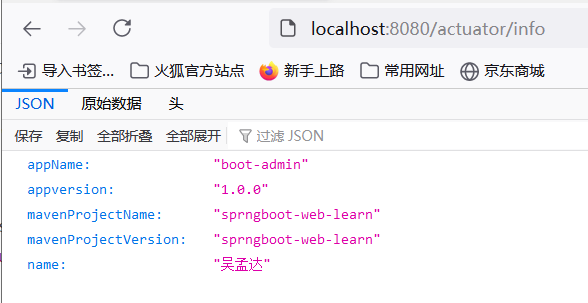
info:
appName: boot-admin
appversion: 1.0.0
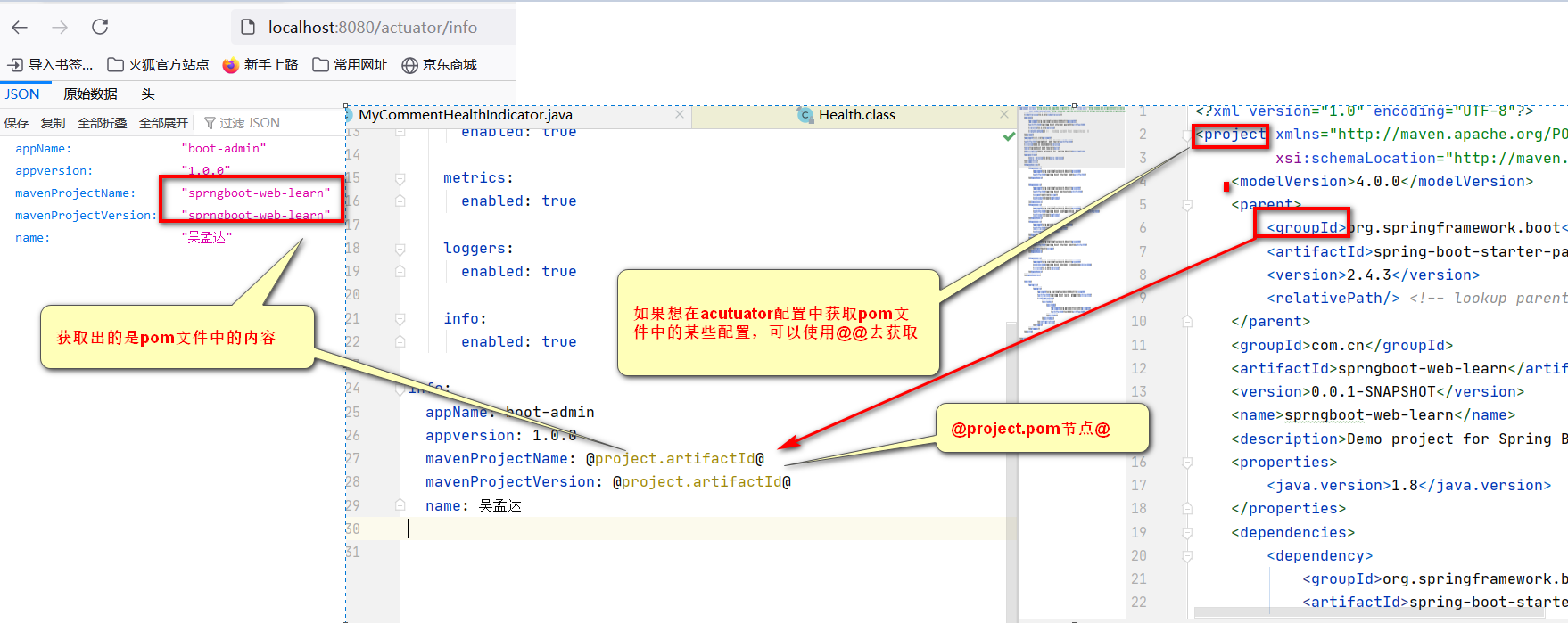
mavenProjectName: @project.artifactId@
mavenProjectVersion: @project.artifactId@
name: 吴孟达注意当没有配置时页面展示为空
2.第二种方式,代码方式
@Component
public class AppInfoContributor implements InfoContributor {
@Override
public void contribute(Info.Builder builder) {
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","刘丹");
map.put("age",18);
builder.withDetail("msg","你好").withDetail("hello","world").withDetails(map);
}
}
这时访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/info
