Stream
1.Stream流的简介

Stream的执行流程
- 创建Stream
- 一个或多个中间操作,连接形成流水线
- 终止操作。除非流水线上触发终止操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何的处理!而在终止操作时一次性全部处理,称为“惰性求值”。
2.流的操作
1.创建流
public class CreateStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用集合自带的stream方法 创建Stream流
List<String> list = new ArrayList();
Stream<String> stream = list.stream();
// 使用Arrays自带的stream方法 创建Stream流
int [] arr= new int[10];
IntStream stream1 = Arrays.stream(arr);
// 使用Stream中的of方法创建stream流
Stream<String> of = Stream.of("a","b","c");
// 无限创建
Stream<Integer> iterate = Stream.iterate(0, x -> x);
//正常生成
Stream<Double> generate = Stream.generate(() -> Math.random());
}
}
2.Stream流中间操作
筛选和切片
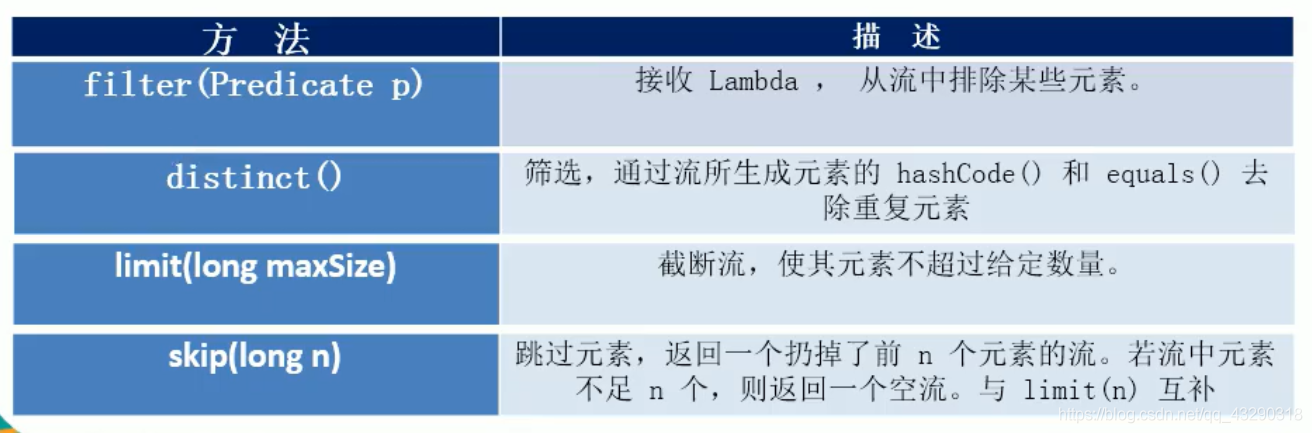
测试代码如下:
@Test
/**
*筛选与切片:
* filter() 过滤条件后的元素
* distinct() 去除重复元素
* limit() 截断流 取指定截断的数量
* skip() 跳过多少个元素
*/
public void middle(){
ArrayList<Human> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Human("胡图图",22,"100","123456789"));
list.add(new Human("牛爷爷",60,"130","1546465464"));
list.add(new Human("光头强",50,"120","4564456464"));
list.add(new Human("光头强",50,"120","4564456464"));
// filter()
// 返回的是中间操作 中间操作不会输出任何值
Stream<Human> stream =list.stream().filter(human->human.getAge()>30);
// 终止操作
stream.forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println("======================这是一个分隔符======================");
// distinct()
list.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println("======================这是一个分隔符======================");
//limit()
list.stream().limit(2).forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println("======================这是一个分隔符======================");
// skip()
list.stream().skip(2).forEach(System.out::print);
}
映射
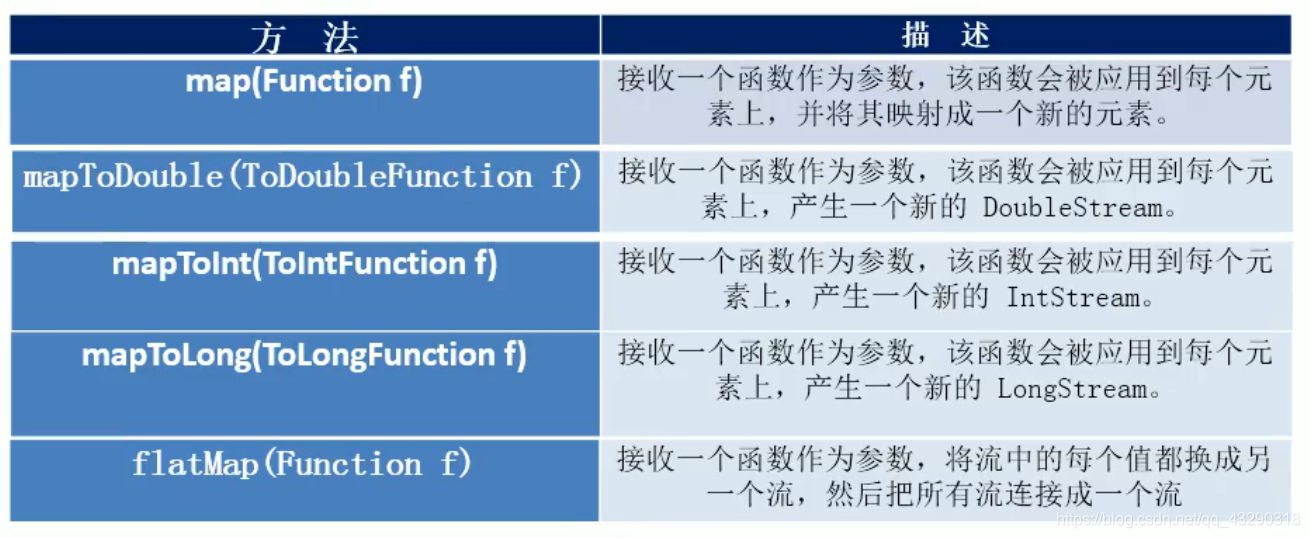
测试代码如下
@Test
/**
* 映射:
* map()
*
*
*/
public void mapping(){
ArrayList<Human> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Human("胡图图",22,"100","123456789"));
list.add(new Human("牛爷爷",60,"130","1546465464"));
list.add(new Human("光头强",50,"120","4564456464"));
// Human::getAge 相当于 调用Human中的getAge()方法,因为lambda 里面不能执行方法,所以需要将 此方法转成方法引用
list.stream().map(Human::getAge).forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
/**
* 需求 将集合中的元素全部拆成字符
*/
public void flatMap(){
//
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa", "bb", "cc", "dd");
// Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream = list.stream().map(StreamTest::filterCharacter);
// streamStream.forEach(
// stream->{
// stream.forEach(System.out::println);
// }
// );
// flatMap接收一个函数作为参数,将每个值替换成流,并且将所有的流连接成一个流 和以上注释的代码效果一样
list.stream().flatMap(StreamTest::filterCharacter).forEach(System.out::println);
