Caffe FCN:可视化featureMaps和Weights(C++)、获取FCN结果
为何不使用C++版本FCN获取最后的分割掩模,何必要使用python呢!因此需要获取网络最后层的featureMaps,featureMaps的结果直接对应了segmentation的最终结果,可以直接用于掩模分析。
caffe源码给出了提取中间层featureMap的源代码,位置在tools/extract_features.cpp。
参考文章链接:
caffe模型可视化featureMaps和Weights(C++) ,文章有大量修改,如有不适,请移步原文。
1. 可视化最后一层featureMap的代码段(稍作修改):
int Classifier::visualize_featuremap( const cv::Mat& img, string layer_name, std::vector<cv::Mat> &Maps )
{
Maps.resize(0);
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
input_layer->Reshape(1, num_channels_, input_geometry_.height, input_geometry_.width);
net_->Reshape();
std::vector<cv::Mat> input_channels;
WrapInputLayer(&input_channels);
Preprocess(img, &input_channels);
net_->Forward();
std::cout << "网络中的Blobs名称为:\n";
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<float> > > blobs = net_->blobs();
vector<string> blob_names = net_->blob_names();
std::cout << blobs.size() << " " << blob_names.size() << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < blobs.size(); i++){
std::cout << blob_names[i] << " " << blobs[i]->shape_string() << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
assert(net_->has_blob(layer_name));
shared_ptr<Blob<float> > conv1Blob = net_->blob_by_name(layer_name);
std::cout << "测试图片的特征响应图的形状信息为:" << conv1Blob->shape_string() << std::endl;
float maxValue = -10000000, minValue = 10000000;
const float* tmpValue = conv1Blob->cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < conv1Blob->count(); i++){
maxValue = std::max(maxValue, tmpValue[i]);
minValue = std::min(minValue, tmpValue[i]);
}
int width = conv1Blob->shape(3); //响应图的高度
int height = conv1Blob->shape(2); //响应图的宽度
int channel = conv1Blob->shape(1); //通道数
int num = conv1Blob->shape(0); //个数
int imgHeight = (int)(1 + sqrt(channel))*height;
int imgWidth = (int)(1 + sqrt(channel))*width;
cv::Mat img(imgHeight, imgWidth, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0));
int kk = 0;
for (int x = 0; x < imgHeight; x += height){
for (int y = 0; y < imgWidth; y += width){
if (kk >= channel)
continue;
cv::Mat roi(height, width, CV_8UC1);
//cv::Mat roi = img(cv::Rect(y, x, width, height));
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++){
float value = conv1Blob->data_at(0, kk, i, j);//速度稍慢,应该有快速复制方法
//roi.at<uchar>(i, j) = (value - minValue) / (maxValue - minValue) * 255;
value = (value - minValue) / (maxValue - minValue);
roi.at<uchar>(i, j) = 255* floor(value / 0.5) ;
}
}
Maps.push_back(roi);
kk++;
}
}
return Maps.size();
}
2. 获取FCN的最终输出
vector<Blob<float>* > outBlob = net_->Forward();//得到的结果仍为151个//输出结果为151个模板 int channel = outBlob[0]->shape(1); int hi = outBlob[0]->shape(2); int wi = outBlob[0]->shape(3); int area = wi*hi; vector<shared_ptr<Blob<float> > > blobs = net_->blobs(); vector<string> blob_names = net_->blob_names();
