TessorFlow学习 之 神经网络的构建
1.建立一个神经网络添加层
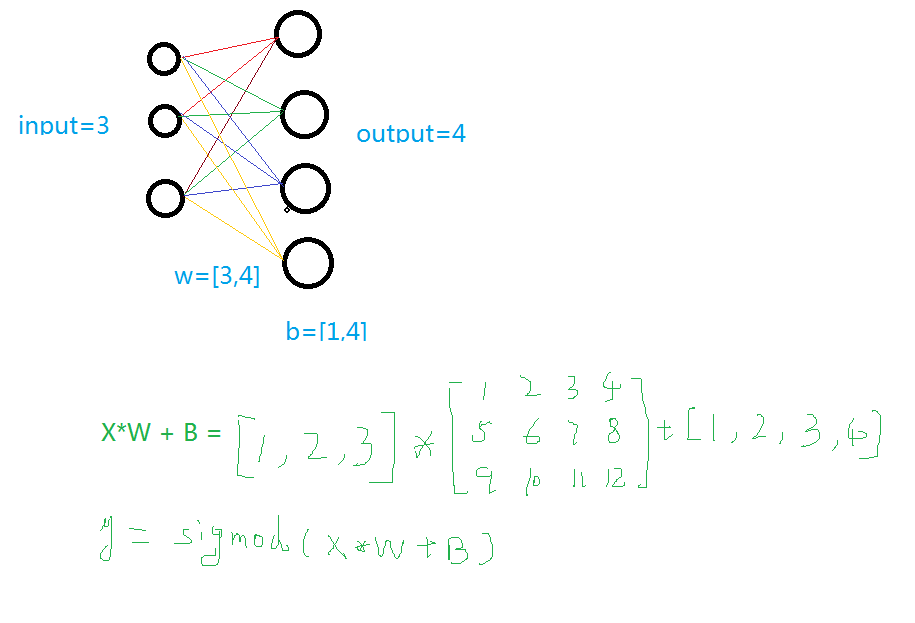
输入值、输入的大小、输出的大小和激励函数
学过神经网络的人看下面这个图就明白了,不懂的去看看我的另一篇博客
1 def add_layer(inputs , in_size , out_size , activate = None): 2 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]))#随机初始化 3 baises = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1)#可以随机但是不要初始化为0,都为固定值比随机好点 4 y = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + baises #matmul:矩阵乘法,multipy:一般是数量的乘法 5 if activate: 6 y = activate(y) 7 return y
2.训练一个二次函数
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 import numpy as np 3 4 def add_layer(inputs , in_size , out_size , activate = None): 5 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]))#随机初始化 6 baises = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1)#可以随机但是不要初始化为0,都为固定值比随机好点 7 y = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + baises #matmul:矩阵乘法,multipy:一般是数量的乘法 8 if activate: 9 y = activate(y) 10 return y 11 if __name__ == '__main__': 12 x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300,dtype=np.float32)[:,np.newaxis]#创建-1,1的300个数,此时为一维矩阵,后面转化为二维矩阵===[1,2,3]-->>[[1,2,3]] 13 noise = np.random.normal(0,0.05,x_data.shape).astype(np.float32)#噪声是(1,300)格式,0-0.05大小 14 y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise #带有噪声的抛物线 15 16 xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1]) #外界输入数据 17 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1]) 18 19 l1 = add_layer(xs,1,10,activate=tf.nn.relu) 20 prediction = add_layer(l1,10,1,activate=None) 21 22 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction),reduction_indices=[1]))#误差 