}
public static Stream<Character> filterCharacter(String str){
ArrayList<Character> characterList = new ArrayList();
for (char ch : str.toCharArray()) {
characterList.add(ch);
}
return characterList.stream();
}
排序
/**
* 排序
* sorted() 自然排序
* sorted(Compartor) 定制排序
*/
@Test
public void sort() {
// 按照String的实现的 Comparable接口中的 compareTo方法 进行 自然排序
List<String> strList = Arrays.asList("aa", "bb", "cc", "ff");
strList.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
// 按照自己定制的规则进行排序
List<Human> list = Arrays.asList(new Human("胡图图", 20, "100", "136695515"),
new Human("小明", 22, "100", "136695515"),
new Human("小张", 19, "120", "136695515"),
new Human("小李", 22, "200", "136695515"),
new Human("小李", 26, "200", "136695515"),
new Human("胡图图", 21, "200", "136695515")
);
list.stream().sorted(
(o1,o2)->{
if (o1.getAge()==o2.getAge()){
return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
}else {
return o1.getAge().compareTo(o2.getAge());
}
}
).forEach(System.out::println);
}
归纳/收集
/**
* 归纳/收集
*/
public class StreamTest {
@Test
public void reduce(){
List<String> str = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "d");
List<Integer> str2 = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6);
// 收集
String a = str.stream().reduce("0", (x, y) -> x += y);
System.out.println(a);
// 求和收集
Optional<Integer> sum= str2.stream().reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println(sum.get());
List<Human> strs = Arrays.asList(
new Human("小张",12,"180","13037117095"),
new Human("小李",20,"150","56143513541"),
new Human("小钱",18,"160","32141456458")
);
Map<Integer, String> collectMap = strs.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Human::getAge, Human::getName));
collectMap.forEach(StreamTest::printMap);
}
public static void printMap(Object k,Object v){
System.out.println(k+"="+v);
}
}
3.终止操作
查找与匹配
- allMatch:检查是否匹配所有元素
- anyMatch:检查是否至少匹配一个元素
- noneMatch:检查是否没有匹配所有元素
- findFirst:返回第一个元素
- findAny:返回当前流中的任意元素
- count:返回流中元素的总个数
- max:返回流中最大值
- min:返回流中最小值
测试代码如下:
/**
* allMatch:检查是否匹配所有元素
* anyMatch:检查是否至少匹配一个元素
* noneMatch:检查是否没有匹配所有元素
* findFirst:返回第一个元素
* findAny:返回当前流中的任意元素
* count:返回流中元素的总个数
* max:返回流中最大值
* min:返回流中最小值
*/
@Test
public void findAndMatch() {
List<Human> list = Arrays.asList(new Human("胡图图", 20, "100", "136695515"),
new Human("小明", 22, "100", "130371179"),
new Human("小张", 19, "120", "136695515"),
new Human("小钱", 22, "200", "130371179"),
new Human("小李", 20, "200", "02121231"),
new Human("小小", 21, "200", "136695515")
);
// allMatch 检查是否匹配所有元素
Boolean b1 = list.stream().allMatch(human -> human.getAge() == 20);
