数据类型内置方法理论
我们之前所学习的每一种数据类型本身都含有一系列的操作方法,内置方法是其中最多的(自带的功能)
在python中数据类型调用内置方法的统一句式为>>>:句点符
'jason'.字符串内置方法
绑定字符串的变量名.字符串内置方法
str.字符串内置方法
ps:数据类型的内置方法比较的多 我们如果想要掌握 不要光靠死记硬背 更多时候靠的是熟能生巧
整型内置方法与操作
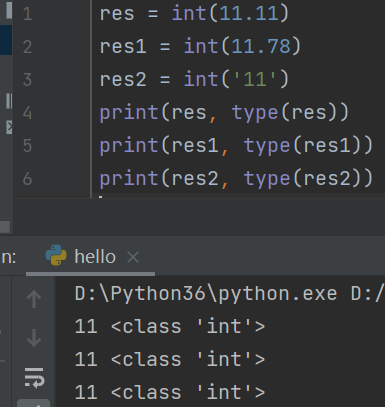
1. 类型转换(将其它数据类型转换成整型)
int(其它数据类型)
ps: 浮点型可以直接转 字符串必须满足内部是纯数字才可以
![image]()
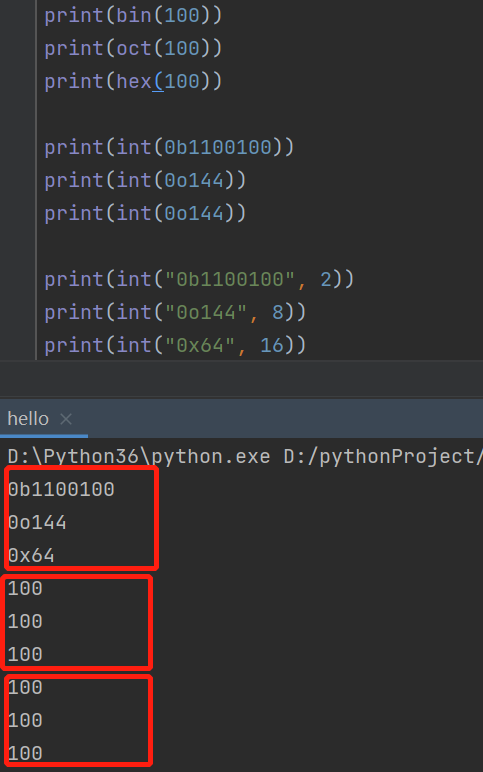
2. 进制数转换
十进制转其它进制
print(bin(100)) # 0b1100100 二进制
print(oct(100)) # 0o144 八进制
print(hex(100)) # 0x64 十六进制
print(int("0b1100100", 2))
print(int("0o144", 8))
print(int("0x64", 16))
![image]()
3. python自身对数字的敏感度较低(精确度低)
python这门语言其实真的一点都不厉害 主要是因为它背后有太多大佬
如果需要精准的计算需要借助于模块numpy......
浮点型内置方法与操作
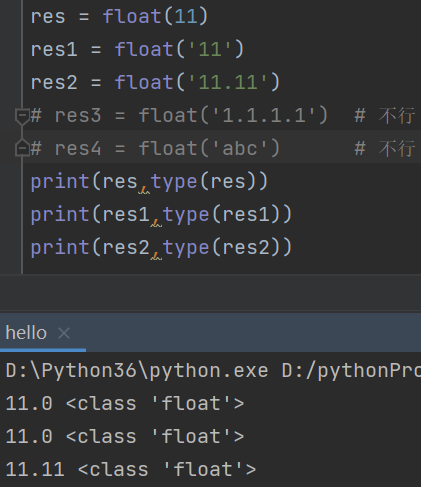
1. 类型转换
float(其它数据类型)
字符串里面可以允许出现一个小数点 其它都必须是纯数字
2. python自身对数字的敏感度较低(精确度低)
python这门语言其实真的一点都不厉害 主要是因为它背后有太多大佬
如果需要精准的计算需要借助于模块numpy...
![image]()
字符串内置方法与操作
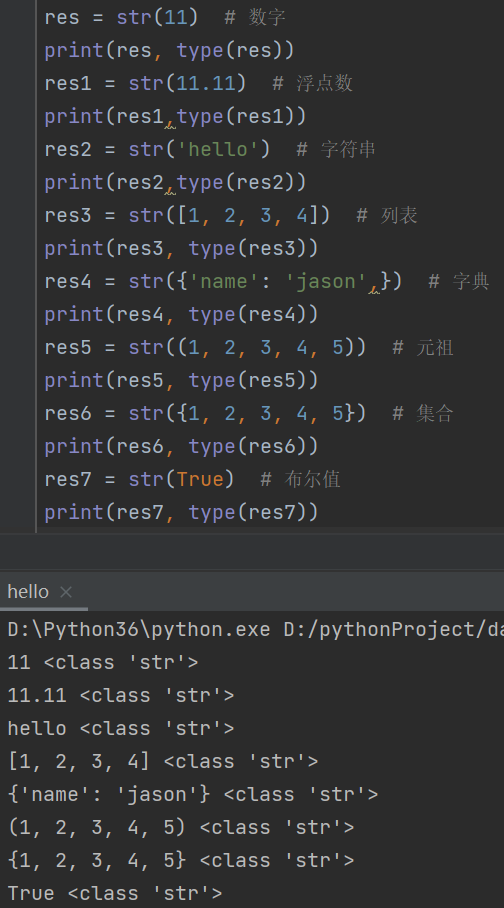
1. 类型转换
str(其它数据类型)
ps:可以转任意数据类型(只需要在前后加引号即可)
![image]()
2. 必须要掌握的方法
