CSP模拟1
T1「Wdsr-2.5」琪露诺的算数游戏
题目描述
游戏概况
《琪露诺的算数游戏》(诨名“⑨牌”),是一款轻松快乐的多玩家卡牌回合制游戏。
注意:这里的规则与市面上的⑨牌规则不尽相同。由于⑨牌种类太多不大容易处理,所以这里的规则更类似于 \(\text{NEU}\) 游戏。
游戏中有 \(n\) 名玩家,围成一圈。一共会进行 \(m\) 轮。每个玩家初始时有 \(3\) 张手牌。游戏有一个 \(k\) 张牌的牌堆。在本题中,你可以认为不会出现牌堆抽完的情况(真的)。此外,根据该题给出的规则,你不需要考虑选手手牌的顺序。
为了简述游戏规则,你可以认为每一轮游戏中有一个整型变量(类似于 \(\text{int}\) 类型寄存器) \(p\) 。玩家打出的牌本质上是对 \(p\) 进行操作。
注:请注意下文中“局”、“轮”、“回合”的关系。本题你只会进行一局游戏,每局有 \(m\) 轮,每一轮会有若干回合,每一回合会有一名玩家出牌。
每一轮开始时,\(p\) 会被初始化为 \(0\) ,然后从初始玩家开始,按照顺时针顺序(\(1,2,3,\cdots n-1,n,1,2,\cdots\) ,逆时针同理),依次出牌。如果这是第一轮,那么初始玩家就是 \(1\) 号玩家。当某个玩家出完某张牌后,如果此时 \(p> 99\) ,视作该玩家成为该局的失败者;否则她就会立刻从牌堆顶部取出一张牌并进入到下一回合。失败者会丢失手上其余的两张牌,并从牌堆顶部依次摸三张牌放入自己的手牌中。同时,失败者会成为下一轮初始玩家。在一局游戏当中,牌堆里的牌只减不增。被使用的牌不会回到牌堆当中。
下面介绍该魔改版游戏的牌型。
基本牌
基本牌可以分为五类:加法牌、减法牌、乘法牌、除法牌、固定牌。
- 加法牌,一共有 \(7\) 种: \(A_{1},A_{2},A_{5},A_{9},A_{19},A_{49},A_{99}\) 。其中, \(A_x\) 的作用效果是,使 \(p\) 加上牌面上的数字。即 \(p\gets p+x\) 。
- 减法牌,一共有 \(3\) 种: \(B_{1},B_{9},B_{19}\) 。作用效果与加法牌类似,只不过会使 \(p\) 减去牌面上的数字。
- 乘法牌,一共只有 \(1\) 种: \(C_2\) 。它的作用效果是令 \(p\) 乘上对应的数字,即 \(p\gets p\times x\) 。
- 除法牌,同样只有 \(1\) 种: \(D_2\) 。会令 \(p\) 除以对应的数字,向下取整。即 \(p\gets \lfloor p\div x\rfloor\) 。
- 固定牌,一共有 \(3\) 种: \(E_{0},E_{49},E_{99}\) ,会将 \(p\) 直接设置为牌面上的数字。
解牌
解牌是可以使一名玩家跳过该回合,并附加一些特殊效果的一类牌。
- \(\tt{PASS}\) ,跳过你,转到下一个玩家。
- \(\tt{TURN}\) ,跳过你,出牌顺序反转(顺时针变为逆时针,逆时针变为顺时针。在下一轮游戏开始时会重置为顺时针)。
- \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) ,跳过你,然后给下一名玩家施加 \(\verb!"DOUBLE"!\) 效果,也即要出两张牌(先打一摸一,再打一摸一,需要保持全程总数不超过 \(99\) 才能保证不失败)。
\(\tt{DOUBLE}\) 效果的一些说明:如果你被施加了 \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) 的效果,但是你第一张出了解牌(三种解牌都可以),那么你就会立即解除 \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) 效果,跳过这一回合,并且将效果转移到下一名玩家。 \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) 效果不能叠加。
在输入文件中,卡牌名会形如 \(\colorbox{#f0f0f0}\verb!A1 A99 D2 PASS DOUBLE!\) 等等。
策略
这一部分将会讲述本题中所有玩家的运行逻辑。
如果无论怎么出都会失败,那么玩家就会随便打出一张牌并成为失败者(显然,打出哪张牌不会对游戏结局产生实质上的影响)。否则会有两种情形:
- 如果此时没有被施加 \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) 效果:
- 每名玩家会优先考虑普通牌,并且选择在不成为失败者的前提下使 \(p\) 变得尽可能大的那种方案(如果有多种方案可以使得 \(p\) 最大,那就会按照乘法牌、加法牌、减法牌、除法牌、固定牌的顺序优先选择。显然,同一类普通牌中的不同种类的牌不会使 \(p\) 产生相同的值)。
- 如果没有普通牌,或者出牌后会成为失败者,那么就考虑使用解牌。玩家会依次考虑手头是否有 \(\tt{PASS,TURN,DOUBLE}\) 牌。如果有,就打出这张牌。
- 如果被施加了 \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) 效果:
- 优先考虑使用解牌。依次考虑\(\tt{PASS,TURN,DOUBLE}\) 。如果有,就打出这张牌。
- 否则,选择在不成为失败者的前提下使 \(p\) 变得尽可能小的那种方案(如果有多种方案可以使得 \(p\) 最小,那就会按照除法牌、减法牌、加法牌、乘法牌、固定牌的顺序优先选择)。此时玩家会被解除 \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) 状态,于是她会按照情形 \(1\) 来决策。
输入格式
第一行三个正整数 \(n,m,k\) ,含义如题面所示。
接下来 \(n\) 行,每行四个字符串 \(name,card_1,card_2,card_3\) ,表示这名玩家的名称以及她的三张手牌。玩家名称仅由大小写英文字母组成,不包含空格,长度不超过 \(20\) 。
接下来一行, \(k\) 个字符串,按照从上至下的顺序描述牌堆里的牌。
详情可以参考输入样例。
输出格式
当新的一轮开始时,你需要输出: \(\colorbox{f0f0f0}\verb!Round XXX:!\) (其中,\(\verb!XXX!\) 表示这是第多少轮)。
每名玩家出牌时,如果她不是失败者,你需要输出: \(\colorbox{f0f0f0}\verb!XXX used YYY,now p=ZZZ.!\) (其中,\(\verb!XXX!\) 是玩家名; \(\verb!YYY!\) 是卡牌名; \(\verb!ZZZ!\) 是当前 \(p\) 的值)。
否则,当一名玩家成为失败者时,该轮结束。你要输出:\(\colorbox{f0f0f0}\verb!XXX lost the game.!\) (其中,\(\verb!XXX!\) 是玩家名)。
详情可以参考输出样例。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
2 1 10
JoesSR B9 A99 PASS
Cirno C2 D2 A49
E49 DOUBLE PASS A19 A49 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99
样例输出 #1
Round 1:
JoesSR used A99,now p=99.
Cirno used D2,now p=49.
JoesSR used E49,now p=49.
Cirno used C2,now p=98.
JoesSR used B9,now p=89.
Cirno used DOUBLE,now p=89.
JoesSR used PASS,now p=89.
Cirno lost the game.
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
3 2 25
Cirno A9 A19 B1
Reimu TURN A9 C2
Marisa DOUBLE D2 D2
A9 B9 C2 PASS PASS A9 A1 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99 A99
样例输出 #2
Round 1:
Cirno used A19,now p=19.
Reimu used C2,now p=38.
Marisa used D2,now p=19.
Cirno used A9,now p=28.
Reimu used A9,now p=37.
Marisa used C2,now p=74.
Cirno used A9,now p=83.
Reimu used B9,now p=74.
Marisa used A9,now p=83.
Cirno used A1,now p=84.
Reimu used PASS,now p=84.
Marisa used D2,now p=42.