System.out.println(b1);
// anyMatch 检查是否至少匹配一个元素
Boolean b2 = list.stream().anyMatch(human -> human.getPhone().equals("130371179"));
System.out.println(b2);
// noneMatch 检查是否没有匹配所有元素
Boolean b3 = list.stream().noneMatch(human -> human.getPhone().equals("111111"));
System.out.println(b3);
// findFirst 返回第一个元素
Optional<Human> optional = list.stream().filter(human -> human.getPhone().equals("130371179")).findFirst();
System.out.println(optional.get());
// findAny 返回当前流中的任意元素
Optional<Human> opt2 = list.stream().filter(human -> human.getAge() > 18).findAny();
System.out.println(opt2.get());
// count 返回流中元素的总个数
long count = list.stream().filter(human -> human.getPhone().contains("13")).count();
System.out.println(count);
// max 返回流中最大值
Optional<Human> max = list.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(Human::getAge));
System.out.println(max.get());
}

/**
* collect() 收集到容器
*/
@Test
public void collect(){
List<Human> list = Arrays.asList(new Human("胡图图", 20, "100", "136695515"),
new Human("小明", 22, "100", "130371179"),
new Human("小张", 19, "120", "136695515"),
new Human("小钱", 22, "200", "130371179"),
new Human("小赵", 20, "200", "02121231"),
new Human("小小", 21, "200", "136695515")
);
// 放入list集合
List<Human> collectList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collectList);
// 放入set集合
Set<Human> collectSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(collectSet);
// 放入map中
Map<String, Human> collectMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Human::getName, i -> i));
System.out.println(collectMap);
// 求总数
Long collectCount = list.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(collectCount);
// 分组
Map<String, List<Human>> groupMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Human::getHeight));
System.out.println(groupMap);
// 求平均值
Double collectAverage = list.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Human::getAge));
System.out.println(collectAverage);
// 求最大值
Optional<Integer> ageMax = list.stream().map(Human::getAge).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(ageMax.get());
// 求最小值
Optional<Integer> ageMin = list.stream().map(Human::getAge).collect(Collectors.minBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(ageMin.get());
// 操作map集合
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap();
map.put("java", "10.0");
map.put("kotlin", "11.0");
map.put("php", "12.0");
Map<String, Object> conditionMap = new HashMap();
conditionMap.put("java", "10.0");
Map<String, Object> maps = map.entrySet().stream()
.peek(obj -> {
if (conditionMap.containsKey(obj.getKey()))
obj.setValue(Float.parseFloat(obj.getValue().toString()));