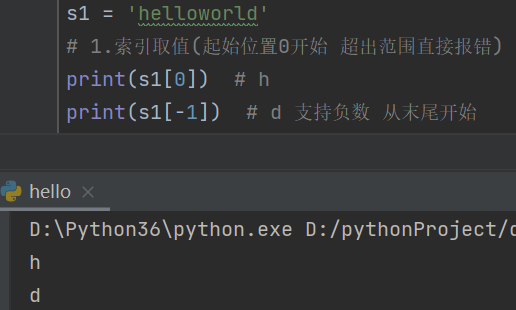
s1 = 'helloworld'
# 1.索引取值(起始位置0开始 超出范围直接报错)
print(s1[0]) # h
print(s1[-1]) # d 支持负数 从末尾开始
![image]()
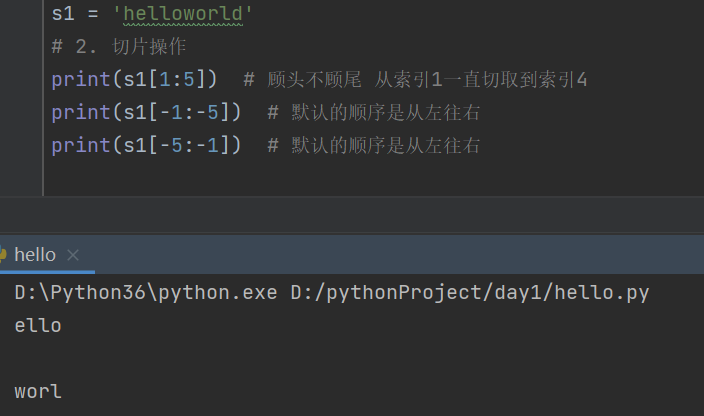
s1 = 'helloworld'
# 2. 切片操作
print(s1[1:5]) # 顾头不顾尾 从索引1一直切取到索引4
print(s1[-1:-5]) # 默认的顺序是从左往右
print(s1[-5:-1]) # 默认的顺序是从左往右
![image]()
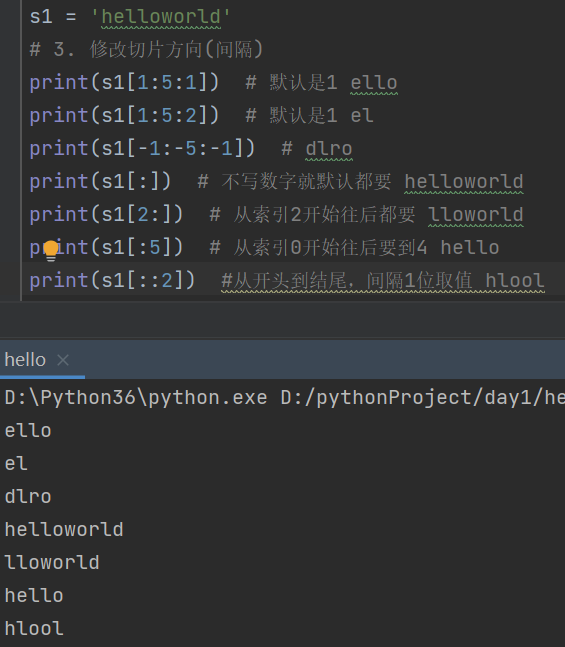
s1 = 'helloworld'
# 3. 修改切片方向(间隔)
print(s1[1:5:1]) # 默认是1 ello
print(s1[1:5:2]) # 默认是1 el
print(s1[-1:-5:-1]) # dlro
print(s1[:]) # 不写数字就默认都要 helloworld
print(s1[2:]) # 从索引2开始往后都要 lloworld
print(s1[:5]) # 从索引0开始往后要到4 hello
print(s1[::2]) #从开头到结尾,间隔1位取值 hlool
![image]()
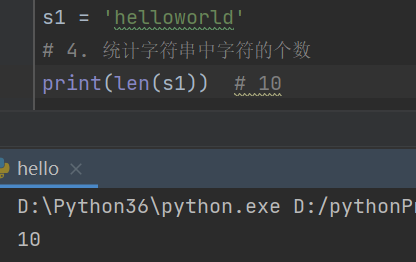
s1 = 'helloworld'
# 4. 统计字符串中字符的个数
print(len(s1)) # 10
![image]()
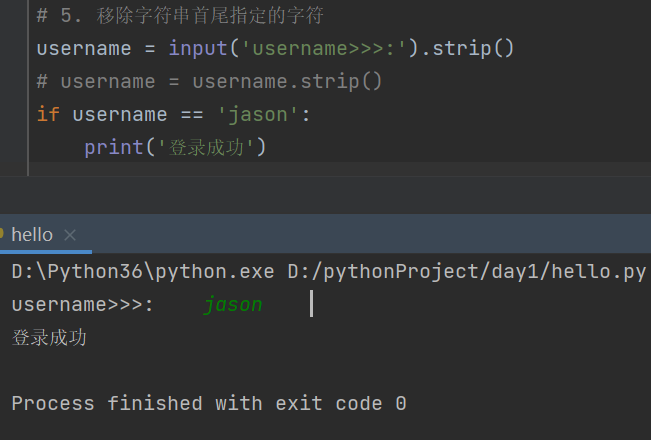
# 5. 移除字符串首尾指定的字符
username = input('username>>>:').strip()
# username = username.strip()
if username == 'jason':
print('登录成功')
![image]()
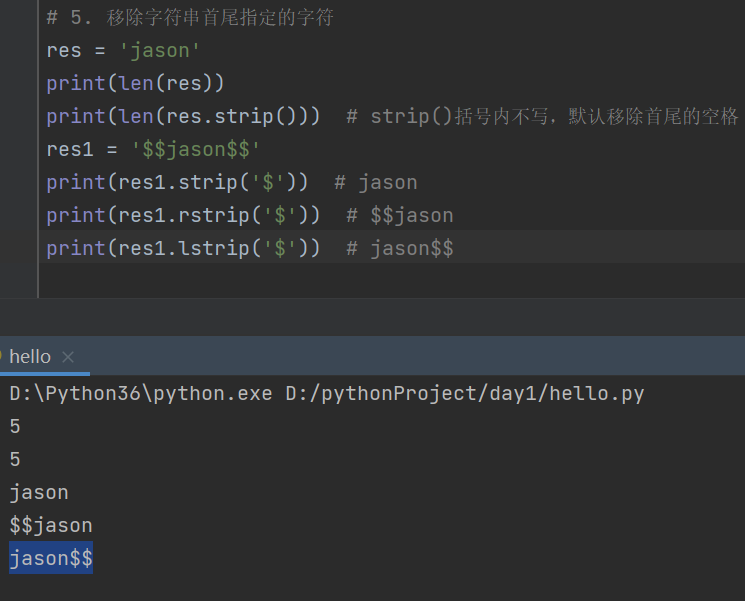
