《图像处理实例》 之 拓扑重建
拓扑重建
这是http://www.imagepy.org/的作者原创,我只是对其理解之后改进和说明,欢迎大家使用这个小软件!
第一个用Python写的小项目,不算自创的,大部分都是参考别人的,由于第一次用python写opencv遇到了无数的问题,最后也算完成了。
opencv的入门我就不写了,以前都学过差不多,在此记录一下基础!
基础操作
首先说一下python条件下用opencv,重点记录,不重点看文档就好!
1.如何创建一个空白图片
A.
1 test = np.array([[0,255,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]])
2 np.array([[0,255,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]],np.uint8)#千万别写成这种格式,他把格式也存进去了
B.
1 showImage = np.zeros((inputImage.shape[0],inputImage.shape[1],3),np.uint8)
C.
1 showImage = inputImage.copy()
2 showImage = cv2.cvtColor(showImage,cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
2.如何读写一个图片
A.
1 img[j,i] = 255#单通道读写
B.
1 #三通道读写
2 img[j,i,0]= 255
3 img[j,i,1]= 255
4 img[j,i,2]= 255
C.
1 img.itemset((10,10,2),100)#写入
2 img.item(10,10,2)#读
3.画图形
1 cv2.circle(showImage,(j+1,i+1), 5, (0,0,255), -1)#画圆注意圆心是X,Y
4.python大部分函数都有返回值
#python的函数貌似都有返回值 img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) ret2,img = cv2.threshold(img,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
5.
1 Shape of image is accessed by img.shape. It returns a tuple of number of rows, columns and channels
1 Total number of pixels is accessed by img.size:
1 Image datatype is obtained by img.dtype:
骨架提取
废话说了不少开始实战了:
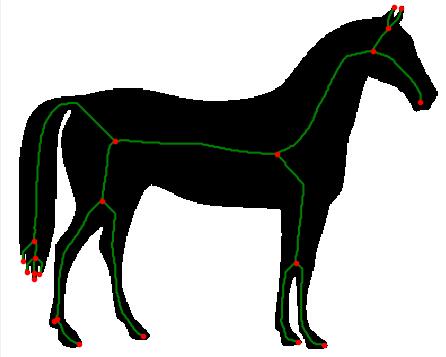
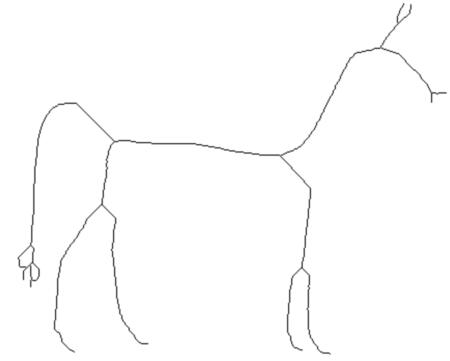
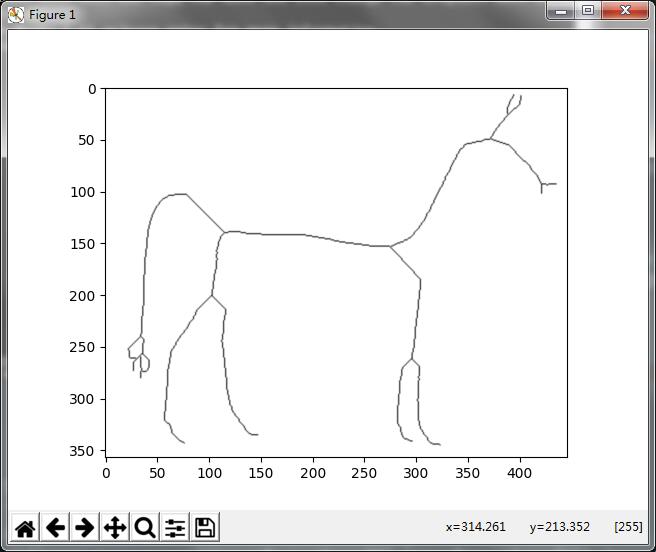
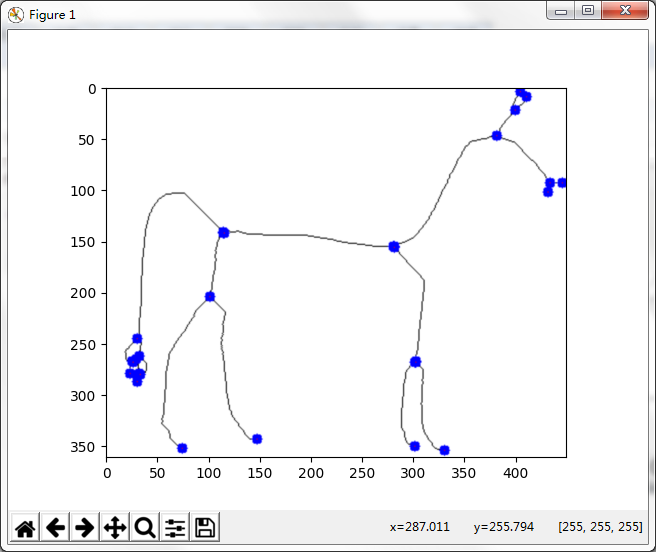
在此说明:
本程序和算法主要参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/xianglan/archive/2011/01/01/1923779.html写的非常好,大家初学直接看大佬的博客就行了。
本文后续拓普重建主要是:https://github.com/yxdragon/sknw没有看这位大佬的程序,但是他的思想帮助我很多。
因为得到别人帮助才有我自己的收获,所以乐于分享其他初学者!