获取最大标记
int Classifier::GetMaxMask( const cv::Mat& img, int layerIdx, double thres,cv::Mat &maskMax )
{
vector<boost::shared_ptr<Blob<float> > > blobs = net_->blobs();
vector<string> blob_names = net_->blob_names();
int num_features = net_->output_blobs()[0]->shape(1);
int channel = net_->output_blobs()[0]->shape(1);
int hi = net_->output_blobs()[0]->shape(2);
int wi = net_->output_blobs()[0]->shape(3);
int area = wi*hi;
std::vector<int> image_indices(num_features, 0);
int i = layerIdx;
const boost::shared_ptr<Blob<float> > feature_blob
= net_->blob_by_name(blob_names[i]);
int batch_size = feature_blob->num();
int dim_features = feature_blob->count() / batch_size;
float maxValue = -10000000, minValue = 10000000;
const float* tmpValue = feature_blob->cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < feature_blob->count(); i++){
maxValue = std::max(maxValue, tmpValue[i]);
minValue = std::min(minValue, tmpValue[i]);
}
std::vector<int> areal(channel);
for (int i = 0; i < channel;++i){
areal[i] = i*area;
}
const float* feature_blob_data;
const float minv = 10000000;
const float maxv = -10000000;
int classI = 0;
for ( int n = 0; n < batch_size; ++n){
feature_blob_data =
feature_blob->cpu_data() + feature_blob->offset(n);
int img_index = 0;
for (int h = 0; h < hi; ++h)
{
uchar* ptr = (unsigned char*)(maskMax.data + h * maskMax.step);
int idxH = h*wi;
img_index = idxH;
for ( int w = 0; w < wi; ++w)
{
float valueG = maxv;
for ( int c = 0; c < channel; ++c){
int datum_index = areal[c] + img_index;// area*c;
float value = static_cast<float>(feature_blob_data[datum_index]);
if ( valueG < value ){
valueG = value;
classI = c;
}
}
*ptr = (uchar)classI;
++ptr;
++img_index;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
获取所有标记
//获取特定的元,使用点数限制
int Classifier::getAllSeg(cv::Mat &im_inp, cv::Mat &maskMax,
std::vector<cv::Mat > &segs,std::vector<std::pair<int,float> > &labels,
const int nPointMin)
{
std::vector<int> numsc(m_nClass);
int h = maskMax.rows;
int w = maskMax.cols;
for (int i = 0; i < maskMax.rows; ++i)
{
uchar *ptrm = maskMax.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < maskMax.cols; ++j)
{
int c = *ptrm;
numsc[c]++;
++ptrm;
}
}
//添加限制,获取分割图
std::map<int, int> maps;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numsc.size();++i){
if (numsc[i]>nPointMin){
auto idx =make_pair(i,1.0f);
labels.push_back(idx);
auto idxm = make_pair(i, k);
maps.insert(idxm);
++k;
}
}
//获取图像
for (int i = 0; i < labels.size(); ++i){
cv::Mat seg(h, w, CV_8UC3);
segs.push_back(seg);
}
std::vector<uchar *> ptres(labels.size());
for (int idx = 0; idx < labels.size(); ++idx){
