使用 Sequelize(ORM) + mysql2 操作 mysql
ORM 是关系对象映射,通过 ORM 框架,可以自动地把程序中的对象和数据库关联,只需要操作对象就可以修改数据库的数据,并且能轻易完成数据库的移植
安装
npm i sequelize npm i mysql2
连接
连接数据库
创建 config 文件夹,在 config 中创建 db.js 文件用于放置数据库的配置项
// config/db.js /** * mysql 数据库配置 */ // 生产环境 let sqlConfig = { host: 'localhost', user: 'root', password: 'sql2008', database: 'books', port: 3306 } // 本地环境 // process.env.NODE_ENV 取决于package.json里面的配置 if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { let sqlConfig = { host: 'localhost', user: 'root', password: 'sql2008', database: 'books', port: 3306 } } module.exports = sqlConfig
与 config 同级,创建一个db文件夹,用于存放数据操作,在 db 文件夹下创建 sequelize.js 文件,进行数据库的连接
// db/sequelize.js const Sequelize = require('sequelize') const {database,host,user,password} = require('../config/db') // 连接数据库 const sequelize = new Sequelize(database,user,password,{ host: host, port: 3306, dialect: 'mysql',// 数据库,默认是 mysql logging: null, // 日志,详情可以去官网看 // 使用数据池 pool: { max: 20, min: 1, acquire: 60000, idle: 10000 }, }) module.exports = sequelize // 测试连接 // sequelize.authenticate().then(_=>{ // console.log('连接成功') // }).catch(err=>{ // console.log('连接失败'+err) // }) // 关闭连接 // sequelize.close()
使用
定义模型
sequelize.define(moduleName,attributes,options)
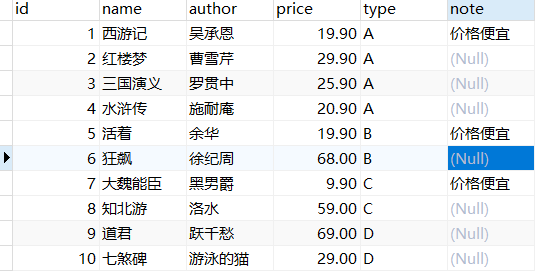
根据数据库建立一个简单的模型
const { DataTypes } = require('sequelize') const sequelize = require('../sequelize') const BooksModel = sequelize.define('mybooks', { id: { type: DataTypes.INTEGER(4), allowNull: false, primaryKey: true, autoIncreament: true }, name: { type: DataTypes.STRING(50), allowNull: false, defaultValue: '没有书名' }, author: { type: DataTypes.STRING(50), defaultValue: '匿名', }, price: { type: DataTypes.DECIMAL(10, 2), allowNull: false, defaultValue: 0.00 }, type: { type: DataTypes.ENUM('A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'N'), allowNull: false, defaultValue: 'N' }, note: { type: DataTypes.STRING, allowNull: true, // 自定义,根据数据库中其他字段的值计算出该字段 // type: DataTypes.VIRTUAL, // get() { // return this.id.toString() + '' + this.name + '€' // } } }, { // 模型不需要添加事件戳,如果不设置,那么保存到数据库中会因为缺少 createAt 和 updateAt 而报错 timestamps: false, // 该模式中会自动将表格名称修改为复数,有两种解决办法:1. 在配置项中设置:freezeTableName: true;2. 直接设置表格名称(在这里我设置成复数) tableName: 'mybooks' }) module.exports = BooksModel
扩展 Model
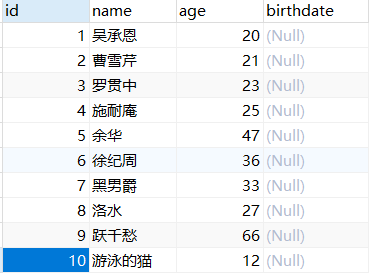
const { DataTypes,Model } = require('sequelize') const sequelize = require('../sequelize') // 继承 Model 类 class UsersModel extends Model{} UsersModel.init({ id: { type: DataTypes.INTEGER(4), allowNull: false, primaryKey: true, autoIncreament: true }, name: { type: DataTypes.STRING(50), allowNull: false, defaultValue: '没有名字' }, age:{ type: DataTypes.INTEGER(3), allowNull: false, defaultValue: 0 }, birthdate:{ type: DataTypes.DATEONLY, allowNull: true, defaultValue: DataTypes.NOW() } }, { // 连接实例 sequelize:sequelize, // 模型名称 moduleName:'UsersModel', timestamps: false, tableName: 'users' }) module.exports = UsersModel