res = 'jason'
print(len(res)) # 5
print(len(res.strip())) # 5 strip()括号内不写,默认移除首尾的空格
res1 = '$$jason$$'
print(res1.strip('$')) # jason
print(res1.rstrip('$')) # $$jason
print(res1.lstrip('$')) # jason$$
![image]()
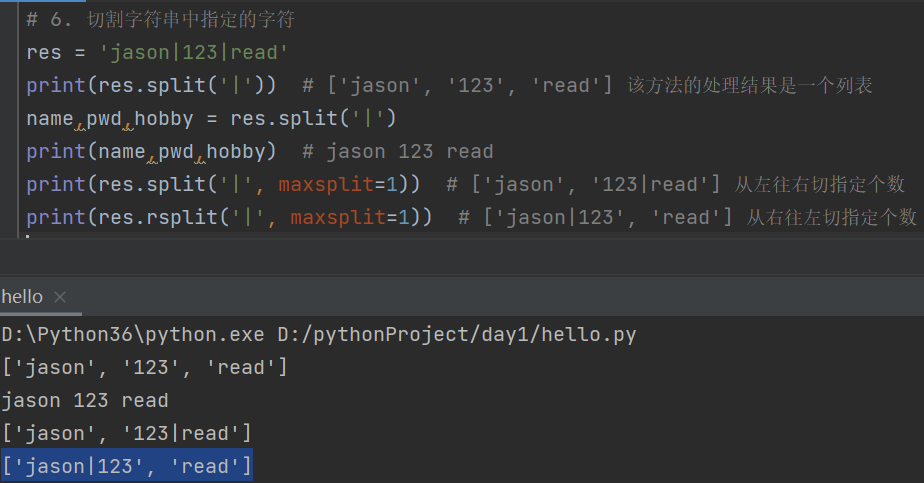
# 6. 切割字符串中指定的字符
res = 'jason|123|read'
print(res.split('|')) # ['jason', '123', 'read'] 该方法的处理结果是一个列表
name,pwd,hobby = res.split('|')
print(name,pwd,hobby) # jason 123 read
print(res.split('|', maxsplit=1)) # ['jason', '123|read'] 从左往右切指定个数
print(res.rsplit('|', maxsplit=1)) # ['jason|123', 'read'] 从右往左切指定个数
![image]()
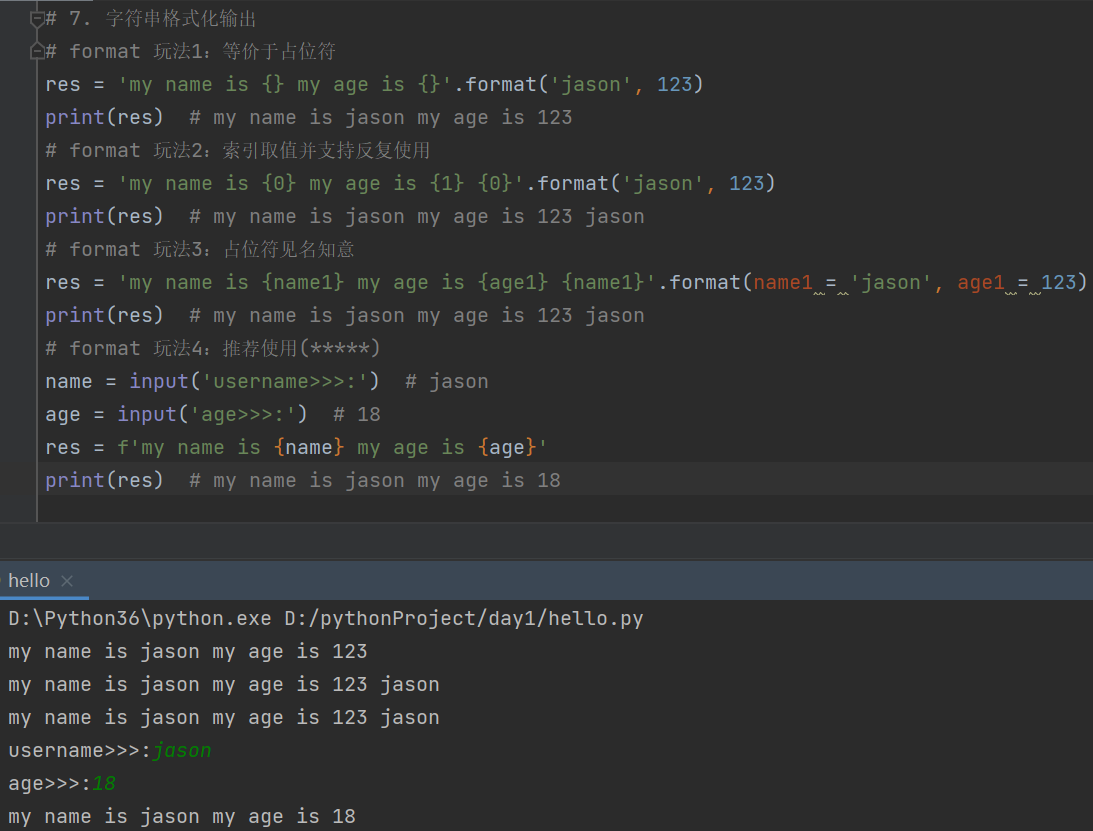
# 7. 字符串格式化输出
# format 玩法1:等价于占位符
res = 'my name is {} my age is {}'.format('jason', 123)
print(res) # my name is jason my age is 123
# format 玩法2:索引取值并支持反复使用
res = 'my name is {0} my age is {1} {0}'.format('jason', 123)
print(res) # my name is jason my age is 123 jason
# format 玩法3:占位符见名知意
res = 'my name is {name1} my age is {age1} {name1}'.format(name1 = 'jason', age1 = 123)
