Linux中du命令,tree命令和realpath学习
1,Linux下du命令详解
Du 是Disk Usage 的缩写,Linux上最受欢迎的命令之一,它是用来估算文件或目录占用磁盘空间,也是基础的命令。
1.1 du 命令及其语法
用法如下:
Usage: du [OPTION]... [FILE]...
du [OPTION]... --files0-from=F
语法如下:
用法:du [选项]... [文件]...
或:du [选项]... --files0-from=F
Summarize disk usage of the set of FILEs, recursively for directories.
必选参数对长短选项同时适用。
-0, --null end each output line with NUL, not newline
-a, --all write counts for all files, not just directories
--apparent-size print apparent sizes, rather than disk usage; although
the apparent size is usually smaller, it may be
larger due to holes in ('sparse') files, internal
fragmentation, indirect blocks, and the like
-B, --block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g.,
'-BM' prints sizes in units of 1,048,576 bytes;
see SIZE format below
-b, --bytes equivalent to '--apparent-size --block-size=1'
-c, --total produce a grand total
-D, --dereference-args dereference only symlinks that are listed on the
command line
-d, --max-depth=N print the total for a directory (or file, with --all)
only if it is N or fewer levels below the command
line argument; --max-depth=0 is the same as
--summarize
--files0-from=F summarize disk usage of the
NUL-terminated file names specified in file F;
if F is -, then read names from standard input
-H equivalent to --dereference-args (-D)
-h, --human-readable print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
--inodes list inode usage information instead of block usage
-k like --block-size=1K
-L, --dereference dereference all symbolic links
-l, --count-links count sizes many times if hard linked
-m like --block-size=1M
-P, --no-dereference don't follow any symbolic links (this is the default)
-S, --separate-dirs for directories do not include size of subdirectories
--si like -h, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
-s, --summarize display only a total for each argument
-t, --threshold=SIZE exclude entries smaller than SIZE if positive,
or entries greater than SIZE if negative
--time show time of the last modification of any file in the
directory, or any of its subdirectories
--time=WORD show time as WORD instead of modification time:
atime, access, use, ctime or status
--time-style=STYLE show times using STYLE, which can be:
full-iso, long-iso, iso, or +FORMAT;
FORMAT is interpreted like in 'date'
-X, --exclude-from=FILE exclude files that match any pattern in FILE
--exclude=PATTERN exclude files that match PATTERN
-x, --one-file-system skip directories on different file systems
--help 显示此帮助信息并退出
--version 显示版本信息并退出
常用的选项如下:
-a: 显示目录中所有文件以及文件夹大小 -h: 以 Kb、Mb 、Gb 等易读的单位显示大小 --si: 类似 -h 选项,但是计算是用 1000 为基数而不是1024 -s: 显示目录总大小 -d: 是 --max-depth=N 选项的简写,表示深入到第几层目录,超过指定层数目录则忽略 -c: 除了显示目录大小外,额外一行显示总占用量 --time: 显示每一个目录下最近修改文件的时间 -t: 是 --threshold=SIZE 的简写,过滤掉小于 SIZE 大小的文件以及目录 --exclude=PATTERN:过滤与 PATTERN 匹配的文件名或者目录名
1.2 基础用法:获取目录总大小
如果只需要子目录及子目录下文件的大小,通过 -s 选项获取目录总大小。
2,Linux下tree命令详解
Linux tree命令用于以树状图列出目录的内容。执行tree指令,它会列出指定目录下的所有文件,包括子目录里的文件。
Tree -a
-a标志可以显示隐藏文件。
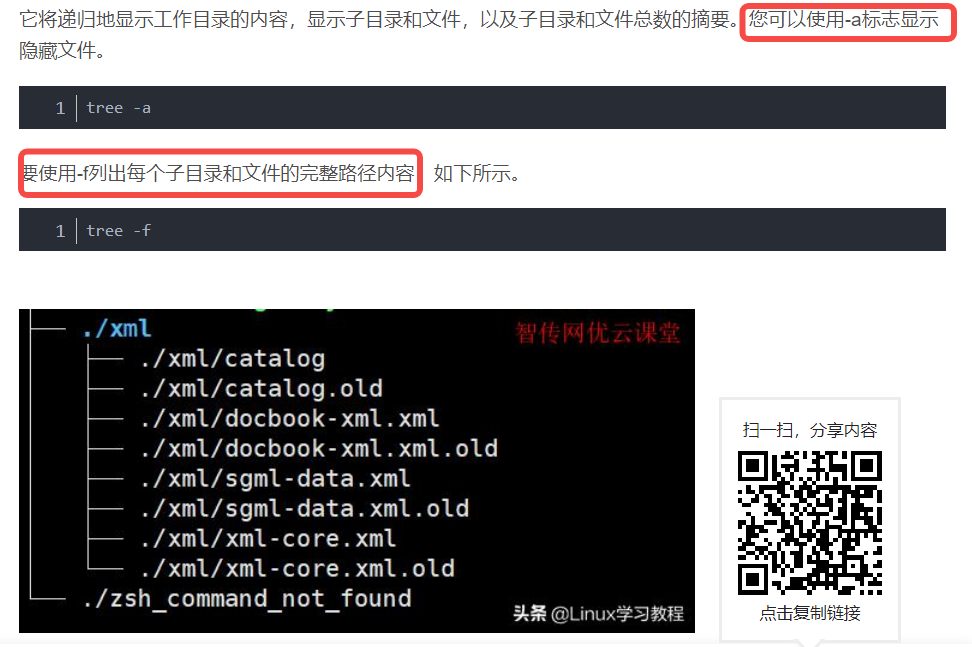
Tree -f
-f 标志列出每个子目录和文件的完整路径内容。
Tree -L
使用-L 选项指定目录树的最大显示深度。例如,希望深度为二,额可以运行以下命令:
tree -f -L 2
Tree -P
3,Linux下realpath命令详解
命令简介:realpath 用于获取指定目录或文件的绝对路径。
虽然编写Shell脚本中,通常会使用相对路径来指明文件,但有时候,我们需要绝对路径,这时候可以使用realpath来获取。
命令格式:
realpath [OPTIONS] FILES
不经一番彻骨寒 怎得梅花扑鼻香



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号