Cirno used B1,now p=41.
Reimu used TURN,now p=41.
Cirno used PASS,now p=41.
Marisa used DOUBLE,now p=41.
Reimu lost the game.
Round 2:
Reimu used A99,now p=99.
Marisa lost the game.
提示
样例 1 说明
牌的使用情况都在输出样例中。这里仅说明每出一张牌后每名玩家当前手牌的情况。具体为什么要使用某张牌,可以参考题目描述。
注:初始回合以及第 \(2,4,6\) 回合都是 \(\text{JoesSR}\) 出牌;第 \(1,3,5,7\) 回合都是琪露诺出牌。值得注意的是,尽管第 \(5\) 回合琪露诺使用了 \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) ,但因为下一回合被 \(\tt{PASS}\) 了,所以第 \(7\) 回合仍然是琪露诺出牌。
此时琪露诺无论如何都会失败,于是琪露诺成为了失败者。
样例 3
见下发附件。
数据规模与约定
- 对于 \(30\%\) 的数据,仅包含普通牌,并且 \(n\le 3\) 。
- 对于另外 \(15\%\) 的数据,不包含 \(\tt{TURN}\) 牌和 \(\tt{PASS}\) 牌。
- 对于另外 \(15\%\) 的数据,不包含 \(\tt{DOUBLE}\) 牌。
- 对于 \(100\%\) 的数据, 满足 \(1\le n\le 30;1\le m\le 100;1\le k\le 3\times 10^5\) 。保证任何时候 \(|p|<10^4\) 。
参考资料
我码力太差了,凹了半天,在\(9G\)帮助下终于凹完了,
细节很多
下面总结一下出错的地方:
- 有\(DOUBLE\)和无\(DOUBLE\)的选择优先级是不一样的
- 注意初始化
- 像这种大模拟代码尽量越简洁越好,勤写注释,多用函数
- \(p\)有可能是负数,所以要注意取整问题,\(C++\)默认负数是向\(0\)取整,但我们并不想要这样
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e5+5;
int n,m,k,p,pai=1,cao=1;
char K[N][15],doub;
char mp[10]={'C','A','B','D','E','P','T','O'};
char mp1[10]={'D','B','A','C','E','P','T','O'};
bool lsd;
struct pp
{
string name;
char op[5][15];
void comp1()
{
char op1[5][15]={};
int cnt=1;
for(int k=0;k<8;k++)
{
// if(cnt==4)break;
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
// cout<<k<<" "<<mp[k]<< ' '<<op[i][2]<<" "<<endl;
if((k==7&&op[i][2]==mp[k]))
{
memcpy(op1[cnt],op[i],sizeof op[i]);
cnt++;
}else if(k!=7&&op[i][1]==mp[k]&&op[i][2]!='O')
{
memcpy(op1[cnt],op[i],sizeof op[i]);
cnt++;
}
}
}
memcpy(op,op1,sizeof op1);
}
void comp2()
{
char op1[5][15]={};
int cnt=1;
for(int k=0;k<8;k++)//按优先级比较
{
// if(cnt==4)break;
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
// cout<<k<<" "<<mp[k]<< ' '<<op[i][2]<<" "<<endl;
if((k==7&&op[i][2]==mp1[k]))//DOUBELE会与Dx冲突
{
memcpy(op1[cnt],op[i],sizeof op[i]);
cnt++;
}else if(k!=7&&op[i][1]==mp1[k]&&op[i][2]!='O')
{
memcpy(op1[cnt],op[i],sizeof op[i]);
cnt++;
}
}
}
memcpy(op,op1,sizeof op1);
}
}pl[35];
ll op(char *s)
{
ll tmp=0;
if(s[3]>='0'&&s[3]<='9')
{
tmp=(s[2]-'0')*10+(s[3]-'0');
}else tmp=(s[2]-'0');
if(s[1]=='A')
{
return p+tmp;
}else if(s[1]=='B')
{
return p-tmp;
}else if(s[1]=='C')
{
return p*2;
}else if(s[1]=='D'&&s[2]!='O')
{
return floor(1.0*p/2.0);//向下取整
}else if(s[1]=='E')
{
return tmp;
}else
{
if(s[1]=='D'&&s[2]=='O')return -1e9-1;//这里值不能太小,因为p可能为负数
if(s[1]=='P')return -1e9-2;
if(s[1]=='T')return -1e9-3;
}
return 0;
}
void getcard(int x)
{
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
cout<<pl[x].op[i]+1<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
ll work(int i)
{
int id=0;
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
