LeetCode入门指南 之 栈和队列
栈
155. 最小栈
设计一个支持
push,pop,top操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x)—— 将元素 x 推入栈中。pop()—— 删除栈顶的元素。top()—— 获取栈顶元素。getMin()—— 检索栈中的最小元素。
class MinStack {
/** initialize your data structure here. */
private Deque<integer> stack;
// 额外用一个栈存储最小值
private Deque<integer> minstack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new LinkedList<>();
minstack = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
if (minstack.isEmpty() || val < minstack.peek()) {
minstack.push(val);
} else {
minstack.push(minstack.peek());
}
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
minstack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minstack.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(val);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
有效的算符包括
+、-、*、/。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。说明:
- 整数除法只保留整数部分。
- 给定逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
class Solution {
/**
* 思路:遇见数字就入栈,遇见操作符就弹出两个操作数进行相应操作并将结果入栈。
* 注意:加法和乘法不需要关注两个数的先后顺序,减法和除法中,后出栈的数在操作符之前
*/
private Deque<integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
String temp;
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++) {
temp = tokens[i];
switch (temp) {
case "+":
stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop());
break;
case "-":
int j = stack.pop();
stack.push(stack.pop() - j);
break;
case "*":
stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop());
break;
case "/":
int k = stack.pop();
stack.push(stack.pop() / k);
break;
default:
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(temp));
}
}
return stack.peekFirst();
}
}
394. 字符串解码
给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串。
编码规则为:
k[encoded_string],表示其中方括号内部的 encoded_string 正好重复 k 次。注意 k 保证为正整数。你可以认为输入字符串总是有效的;输入字符串中没有额外的空格,且输入的方括号总是符合格式要求的。
此外,你可以认为原始数据不包含数字,所有的数字只表示重复的次数 k ,例如不会出现像
3a或2[4]的输入。
思路:栈,思路简单,关键在于字符串拼接顺序的细节问题。
class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
Deque<string> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
String str = s.substring(i, i + 1);
if (str.equals("]")) {
//拼接 [] 之间的字符,这里得到的是逆序,不用反转
StringBuilder strSB = new StringBuilder();
while (!stack.peek().equals("[")) {
strSB.append(stack.pop());
}
//弹出 [
stack.pop();
//拼接 [ 之前的重复次数
StringBuilder reTimesSB = new StringBuilder();
while (!stack.isEmpty() && isDigit(stack.peek())) {
reTimesSB.append(stack.pop());
}
//根据重复次数拼接字符串,反转后转为整型
int reTimes = Integer.parseInt(reTimesSB.reverse().toString());
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (reTimes > 0) {
sb.append(strSB);
reTimes--;
}
//新字符串入栈
stack.push(sb.toString());
} else {
stack.push(str);
}
}
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
res.append(stack.pop());
}
//由于之前的字符拼接都是逆序的,反转后再返回
return res.reverse().toString();
}
//首字符是否为数字
private boolean isDigit(String str) {
char ch = str.charAt(0);
return ch >= '0' && ch <= '9';
}
}
133. 克隆图
给你无向 连通 图中一个节点的引用,请你返回该图的 深拷贝(克隆)。
图中的每个节点都包含它的值
val(int) 和其邻居的列表(list[Node])。class Node { public int val; public List<node> neighbors; }
class Solution {
private HashMap<node, node=""> visited = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 函数定义:
* 克隆当前结点开始的图并返回当前结点
*/
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
//base case 已经克隆过的结点就直接返回
if (visited.containsKey(node)) {
