C++ 平面拟合的实现
4.3.2 C++ 平面拟合的实现
参考教程:
gaoxiang12/slam_in_autonomous_driving: 《自动驾驶中的SLAM技术》对应开源代码 (github.com)
1. 编写 Plane fitting
1.1 创建文件夹
通过终端创建一个名为Plane_fitting的文件夹以保存我们的VSCode项目,在/Plane_fitting目录下打开vscode
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~$ mkdir -p Plane_fitting
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~$ cd Plane_fitting/
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~/Plane_fitting$ code .
1.2 编写平面拟合程序
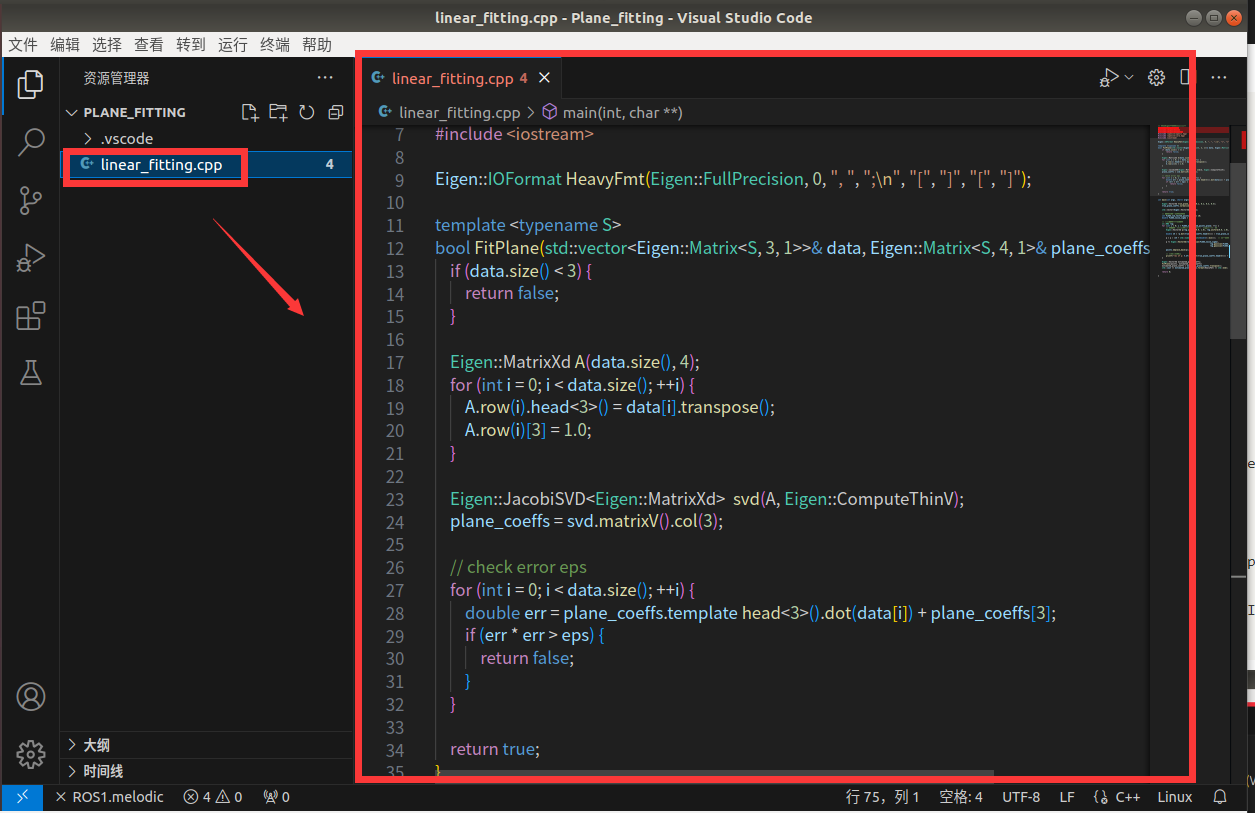
新建文件linear_fitting.cpp
使用快速 SVD 分解,仅计算 A 矩阵 SVD 结果的最后一列。在计算完成后,将点的具体取值代入本方程,要求它们的平方误差不超过预设的阈值。下面这段测试程序把随机生成的平面参数作为真值,在平面上取若干个点,再加入噪声,做平面拟合。
在linear_fitting.cpp粘贴如下代码并保存(Ctrl+S)
// 引入Eigen头文件与常用类型
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <iostream>
Eigen::IOFormat HeavyFmt(Eigen::FullPrecision, 0, ", ", ";\n", "[", "]", "[", "]");
template <typename S>
bool FitPlane(std::vector<Eigen::Matrix<S, 3, 1>>& data, Eigen::Matrix<S, 4, 1>& plane_coeffs, double eps = 1e-2) {
if (data.size() < 3) {
return false;
}
Eigen::MatrixXd A(data.size(), 4);
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); ++i) {
A.row(i).head<3>() = data[i].transpose();
A.row(i)[3] = 1.0;
}
Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svd(A, Eigen::ComputeThinV);
plane_coeffs = svd.matrixV().col(3);
// check error eps
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); ++i) {