以下是和大佬的对话,没经过本人同意所以打了马,非常乐于助人的大佬!

1 import cv2 2 import numpy as np 3 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 4 5 array = [0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,\ 6 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,\ 7 0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,\ 8 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,\ 9 1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,\ 10 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,\ 11 1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,\ 12 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,\ 13 0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,\ 14 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,\ 15 0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,\ 16 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,\ 17 1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,\ 18 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,\ 19 1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,\ 20 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0] 21 22 def Thin(image,array): 23 '''未改进算法''' 24 #midImage = image.copy() 25 for i in range(image.shape[0]-2): 26 for j in range(image.shape[1]-2): 27 if image[i+1,j+1] == 0: 28 a = [1]*9 #定义list[9] 29 for k in range(3): 30 for l in range(3): 31 a[k*3+l] = 0 if image[i+k,j+l]==0 else 1 32 sum = a[0]*1+a[1]*2+a[2]*4+a[3]*8+a[5]*16+a[6]*32+a[7]*64+a[8]*128 33 image[i+1,j+1] = array[sum]*255 34 return image 35 36 def HThin(image,array): 37 flag = True #如果该点被删除,跳过下一个点 38 midImage = image.copy() 39 for i in range(image.shape[0]-2): 40 for j in range(image.shape[1]-2): 41 if flag == False: 42 flag == True 43 else: 44 if image[i+1,j+1] == 0 and (image[i+1,j] != 0 or image[i+1,j+2] != 0):#左右都为黑点不处理 45 a = [1]*9 #定义list[9] 46 for k in range(3): 47 for l in range(3): 48 a[k*3+l] = 0 if midImage[i+k,j+l]==0 else 1 49 sum = a[0]*1+a[1]*2+a[2]*4+a[3]*8+a[5]*16+a[6]*32+a[7]*64+a[8]*128 50 midImage[i+1,j+1] = array[sum]*255 51 return midImage 52 def VThin(image,array): 53 flag = True #如果该点被删除,跳过下一个点 54 midImage = image.copy() 55 for i in range(image.shape[1]-2): 56 for j in range(image.shape[0]-2): 57 if flag == False: 58 flag == True 59 else: 60 if image[j+1,i+1] == 0 and (image[j,i+1] != 0 or image[j+2,i+1] != 