return visited.get(node);
}
/**
* 对于node来说,克隆整个图就是先克隆自己,再克隆所有以其子结点开始的图,然后返回
* 根据函数定义易写出如下代码
*/
Node cloneNode = new Node (node.val, new ArrayList<>());
visited.put(node, cloneNode);
for (Node tempNode : node.neighbors) {
cloneNode.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(tempNode));
}
return cloneNode;
}
}
- 做了此题再看看138. 复制带随机指针的链表递归解法
class Solution {
HashMap<node, node=""> map = new HashMap<>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
//base case
if (map.containsKey(head)) {
return map.get(head);
}
/**
* 对当前结点来说,克隆整个链表等于先克隆自己,再克隆next和random子结点开始的链表
*/
Node cloneNode = new Node(head.val);
map.put(head, cloneNode);
cloneNode.next = copyRandomList(head.next);
cloneNode.random = copyRandomList(head.random);
return cloneNode;
}
}
200. 岛屿数量
给你一个由
'1'(陆地)和'0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
思路:DFS。
- 对于二维矩阵中每个结点来说,他有上、下、左、右四个邻居,因此可以将每个岛屿都看成一个图。
- 从任意一个陆地进入开始遍历,遍历完 1 次就代表发现了 1 个岛屿。 注:图不像树那样是有向的,遍历可能会访问重复结点,一般需要用额外结构表示结点是否已经被访问过。此题可以直接在矩阵上将 1 修改为 2 表示结点已经访问过。
在原矩阵中标记是否访问过:
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
dfs(grid, i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int row, int col) {
//base case,越界
if (!inArea(grid, row, col)) {
return;
}
//base case,是水 或 已经访问过的陆地
if (grid[row][col] != '1') {
return;
}
//标记为已访问
grid[row][col] = '2';
dfs(grid, row + 1, col);
dfs(grid, row - 1, col);
dfs(grid, row, col + 1);
dfs(grid, row, col - 1);
}
private boolean inArea(char[][] grid, int row, int col) {
return row >= 0 && row < grid.length &&
col >= 0 && col < grid[0].length;
}
}
使用额外空间标记是否已经访问过:
class Solution {
// 标记是否访问过
private boolean[][] visited;
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
visited = new boolean[row][col];
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]) {
dfs(grid, i, j);
cnt++;
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
private void dfs (char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
if (!inArea(grid, i, j)) {
return;
}
if (grid[i][j] != '1' || visited[i][j]) {
return;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
dfs(grid, i + 1, j);
dfs(grid, i, j + 1);
dfs(grid, i - 1, j);
dfs(grid, i, j - 1);
}
private boolean inArea(char[][] grid, int row, int col) {
return row >= 0 && row < grid.length &&
col >= 0 && col < grid[0].length;
}
}
推荐阅读:岛屿类问题的通用解法、DFS 遍历框架,最大人工岛
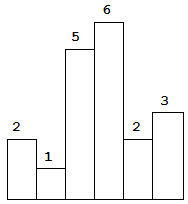
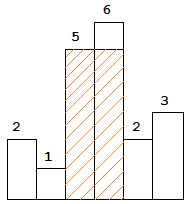
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
以上是柱状图的示例,其中每个柱子的宽度为 1,给定的高度为
[2,1,5,6,2,3]。
图中阴影部分为所能勾勒出的最大矩形面积,其面积为
10个单位。
思路:单调递增栈,依次遍历数组,大于等于栈顶元素直接入栈,小于则弹栈并计算一次面积。
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int len = heights.length;
int[] newHeight = new int[len + 2];
//将 heights 复制到 newHeight,同时将首尾各填充一个 -1
newHeight[0] = -1;
newHeight[len - 1] = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++) {
newHeight[i] = heights[i - 1];
}
int maxArea = 0;
Deque<integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < newHeight.length; i++) {
//出栈
while (!stack.isEmpty() && newHeight[stack.peek()] > newHeight[i]) {
int high = newHeight[stack.pop()];
int width = i - stack.peek() - 1; // 下标 [stack.peek() + 1, i - 1] 对应元素都 大于等于 high
int area = high * width;
maxArea = Math.max(area, maxArea);
}
//入栈
stack.push(i);
}
return maxArea;
}
}
推荐阅读:详解单调栈,🤷♀️必须秒懂!