double err = plane_coeffs.template head<3>().dot(data[i]) + plane_coeffs[3];
if (err * err > eps) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char argv) {
Eigen::Vector4d true_plane_coeffs(0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4);
true_plane_coeffs.normalize();
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> points;
// 生成平面中的点的数量
int FLAGS_num_tested_points_plane = 10;
double FLAGS_noise_sigma = 0.01;
// 随机生成仿真平面点
cv::RNG rng;
for (int i = 0; i < FLAGS_num_tested_points_plane; ++i) {
// 先生成一个随机点,计算第四维,增加噪声,再归一化
Eigen::Vector3d p(rng.uniform(0.0, 1.0), rng.uniform(0.0, 1.0), rng.uniform(0.0, 1.0));
double n4 = -p.dot(true_plane_coeffs.head<3>()) / true_plane_coeffs[3];
p = p / (n4 + std::numeric_limits<double>::min()); // 防止除零
p += Eigen::Vector3d(rng.gaussian(FLAGS_noise_sigma),
rng.gaussian(FLAGS_noise_sigma),
rng.gaussian(FLAGS_noise_sigma));
points.emplace_back(p);
// 验证在平面上
printf("res of p: %.2f\n",p.dot(true_plane_coeffs.head<3>()) + true_plane_coeffs[3] );
}
Eigen::Vector4d estimated_plane_coeffs;
FitPlane(points, estimated_plane_coeffs);
estimated_plane_coeffs = estimated_plane_coeffs.transpose();
std::cout << estimated_plane_coeffs.format(HeavyFmt) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
2. 新建 CMakeLists.txt 文件
新建CMakeLists.txt文件
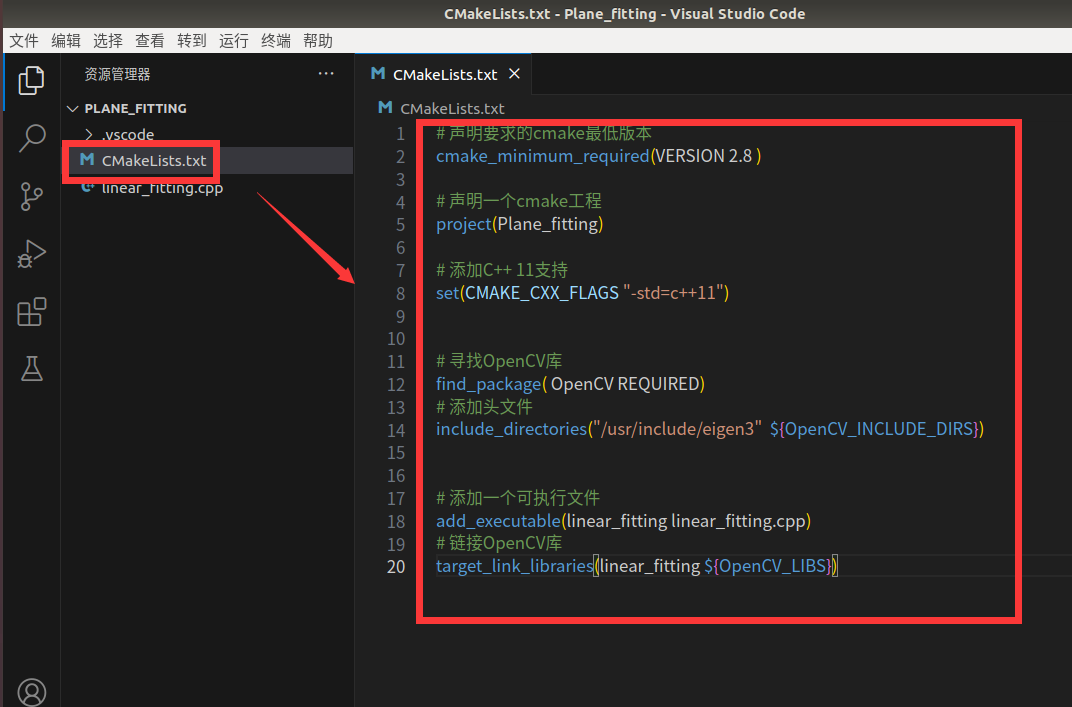