0):#左右都为黑点不处理 61 a = [1]*9 #定义list[9] 62 for k in range(3): 63 for l in range(3): 64 a[k*3+l] = 0 if midImage[j+k,i+l]==0 else 1 65 sum = a[0]*1+a[1]*2+a[2]*4+a[3]*8+a[5]*16+a[6]*32+a[7]*64+a[8]*128 66 midImage[j+1,i+1] = array[sum]*255 67 return midImage 68 69 def wjy_Bone(inputImage,num=100): 70 '''改进算法''' 71 for i in range(num): 72 inputImage = VThin(HThin(inputImage,array),array) 73 return inputImage 74 75 def ThredImage(image,thred): 76 '''二值化图像''' 77 imageGray = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 78 midimage = np.zeros((imageGray.shape[0],imageGray.shape[1]),imageGray.dtype) 79 for i in range(imageGray.shape[0]): 80 for j in range(imageGray.shape[1]): 81 midimage[i,j] = 0 if imageGray[i,j] < int(thred) else 255 82 return midimage 83 84 def drawBone(inputImage): 85 #showImage = np.zeros((inputImage.shape[0],inputImage.shape[1],3),np.uint8) 86 showImage = inputImage.copy() 87 showImage = cv2.cvtColor(showImage,cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) 88 for i in range(inputImage.shape[0]-2): 89 for j in range(inputImage.shape[1]-2): 90 if inputImage[i+1,j+1] == 255 : continue 91 flag = -1 92 for J in range(3): 93 for K in range(3): 94 if inputImage[i+J,j+K] == 0: 95 flag += 1 96 if(flag==1 or flag>=3): 97 showImage = cv2.circle(showImage,(j+1,i+1), 5, (0,0,255), -1) 98 showImage[i+1,j+1,0] = 255 99 showImage[i+1,j+1,1] = 0 100 showImage[i+1,j+1,2] = 0 101 return showImage 102 103 if __name__ == '__main__': 104 img = cv2.imread("5.jpg") 105 #test = np.array([[0,255,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]) 106 #千万写写成np.array([[0,255,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]],np.uint8) 107 img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 108 ret2,img = cv2.threshold(img,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU) 109 #testImage = Thin(img,array) 110 #testImage = wjy_Bone(img) 111 testImage = drawBone(wjy_Bone(img,10)) 112 plt.imshow(testImage,cmap='gray',interpolation = 'bicubic') 113 plt.show() 114
轮廓追溯
第一步:
对骨架提取之后的图片变换成(0,1)图,骨架为0,背景为1
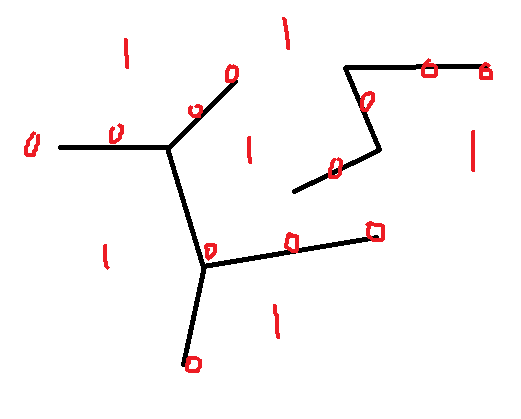
第二步:
提取骨架角点,方法在骨架提取的时候有说明。

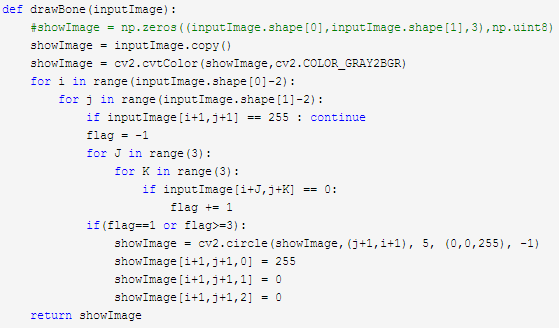
第三步:
在提取角点的基础上标记骨架图,对角点标记为2,对轮廓标记为1,对背景标记为0
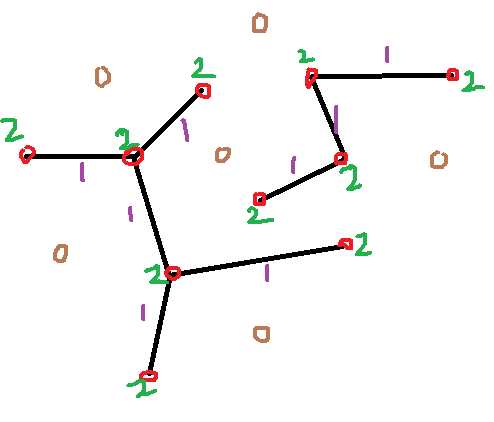
第四步:
对角点进行标记区分,10、11、12、13.......