print(res) # my name is jason my age is 123 jason
# format 玩法4:推荐使用(*****)
name = input('username>>>:') # jason
age = input('age>>>:') # 18
res = f'my name is {name} my age is {age}'
print(res) # my name is jason my age is 18
![image]()
字符串需要了解的方法
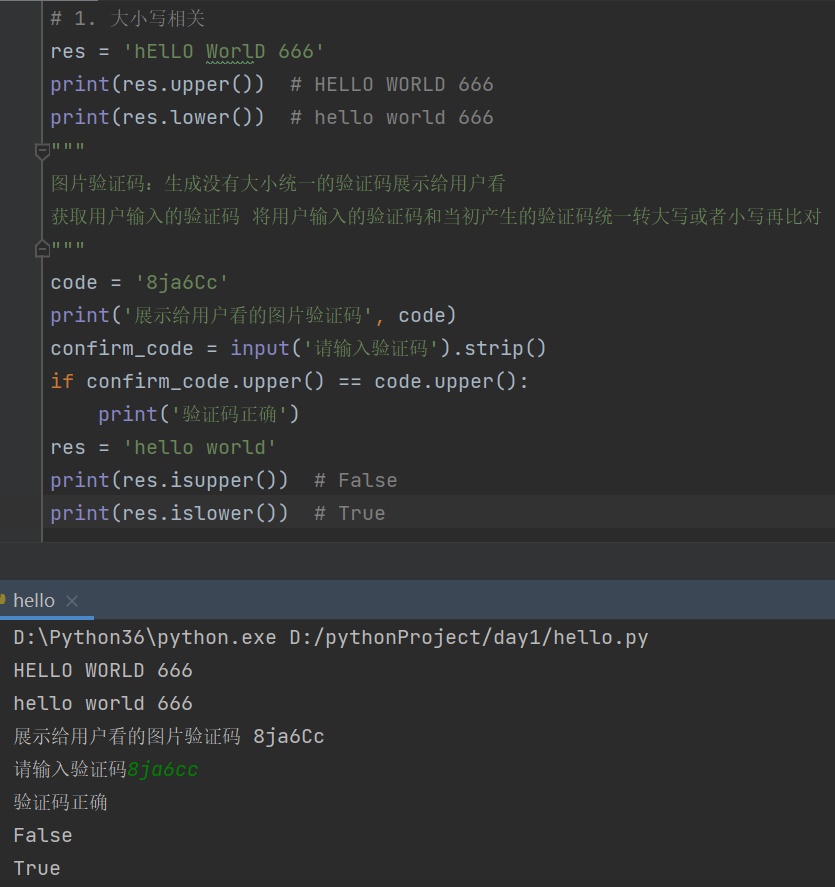
# 1. 大小写相关
res = 'hElLO WorlD 666'
print(res.upper()) # HELLO WORLD 666
print(res.lower()) # hello world 666
"""
图片验证码:生成没有大小统一的验证码展示给用户看
获取用户输入的验证码 将用户输入的验证码和当初产生的验证码统一转大写或者小写再比对
"""
code = '8ja6Cc'
print('展示给用户看的图片验证码', code)
confirm_code = input('请输入验证码').strip()
if confirm_code.upper() == code.upper():
print('验证码正确')
res = 'hello world'
print(res.isupper()) # False
print(res.islower()) # True
![image]()
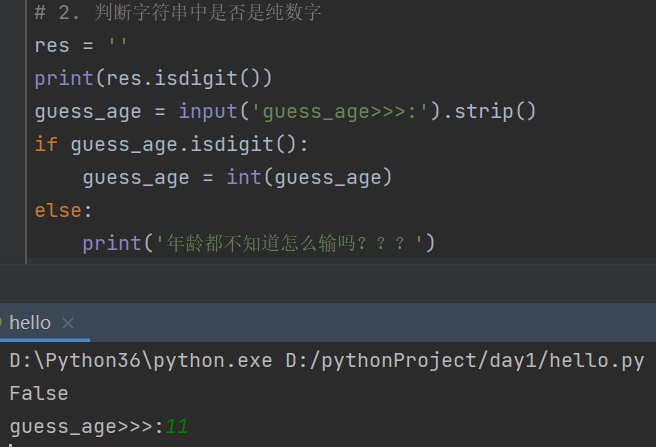
# 2. 判断字符串中是否是纯数字
res = ''
print(res.isdigit())
guess_age = input('guess_age>>>:').strip()
if guess_age.isdigit():
guess_age = int(guess_age)
else:
print('年龄都不知道怎么输吗???')