在CMakeLists.txt中添加如下内容:
# 声明要求的cmake最低版本
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8 )
# 声明一个cmake工程
project(Plane_fitting)
# 添加C++ 11支持
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11")
# 寻找OpenCV库
find_package( OpenCV REQUIRED)
# 添加头文件
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3" ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# 添加一个可执行文件
add_executable(linear_fitting linear_fitting.cpp)
# 链接OpenCV库
target_link_libraries(linear_fitting ${OpenCV_LIBS})
3. 编译并执行
ctrl+alt+T打开终端,执行如下指令进行cmake编译
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~$ cd Plane_fitting/
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~/Plane_fitting$ mkdir build
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~/Plane_fitting$ cd build/
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~/Plane_fitting/build$ cmake ..
接着make对工程进行编译
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~/Plane_fitting/build$ make
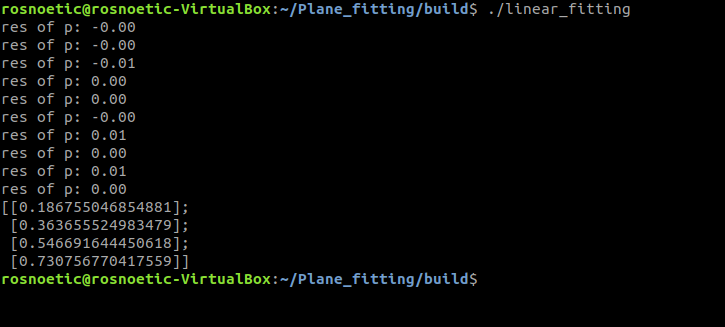
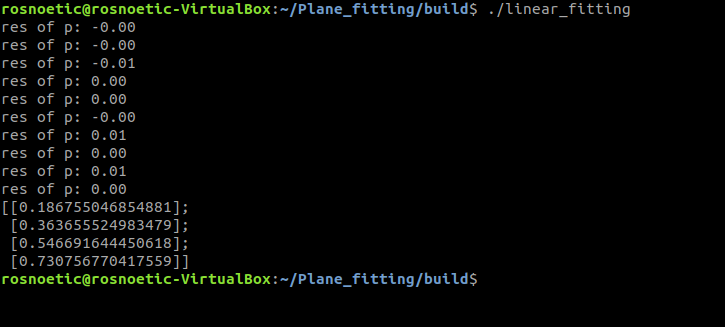
进一步的调用可执行文件linear_fitting :
rosnoetic@rosnoetic-VirtualBox:~/Plane_fitting/build$ ./linear_fitting
res of p: -0.00
res of p: -0.00
res of p: -0.01
res of p: 0.00
res of p: 0.00
res of p: -0.00
res of p: 0.01
res of p: 0.00
res of p: 0.01
res of p: 0.00
[[0.186755046854881];
[0.363655524983479];
[0.546691644450618];
[0.730756770417559]]