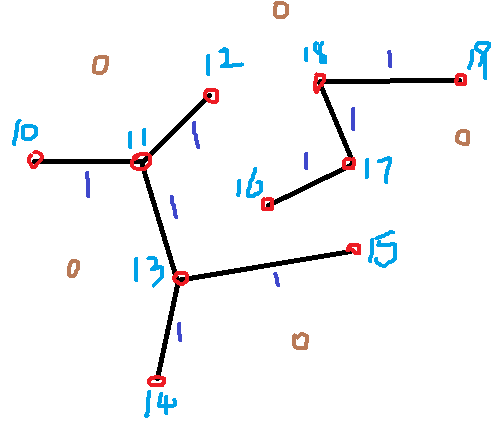
第五步:(此处是对程序的另行说明,是整个程序核心点)
对标号点进行路径追溯操作
先说本程序使用的方法:
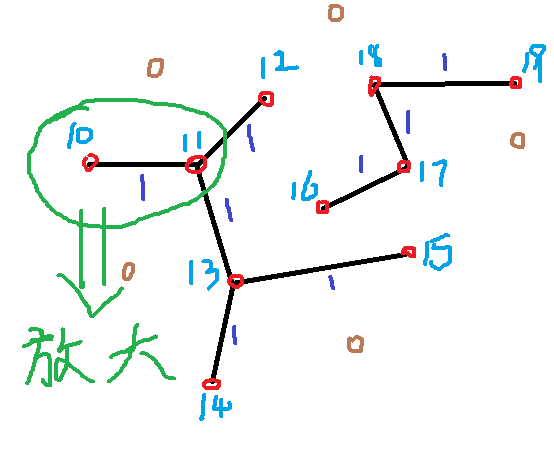
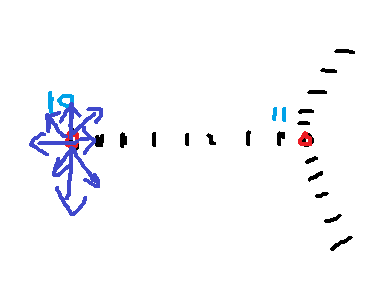
先从角点进行周围检测,找边缘
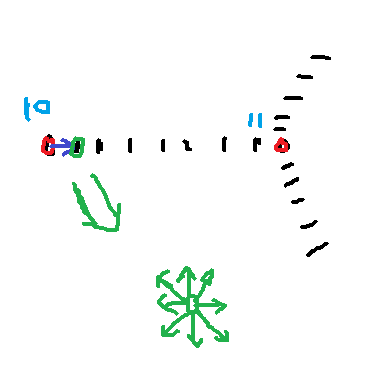
以找到的边界点为中心向四周寻找边界(角点)
在寻找路径的过程中把路径的点记录下来。
防止寻找重复,就是在寻找之后把路径清除。
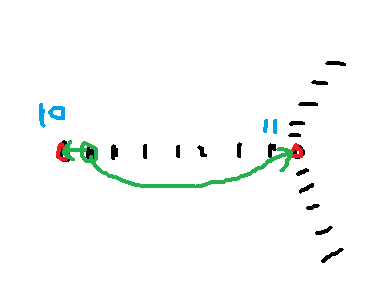
找的结果就是10和11这两个点
再说说我自己的想法:
我的想法比本程序的稍微简单一些,思路基本是相同的。就是直接以角点为基础向四周寻找角点。

第六步:
把得到的角点和路径存放到一个“图”中,这样使用的时候就非常方便了
PS:图我还没有学过,这里不过多说明。
上代码:
1 from cv2 import * 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import networkx as nx 5 from numba import jit 6 7 @jit# get neighbors d index 8 #得到领域的坐标(如果是二维直接算可以,但如果是三维就不一样了) 9 #这里是作者的改进适合多维图像,每句话的含义我没有弄懂 10 def neighbors(shape):#传进来的是二值图,所以维度是2 11 '''答案是:[-1921 -1920 -1919 -1 1 1919 1920 1921]''' 12 dim = len(shape) 13 block = np.ones([3]*dim) #维度为dim,数据3X3 14 block[tuple([1]*dim)] = 0 #取[1,1]位置为0 15 idx = np.where(block>0) #非零区域的位置信息 16 idx = np.array(idx, dtype=np.uint8).T #idx转换成矩阵,并且转置 17 idx = np.array(idx-[1]*dim) #全部值减一 18 acc = np.cumprod((1,)+shape[::-1][:-1]) #叠乘 19 return np.dot(idx, acc[::-1]) #点乘 20 21 @jit # my mark 22 #标记骨架图每个点的含义 23 #0:不是骨架 24 #1:骨架路径上的点 25 #2:端点或者角点 26 def mark(img): # mark the array use (0, 1, 2) 27 nbs = neighbors(img.shape) 28 img = img.ravel() 29 for p in range(len(img)): 30 if img[p]==0:continue 31 s = 0 32 '''判断中心点领域八个点的情况''' 33 for dp in nbs: 34 if img[p+dp]!=0:s+=1 35 if s==2:img[p]=1 36 else:img[p]=2 37 38 39 @jit # trans index to r, c... 40 # 坐标转换,图像被转换成一行处理,现在得把关键点转换回来(x,y) 41 def idx2rc(idx, acc): 42 rst = np.zeros((len(idx), len(acc)), dtype=np.int16) 43 for i in range(len(idx)): 44 for j in range(len(acc)): 45 rst[i, j] = idx[i] // acc[j] 46 idx[i] -= rst[i, j] * acc[j] 47 return rst 48 49 50 @jit # fill a node (may be two or more points) 51 # 标记节点,把节点打上不同的编码img.copy()=(2,2,2,2.....)----->>>>(10,11,12,13......) 52 # 并且把行坐标转换成(x,y)类型的坐标存放 53 def fill(img, p, num, nbs, acc, buf): 54 back = img[p] # 位置点的值存放 55 img[p] = num # 计数值 56 buf[0] = p # 位置点存放 57 cur = 0; 58 s = 1; 59 while True: 60 p = buf[cur] # 61 for dp in nbs: 62 cp = p + dp 63 if img[cp] == back: 64 img[cp] = num 65 buf[s] = cp 66 s += 1 67 cur += 1 68 if cur == s: break 69 return idx2rc(buf[:s], acc) 70 71 72 @jit # trace the edge and use a buffer, then buf.copy, if use [] numba not works 73 #路径跟踪找边缘 74 def trace(img, p, nbs, acc, buf): 75 '''这里的c1和c2是找的一条路径的两个端点,存放的端点标记>=10''' 76 c1 = 0 77 c2 = 0 78 newp = 0 #更新之后的位置 79 cur = 0 #计数,用来计算路径上点的数量 80 81 b = p==97625 #b = (p==97625) 82 #while找的是一条路径(具体说明请看附图) 83 while True: 84 buf[cur] = p#位置存储 85 img[p] = 0 #当前位置置0(搜索过得路径置0,防止重复搜索) 86 cur += 1 #光标加一(移动一个位置) 87 for dp in nbs: 88 cp = p + dp 89 if img[cp] >= 10:#判断是否为端点 90 if c1==0: c1=img[cp]#找的第一个端点() 91 else: c2 = img[cp]# 92 if img[cp] == 1: 93 newp = cp 94 p = newp 95 if c2!