int tmp=op(pl[i].op[j]);
if(tmp<-1e9)
{
id=j;
doub=pl[i].op[j][1];
break;
}
}
return id;
}
void get(int i,int id)//摸一张牌
{
memcpy(pl[i].op[id],K[pai],sizeof K[pai]);pai++;
pl[i].comp1();
}
void jd()//PASS情况不用管,DOUBLE情况要标记
{
if(doub)
{
if(doub=='T')
{
cao=-cao;
}
else if(doub=='D')
{
lsd=1;
}
doub=0;
}
}
int main()
{
// freopen("A.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("AA.out","w",stdout);
// cout<<"((("<<endl;
cin>>n>>m>>k;
int st=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>pl[i].name>>pl[i].op[1]+1>>pl[i].op[2]+1>>pl[i].op[3]+1;
pl[i].comp1();//排序
}
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)cin>>K[i]+1;
for(int rd=1;rd<=m;rd++)
{
printf("Round %d:\n",rd);
cao=1;p=0; //注意初始化
doub=0;//当前解牌
lsd=0;//是否有double效果
for(int i=st;;i+=cao)
{
if(i>n)i=1;
if(i==0)i=n;
// cout<<i<<endl;
// getcard(i);
ll ans=-1e9;
int id=0;
if(lsd)
{
// cout<<"*****"<<endl;
id=work(i);//先查找解牌
if(!id)
{
pl[i].comp2();
lsd=0; ans=1e9;
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
int tmp=op(pl[i].op[j]);
if(tmp>-1000000000ll&&tmp<=99&&tmp<ans)//注意这里是找最小值
{
ans=tmp;
id=j;
}
}
if(!id)//一定要注意判断输了的情况
{
st=i;
cout<<pl[i].name<<" lost the game."<<endl;
memcpy(pl[i].op[1],K[pai],sizeof K[pai]);pai++;
memcpy(pl[i].op[2],K[pai],sizeof K[pai]);pai++;
memcpy(pl[i].op[3],K[pai],sizeof K[pai]);pai++;
pl[i].comp1();
break;
}
if(id)p=ans;
// cout<<"&&&"<<ans<<endl;
cout<<pl[i].name<<" used "<<pl[i].op[id]+1<<",now p="<<p<<"."<<endl;
get(i,id);
}
else
{
cout<<pl[i].name<<" used "<<pl[i].op[id]+1<<",now p="<<p<<"."<<endl;
get(i,id); jd();
continue;
}
}
ans=-1e9; id=0;
// getcard(i);
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
ll tmp=op(pl[i].op[j]);
// cout<<tmp<<" "<<p<<" "<<pl[i].op[j]+1<<endl;
if(tmp>-1000000000ll&&tmp<=99&&tmp>ans)//正常先找普通牌,没有的话再找解牌
{
ans=tmp;
id=j;
}
}//common
if(id)p=ans;
if(!id)
{
id=work(i);
}//special
// cout<<id<<endl;
if(!id)
{
st=i;
cout<<pl[i].name<<" lost the game."<<endl;
memcpy(pl[i].op[1],K[pai],sizeof K[pai]);pai++;
memcpy(pl[i].op[2],K[pai],sizeof K[pai]);pai++;
memcpy(pl[i].op[3],K[pai],sizeof K[pai]);pai++;
pl[i].comp1();
break;
}
cout<<pl[i].name<<" used "<<pl[i].op[id]+1<<",now p="<<p<<"."<<endl;
get(i,id);
jd();
}
}
return 0;
}
造数据程序
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rand(a,b) (rand()%((b)-(a)+1)+(a))
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
string card[]={"","A1","A2","A5","A9","A19","A49","A99","B1","B9","B19","C2","D2","E0","E49","E99","PASS","TURN","DOUBLE"};
string name[]={"","Player1","Player2","Player3","Player4","Player5"};
int main(){
freopen("A.in","w",stdout);
srand(time(0));
int n=rand(2,5),m=1,k=3e5;
cout<<n<<" "<<m<<" "<<k<<"\n";