![image]()
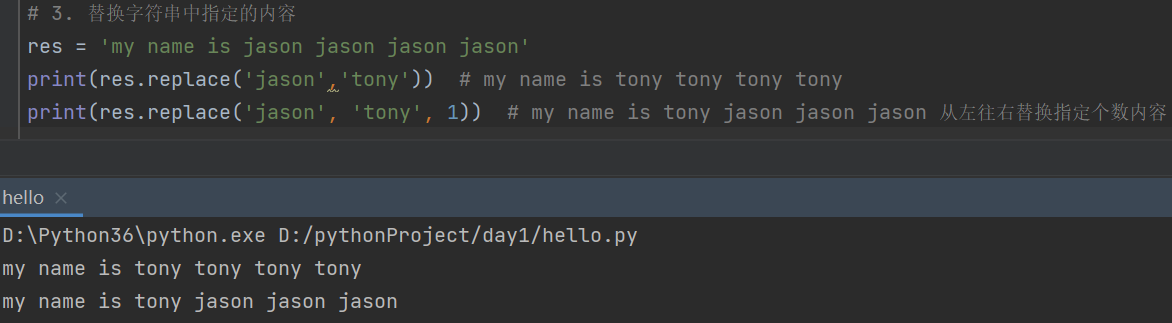
# 3. 替换字符串中指定的内容
res = 'my name is jason jason jason jason'
print(res.replace('jason','tony')) # my name is tony tony tony tony
print(res.replace('jason', 'tony', 1)) # my name is tony jason jason jason 从左往右替换指定个数内容
![image]()
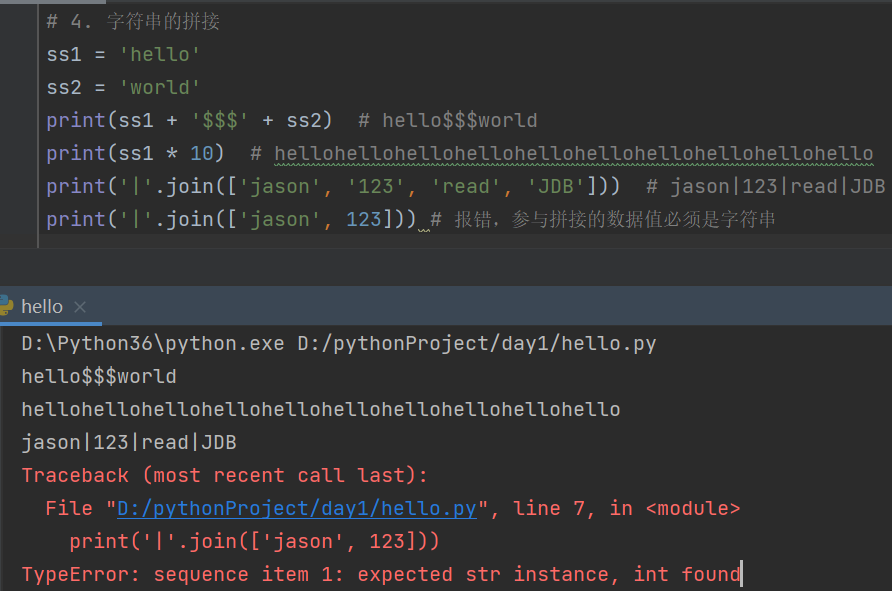
# 4. 字符串的拼接
ss1 = 'hello'
ss2 = 'world'
print(ss1 + '$$$' + ss2) # hello$$$world
print(ss1 * 10) # hellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohellohello
print('|'.join(['jason', '123', 'read', 'JDB'])) # jason|123|read|JDB
print('|'.join(['jason', 123])) # 报错,参与拼接的数据值必须是字符串
![image]()
# 5. 统计指定字符出现的次数
res = 'hello world'
print(res.count('l')) # 3
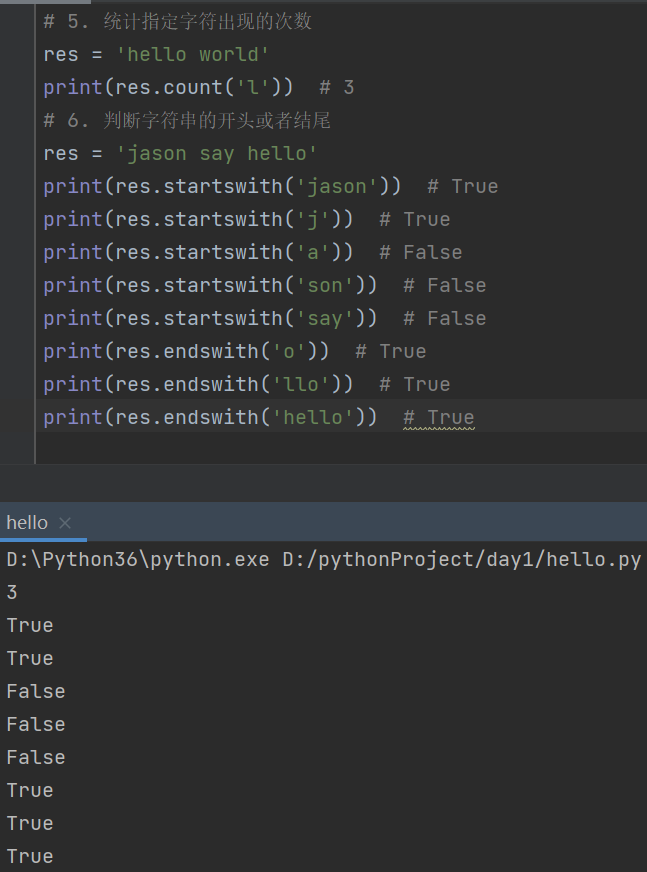
# 6. 判断字符串的开头或者结尾
res = 'jason say hello'
print(res.startswith('jason')) # True
print(res.startswith('j')) # True
print(res.startswith('a')) # False
print(res.startswith('son')) # False
print(res.startswith('say')) # False
print(res.endswith('o')) # True
print(res.endswith('llo')) # True
print(res.endswith('hello')) # True
![image]()
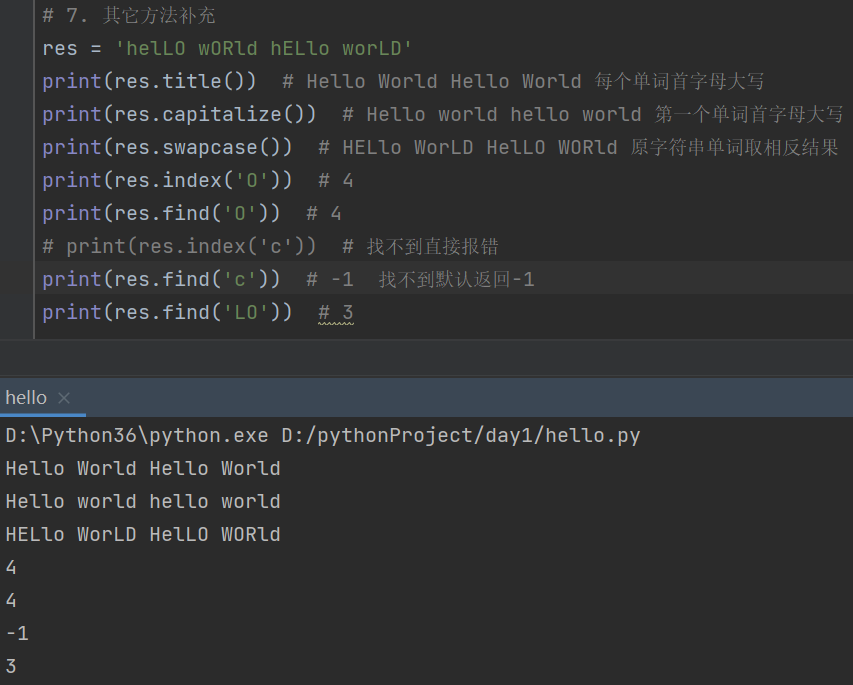
# 7. 其它方法补充
res = 'helLO wORld hELlo worLD'
print(res.title()) # Hello World Hello World 每个单词首字母大写
print(res.capitalize()) # Hello world hello world 第一个单词首字母大写
print(res.swapcase()) # HELlo WorLD HelLO WORld 原字符串单词取相反结果
print(res.index('O')) # 4
print(res.find('O')) # 4
# print(res.index('c')) # 找不到直接报错
print(res.find('c')) # -1 找不到默认返回-1
print(res.find('LO')) # 3
![image]()
列表内置方法与操作
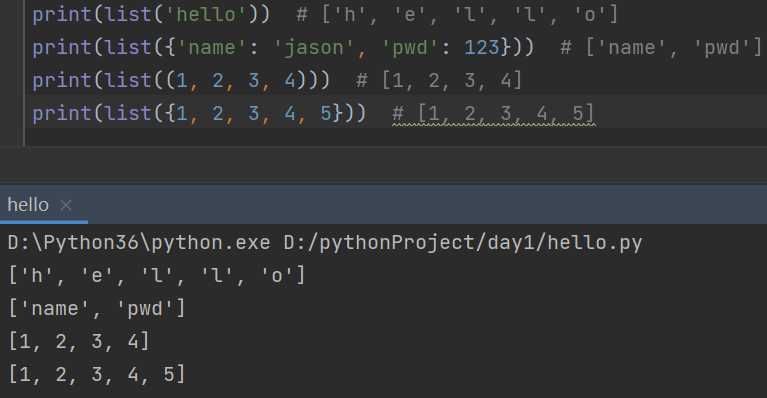
1. 类型转换
list(其它数据类型)
ps:能够被for循环的数据类型都可以转成列表
