222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
题目链接:
题目描述
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
示例 1:
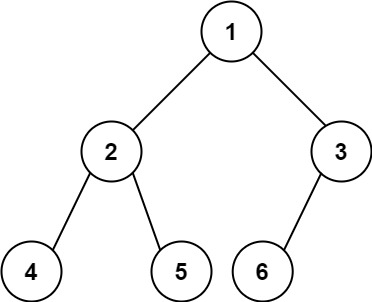
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
提示:
-
树中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5 * 104] -
0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 104 -
题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
进阶:遍历树来统计节点是一种时间复杂度为 O(n) 的简单解决方案。你可以设计一个更快的算法吗?
题解
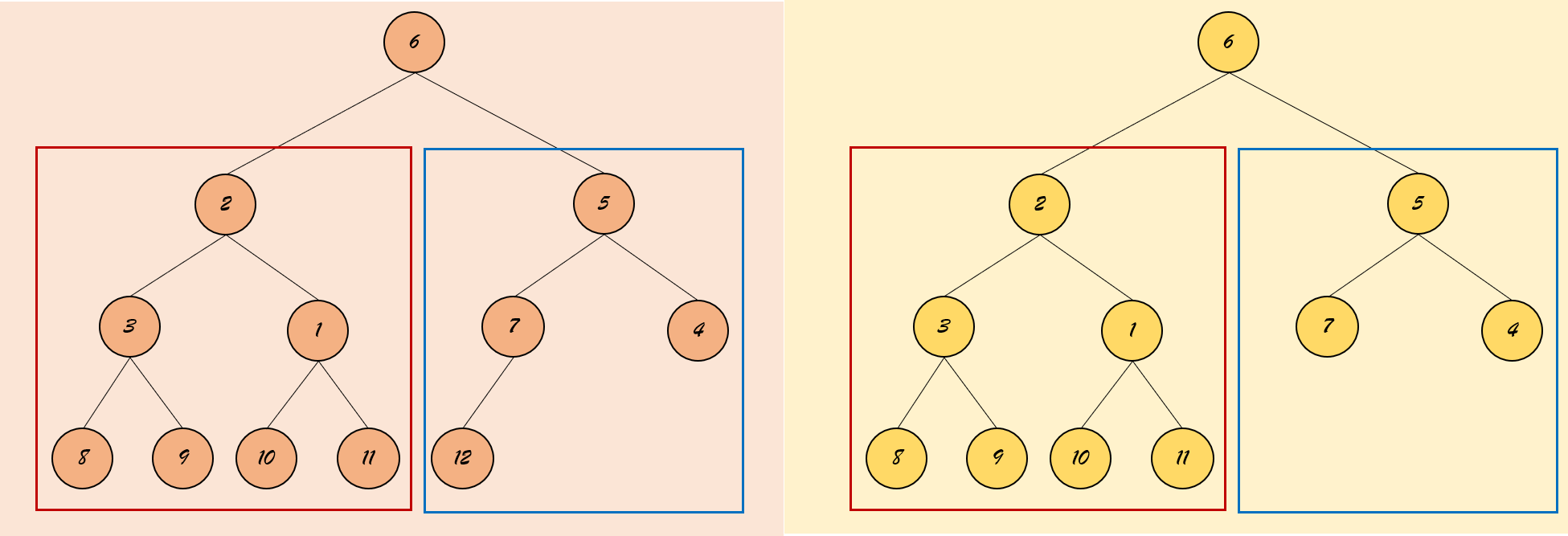
思路:不考虑”进阶“,完全二叉树就是一棵二叉树,求节点的个数和遍历节点类似。但由于完全二叉树的特殊性。由下图我们可以发现:如果左子树的深度等于右子树的深度,则左子树为满二叉树;如果左子树的深度大于右子树的深度,则右子树为满二叉树。
代码(C++):
struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode* left; TreeNode* right; TreeNode(int value) : val(value), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} }; class Solution1 { public: //按照一般的二叉树来求,有递归法和迭代法 //方法一:后序遍历(递归法) int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; int leftNums = countNodes(root->left); int rightNums = countNodes(root->right); int nums =leftNums + rightNums + 1; return nums; } }; class Solution2 { public: //按照一般的二叉树来求,有递归法和迭代法 //方法二:层次遍历(迭代法) int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> que; if (root != nullptr) que.push(root); int nums = 0; while (!que.empty()) { TreeNode* node = que.front(); que.pop(); nums++; if (node->left) que.push(node->left); if (node->right) que.push(node->right); } return nums; } }; class Solution3 { public: //完全二叉树是特殊的二叉树 //方法三: int getDepth (TreeNode* node) { int depth = 0; while (node) { depth++; node = node->left; } return depth; } int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; // 以根节点分成左子树和右子树,分别求他们的深度 int leftDepth = getDepth(root->left); int rightDepth = getDepth(root->right); if (leftDepth == rightDepth) { return countNodes(root->right) + (pow(2,leftDepth) - 1) + 1; } else { return (pow(2,rightDepth) - 1 ) + countNodes(root->left) + 1; } } };
代码(JavaScript):
//构造函数 function TreeNode(val, left, right) { this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val); this.left = (left === undefined ? null : left); this.right = (right == undefined ? null : right); } var root = new TreeNode(); //方法一:递归法(后序遍历) var countNodes = function(root) { if (root === null) return 0; var leftNums = countNodes(root.left); var rightNums = countNodes(root.right); return rightNums + leftNums + 1; }; //方法二:迭代法(层次遍历) var countNodes1 = function(root) { var que = new Array(); if (root != null) que.push(root); var Nums = 0; while (que.length != 0) { var node = que.shift(); Nums++; if (node.left) que.push(node.left); if (node.right) que.push(node.right); } return Nums; }; //方法三:利用二叉树的性质 function getDepth(node) { var depth = 0; while (node) { depth++; node = node.left; } return depth; } var countNodes2 = function(root) { if (root === null) return 0; var leftDepth = getDepth(root.left); var rightDepth = getDepth(root.right); if (leftDepth === rightDepth) { return countNodes(root.right) + (Math.pow(2, leftDepth) - 1) + 1; } else { return (Math.pow(2, rightDepth) - 1) + countNodes(root.left) + 1; } };
分析:
普通二叉树的方法(方法一,方法二)
-
时间复杂度:O(N),N是树的节点个数
-
空间复杂度:方法一(O(logN)),递归中栈的开销;方法二(O(N)),迭代中队列的开销;
满二叉树(方法三)
-
时间复杂度:O(logN * logN)
-


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号