数据操作
与 model 文件夹同级,新建 service 文件夹,用于数据操作
新增
build()+save()
const addbooks = async(id,name,price,author,type) =>{ let books = BookModel.build({ id:id, name:name, price:price, author:author, type:type }) books = await books.save() // 将模型实例直接返回会有很多问题,因为实例上有许多附加条件,可以使用 .toJSON() 或者 JSON.stringify() 操作后返回 return books.toJSON() } addbooks(11,'静夜思',10,'李白','D').then(data=>console.log(data))
create()
- create()
实际上就是 build() + save(),操作起来更快
// db/service/BookService.js const BookModel = require('../model/BookModel'); const UserModel = require('../model/UserModel') const { Op } = require('sequelize'); const sequelize = require('../db/sequelize') const addbooks = async(id,name,price,author,type) =>{ const books = await BookModel.create({ id:id, name:name, price:price, author:author, type:type }) return books.toJSON() } addbooks(11,'静夜思',10,'李白','D').then(data=>console.log(data))
删除
- destroy()
// where 条件匹配,用的非常多,可以去官网仔细看看 const deletebooks = async(name)=>{ const books = await BookModel.destroy({ where:{name:name} }) return books } deletebooks('静夜思').then(data=>console.log(data))
修改
- update
const updatebooks = async()=>{ const books = await BookModel.update({note:'价格便宜'},{ where:{ price:{ // 查找价格小于 20 的 [Op.lt]:20 } } }) return books; } updatebooks().then(data=>console.log(data))
操作符(官网上的)
where: { [Op.and]: [{ a: 5 }, { b: 6 }], // (a = 5) AND (b = 6) [Op.or]: [{ a: 5 }, { b: 6 }], // (a = 5) OR (b = 6) someAttribute: { // 基本 [Op.eq]: 3, // = 3 [Op.ne]: 20, // != 20 [Op.is]: null, // IS NULL [Op.not]: true, // IS NOT TRUE [Op.or]: [5, 6], // (someAttribute = 5) OR (someAttribute = 6) // 使用方言特定的列标识符 (以下示例中使用 PG): [Op.col]: 'user.organization_id', // = "user"."organization_id" // 数字比较 [Op.gt]: 6, // > 6 [Op.gte]: 6, // >= 6 [Op.lt]: 10, // < 10 [Op.lte]: 10, // <= 10 [Op.between]: [6, 10], // BETWEEN 6 AND 10 [Op.notBetween]: [11, 15], // NOT BETWEEN 11 AND 15 // 其它操作符 [Op.all]: sequelize.literal('SELECT 1'), // > ALL (SELECT 1) [Op.in]: [1, 2], // IN [1, 2] [Op.notIn]: [1, 2], // NOT IN [1, 2] [Op.like]: '%hat', // LIKE '%hat' [Op.notLike]: '%hat', // NOT LIKE '%hat' [Op.startsWith]: 'hat', // LIKE 'hat%' [Op.endsWith]: 'hat', // LIKE '%hat' [Op.substring]: 'hat', // LIKE '%hat%' [Op.iLike]: '%hat', // ILIKE '%hat' (不区分大小写) (仅 PG) [Op.notILike]: '%hat', // NOT ILIKE '%hat' (仅 PG) [Op.regexp]: '^[h|a|t]', // REGEXP/~ '^[h|a|t]' (仅 MySQL/PG) [Op.notRegexp]: '^[h|a|t]', // NOT REGEXP/!~ '^[h|a|t]' (仅 MySQL/PG) [Op.iRegexp]: '^[h|a|t]', // ~* '^[h|a|t]' (仅 PG) [Op.notIRegexp]: '^[h|a|t]', // !~* '^[h|a|t]' (仅 PG) [Op.any]: [2, 3], // ANY ARRAY[2, 3]::INTEGER (仅 PG) [Op.match]: Sequelize.fn('to_tsquery', 'fat & rat') // 匹配文本搜索字符串 'fat' 和 'rat' (仅 PG) // 在 Postgres 中, Op.like/Op.iLike/Op.notLike 可以结合 Op.any 使用: [Op.like]: { [Op.any]: ['cat', 'hat'] } // LIKE ANY ARRAY['cat', 'hat'] } }