发现页面上的展示数据是配置文件和代码的结合,并且如果配置文件和代码重复设置,是以代码的为主,例如下述的name属性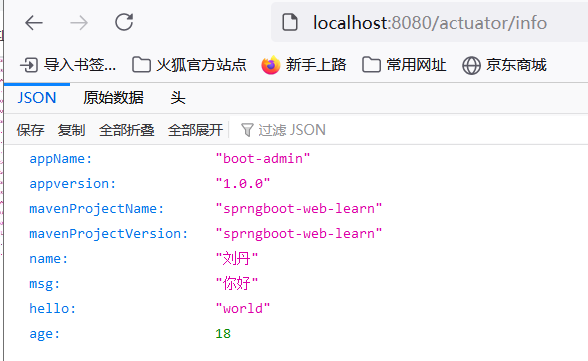
3.3定制Metrics信息
1.监控系统的各项指标
2.如何定制
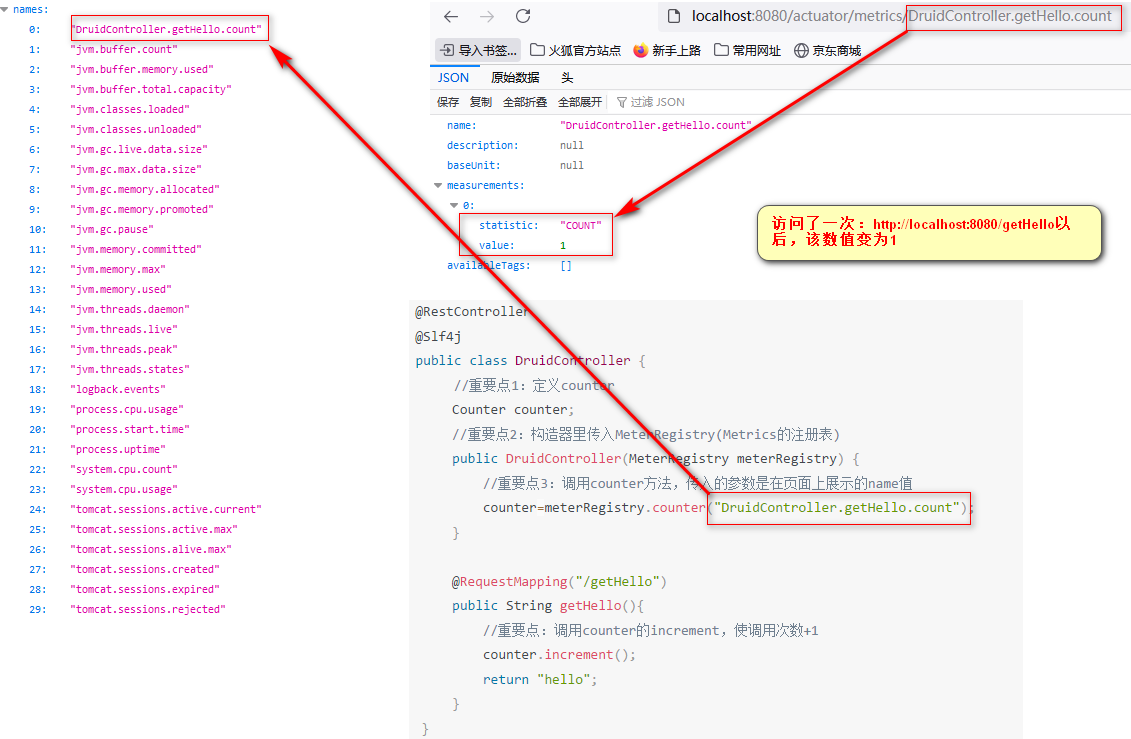
业务场景,如何统计某个方法被调用多少次呢?例如统计getHello方法调用的次数
样例:
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class DruidController {
//重要点1:定义counter
Counter counter;
//重要点2:构造器里传入MeterRegistry(Metrics的注册表)
public DruidController(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
//重要点3:调用counter方法,传入的参数是在页面上展示的name值
counter=meterRegistry.counter("DruidController.getHello.count");
}
@RequestMapping("/getHello")
public String getHello(){
//重要点:调用counter的increment,使调用次数+1
counter.increment();