print(list('hello')) # ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
print(list({'name': 'jason', 'pwd': 123})) # ['name', 'pwd']
print(list((1, 2, 3, 4))) # [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(list({1, 2, 3, 4, 5})) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
![image]()
列表需要掌握的方法
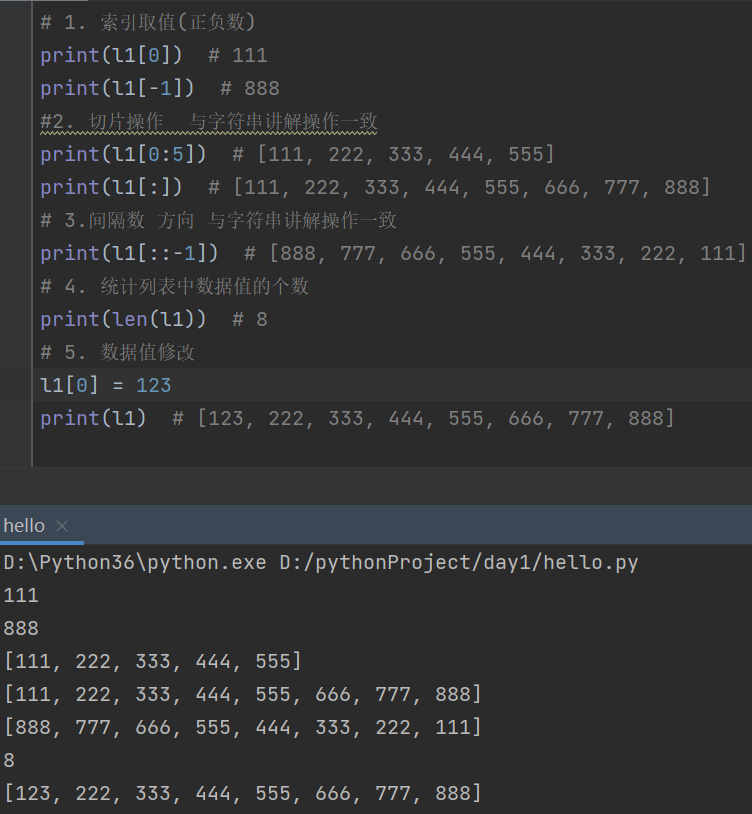
# 1. 索引取值(正负数)
print(l1[0]) # 111
print(l1[-1]) # 888
#2. 切片操作 与字符串讲解操作一致
print(l1[0:5]) # [111, 222, 333, 444, 555]
print(l1[:]) # [111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888]
# 3.间隔数 方向 与字符串讲解操作一致
print(l1[::-1]) # [888, 777, 666, 555, 444, 333, 222, 111]
# 4. 统计列表中数据值的个数
print(len(l1)) # 8
# 5. 数据值修改
l1[0] = 123
print(l1) # [123, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888]
![image]()
l1 = [111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888]
# 6. 列表添加数据值
# 方式1:尾部添加数据值
l1.append('干饭')
print(l1) # [111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888, '干饭']
l1.append(['jason', 'kevin', 'jerry'])
print(l1) # [111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888, ['jason', 'kevin', 'jerry']]
# 方式2:任意位置插入数据值
l1.insert(0, 'jason')
print(l1) # ['jason', 111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888]
l1.insert(1, [11, 22, 33, 44])
print(l1) # [111, [11, 22, 33, 44], 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888]
# 方式3: 扩展列表 合并列表
ll1 = [11, 22, 33]
ll2 = [44, 55, 66]
print(ll1 + ll2) # [11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66]
ll1.extend(ll2)
print(ll1) # [11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66]