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<name[i]<<" ";
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++){
cout<<card[rand(1,18)]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
while(k--){
cout<<card[rand(1,18)]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
Minesweeper 1D
题面翻译
给定一个串,由 0,1,2,*,? 组成。求将?替换成其他字符中的任意一个,使原串合法的方案数。将*视为雷,数字就是数字,合法为扫雷地图的合法性。
PS:数字 \(i\) 表示以 \(i\) 为中心的九宫格中只有 \(i\) 个雷。如 2* 是非法的,而 *2* 是合法的。
题目描述
Game "Minesweeper 1D" is played on a line of squares, the line's height is 1 square, the line's width is $ n $ squares. Some of the squares contain bombs. If a square doesn't contain a bomb, then it contains a number from 0 to 2 — the total number of bombs in adjacent squares.
For example, the correct field to play looks like that: 001*2***101*. The cells that are marked with "*" contain bombs. Note that on the correct field the numbers represent the number of bombs in adjacent cells. For example, field 2* is not correct, because cell with value 2 must have two adjacent cells with bombs.
Valera wants to make a correct field to play "Minesweeper 1D". He has already painted a squared field with width of $ n $ cells, put several bombs on the field and wrote numbers into some cells. Now he wonders how many ways to fill the remaining cells with bombs and numbers are there if we should get a correct field in the end.
输入格式
The first line contains sequence of characters without spaces $ s_{1}s_{2}...\ s_{n} $ $ (1<=n<=10^{6}) $ , containing only characters "*", "?" and digits "0", "1" or "2". If character $ s_{i} $ equals "*", then the $ i $ -th cell of the field contains a bomb. If character $ s_{i} $ equals "?", then Valera hasn't yet decided what to put in the $ i $ -th cell. Character $ s_{i} $ , that is equal to a digit, represents the digit written in the $ i $ -th square.
输出格式
Print a single integer — the number of ways Valera can fill the empty cells and get a correct field.
As the answer can be rather large, print it modulo $ 1000000007 $ $ (10^{9}+7) $ .
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
?01???
样例输出 #1
4
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
?
样例输出 #2
2
样例 #3
样例输入 #3
**12
样例输出 #3
0
样例 #4
样例输入 #4
1
样例输出 #4
0
提示
In the first test sample you can get the following correct fields: 001**1, 001***, 001*2*, 001*10.
线性DP,设\(dp_{i,0/1/2}\),表示第\(i\)位的后一位(0不是雷,1是雷),\(2\)表示自身是雷
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+5,mod=1e9+7;
char s[N];int len,ans;
int dp[N][6];
int main()
{
// freopen("B.in","r",stdin);
cin>>s+1;
len=strlen(s+1);
dp[0][0]=1;dp[0][1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++)
{
if(s[i]=='?')