return "hello";
}
}效果:
4.定制Endpoint
代码示例如下:
@Component
//重点1:使用@Endpoint标签,传入的参数是http://localhost:8080/actuator后页面上的id值
@Endpoint(id = "wmdService")
@Slf4j
public class MyserviceEndpoint {
//重点2:此处为读取操作,一定不能传参
@ReadOperation
public Map getDockerInfo(){
Map<String, Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("dockerInfo", "docker started");
return map;
}
//重点3:
@WriteOperation
public void stopDocker(){
log.info("停止docker容器...");
}
}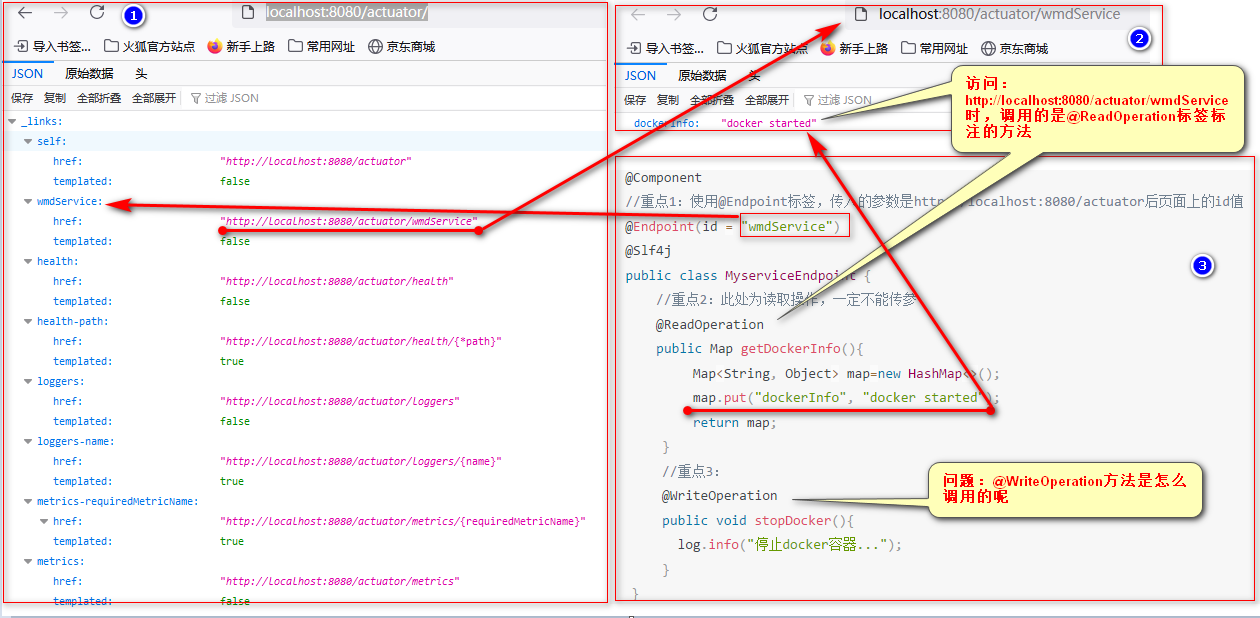
上述结论:
1.@Endpoint(id = "wmdService")标签标注的是http://localhost:8080/actuator路径访问时的大节点(和info、health、metric一个级别)
