排序
选择排序
简单选择排序:对一个序列A中的元素A[1]~A[n],令i从1到n枚举,进行n趟操作,每趟从待排序部分[i,n]中选择最小的元素,令其与待排序部分的第一个元素A[j]进行交换。进行n趟操作后,所有元素就会有序。
复杂度为:O(n^2)
1 void selectsort(){ 2 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) //进行n趟操作 3 { 4 int k=i; 5 for(int j=i;j<=n;j++) //选出[i,n]中最小的元素,下标为k 6 { 7 if(A[j]<A[k]) 8 k=j; 9 } 10 int temp=A[i]; //交换A[K]和A[i] 11 A[i]=A[k]; 12 A[k]=temp; 13 } 14 }
直接插入排序
将待插入元素一个个插入初始已有序部分中的过程,插入位置的选择遵循使插入后仍然保持有序的原则,具体做法一般是从后往前枚举已有序部分来确定插入位置。
1 //简单插入排序 2 int A[maxn],n; //n为元素个数,数组下标为1~n 3 void insertSort() 4 { 5 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) //进行n-1趟排序 6 { 7 int temp=A[i],j=i; //temp临时存放A[i],j从i开始往前枚举 8 while(j>1&&temp<A[j-1]) 9 { 10 A[j]=A[j-1]; //把A[j-1]后移一位至A[j] 11 j--; 12 } 13 A[j]=temp; 14 } 15 }
sort函数的应用
1.相关结构体的定义
//学生结构体 struct Student{ char name[10]; //姓名 char id[10];//学号 int score; //分数 int r; //排名 }stu[1000];
2.cmph函数的编写
例:排序规则如下
- 分数不同,则高分在前
- 分数相同,姓名字典顺序小的在前
bool cmp(Student a,Student b) { if(a.score!=b.score) return a.score>b.score; else return strcmp(a.name,b.name)<0; }
3. 排名的实现
分数不同的排名不同,分数相同的排名相同但占用一个排位。
情况一:数组下标从0开始,先将数组第一个个体的排名为1,然后遍历剩余个体;如果当前个体的分数等于上一个个体的分数,那么当前个体的排名等于上一个个体的排名,否则当前个体排名等于数组下标加1.
stu[0].r=1; for(int i=1;i<n;i++) { if(stu[i].score==stu[i-1].score) { stu[i].r=stu[i-1].r; } else stu[i].r=i+1; }
情况二:不需要把排名记录下来,直接输出。令int型变量r初值为1,然后遍历所有个体:如果当前个体不是第一个个体且当前个体的分数不等于上一个个体分数,令r等于数组下标+1.
1 int r=1; 2 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 3 { 4 if(i>0&&stu[i].score != stu[i-1].score) 5 r=i+1; 6 //输出当前个体信息或者令stu[i].r=r; 7 }
例题
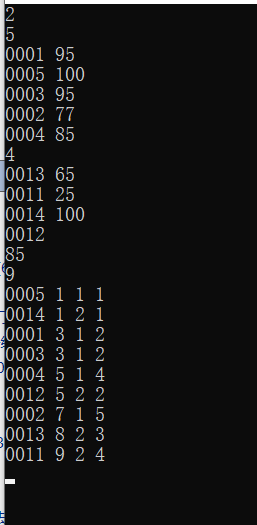
题干:有n个考场,每个考场有若干数量的考生,现给出每个考场中考生的准考证号与分数,要求将所有考生按分数从高到低排序,并顺序输出所有考生的准考证号,排名,考场号以及考场内排名。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #include<cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 struct Student{ 6 char id[15]; //准考证号 7 int score; 8 int location_number; //考场号 9 int local_rank; //考场内排名 10 }stu[30010]; 11 12 bool cmp(Student a,Student b) 13 { 14 if(a.score!=b.score) 15 return a.score>b.score; 16 else 17 return strcmp(a.id,b.id)<0; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 int n,num=0,k; 22 while(cin >> n) //n为考场数 23 { 24 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 25 { 26 cin >> k; //该考场内人数 27 for(int j=0;j<k;j++) 28 { 29 cin >> stu[num].id >> stu[num].score; 30 stu[num].location_number=i; //该考生的考场号为i 31 num++; //总考生数+1 32 } 33 //将考场的考生排序 34 sort(stu+num-k,stu+num,cmp); 35 stu[num-k].local_rank=1;//该考场的第一名记为1 36 for(int j=num-k+1;j<num;j++) //对该场剩余的考生 37 { 38 if(stu[j].score==stu[j-1].score) 39 stu[j].local_rank=stu[j-1].local_rank; 40 else 41 stu[j].local_rank=j+1-(num-k); 42 } 43 } 44 45 cout << num << endl; //输出学生总人数 46 //为所有考生排序 47 sort(stu,stu+num,cmp); 48 int r=1; 49 for(int i=0;i<num;i++) 50 { 51 if(i>0&&stu[i].score!=stu[i-1].score) 52 r=i+1; 53 cout << stu[i].id << ' '; 54 cout << r << ' ' << stu[i].location_number << ' ' << stu[i].local_rank << endl; 55 } 56 } 57 return 0; 58 }
You want something.Go get it!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号