for i in ll2: # 等价于上面extend
ll1.append(i)
print(ll1)
l1 = [111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888]
# 7. 删除列表数据
# 方式1:通用的删除关键字del
del l1[0]
print(l1) # [222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888]
# 方式2:remove
l1.remove(444) # 括号内填写数据值
print(l1) # [111, 222, 333, 555, 666, 777, 888]
# 方式3:pop
l1.pop(3) # 括号内填写索引值
print(l1)
l1.pop() # 默认尾部弹出数据值
print(l1) # [111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777]
res = l1.pop(3)
print(res) # 444
res1 = l1.remove(444)
print(res1) # None
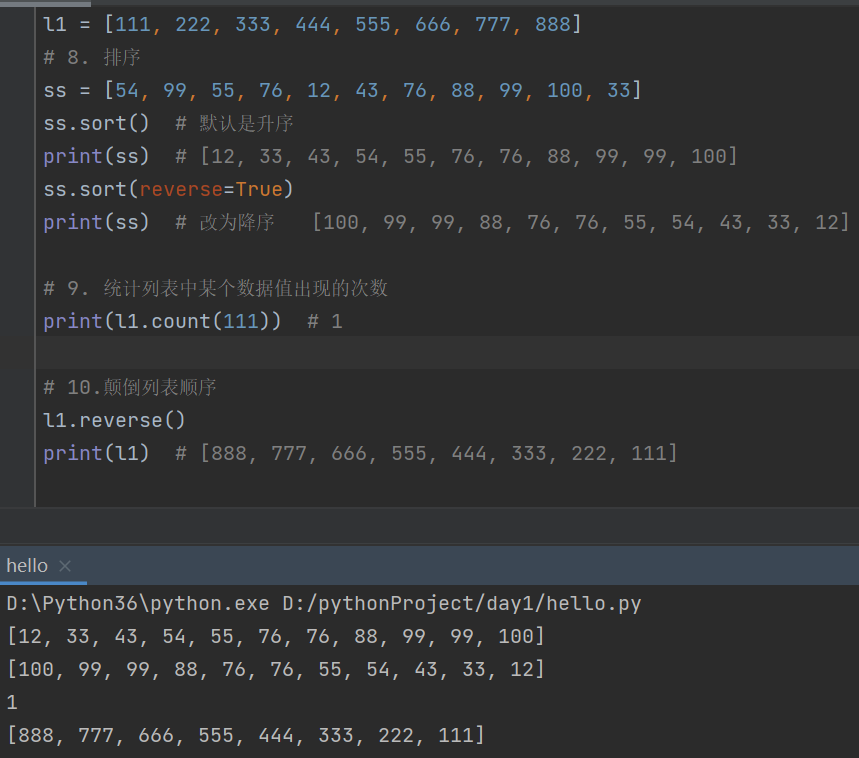
l1 = [111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 666, 777, 888]
# 8. 排序
ss = [54, 99, 55, 76, 12, 43, 76, 88, 99, 100, 33]
ss.sort() # 默认是升序
print(ss) # [12, 33, 43, 54, 55, 76, 76, 88, 99, 99, 100]
ss.sort(reverse=True)
print(ss) # 改为降序 [100, 99, 99, 88, 76, 76, 55, 54, 43, 33, 12]
# 9. 统计列表中某个数据值出现的次数
print(l1.count(111)) # 1
# 10.颠倒列表顺序
l1.reverse()
print(l1) # [888, 777, 666, 555, 444, 333, 222, 111]
![image]()
可变类型与不可变类型
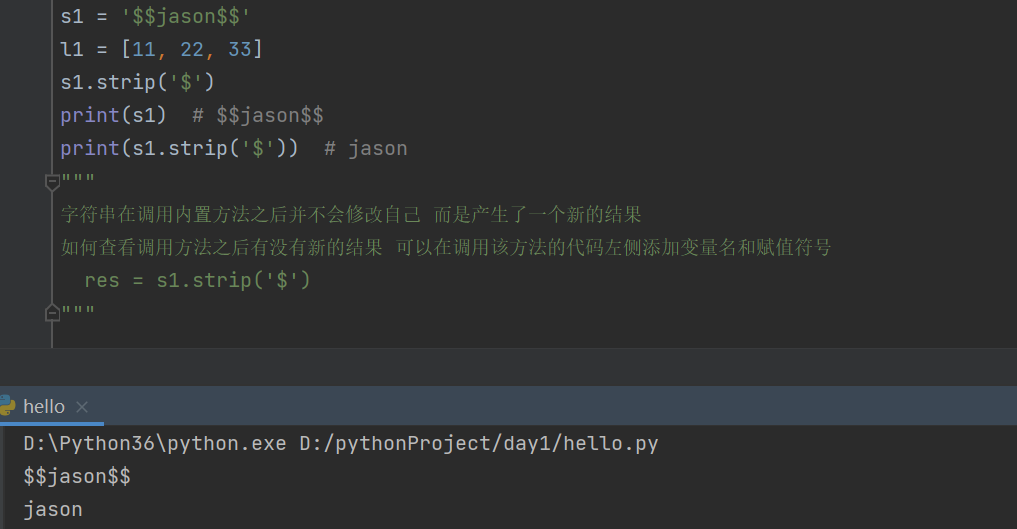
s1 = '$$jason$$'
l1 = [11, 22, 33]
s1.strip('$')
print(s1) # $$jason$$
print(s1.strip('$')) # jason
"""
字符串在调用内置方法之后并不会修改自己 而是产生了一个新的结果
如何查看调用方法之后有没有新的结果 可以在调用该方法的代码左侧添加变量名和赋值符号
res = s1.strip('$')
"""
![image]()
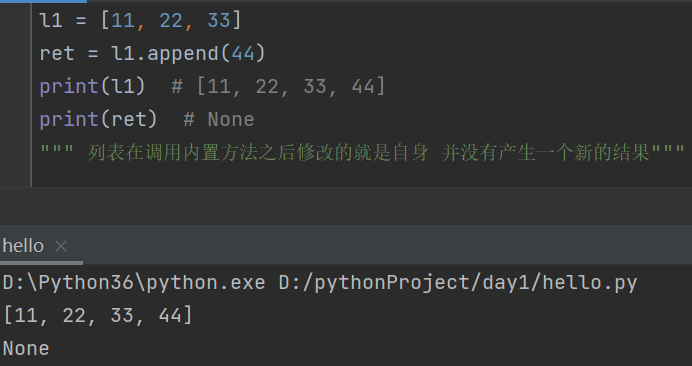
l1 = [11, 22, 33]
ret = l1.append(44)
print(l1) # [11, 22, 33, 44]
print(ret) # None
""" 列表在调用内置方法之后修改的就是自身 并没有产生一个新的结果"""
![image]()
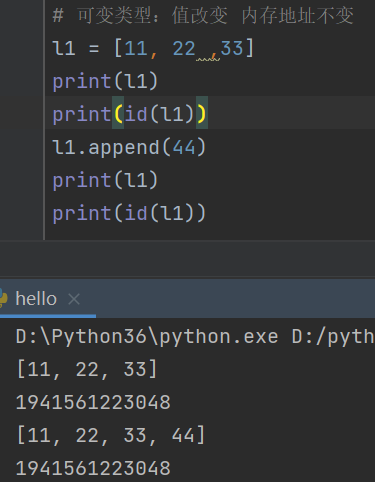
# 可变类型:值改变 内存地址不变
l1 = [11, 22 ,33]
print(l1)
print(id(l1))
l1.append(44)
print(l1)
print(id(l1))
