IO in JAVA
java io 涉及应用程序的网络通信 or 文件读取. 采用了装饰者模式可以为不同的流添加不同的功能.
java io提供了 BIO/NIO/AIO的支持
java Netty
IO stream
- inputSream InputStreamReader BufferedReader
private String getStream(String url){
try {
InputStream in = new URL(url).openStream();
InputStreamReader isr= new InputStreamReader(in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String results= "";
String newLine="";
while((newLine=br.readLine())!=null) {
results += newLine + "\n";
}
return results;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String URL = "http://www.baidu.com";
CTest test= new CTest();
System.out.println(test.getStream(URL));
}
}
- data inputstream(与机器无关的方式读取数据), BufferedInputStream, PipedInputStream, PrintStream
Unix IO
同步IO: 阻塞式IO 非阻塞式IO IO复用 信号驱动IO
异步IO
同步/异步=>操作系统在IO操作完成后不会主动通知进程
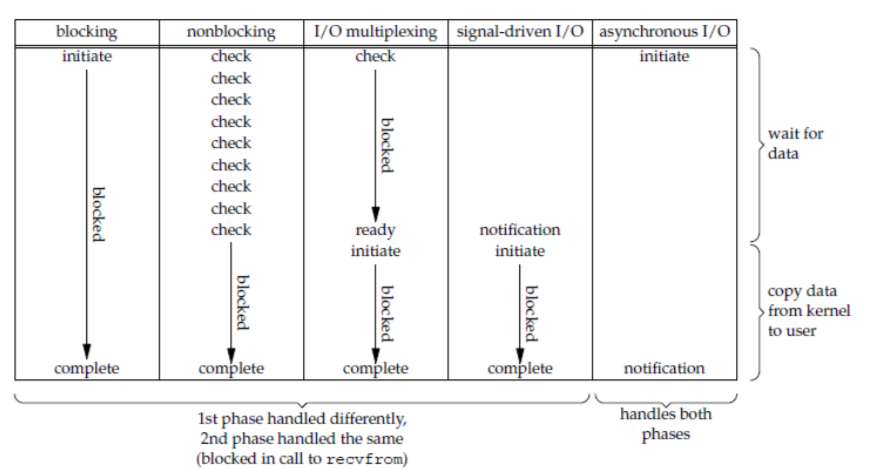
java IO
客户端,服务端通信的过程中 IO方式的判定主要是看 accept()的 阻塞or not, 异步or同步, accept相对读写操作更耗时
BIO
客户端使用socket 服务端使用serverSocket
可以在服务端使用线程池技术 进行伪异步的模拟
NIO
同步 非阻塞(不会阻塞在单个channel上)
面向块的IO 使用了channel Buffer
其中Buffer 状态变量有 capacity position limit, 读写转换的时候要使用 flip()和clean() 方法.
使用Selector可以通过轮询的方式监听多个channel上的事件(非阻塞)
Buffer操作
mark position limit capacity指针
写入的时候 mark=-1 position=下一个写入的位置 limit=capacity
读取的时候 position=读取的地方 limit=数据最大的位置
flip=> 重新读取已经读取的地方(rewind+limit<=position) or 写模式切换到读模式
rewind=> 重读缓冲区(重置 position和mark)
clear() or compact() 读模式切换到写模式(limit=0和position=cap)
socketchannel和socket的区别
Socket在java.net包中,而SocketChannel在java.nio包中
Socket是阻塞连接(当然我们可以自己实现非阻塞),SocketChannel可以设置非阻塞连接。 (configureBlocking(false)😉
Selector :为ServerSocketChannel监控接收客户端连接就绪事件, 为SocketChannel监控连接服务器读就绪和写就绪事件
SelectionKey :代表ServerSocketChannel及SocketChannel向Selector注册事件的句柄。当一个
SelectionKey对象位于Selector对象的selected-keys集合中时,就表示与这个SelectionKey对象相关的事件发生了。 =>可以通过key取到socketchannel, key使用完必须手动清除
实例
主要三要素 selector channel buffer
// Server
public class Server {
static final int port=8888;
static final String IP="localhost";
static String readFromSocket(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws IOException{
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
StringBuilder data=new StringBuilder();
//可能需要多次读写 因为开的buffer大小有限
while(true){
buffer.clear();
int n=socketChannel.read(buffer);
if(n==-1) break;
buffer.flip();
int limit=buffer.limit();
char[] dst= new char[limit];
for(int i=0;i<limit;++i){
dst[i]=(char)buffer.get(i);
}
data.append(dst);
buffer.clear();
}
return data.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
Selector selector= Selector.open();){
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(IP,port));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);//监听的channel为非阻塞的
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(true){
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> keys=selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator=keys.iterator();
while(keyIterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key=keyIterator.next();
if(key.isAcceptable()){