})
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue));
System.out.println(maps.toString());
// 转为忽略大小写map
List<User> list = new ArrayList() {{
add(new User(1001L, "qq音乐", "aa"));
add(new User(1002L, "qq象棋", "aa"));
}};
Map<String, Long> collect = list.stream().collect(
toMap(
User::getName,
User::getId,
(value1, value2) -> value2,
()->new TreeMap<>(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER)
)
);
System.out.println(collect.get("QQ音乐"));
}
集合之间过滤数据
// list2 中过滤list中数据
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new User(1001L,"wl00","北京"));
list.add(new User(1002L,"wl01","上海"));
list.add(new User(1003L,"wl02","深圳"));
list.add(new User(1004L,"wl03","北京"));
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add("1001");
list2.add("1002");
list2.add("1003");
// list2 中过滤list中数据
List<String> collect = list2.stream().filter(
l2 -> list.stream().anyMatch(
l1 -> l1.getId().toString().equals(l2)
)
).collect(toList());
System.out.println(collect);
将集合转换为map key是索引 value是集合的值
// 将集合转换为map key是索引 value是集合的值
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a1");
list.add("a2");
list.add("a3");
list.add("a4");
list.add("a5");
list.add("a6");
list.add("a7");
list.add("a8");
Map<Integer, String> collect = IntStream.range(0, list.size()).boxed().collect(toMap(i -> i, list::get));
System.out.println(collect);
结果如下
{0=a1, 1=a2, 2=a3, 3=a4, 4=a5, 5=a6, 6=a7, 7=a8}
1.去重复,返回List集合
应用场景:比如想知道一个用户一个月内登陆了哪几天,去数据库获取登录日志,但是一个用户可以一天内登录很多次,但是只想要确定这一天是否登录,所以需要将一天的日志信息去重,保留一个就行。然后将List集合转换为map键值对,这个场景就用到了以下案列:
public class TestStream {
@Test
void test01() {
People p = new People(1, "北京");
People p1 = new People(1, "北京");
People p2 = new People(1, "上海");
People p3 = new People(1, "天津");
People p4 = new People(2, "武汉");
People p5 = new People(2, "天津");
People p6 = new People(2, "武汉");
People p7 = new People(2, "合肥");
List<People> people = Arrays.asList(p, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7);
// 去重
ArrayList<People> result = people.stream().collect(collectingAndThen(
toCollection(
() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(l->l.getId()+"-"+l.getAddress()))
), ArrayList::new
)
);
result.forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
// 根据 一个 id 对应一个map集合
Map<Integer, List<People>> peopleMap = result.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(People::getId));
peopleMap.forEach(
(k,v)->{
System.out.println(k);
v.forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
}
);
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
class People {
private int id;
private String address;
}