ptres[idx] = (uchar *)segs[idx].data;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < maskMax.rows; ++i )
{
uchar *ptr = im_inp.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar *ptrm = maskMax.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int n = 0; n < labels.size(); ++n)
ptres[n] = (uchar *)segs[n].ptr<uchar>(i);
for ( int j = 0; j < maskMax.cols; ++j )
{
int c = *ptrm;
int pos;// = maps[c];
auto l_it = maps.find(c);
if ( l_it == maps.end() )
pos = -1;
else
pos = l_it->second;
if ( pos>-1) *(ptres[pos]) = *ptr;
++ptr;
for (int n = 0; n < labels.size();++n) ++ptres[n];
if (pos>-1) *(ptres[pos]) = *ptr;
++ptr;
for (int n = 0; n < labels.size(); ++n) ++ptres[n];
if (pos>-1) *(ptres[pos]) = *ptr;
++ptr;
for (int n = 0; n < labels.size(); ++n) ++ptres[n];
++ptrm;
}
}
int nseg = segs.size();
return nseg;
}
3.此外,可视化权值的代码段,直接摘抄
cv::Mat visualize_weights(string prototxt, string caffemodel, int weights_layer_num)
{
::google::InitGoogleLogging("0");
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::CPU);
#else
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::GPU);
#endif
Net<float> net(prototxt, TEST);
net.CopyTrainedLayersFrom(caffemodel);
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<float> > > params = net.params();
std::cout << "各层参数的维度信息为:\n";
for (int i = 0; i<params.size(); ++i)
std::cout << params[i]->shape_string() << std::endl;
int width = params[weights_layer_num]->shape(3); //宽度
int height = params[weights_layer_num]->shape(2); //高度
int channel = params[weights_layer_num]->shape(1); //通道数
int num = params[weights_layer_num]->shape(0); //个数
int imgHeight = (int)(1 + sqrt(num))*height;
int imgWidth = (int)(1 + sqrt(num))*width;
Mat img(imgHeight, imgWidth, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
float maxValue = -1000, minValue = 10000;
const float* tmpValue = params[weights_layer_num]->cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i<params[weights_layer_num]->count(); i++){
maxValue = std::max(maxValue, tmpValue[i]);
minValue = std::min(minValue, tmpValue[i]);
}
int kk = 0;
for (int y = 0; y<imgHeight; y += height){
for (int x = 0; x<imgWidth; x += width){
if (kk >= num)
continue;
Mat roi = img(Rect(x, y, width, height));
for (int i = 0; i<height; i++){
for (int j = 0; j<width; j++){
for (int k = 0; k<channel; k++){
float value = params[weights_layer_num]->data_at(kk, k, i, j);
roi.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[k] = (value - minValue) / (maxValue - minValue) * 255; }
}
}
++kk;
}
}
return img;
}
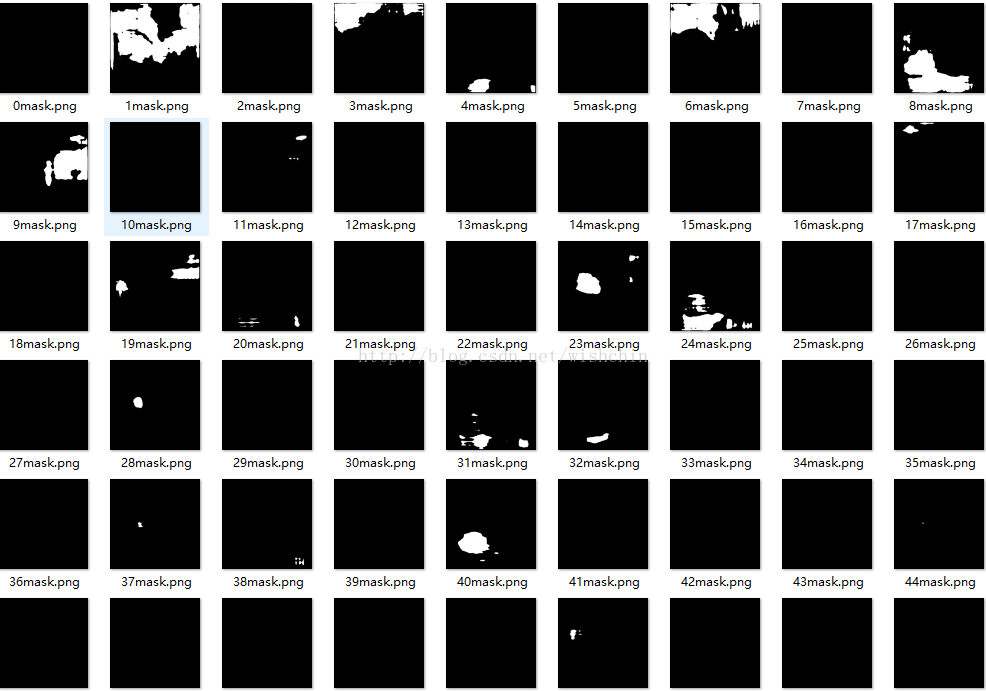
3.FeatureMap获取结果
原图:
分割结果显示:
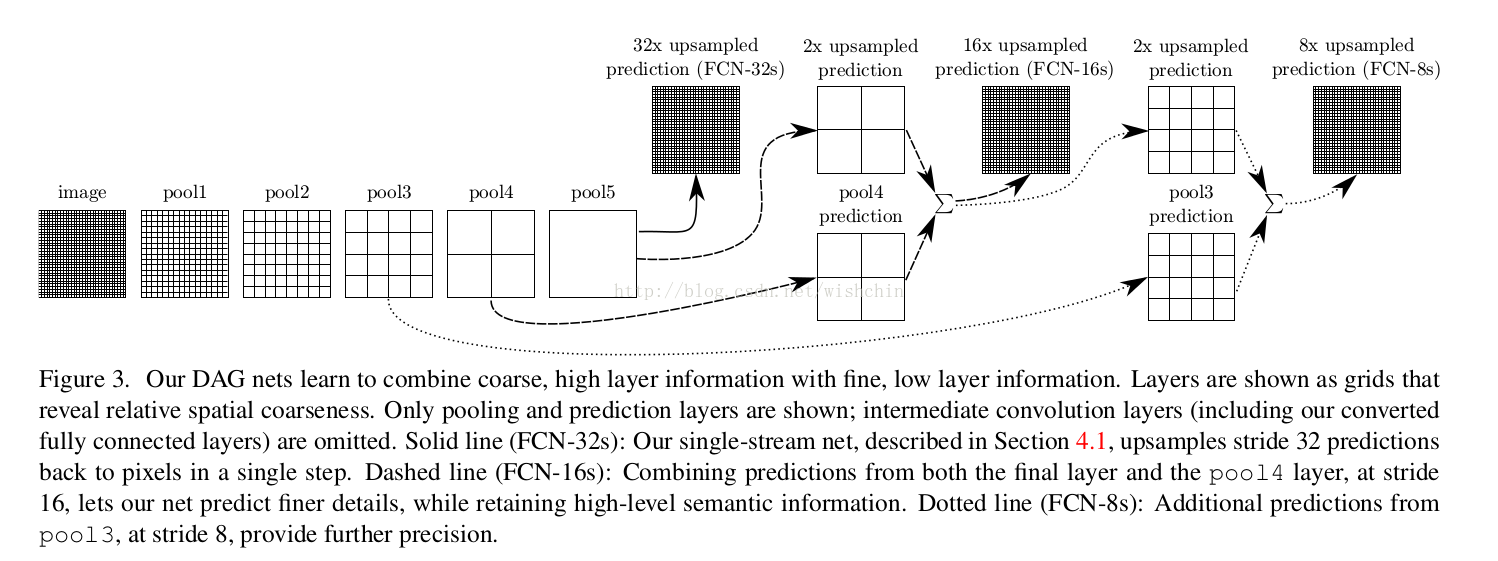
参考:经典论文 Fully Convolutional Networks for semantic Segmentation
作者又翻译了一遍
总结:
pooling层的多层分布,最终用于预测每个点的类别信息,pooling层的粒度与最终分割的精度产生关联。