23 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)#对误差进行梯度优化,步伐为0.1 24 25 sess = tf.Session() 26 sess.run( tf.global_variables_initializer()) 27 for i in range(1000): 28 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})#训练 29 if i%50 == 0: 30 print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))#查看误差

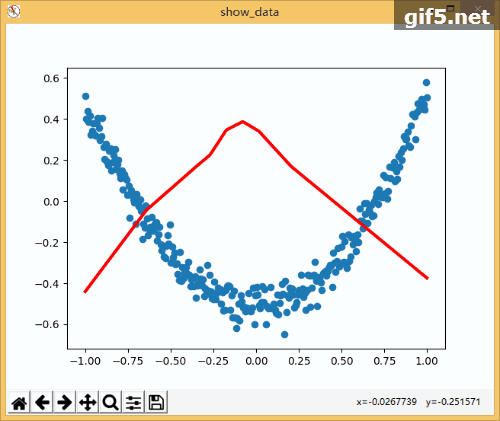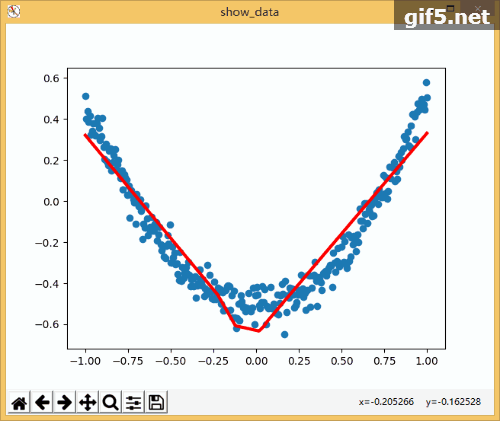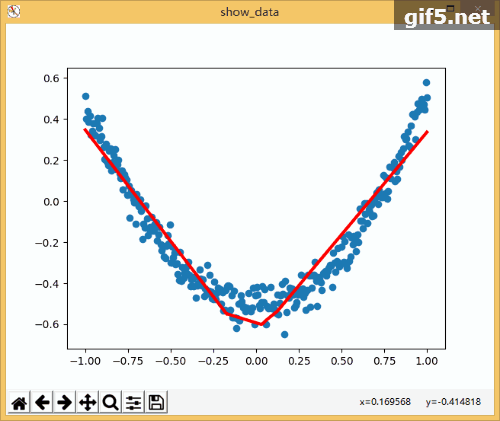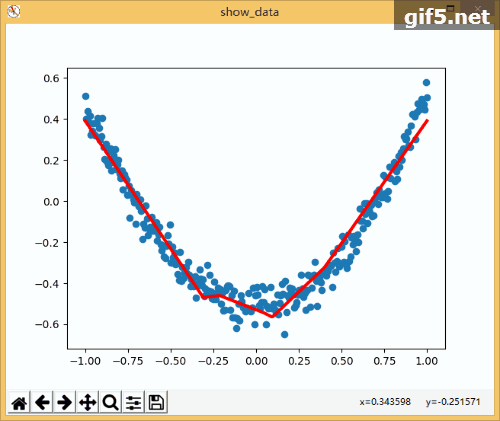
3.动态显示训练过程
显示的步骤程序之中部分进行说明,其它说明请看其它博客
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 5 def add_layer(inputs , in_size , out_size , activate = None): 6 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]))#随机初始化 7 baises = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1)#可以随机但是不要初始化为0,都为固定值比随机好点 8 y = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + baises #matmul:矩阵乘法,multipy:一般是数量的乘法 9 if activate: 10 y = activate(y) 11 return y 12 if __name__ == '__main__': 13 x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300,dtype=np.float32)[:,np.newaxis]#创建-1,1的300个数,此时为一维矩阵,后面转化为二维矩阵===[1,2,3]-->>[[1,2,3]] 14 noise = np.random.normal(0,0.05,x_data.shape).astype(np.float32)#噪声是(1,300)格式,0-0.05大小 15 y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise #带有噪声的抛物线 16 fig = plt.figure('show_data')# figure("data")指定图表名称 17 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 18 ax.scatter(x_data,y_data) 19 plt.ion() 20 plt.show() 21 xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1]) #外界输入数据 22 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1]) 