2.继续深入访问时:http://localhost:8080/actuator,显示调用的是自定义的@ReadOperation标注的方法(@ReadOperation标注的方法不能传参)
3.@WriteOperation标注的方法何时调用呢
Endpoints节点对外暴露时以两种方式暴露:
1.web形式(即页面访问时以json的形式返回)
2.JMX形式(只能通过jconsole方式去调用)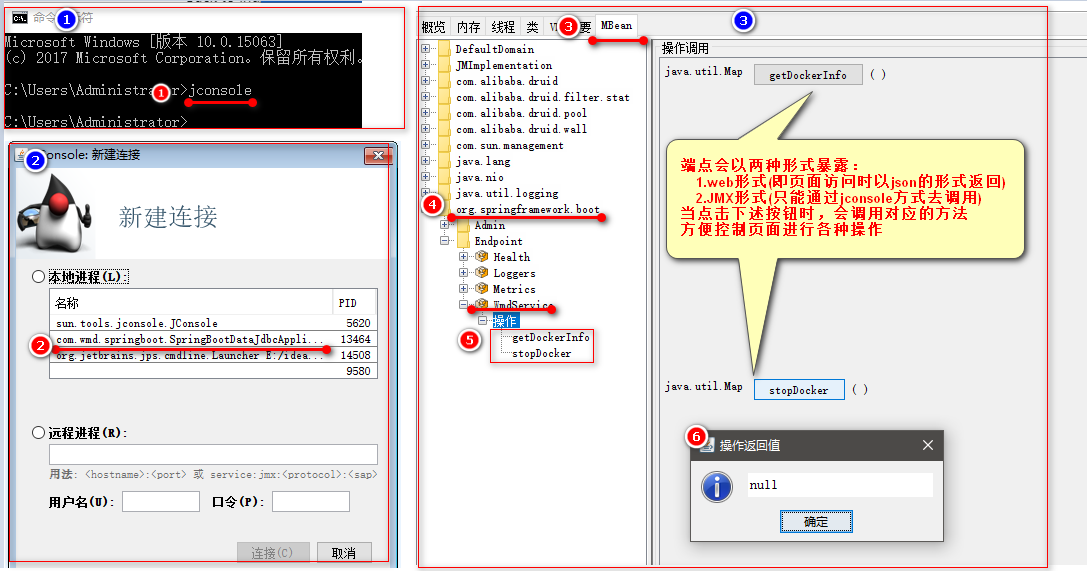
一个开源的springboot监控面板
参考地址:https://github.com/codecentric/spring-boot-admin
快速开始参考地址:https://codecentric.github.io/spring-boot-admin/2.3.1/#getting-started
1.创建一个springboot应用作为控制面板的服务端:
1.1pom文件中导入:
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
</dependency>
1.2在springboot的启动类上加上 @EnableAdminServer标签
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAdminServer
public class SpringbootAdminServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootAdminServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
1.3在配置文件中配置server的启动端口,和客户端的区分开
server:
port: 8081
2.在各项应用中的配置:
2.1在pom文件中引入客户端的包
<!--在客户端节点上因为以下包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
</dependency>
2.2在配置文件中配置
spring:
boot:
admin:
client:
#重点1:服务端的地址
url: http://localhost:8081
重点2:该配置是以服务器的ip进行url注册,默认是false(以主机名称进行注册,可能会出现问题)
instance:
prefer-ip: true
#重点三:设置该服务在控制面板的显示名称
application:
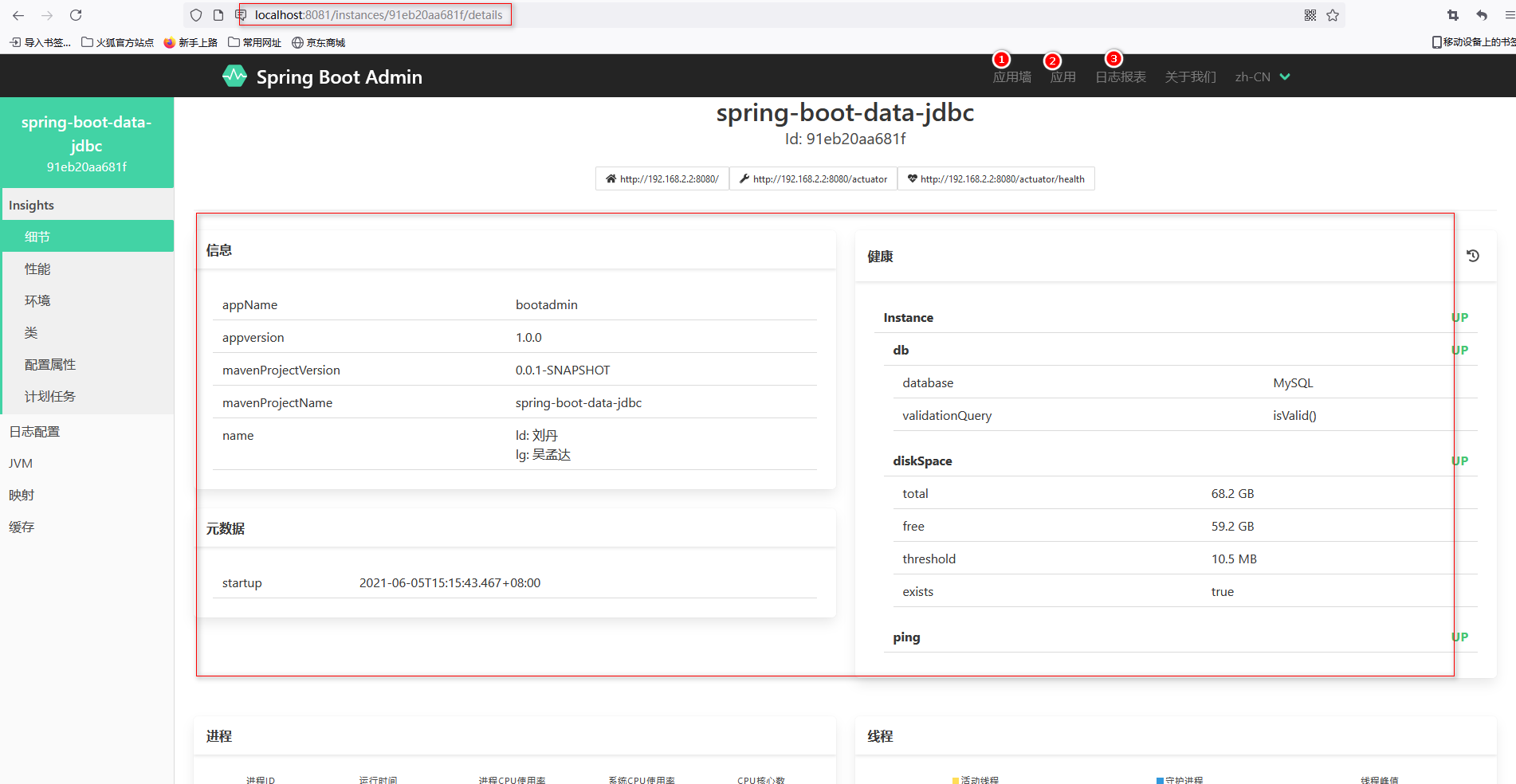
name: spring-boot-data-jdbc页面访问服务端的地址:http://localhost:8081是会展示配置了服务端连接的所有客户端,并展示其详细信息




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)