{
dp[i][2]+=dp[i-1][1]+dp[i-1][2];
dp[i][0]+=dp[i-1][0]+dp[i-1][2];
dp[i][1]+=dp[i-1][0]+dp[i-1][2];
}
else if(s[i]=='1')
{
dp[i][1]+=dp[i-1][0];
dp[i][0]+=dp[i-1][2];
}
else if(s[i]=='2')
{
dp[i][1]+=dp[i-1][2];
}
else if(s[i]=='*')
{
dp[i][2]+=dp[i-1][2]+dp[i-1][1];
}else if(s[i]=='0')
{
dp[i][0]+=dp[i-1][0];
}
dp[i][0]%=mod;dp[i][1]%=mod;dp[i][2]%=mod;
}
cout<<(dp[len][2]+dp[len][0])%mod<<endl;
return 0;
}
Description
已知两个数 x,yx,y 求有多少个正整数不能被 \(a\times x+b\times y,a\ge0,b\ge0a×x+b×y,a≥0,b≥0\) 表示
Input Format
一行两个整数表示 x,yx,y
Output Format
一行一个整数表示答案,若有无穷个数无法被表示,输出-1
Sample
样例输入
2 3
样例输出
1
Hint
对于全部测试点,\(1\le x,y\le10^81≤x,y≤10\)
8
子任务 1(10 分):\(1\le x,y\le10001≤x,y≤1000\)
子任务 2(20 分):\(|y-x|=1∣y−x∣=1\)
子任务 3(30 分):x,yx,y 互质
子任务 4(40 分):无特殊性质
首先子任务\(3\)的部分分很好拿
if(x>y)swap(x,y);
ll n=x-2;
ll ans=x-1+n*(n+1)/2;
然后我们发现如果两个数不互质,那么只能是\(lcm(x,y)\)的倍数,一定能过输出\(-1\)
在考虑两数互质时,
我们知到,若\(a_i\)构成模\(n\)的完系,\(k,m \in Z (m,n)=1_,\)则\(k+ma_i\),也
构成模\(n\)的完系.
我们可以考虑模\(b\)时什么时候\([1,b-1]\)出现,当一个余数第一次出现,以后一定可以出现
在互质的条件下,本题中\(x\)可以变相的写成\(k+ay\)的形式,那么\([1,y-1]\)都会从\(i\times (k+ay)\mod y\)中出现,出现的顺序不一样,但一定都会出现,那么第一次出现这个余数之前所有模\(y\)等于这个余数的数量和即为答案,即\(\sum_{i=1}^{y-1}\frac{ix}{y}\)
然后这是\(O(y)\)的复杂度,可以优化成\(O(1)\),就是把上面的式子化成\(ty=\sum ix-\sum (ix \mod y)\)
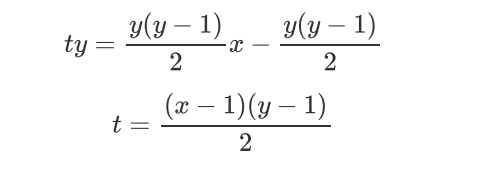
春节十二响
启发式合并
满足\(f_i<i\)所以倒序更新就行了
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6+5;
ll n,f[N],m[N],t[N],tot;
priority_queue <ll> q[N];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>m[i];
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)cin>>f[i];
for(int i=n;i>1;i--)
{
int x=i;int y=f[i];q[x].push(m[x]);tot=0;
if(q[x].size()>q[y].size())swap(q[x],q[y]);
while(!q[x].empty())
{
t[++tot]=max(q[x].top(),q[y].top());
q[x].pop();q[y].pop();
}
for(int j=1;j<=tot;j++)
{
q[y].push(t[j]);
}
}
ll ans=m[1];
while(q[1].size())
{
ans+=q[1].top();
q[1].pop();
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6+5;
ll n,f[N],m[N],t[N],tot;
priority_queue <ll> q[N];
vector <int> edge[N];
void merge(int x,int y)
{
tot=0;
if(q[x].size()>q[y].size())swap(q[x],q[y]);
while(!q[x].empty())
{
t[++tot]=max(q[x].top(),q[y].top());
q[x].pop();q[y].pop();
}
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)q[y].push(t[i]);
}
void dfs(int u)
{
for(auto to:edge[u])
{
dfs(to);
merge(to,u);//统一合并到根节点
}
q[u].push(m[u]);//一定要放最后,他不能与to放在一块
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>m[i];
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)cin>>f[i],edge[f[i]].push_back(i); //建边
dfs(1);
ll ans=0;
while(q[1].size())
{
ans+=q[1].top();
q[1].pop();
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号