机器人是否能应用于服务最终还是那两条腿值多少钱,而与人交互,能真正地做“服务”工作,还是看那两条胳膊怎么工作。大脑的智能化还是非常遥远的,还是先把感受器和效应器做好才是王道。
关于强化学习,根据Agent对策略的主动性不同划分为主动强化学习(学习策略:必须自己决定采取什么行动)和被动强化学习(固定的策略决定其行为,为评价学习,即Agent如何从成功与失败中、回报与惩罚中进行学习,学习效用函数)。
被动强化学习:EnforceLearning-被动强化学习
主动强化学习:EnforceLearning-主动强化学习
文章:SACX新范式,训练用于机器人抓取任务
DeepMind提出调度辅助控制(Scheduled Auxiliary Control,SACX),这是强化学习(RL)上下文中一种新型的学习范式。SAC-X能够在存在多个稀疏奖励信号的情况下,从头开始(from scratch)学习复杂行为。为此,智能体配备了一套通用的辅助任务,它试图通过off-policy强化学习同时从中进行学习。
这个长向量的形式化以及优化为论文的亮点。
In this paper, we introduce a new method dubbed Scheduled Auxiliary Control (SAC-X), as a first step towards such an approach. It is based on four main principles:
1. Every state-action pair is paired with a vector of rewards, consisting of ( typically sparse ) externally provided rewards and (typically sparse) internal auxiliary rewards.
2. Each reward entry has an assigned policy, called intention in the following, which is trained to maximize its corresponding cumulative reward.
3. There is a high-level scheduler which selects and executes the individual intentions with the goal of improving performance of the agent on the external tasks.
4. Learning is performed off-policy ( and asynchronouslyfrom policy execution ) and the experience between intentions is shared – to use information effectively. Although the approach proposed in this paper is generally applicable to a wider range of problems, we discuss our method in the light of a typical robotics manipulation applica tion with sparse rewards: stacking various objects and cleaning a table。
由四个基本准则组成:状态配备多个稀疏奖惩向量-一个稀疏的长向量;每个奖惩被分配策略-称为意图,通过最大化累计奖惩向量反馈;建立一个高层的选择执行特定意图的机制用以提高Agent的表现;学习是基于off-policy(新策略,Q值更新使用新策略),且意图之间的经验共享增加效率。总体方法可以应用于通用领域,在此我们以典型的机器人任务进行演示。
基于Off-Play的好处:https://www.zhihu.com/question/57159315
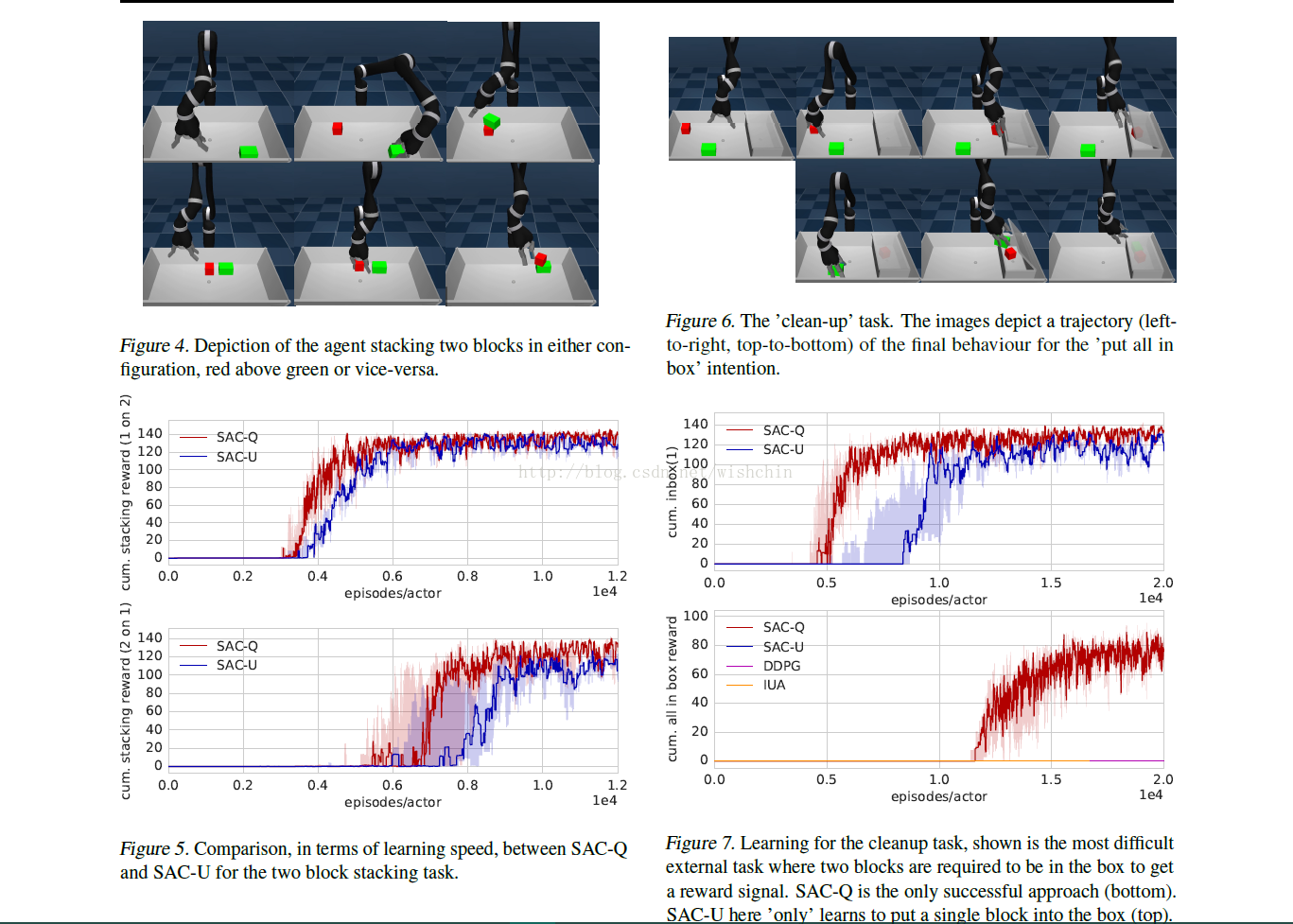
论文:Learning by Playing – Solving Sparse Reward Tasks from Scratch





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架