2.过滤并转换为list集合
List<UserInfo>list = list.stream().filter(userInfo -> userInfo.getIsEnable() == 1).collect(Collectors.toList());
3.在开发中,如果一个list会被频繁的使用,建议转成Map集合,因为list使用一般都会伴随着遍历
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("北京市","1001",0));
list.add(new Student("上海市","1002",0));
list.add(new Student("杭州市","1003",0));
list.add(new Student("苏州市","1004",0));
Map<String, Student> studentMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((Student::getName), i -> i));
// System.out.println(studentMap.toString());
test1(list);
test2(studentMap);
}
public static void test1(ArrayList<Student> list){
list.forEach(
stu->{
if (stu.getName()=="1001"){
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
);
}
public static void test2(ArrayList<Student> list){
list.forEach(
stu->{
if (stu.getAddress()=="1002"){
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
);
}
public static void test2(Map<String,Student> studentMap){
if (studentMap.get("1001")!=null){
System.out.println(studentMap.get("1001"));
}
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student implements People {
private String address;
private String name;
private int status;
}
3.Fork/join
Fork/join采用的是分治思想,将大任务拆分成若干个小任务,然后再逐步合并结果
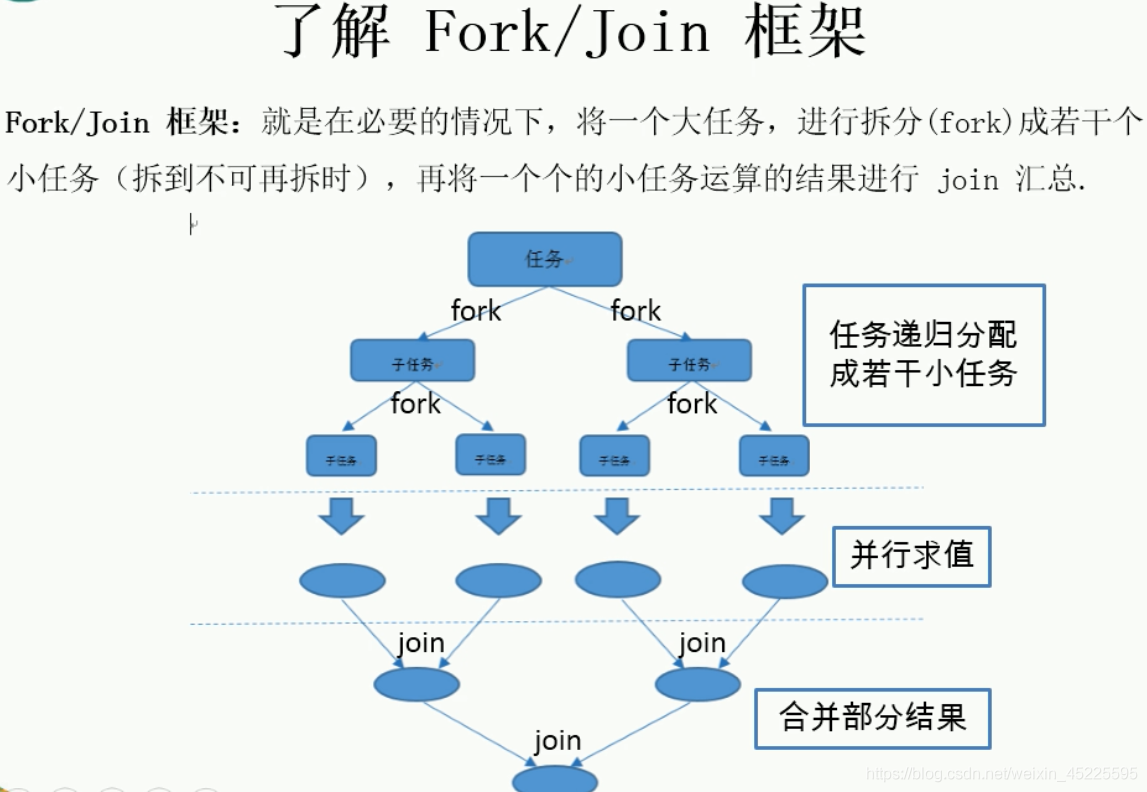
计算累加使用fork join 框架
package com.oasisgames
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask
/**
*@author 没有梦想的java菜鸟
* @date 2022/02/23 11:17 上午
*/
data class ForkJoinCalculation(var begin: Long, var end: Long) : RecursiveTask<Long>() {
private val threshold: Long = 10000
override fun compute(): Long {
return if (begin - end <=threshold) {
var sum: Long = 0
for (i in begin..end) {
sum += i
}
sum
} else {
var middle = (begin + end) / 2
val left = ForkJoinCalculation(begin, middle)
left.fork()
val right = ForkJoinCalculation(middle + 1, end)
right.fork()
left.join() + right.join()
}
}
}
测试代码
import com.oasisgames.ForkJoinCalculation
import org.junit.Test
import java.time.Duration
import java.time.Instant
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool
/**
*@author 没有梦想的java菜鸟
* @date 2022/02/23 11:17 上午
*/
class ForkJoinTest {
@Test
fun forkJoin() {
// 264409000
val start = Instant.now()
val pool = ForkJoinPool()
val calculation = ForkJoinCalculation(0, 10000000000L)
println(pool.invoke(calculation))
val end = Instant.now()
println(Duration.between(start, end).nano)
}
@Test
fun forTest() {
// 937329000
val start = Instant.now()
var sum = 0L
for (i in 0L..10000000000L) {
sum += i
}
println(sum)
val end = Instant.now()
println(Duration.between(start, end).nano)
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号