42.接雨水
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:
输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 输出:6 解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。示例 2:
输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5] 输出:9
推荐一种不使用单调栈而是使用备忘录的解法:
思路:在左边找大于等于当前高度的最大值,右边也找大于等于当前高度的最大值,两者取最小值再减去当前高度即为当前下标所能接的雨水量。
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length <= 2) {
return 0;
}
int len = height.length;
//分别记录元素左边和右边的最大值
int[] leftMax = new int[len];
int[] rightMax = new int[len];
//最左边元素左边的最大值
leftMax[0] = height[0];
//最右边元素右边的最大值
rightMax[len - 1] = height[len - 1];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i - 1], height[i]);
}
for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i + 1], height[i]);
}
int area = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < len - 1; i++) {
area += Math.min(leftMax[i], rightMax[i]) - height[i];
}
return area;
}
}
队列
232. 用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(
push、pop、peek、empty):实现
MyQueue类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
class MyQueue {
private Deque<integer> instack;
private Deque<integer> outstack;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
instack = new LinkedList<>();
outstack = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
instack.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (outstack.isEmpty()) {
while (!instack.isEmpty()) {
outstack.push(instack.pop());
}
}
return outstack.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if (outstack.isEmpty()) {
while (!instack.isEmpty()) {
outstack.push(instack.pop());
}
}
return outstack.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return instack.isEmpty() && outstack.isEmpty();
}
}
542. 01 矩阵
给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵,找出每个元素到最近的 0 的距离。
两个相邻元素间的距离为 1 。
BFS:
class Solution {
/**
* 思路:
* 同样将矩阵看成图的结构,每个位置有上下左右四个邻居,所有的0都作为图的源点开始bfs
*/
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
//0作为源点全部加入队列
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
queue.offer(new Integer[] {i, j});
//1置为-1表示未访问过的点
} else if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {
matrix[i][j] = -1;
}
}
}
//将队首元素出队并访问其上下左右四个未访问的邻居,然后加入队尾
int[][] directions = new int[][] {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer[] point = queue.poll();
int x = point[0];
int y = point[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = x + directions[i][0];
int newY = y + directions[i][1];
if (newX >= 0 && newX < matrix.length &&
newY >= 0 && newY < matrix[0].length &&
matrix[newX][newY] == -1) {
matrix[newX][newY] = matrix[x][y] + 1;
queue.offer(new Integer[] {newX, newY});
}
}
}
return matrix;
}
private Deque<integer[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
动态规划(学习了动态规划再回过头来看):
当前点到最近0的距离取决于其四个邻居到最近0的距离的最小值加1,应尝试用动态规划来解决。
class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
//dp元素表示当前下标的点到其最近0的距离
int rows = matrix.length;
int cols = matrix[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
dp[i][j] = 0;
} else if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {
//求最小值先初始化为足够大,初始化为Integer.MAX_VALUE会越界
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 1;
}
}
}
/**
* 一个点的dp值是由其上下左右四个状态来决定,无法从一个方向开始递推!
* 最简单的方式是从四个方向分别递推一次
*/
//上到下
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (i - 1 >= 0) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j] + 1);
}
}
}
//左到右
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (j - 1 >= 0) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
//下到上
for (int i = rows - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = cols - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (i + 1 < rows) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i + 1][j] + 1);
}
}
}
//右到左
for (int i = rows - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = cols - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (j + 1 < cols) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i][j + 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp;
}
}
仔细观察发现其实可以将前两次递推合并,后两次递推也可以合并。
class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
//dp元素表示当前下标的点到其最近0的距离
int rows = matrix.length;
int cols = matrix[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
dp[i][j] = 0;
} else if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {
//求最小值先初始化为足够大,初始化为Integer.MAX_VALUE会越界
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 1;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (i - 1 >= 0) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j] + 1);
}
if (j - 1 >= 0) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
for (int i = rows - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = cols - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (i + 1 < rows) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i + 1][j] + 1);
}
if (j + 1 < cols) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i][j + 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp;
}
}
225. 用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通队列的全部四种操作(
push、top、pop和empty)。实现
MyStack类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 压入栈顶。int pop()移除并返回栈顶元素。int top()返回栈顶元素。boolean empty()如果栈是空的,返回true;否则,返回false。
class MyStack {
private Deque<integer> inQueue;
private Deque<integer> outQueue;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
inQueue = new LinkedList<>();
outQueue = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
inQueue.offer(x);
while (!outQueue.isEmpty()) {
inQueue.offer(outQueue.poll());
}
Deque<integer> temp = inQueue;
inQueue = outQueue;
outQueue = temp;
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return outQueue.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return outQueue.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return outQueue.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
用一个队列实现栈:
class MyStack {
private Deque<integer> queue;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
int size = queue.size();
//先将新元素入队
queue.offer(x);
//将其前面的元素依次出队并重新入队
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
queue.offer(queue.poll());
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
</integer[]></node,></node,>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号