查看
// 查找给定类别、给定价格区间内的书本,只要求输出 name,作者和 price,并按照 id 倒序输出 const getbook = async (price1, price2, type) => { const books = await BookModel.findAll({ attributes: ['name', ['author', '作者'], 'price'], where: { [Op.and]: [ { price: { [Op.gt]: price1, [Op.lt]: price2, } }, { type: type } ] }, order: [ ['id', 'DESC'] ] }) return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(books)); } getbook(10, 50, 'A').then(data => console.log(data))
- 聚类统计问题
// 统计出给定类的书本价格之和,使用的是聚合函数 SUM 和 group const getbooks = async (type) => { const books = await BookModel.findAll({ attributes: [ 'type', [sequelize.fn('SUM', sequelize.col('price')), 'sum'] ], group: 'type', where:{ type:type } }) return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(books)); } getbooks('A').then(data => console.log(data))
- 分页问题
// 给定页面大小和页码数,搜索符合要求的书本,默认按照 id 排序 const getbooks = async (pageNum, pageSize) => { const books = await BookModel.findAll({ attributes: { exclude: ['note', 'type'] }, // 跳过 offset: (pageNum - 1) * pageSize, // 截取 limit: pageSize, }) return books } // 再调用函数外面使用 toJSON() 也是可以的 getbooks(3, 4).then(data => { data.length ? data.map(book => console.log(book.toJSON())) : console.log('No data') })
- 关联问题
// 使用 id join,成功! UserModel.hasOne(BookModel,{foreignKey:'id'}) // 添加 UserModel 的外键为 id BookModel.belongsTo(UserModel,{foreignKey:'id'}) // 添加 BookModel 的外键为 id const getbooks = async () => { const books = await BookModel.findAll({ include:{ model:UserModel } }) return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(books)) } getbooks().then(data => console.log(data)) // 使用 author 和 name join,失败! UserModel.hasOne(BookModel,{foreignKey:'name'}) BookModel.belongsTo(UserModel,{foreignKey:'author'}) const getbooks = async () => { const books = await BookModel.findAll({ include:{ model:UserModel } }) return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(books)) } getbooks().then(data => console.log(data))
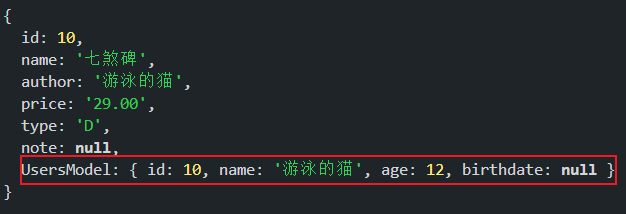
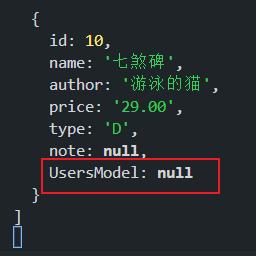
上面的关联问题中,两表之间的 id 关联成功,两表之间的 author 和 name 关联失败,明明关联的数据值是相等的,为什么一个成功,一个失败呢?
其实只需要把 UsersModel 的主键改成 name 就可以关联成功,这有必要回忆一下主键和外键
- 主键:主键表示唯一标识一条记录,不能有重复的,不允许为空
- 外键:外键用于与另一张表的关联。是能确定另一张表记录的字段,用于保持数据的一致性
也就是说 B 表的主键 b,就可以是 A 表的外键 b,A 表内的外键 b 在 A 表内可以有重复,但是在 B 表内必须是唯一值



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具