=0:break 96 return (c1-10, c2-10, idx2rc(buf[:cur], acc)) 97 98 99 @jit # parse the image then get the nodes and edges 100 # 找节点和边缘 101 def parse_struc(img): 102 nbs = neighbors(img.shape) 103 acc = np.cumprod((1,) + img.shape[::-1][:-1])[::-1] # (1,img.shape[0]) 104 img = img.ravel() 105 pts = np.array(np.where(img == 2))[0] 106 buf = np.zeros(20, dtype=np.int64) 107 num = 10 108 nodes = [] 109 for p in pts: 110 if img[p] == 2: 111 nds = fill(img, p, num, nbs, acc, buf) 112 num += 1 113 nodes.append(nds) 114 115 buf = np.zeros(10000, dtype=np.int64) 116 edges = [] 117 # 这个for循环是找一个点上对应的多个路径 118 for p in pts: 119 for dp in nbs: 120 if img[p + dp] == 1: # 找路径,img路径点值为1 121 edge = trace(img, p + dp, nbs, acc, buf) 122 edges.append(edge) 123 return nodes, edges 124 125 126 # use nodes and edges build a networkx graph 127 #将建立的节点和路径存放到NX的图中 128 def build_graph(nodes, edges): 129 graph = nx.Graph() 130 for i in range(len(nodes)): 131 graph.add_node(i, pts=nodes[i], o=nodes[i].mean(axis=0)) 132 for s,e,pts in edges: 133 l = np.linalg.norm(pts[1:]-pts[:-1], axis=1).sum() 134 graph.add_edge(s,e, pts=pts, weight=l) 135 return graph 136 #建立一个图 137 def build_sknw(ske): 138 mark(ske) 139 nodes, edges = parse_struc(ske.copy()) 140 return build_graph(nodes, edges) 141 #画出一个'图' 142 # draw the graph 143 def draw_graph(img, graph): 144 for idx in graph.nodes(): 145 pts = graph.node[idx]['pts'] 146 img[pts[:,0], pts[:,1]] = 255 147 for (s, e) in graph.edges(): 148 pts = graph[s][e]['pts'] 149 img[pts[:,0], pts[:,1]] = 128 150 151 array = [0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1, 152 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1, 153 0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1, 154 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1, 155 1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0, 156 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0, 157 1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1, 158 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0, 159 0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1, 160 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1, 161 0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1, 162 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0, 163 1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0, 164 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0, 165 1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0, 166 1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0] 167 168 @jit#横向细化 169 def HThin(image,array): 170 flag = True #如果该点被删除,跳过下一个点 171 midImage = image.copy() 172 for i in range(image.shape[0]-2): 173 for j in range(image.shape[1]-2): 174 if flag == False: 175 flag = True 176 else: 177 if image[i+1,j+1] == 0 and (image[i+1,j] != 0 or image[i+1,j+2] != 0):#左右都为黑点不处理 178 a = [0]*9 #定义list[9] 179 for k in range(3): 180 for l in range(3): 181 a[k*3+l] = 0 if midImage[i+k,j+l]==0 else 