23 24 l1 = add_layer(xs,1,10,activate=tf.nn.relu) 25 prediction = add_layer(l1,10,1,activate=None) 26 27 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction),reduction_indices=[1]))#误差 28 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)#对误差进行梯度优化,步伐为0.1 29 30 sess = tf.Session() 31 sess.run( tf.global_variables_initializer()) 32 for i in range(1000): 33 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})#训练 34 if i%50 == 0: 35 try: 36 ax.lines.remove(lines[0]) 37 except Exception: 38 pass 39 prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data}) 40 lines = ax.plot(x_data,prediction_value,"r",lw = 3) 41 print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))#查看误差 42 plt.pause(2) 43 while True: 44 plt.pause(0.01)
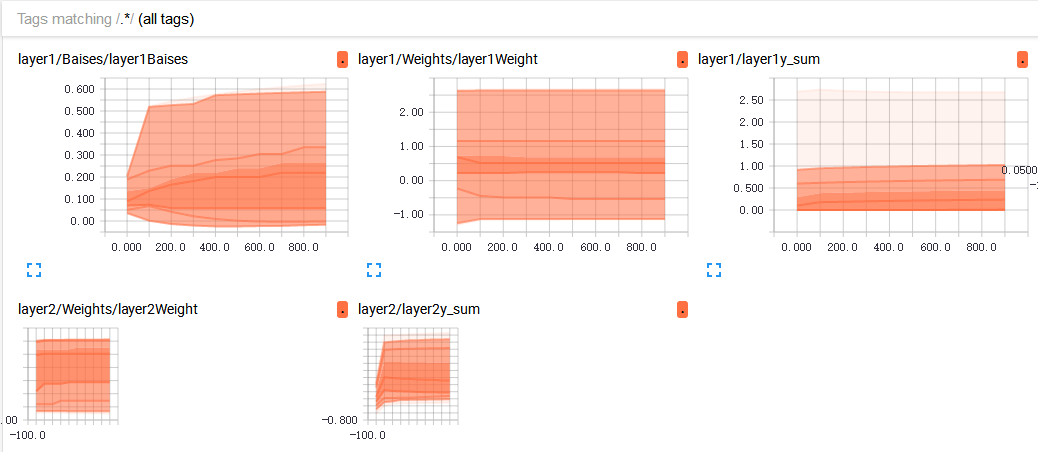
4.TensorBoard整体结构化显示
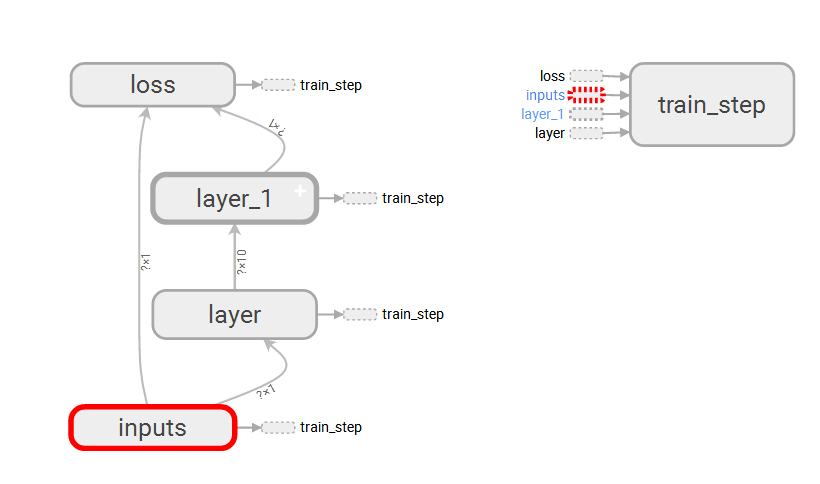
A.利用with tf.name_scope("name")创建大结构、利用函数的name="name"去创建小结构:tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name="x_data")
B.利用writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("G:/test/",graph=sess.graph)创建一个graph文件
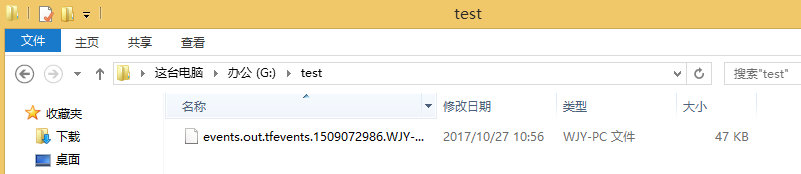
C.利用TessorBoard去执行这个文件
这里得注意--->>>首先到你存放文件的上一个目录--->>然后再去运行这个文件
tensorboard --logdir=test

5.TensorBoard局部结构化显示
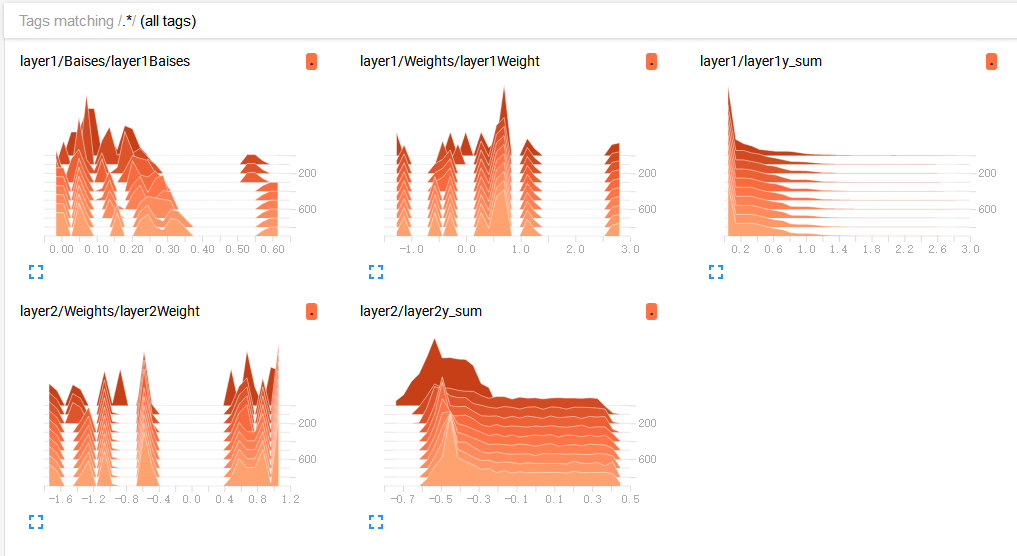
A. tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+"Weight",Weights):直方图显示
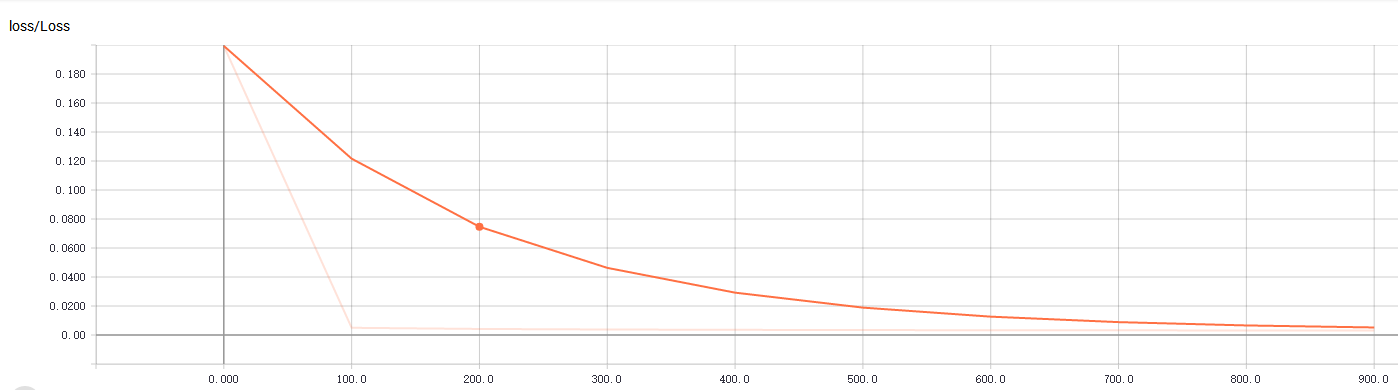
B. tf.summary.scalar("Loss",loss):折线图显示,loss的走向决定你的网络训练的好坏,至关重要一点
C.初始化与运行设定的图表