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel1=(ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
// accpet过程=> 与AIO不同的是还是要自己处理or开线程处理(类比从内核复制到用户空间 需要cpu参与)
SocketChannel socketChannel=serverSocketChannel.accept();//阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//同一个channel可能有多个selectionkey 一旦监听到就加selectionkey入keys 处理完必须移除
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(key.isReadable()){
SocketChannel socketChannel= (SocketChannel) key.channel();
System.out.println(readFromSocket(socketChannel));
socketChannel.close(); //短链接 每次读完都关闭 需要重新连接
}
keyIterator.remove();//只会移除selectionkey 不会移除channel
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//channel+buffer==带buffer的socket
Socket socket= new Socket("localhost",8888);
OutputStream out=socket.getOutputStream();
String s="hello world111";
out.write(s.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
out.close();
}
}
Reactor模型
事件驱动模型+将业务处理和IO分离+并发读写(线程池)

异步IO
JAVA AIO框架在windows下使用windows IOCP技术,在Linux下使用epoll多路复用IO技术模拟异步IO=> jdk1.7实现了异步非阻塞 NIO2(AIO)
Proactor模型
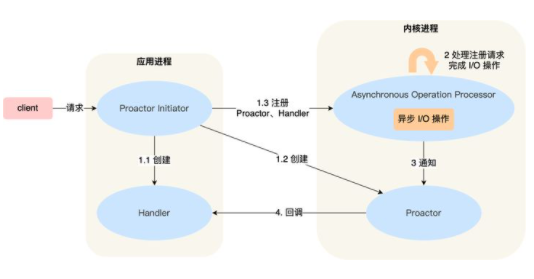
主要的api
使用了AsynchronousSocketChannel, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel 异步通道
java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler<V,A>事件处理接口 异步操作回调
java.util.concurrent.Future 对象 可以通过Future.get()实现阻塞回调
AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(ExecutorService executor,int initialSize);可以指定异步IO以及回调的线程池(Proactor)
基于Future的AIO
//client
public class ClientOnFuture {
static final int port=10000;
static final String IP="localhost";
static ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel=AsynchronousSocketChannel.open()){
// 异步 connect
Future<Void> connect =socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(IP,port));
Void avoid =connect.get();
//null表示连接成功
if(avoid==null){
//BUffer.wrap 用buffer包装底层的数组
Future<Integer> write=socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("客户端: 连接成功!".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
Integer write_out=write.get();
System.out.println("服务器接受的长度: "+write_out);
//客户端操作=> 读取服务端的数据 并 随机发送下一次信息
//接受数据
while(socketChannel.read(buffer).get()!=-1){
buffer.flip();
CharBuffer decode= Charset.defaultCharset().decode(buffer);
System.out.println(decode.toString());
if(buffer.hasRemaining()){
buffer.compact();
}else{
buffer.clear();
}
//继续写入
int r = new Random().nextInt(10);
if (r == 5) {
System.out.println("客户端关闭!");
break;
} else {
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(("客户端发送的数据:" + r).getBytes())).get();
}
}
}else{
System.out.println("无法建立连接!!");
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//server
public class ServerOnFuture {
static final int port=10000;
static final String IP="localhost";
static ByteBuffer buffer =ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//try-with-resources
try(AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()){
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(IP,port));
while(true){
//Future实现阻塞异步IO=> accept read write ...
Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> channelFuture=serverSocketChannel.accept();
//可以利用线程池实现多客户端并发
try(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel= channelFuture.get()){
//服务端操作=> 接受客户端数据 再返回给客户端
while(socketChannel.read(buffer).get()!=-1){
buffer.flip();//写转换成读
//多次读取buffer需要 复制一个新的buffer(两个的buffer会操纵同一个底层的数组)
ByteBuffer duplicate = buffer.duplicate();
CharBuffer decode = Charset.defaultCharset().decode(duplicate);
System.out.println("收到客户端数据: "+decode);
//写回数据
socketChannel.write(buffer).get();
//清理buffer 读转换成写
if(buffer.hasRemaining()){
buffer.compact();
}else{
buffer.clear();
}
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
基于Callback的AIO
//client
public class Client {
static final int PORT = 10000;
static final String IP = "localhost";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel= AsynchronousSocketChannel.open()){
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(IP, PORT),null,
new CompletionHandler<Void,Void>() {
@Override
public void completed(Void result, Void attachment) {
//发送
int r = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(("客户端信息: "+String.valueOf(r)).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))).get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//接受 返回信息
//HeapByteBuffer和DirectByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
try {
socketChannel.read(buffer).get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(Charset.defaultCharset().decode(buffer).toString());
//阻塞异步代码
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//退出 客户端
System.out.println("客户端退出");
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
System.out.println("连接失败!");
}
});
System.in.read();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//server
public class Server {
static final int port=10000;
static final String IP="localhost";
//channel group=> channel的共享资源
static AsynchronousChannelGroup threadGroup=null;
static ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
threadGroup=AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(executorService,5);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
try(AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(threadGroup)){
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(IP,port));
//accept(A, completionHandler<R,A> )-> R
serverSocketChannel.accept(serverSocketChannel, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel result, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel attachment) {
System.out.println("aaaaa");
//并发连接
attachment.accept(attachment,this);
//接受
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
try{
while(result.read(buffer).get()!=-1){
buffer.flip();
ByteBuffer duplicate=buffer.duplicate();
CharBuffer decode= Charset.defaultCharset().decode(duplicate);
System.out.println(decode.toString());
//发送
result.write(buffer).get();
if(buffer.hasRemaining()){
buffer.compact();
}else
buffer.clear();
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//关闭与 客户端的连接
try {
result.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel attachment) {
attachment.accept(attachment, this);
System.out.println("连接失败!");
}
});
//阻塞异步代码
threadGroup.awaitTermination(Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
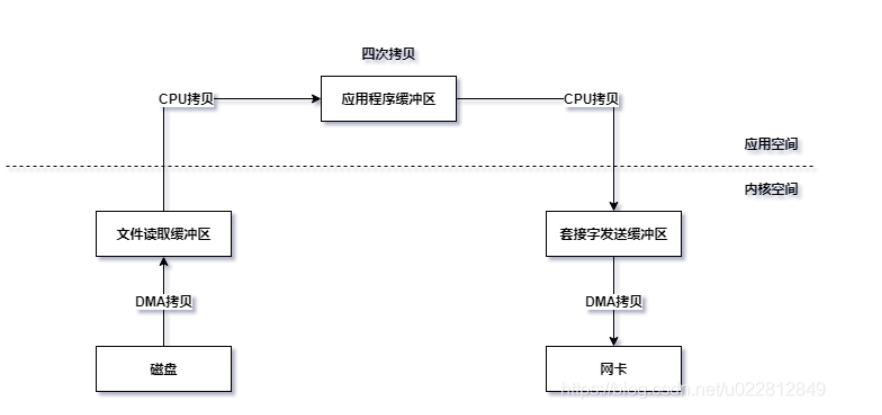
零拷贝
java中的零拷贝主要是基于 linux提供的零拷贝api=>mmap内存映射, sendfile 可以减少不必要的拷贝次数
正常的四次拷贝
虽然使用了DMA来代替CPU的中断请求, 但是存在多余的拷贝操作
使用mmap内存映射
使用了MappedByteBuffer缓冲区, channel.map(mode,begin,length);

/**
* nio之mmap
*/
public class MappedByteBufferDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("MappedByteBufferDemo.java");
System.out.println("file size:" + f.length());
//直接将channel的缓冲映射到用户缓冲区 使用MappedByteBuffer
//buffer.get() 只拷贝一次
MappedByteBuffer byteBuffer = new RandomAccessFile(f, "r").getChannel().map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, f.length());
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) f.length()];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
byteBuffer.clear();
}
}
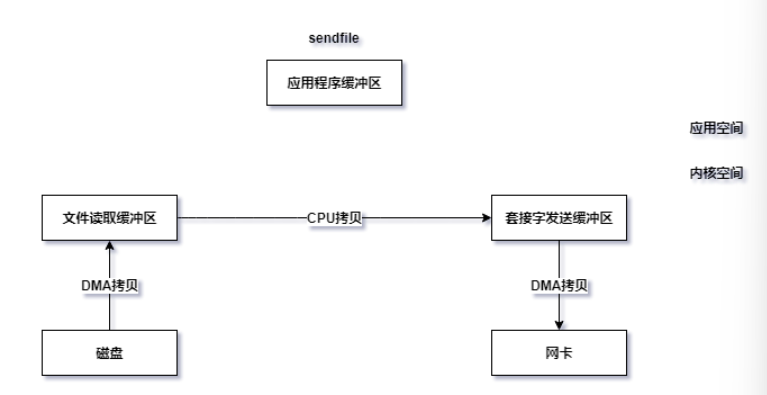
使用sendfile方式
Java NIO中提供的FileChannel拥有transferTo和transferFrom两个方法,可直接把FileChannel中的数据拷贝到另外一个Channel
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File srcFile = new File("FileChannelDemo.java");
File descFile = new File("FileChannelDemo2.java");
System.out.println("file size:" + srcFile.length());
FileChannel srcFileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(srcFile, "r").getChannel();
FileChannel descFileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(descFile, "rw").getChannel();
//channel与channel的直接交互
srcFileChannel.transferTo(0, srcFile.length(), descFileChannel);
}
Netty的实现
接收和发送ByteBuffer采用直接内存,使用堆外直接内存进行Socket读写,不需要进行字节缓冲区的二次拷贝.