1 182 sum = a[0]*1+a[1]*2+a[2]*4+a[3]*8+a[5]*16+a[6]*32+a[7]*64+a[8]*128 183 midImage[i+1,j+1] = array[sum]*255 184 return midImage 185 @jit#纵向细化 186 def VThin(image,array): 187 flag = True #如果该点被删除,跳过下一个点 188 midImage = image.copy() 189 for i in range(image.shape[1]-2): 190 for j in range(image.shape[0]-2): 191 if flag == False: 192 flag = True 193 else: 194 if image[j+1,i+1] == 0 and (image[j,i+1] != 0 or image[j+2,i+1] != 0):#左右都为黑点不处理 195 a = [0]*9 #定义list[9] 196 for k in range(3): 197 for l in range(3): 198 a[k*3+l] = 0 if midImage[j+k,i+l]==0 else 1 199 sum = a[0]*1+a[1]*2+a[2]*4+a[3]*8+a[5]*16+a[6]*32+a[7]*64+a[8]*128 200 midImage[j+1,i+1] = array[sum]*255 201 return midImage 202 @jit#横向和纵向合并 203 def wjy_Bone(inputImage,num=100): 204 '''改进算法''' 205 for i in range(num): 206 inputImage = VThin(HThin(inputImage,array),array) 207 return inputImage 208 @jit#骨架提取 209 def drawBone(inputImage): 210 #showImage = np.zeros((inputImage.shape[0],inputImage.shape[1],3),np.uint8) 211 showImage = inputImage.copy() 212 showImage = cvtColor(showImage,COLOR_GRAY2BGR) 213 for i in range(inputImage.shape[0]-2): 214 for j in range(inputImage.shape[1]-2): 215 if inputImage[i+1,j+1] > 0 : continue 216 flag = -1 217 for J in range(3): 218 for K in range(3): 219 if inputImage[i+J,j+K] == 0: 220 flag += 1 221 if(flag==1 or flag>=3): 222 showImage = circle(showImage,(j+1,i+1), 5, (0,0,255), -1) 223 showImage[i+1,j+1,0] = 255 224 showImage[i+1,j+1,1] = 0 225 showImage[i+1,j+1,2] = 0 226 return showImage 227 228 if __name__ == '__main__': 229 img = imread('5.jpg') 230 img = cvtColor(img,COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 231 ret2, img = threshold(img, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY | THRESH_OTSU) 232 #wjy2 = drawBone(wjy_Bone(img, num = 500)) 233 img = wjy_Bone(img,num=500).astype(np.uint16)#细化之后从uint8转换到uint16 234 img = np.where(img > 0, np.uint16(img/255),0) 235 img = np.where(img > 0, img - 1 , img + 1) 236 graph = build_sknw(img)#这里传进来的图像数值为(0 or 1) ,类型是uint16 237 238 plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray') 239 for (s, e) in graph.edges(): 240 ps = graph[s][e]['pts'] 241 plt.plot(ps[:, 1], ps[:, 0], 'green') 242 243 node, nodes = graph.node, graph.nodes() 244 ps = np.array([node[i]['o'] for i in nodes]) 245 plt.plot(ps[:, 1], ps[:, 0], 'r.') 246 plt.title('Build Graph') 247 plt.show()
不是太完美的图,应该是细化出问题了
推广一下大佬的开源项目:http://www.imagepy.org/开源的精神值得我们学习,问问题的时候尽量发个红包,不在多少在心意。
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/sunny2038/article/details/9080047 (基础操作)
http://opencv-python-tutroals.readthedocs.io/en/latest/py_tutorials/py_core/py_basic_ops/py_basic_ops.html#basic-ops (英文文档)
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:衣带渐宽终不悔,为伊消得人憔悴!
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得关注再下的公众号,同时在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!