1 merge = tf.summary.merge_all()#合并图表 2 writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("G:/test/",graph=sess.graph)#写进文件 3 result = sess.run(merge,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data})#运行打包的图表merge 4 writer.add_summary(result,i)#写入文件,并且单步长50
完整代码及显示效果:
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 5 def add_layer(inputs , in_size , out_size , n_layer = 1 , activate = None): 6 layer_name = "layer" + str(n_layer) 7 with tf.name_scope(layer_name): 8 with tf.name_scope("Weights"): 9 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]),name="W")#随机初始化 10 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+"Weight",Weights) 11 with tf.name_scope("Baises"): 12 baises = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1,name="B")#可以随机但是不要初始化为0,都为固定值比随机好点 13 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+"Baises",baises) 14 y = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + baises #matmul:矩阵乘法,multipy:一般是数量的乘法 15 if activate: 16 y = activate(y) 17 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+"y_sum",y) 18 return y 19 if __name__ == '__main__': 20 x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300,dtype=np.float32)[:,np.newaxis]#创建-1,1的300个数,此时为一维矩阵,后面转化为二维矩阵===[1,2,3]-->>[[1,2,3]] 21 noise = np.random.normal(0,0.05,x_data.shape).astype(np.float32)#噪声是(1,300)格式,0-0.05大小 22 y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise #带有噪声的抛物线 23 fig = plt.figure('show_data')# figure("data")指定图表名称 24 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 25 ax.scatter(x_data,y_data) 26 plt.ion() 27 plt.show() 28 with tf.name_scope("inputs"): 29 xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name="x_data") #外界输入数据 30 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name="y_data") 31 l1 = add_layer(xs,1,10,n_layer=1,activate=tf.nn.relu) 32 prediction = add_layer(l1,10,1,n_layer=2,activate=None) 33 with tf.name_scope("loss"): 34 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction),reduction_indices=[1]))#误差 35 tf.summary.scalar("Loss",loss) 36 with tf.name_scope("train_step"): 37 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)#对误差进行梯度优化,步伐为0.1 38 39 sess = tf.Session() 40 merge = tf.summary.merge_all()#合并 41 writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("G:/test/",graph=sess.graph) 42 sess.run( tf.global_variables_initializer()) 43 for i in range(1000): 44 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})#训练 45 if i%100 == 0: 46 result = sess.run(merge,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data})#运行打包的图表merge 47 writer.add_summary(result,i)#写入文件,并且单步长50
 注意: 假设你的py文件中写了tf的summary,并且存放在了此目录下“D:\test\logs” 调出cmd,cd到D:\test,然后输入tensorboard –logdir=logs。一定要cd到logs这个文件夹的上一级,其他会出现No graph definition files were found.问题。
注意: 假设你的py文件中写了tf的summary,并且存放在了此目录下“D:\test\logs” 调出cmd,cd到D:\test,然后输入tensorboard –logdir=logs。一定要cd到logs这个文件夹的上一级,其他会出现No graph definition files were found.问题。
主要参考莫凡大大:https://morvanzhou.github.io/
可视化出现问题了,参考这位大神:http://blog.csdn.net/fengying2016/article/details/54289931
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:衣带渐宽终不悔,为伊消得人憔悴!
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得关注再下的公众号,同时在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!