基本配置
一、创建django程序
- 终端命令:django-admin startproject sitename
- IDE创建Django程序时,本质上都是自动执行上述命令
其他常用命令:
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0
python manage.py startapp appname
python manage.py syncdb(1.7版本后不用)
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py createsuperuser
二、程序目录
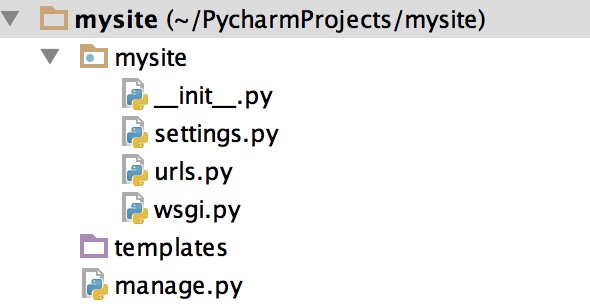
三、配置文件
1、数据库
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', 'NAME':'dbname', 'USER': 'root', 'PASSWORD': 'xxx', 'HOST': '', 'PORT': '', }} |
2、模版
|
1
2
3
|
TEMPLATE_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'templates'), ) |
3、静态文件
|
1
2
3
|
STATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static'), ) |
路由系统
1、每个路由规则对应一个view中的函数
|
1
2
3
|
url(r'^index/(\d*)', views.index),url(r'^manage/(?P<name>\w*)/(?P<id>\d*)', views.manage),url(r'^manage/(?P<name>\w*)', views.manage,{'id':333}), |
2、根据app对路由规则进行一次分类
|
1
|
url(r'^web/',include('web.urls')), |
django中的路由系统和其他语言的框架有所不同,在django中每一个请求的url都要有一条路由映射,这样才能将请求交给对一个的view中的函数去处理。其他大部分的Web框架则是对一类的url请求做一条路由映射,从而是路由系统变得简洁。
通过反射机制,为django开发一套动态的路由系统Demo: 点击下载
模板
1、模版的执行
模版的创建过程,对于模版,其实就是读取模版(其中嵌套着模版标签),然后将 Model 中获取的数据插入到模版中,最后将信息返回给用户。
 View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code2、模版语言
模板中也有自己的语言,该语言可以实现数据展示
- {{ item }}
- {% for item in item_list %} <a>{{ item }}</a> {% endfor %}
forloop.counter
forloop.first
forloop.last - {% if ordered_warranty %} {% else %} {% endif %}
- 母板:{% block title %}{% endblock %}
子板:{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block title %}{% endblock %} - 帮助方法:
{{ item.event_start|date:"Y-m-d H:i:s"}}
{{ bio|truncatewords:"30" }}
{{ my_list|first|upper }}
{{ name|lower }}
3、自定义simple_tag
a、在app中创建templatetags模块
b、创建任意 .py 文件,如:xx.py
c、在使用自定义simple_tag的html文件中导入之前创建的 xx.py 文件名
|
1
|
{% load xx %} |
d、使用simple_tag
|
1
2
|
{% my_simple_time 1 2 3%}{% my_input 'id_username' 'hide'%} |
e、在settings中配置当前app,不然django无法找到自定义的simple_tag