支持buffer的wrap和slice
文件传输上使用了sendfile
Netty框架
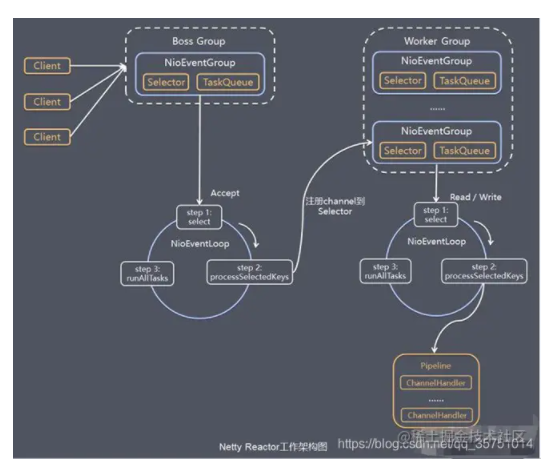
Netty维护了两组线程池=>(Boss Group 和 Worker Group).
其中每个Group都存在多个的NIOEVENTLOOP, 使用一个线程+selector+TaskQueue进行多路复用.
使用了Channel作为数据传输流,每一个channel都包含一个channelPipeline(channelHandle+channelHandleContext)
常用的channel有 NioSocketChannel NioServerSocketChannel(异步非阻塞) 虽然底层调用的java.NIO2的channel是同步非阻塞的.
channelPipeline中的handler有两种=>ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(入站处理器)、ChannelOutboundHandler(出站处理器). 入站对应从java NIO channel到Netty Channel(head->tail); 出站对应从Netty到底层.
样例
实现一个自带编码器的客户端/服务端 通信例子
//server
// 用于socketchannel的创建 => workgroup对应的channel的初始化类
class MyServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>{
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//netty的channel可以看作是 java.NIO的channel+pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline=socketChannel.pipeline();
//加入入站的decoder和出站的encoder
pipeline.addLast(new MyByteToLongDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(new MyLongToByteEncoder());
//加入handler 处理业务逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new MyHandler());
}
}
class MyByteToLongDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder{
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception {
System.out.println("入站的decoder被调用");
if(byteBuf.readableBytes()>=8){
// System.out.println("aaaa");
list.add(byteBuf.readLong());
}
}
}
class MyLongToByteEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<Long>{
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Long o, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("出站的encoder的方法被调用");
byteBuf.writeLong(o);
}
}
class MyHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Long>{
//处理业务逻辑
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Long aLong) throws Exception {
//通过handlerContext可以获取到channel pipeline对象(handler)
System.out.println("从客户端"+channelHandlerContext.channel().remoteAddress()+": "+aLong);
}
}
public class server {
// 服务端逻辑=>
// 创建服务端启动类并配置channel和handler(pipeline)
// 绑定端口并使用future 同步化
// 监听关闭事件 从而进行同步化
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup= new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup= new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap=new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer());
//sync前后是同一个对象
ChannelFuture channelFuture=serverBootstrap.bind(6666).sync();
//同步关闭事件
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//会关闭所有的child Channel。关闭之后,释放掉底层的资源。
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
//client
class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("channel初始化", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// System.out.println("aaaa");
ctx.writeAndFlush(123465L);
}
}
public class Client {
//客户端 逻辑
// 使用并配置bootstrap启动类(只需要一个eventloopgroup
// 同步
//
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup eventExecutors=new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
Bootstrap bootstrap=new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(eventExecutors)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
// connect的时候创建channel;
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new MyLongToByteEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
//connect会创建channel并返回
ChannelFuture channelFuture=bootstrap.connect("localhost",6666).sync();
// channelFuture.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("第二次的客户端发送",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
channelFuture.channel().writeAndFlush(123465L);
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
eventExecutors.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
长连接
长连接的原理: 客户端会定时向服务端发送heartBreak包,用于维持连接(子线程)
服务端会定时清除(主动关闭)长时间没接受数据的socket连接
同时长连接需要保持状态, 需要在服务端和客户端设置ObjectMapping和ObjectAction. 或者Channelmapping
socket实现长连接
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1640058
Netty实现长连接
//客户端 实现心跳检测
//增加 idleStateHandler的处理件
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(20,10,0));//read write r&w
// idleStateHandle会在底层开一个定时线程 检测超时 会向后传递IdleStateEvent 事件
//在 业务处理层 增加userEventTriggered处理idle事件
//服务端定时清除长连接 也可以使用IdleStateHandler组件检测超时
//状态可以封装message格式 增加userID字段
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43935927/article/details/112001309#:~:text=在Netty 中,实现心跳,连接、重新连接等等。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通