第3章. 列表简介
- 3.1 列表是什么
- 3.1.1 访问列表元素
- 3.1.2 索引从0而不是1开始
- 3.1.3 使用列表中的各个值
- 3.2 修改、添加和删除元素
- 3.2.1 修改列表元素
- 3.2.2 在列表中添加元素
- 3.2.3 从列表中删除元素
- 3.3 组织列表
- 3.3.1 使用方法 sort() 对列表永久排序
- 3.3.2 使用函数 sorted() 对列表临时排序
- 3.3.3 倒着打印列表
- 3.3.4 确定列表的长度
- 3.1 列表是什么
可以将任何东西加入列表中,其中的元素之间可以没有任何关系。
在 Python 中,用方括号 [] 来表示列表,并用逗号来分隔其中的元素。
1 arrays = ["abc",1,2,3,"123"]
2 print(arrays)
运行结果:
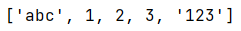
Python 将打印列表的内部标识,包括方括号。下面学习如何访问列表元素
- 3.1.1 访问列表元素
要访问列表元素,可指出列表的名称,再指出元素的索引,并将其放在方括号内。
当你请求获取列表元素时,Python 只返回该元素,而不包括方括号和引号。
1 arrays = ["abc",1,2,3,"123"]
2 print(arrays[0])
3 print(arrays[1])
运行结果:
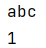
- 3.1.2 索引从0而不是1开始
通过将索引指定为 -1 ,可让 Python 返回最后一个列表元素;索引 -2 返回倒数第二个列表元素,索引 -3 返回倒数第三个列表元素,以此类推。
1 arrays = ["abc",1,2,3,"123"]
2 print(arrays[0])
3 print(arrays[1])
4 print(arrays[-1])
5 print(arrays[-3])
运行结果:
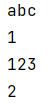
- 3.1.3 使用列表中的各个值
1 bicycles = ["trek","cannondale","redline","specialized"]
2 message = f"My first bicycle was a {bicycles[0].title()}."
3 print(message)
运行结果:
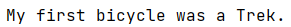
- 3.2.1 修改列表元素
要修改列表元素,可指定列表名和要修改的元素的指引,再指定该元素的新值。
1 bicycles = ["trek","cannondale","redline","specialized"]
2 print(bicycles)
3 bicycles[0] = "abc"
4 print(bicycles)
运行结果:

- 3.2.2 在列表中添加元素
- 1. 在列表末尾添加元素 append()
1 motorcycles = [] # 创建一个空列表2 print(motorcycles)
3 motorcycles.append("honda")
4 print(motorcycles)
5 motorcycles.append('yamaha')
6 motorcycles.append('suzuki')
7 print(motorcycles)
运行结果:

- 2. 在列表中插入元素 insert()
需要指定新元素的索引和值
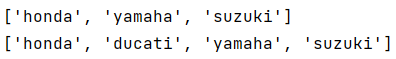
1 motorcycles = ['honda','yamaha','suzuki']
2 print(motorcycles)
3 motorcycles.insert(1,'ducati')
4 print(motorcycles)
运行结果:
- 3.2.3 从列表中删除元素
- 1. 使用 del 语句删除元素
如果知道要删除的元素在列表中的位置,可使用 del 语句
1 motorcycles = ['honda','yamaha','suzuki']
2 print(motorcycles)
3 del motorcycles[1]
4 print(motorcycles)
运行结果:

- 2. 使用方法 pop() 删除元素
方法 pop() 删除列表末尾的元素,并让你能够接着使用它。
每当你使用 pop() 时,被弹出的元素就不再列表中了。
1 motorcycles = ['honda','yamaha','suzuki']
2 print(motorcycles)
3 popped_motorcycle = motorcycles.pop()
4 print(motorcycles)
5 print(popped_motorcycle)
运行结果:

- 3. 弹出列表中任何位置处的元素
可以使用 pop() 来删除列表中任意位置的元素,只需在圆括号中指定要删除元素的索引即可。
1 motorcycles = ['honda','yamaha','suzuki']
2 popped_motorcycle = motorcycles.pop(1)
3 print(motorcycles)
4 print(popped_motorcycle)
运行结果:

- 4. 根据值删除元素
如果只知道要删除的元素的值,可使用方法 remove()
remove() 只删除第一个指定的值。如果要删除的值可能在列表中出现多次,就需要使用循环来确保每个值都删除(以后的内容会涉及到循环)。
1 motorcycles = ['honda','yamaha','suzuki','ducati']
2 print(motorcycles)
3 motorcycles.remove('ducati')
4 print(motorcycles)
运行结果:

- 3.3.1 使用方法 sort() 对列表永久排序
方法 sort() 永久性地修改列表元素的排列顺序。
还可以按相反的顺序排列列表元素,只需向 sort() 方法传递参数 reverse=True 即可。(True 的 T 必须大写)
1 cars = ['bmw','audi','toyota','subaru']
2 cars.sort()
3 print(cars)
4 cars.sort(reverse=True)
5 print(cars)
6 nums = [1,3,4,23,234,3]
7 nums.sort()
8 print(nums)
运行结果:

- 3.3.2 使用函数 sorted() 对列表临时排序
函数 sorted() 让你能够按特定顺序显示列表元素,同时不影响它们在列表中的原始排列顺序。
如果要按相反的顺序显示列表,也可向函数 sorted() 传递参数 reverse=True
1 cars = ['bmw','audi','toyota','subaru']
2 print("Here is the original list:")
3 print(cars)
4 print("Here is the sorted list:")
5 print(sorted(cars))
6 print("Here is the original list again:")
7 print(cars)
8 print("reverse:")
9 print(sorted(cars,reverse=True))
运行结果:

- 3.3.3 倒着打印列表
要反转列表的排列顺序,可使用方法 reverse()。
方法 reverse() 永久地修改列表元素的排列顺序,要恢复到原来的顺序,只需再次调用 reverse()
1 cars = ['bmw','audi','toyota','subaru']
2 print(cars)
3 cars.reverse()
4 print(cars)
运行结果:

- 3.3.4 确定列表的长度
使用函数 len() 可快速获悉列表的长度
1 cars = ['bmw','audi','toyota','subaru']
2 length = len(cars)
3 print(length)
运行结果:
(〃>_<;〃)(〃>_<;〃)(〃>_<;〃)


