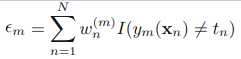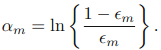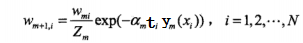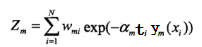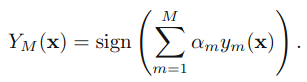AdaBoost--从原理到实现(Code:Python)
本文对原文有修改,若有疑虑,请移步原作者. 原文链接:blog.csdn.net/dark_scope/article/details/14103983
集成方法在函数模型上等价于一个多层神经网络,两种常见的集成方法为Adaboost模型和RandomTrees模型。其中随机森林可被视为前馈神经网络,而Adaboost模型则等价于一个反馈型多层神经网络。
一.引入
对于Adaboost,可以说是久闻大名,据说在Deep Learning出来之前,SVM和Adaboost是效果最好的 两个算法,而Adaboost是提升树(boosting tree),所谓“ 提升树 ” 就是把“弱学习算法”提升(boost)为“强学习算法”(语自《统计学习方法》),而其中最具代表性的也就是Adaboost了,貌似Adaboost的结构还和Neural Network有几分神似,我倒没有深究过,不知道是不是有什么干货。
二.过程
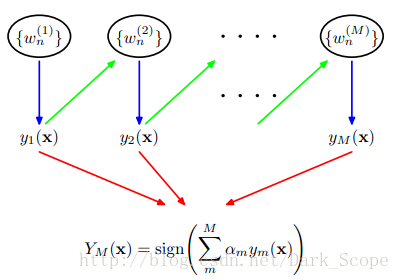
这就是Adaboost的结构,最后的分类器YM是由数个弱分类器(weak classifier)组合而成的,相当于最后m个弱分类器来投票决定分类,而且每个弱分类器的“话语权”α不一样。
这里阐述下算法的具体过程:
1.初始化所有训练样例的权重为1 / N,其中N是样例数
2.for m=1,……M:
a).训练弱分类器ym(),使其最小化权重误差函数(weighted error function):
b)接下来计算该弱分类器的话语权α:
c)更新权重:
其中Zm:
是规范化因子,使所有w的和为1。(这里公式稍微有点乱)
3.得到最后的分类器:
三.原理
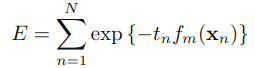
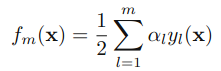
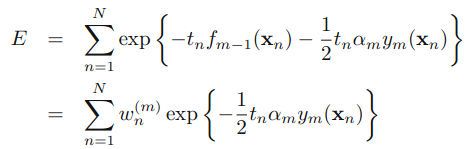
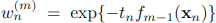 ,可以被看做一个常量,因为它里面没有αm和ym:
,可以被看做一个常量,因为它里面没有αm和ym: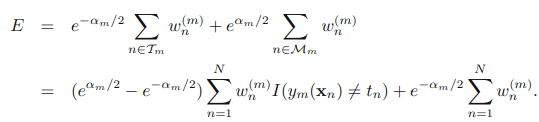
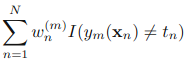
四.实现
 )
) # coding: UTF-8
from __future__ import division
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
from weakclassify import WEAKC
from dml.tool import sign
class ADABC:
def __init__(self,X,y,Weaker=WEAKC):
'''''
Weaker is a class of weak classifier
It should have a train(self.W) method pass the weight parameter to train
pred(test_set) method which return y formed by 1 or -1
see detail in <统计学习方法>
'''
self.X=np.array(X)
self.y=np.array(y)
self.Weaker=Weaker
self.sums=np.zeros(self.y.shape)
self.W=np.ones((self.X.shape[1],1)).flatten(1)/self.X.shape[1]
self.Q=0
#print self.W
def train(self,M=4):
'''''
M is the maximal Weaker classification
'''
self.G={}
self.alpha={}
for i in range(M):
self.G.setdefault(i)
self.alpha.setdefault(i)
for i in range(M):
self.G[i]=self.Weaker(self.X,self.y)
e=self.G[i].train(self.W)
#print self.G[i].t_val,self.G[i].t_b,e
self.alpha[i]=1/2*np.log((1-e)/e)
#print self.alpha[i]
sg=self.G[i].pred(self.X)
Z=self.W*np.exp(-self.alpha[i]*self.y*sg.transpose())
self.W=(Z/Z.sum()).flatten(1)
self.Q=i
#print self.finalclassifer(i),'==========='
if self.finalclassifer(i)==0:
print i+1," weak classifier is enough to make the error to 0"
break
def finalclassifer(self,t):
'''''
the 1 to t weak classifer come together
'''
self.sums=self.sums+self.G[t].pred(self.X).flatten(1)*self.alpha[t]
#print self.sums
pre_y=sign(self.sums)
#sums=np.zeros(self.y.shape)
#for i in range(t+1):
# sums=sums+self.G[i].pred(self.X).flatten(1)*self.alpha[i]
# print sums
#pre_y=sign(sums)
t=(pre_y!=self.y).sum()
return t
def pred(self,test_set):
sums=np.zeros(self.y.shape)
for i in range(self.Q+1):
sums=sums+self.G[i].pred(self.X).flatten(1)*self.alpha[i]
#print sums
pre_y=sign(sums)
return pre_y 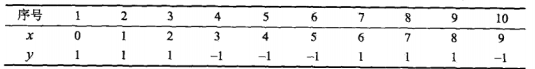
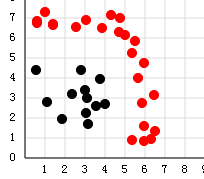
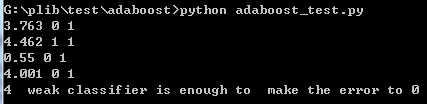
 )
)