![image]()
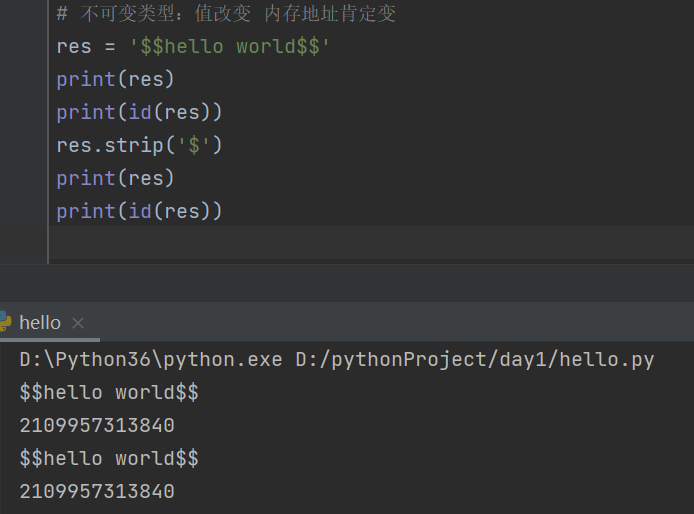
# 不可变类型:值改变 内存地址肯定变
res = '$$hello world$$'
print(res)
print(id(res))
res.strip('$')
print(res)
print(id(res))
![image]()
作业
2.基于字符串充当数据库完成用户登录(基础练习)
data_source = 'jason|123' # 一个用户数据
获取用户用户名和密码 将上述数据拆分校验用户信息是否正确
user,pwd = data_source.split('|')
username = input('请输入用户名>>>:').strip()
password = input('请输入密码>>>:').strip()
if username == user and password == pwd:
print('用户登录成功')
else:
print('用户名或密码错误')
# 3.基于列表充当数据库完成用户登录(拔高练习) # 多个用户数据
data_source = ['jason|123', 'kevin|321', 'oscar|222']
username = input('请输入用户名>>>:').strip()
password = input('请输入密码>>>:').strip()
for i in data_source:
#循环遍历用户名和密码,并和用户输入的用户名及密码做对比
if username == i.split('|')[0] and password == i.split('|')[1]:
print('用户成功')
break # 对比成功,不往下走,直接退出循环
else:
print('用户名或密码失败') # 循环遍历后还是没有找到,说明用户不存在,直接打印错误
4.利用列表编写一个员工姓名管理系统
输入1执行添加用户名功能
输入2执行查看所有用户名功能
输入3执行删除指定用户名功能
'''分析 用户输入的不同 可以执行不同的代码'''
# ps: 思考如何让程序循环起来并且可以根据不同指令执行不同操作
# 提示: 循环结构 + 分支结构
#
# 拔高: 是否可以换成字典或者数据的嵌套使用完成更加完善的员工管理而不是简简单单的一个用户名(能写就写不会没有关系)
l1 = []
info ="""
1.添加用户
2.查看用户
3.删除用户
4.退出
"""
while True:
# 打印用户界面信息
print(info)
# 根据用户输入进行判断
cmd = input('请根据提示输入对应指令>>>:').strip()
# 根据用户输入判断是否为数字
if cmd.isdigit():
cmd = int(cmd)
else:
print('输入正确数字')
if cmd == 1:
username=input('请输入用户').strip()
l1.append(username)
print(f'用户{username}添加成功')
elif cmd == 2:
print(l1)
elif cmd == 3:
username = input('请输入用户名').strip()
if username in l1:
l1.remove(username)
print(f'用户{username}删除成功')
else:
print('删除的用户不存在')
elif cmd == 4:
break



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号