学习Faster R-CNN代码roi_pooling(三)
这一篇单独拿出来了解一下roi_pooling/src/roi_pooling.c中C代码:
说明
我查过一些,但没有查到太多有用的信息,连百度#include <TH/TH.h>都百度不出太多信息,更不知道THFloatTensor_data,THFloatTensor_size具体怎么用。可能我查到的信息还是太少了吧,下面说一下我自己的理解吧,不能保证正确。
1.关于头文件TH/TH.h
#include<TH/TH.h>包括了 pytorch C 代码数据结构和函数的声明,这是pytorch底层接口。
2.roi_pooling_forward的参数
1 int roi_pooling_forward(int pooled_height, int pooled_width, float spatial_scale, 2 THFloatTensor * features, THFloatTensor * rois, THFloatTensor * output)
pooled_height pooling后的高;
pooled_width pooling后的宽;
spatial_scale 空间尺度,输入图片与feature map之前的比值,这个feature map指roi pooling层的输入;
features 第一个网络卷积后的特征图;
rois 所有感兴趣区域;
output 指的是pooling后的结果?
3.函数里面的变量
1 // Grab the input tensor 2 float * data_flat = THFloatTensor_data(features); 3 float * rois_flat = THFloatTensor_data(rois); 4 5 float * output_flat = THFloatTensor_data(output);
把这几个参数值提取出来。在C里面就是开辟一块连续的内存来存储这些数据。
THFloatTensor_data作用就是提取值吧。
1 // Number of ROIs 2 int num_rois = THFloatTensor_size(rois, 0); 3 int size_rois = THFloatTensor_size(rois, 1);
根据上面代码rois信息包括num_rois和size_rois,即感兴趣区域的数量和大小(这里的大小指的是roi的大小,准确的说是占据的内存区域)。
1 // batch size 2 int batch_size = THFloatTensor_size(features, 0); 3 if(batch_size != 1) 4 { 5 return 0; 6 } 7 // data height 8 int data_height = THFloatTensor_size(features, 1); 9 // data width 10 int data_width = THFloatTensor_size(features, 2); 11 // Number of channels 12 int num_channels = THFloatTensor_size(features, 3);
features信息包括batch_size,data_height,data_width,num_channels即批尺寸,特征数据高度,特征数据宽度,特征的通道数。
1 // Set all element of the output tensor to -inf. 2 THFloatStorage_fill(THFloatTensor_storage(output), -1);
开始是把所有输出张量的元素设置为负无穷。
接下来就要对每个ROI进行max pool了。
// For each ROI R = [batch_index x1 y1 x2 y2]: max pool over R int index_roi = 0; int index_output = 0; int n; for (n = 0; n < num_rois; ++n)
初始化roi索引是0;初始化输出索引是0。然后开始遍历所有的感兴趣区域。
1 int roi_batch_ind = rois_flat[index_roi + 0]; 2 int roi_start_w = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 1] * spatial_scale); 3 int roi_start_h = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 2] * spatial_scale); 4 int roi_end_w = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 3] * spatial_scale); 5 int roi_end_h = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 4] * spatial_scale);
上面代码是取出roi的信息,roi_batch_ind,roi_start_w,roi_start_h,roi_end_w,roi_end_h,包括批的索引,ROI左上角和右下角的坐标。
对于每个ROI,从rois_flat中取出索引以及坐标信息,坐标信息乘以spatial_scale是因为这个值是输入图片与feature map之前的比值所以乘上这个比值就是把坐标映射到了原图像上,而不是在featuremap上。映射到原图像时可能不是对齐的,所以这里要四舍五入取整。
1 int roi_height = fmaxf(roi_end_h - roi_start_h + 1, 1); 2 int roi_width = fmaxf(roi_end_w - roi_start_w + 1, 1); 3 float bin_size_h = (float)(roi_height) / (float)(pooled_height); 4 float bin_size_w = (float)(roi_width) / (float)(pooled_width);
得到ROI的高度和宽度,pooling后bin的高和宽,这里bin的长宽是个浮点数,不一定是整数。(这里bin指的是pooling后的一小块,即后文中的sections,这里引入bin的目的是将不同大小尺度的ROI,resize成相同大小的尺寸的feature map,便于之后的分类工作)
1 int index_data = roi_batch_ind * data_height * data_width * num_channels; 2 const int output_area = pooled_width * pooled_height;
index_data指什么?是批索引乘以特征图高度乘以特征图宽度乘以特征图通道数。
output_area是pooling后输出的大小,因为pooling大小是固定的,这个值是不变的。
1 int c, ph, pw; 2 for (ph = 0; ph < pooled_height; ++ph) 3 { 4 for (pw = 0; pw < pooled_width; ++pw) 5 {
上面代码就是进行对每个bin进行pooling了。
1 int hstart = (floor((float)(ph) * bin_size_h)); 2 int wstart = (floor((float)(pw) * bin_size_w)); 3 int hend = (ceil((float)(ph + 1) * bin_size_h)); 4 int wend = (ceil((float)(pw + 1) * bin_size_w));
hstart和wstart是每个bin的在ROI的左上角位置。ceil函数是返回不小于这个数的整数,hend和wend就是bin在ROI的右下角位置。因为是ceil函数,所以左上角的bin不小于右下角的bin。
1 hstart = fminf(fmaxf(hstart + roi_start_h, 0), data_height); 2 hend = fminf(fmaxf(hend + roi_start_h, 0), data_height); 3 wstart = fminf(fmaxf(wstart + roi_start_w, 0), data_width); 4 wend = fminf(fmaxf(wend + roi_start_w, 0), data_width);
hstart、wstart、hend和wend就是返回bin在原图的位置,原本是在ROI中的位置。
1 int h, w, c; 2 for (h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) 3 { 4 for (w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) 5 { 6 for (c = 0; c < num_channels; ++c) 7 { 8 const int index = (h * data_width + w) * num_channels + c; 9 if (data_flat[index_data + index] > output_flat[pool_index + c * output_area]) 10 { 11 output_flat[pool_index + c * output_area] = data_flat[index_data + index]; 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 }
上面循环就是bin的高度嵌套宽度嵌套通道数,然后就取这个bin中的最大值。
1 // Increment ROI index 2 index_roi += size_rois; 3 index_output += pooled_height * pooled_width * num_channels;
当处理完一个ROI之后,更新index_roi和index_output 信息,因为C语言中是连续内存,ROI索引就是加上size_rois即ROI大小,输出索引就是加上pooling后占据的内存大小。
简单总结一下:

(2)region proposal 投影之后位置(左上角,右下角坐标):(0,3),(7,8)。
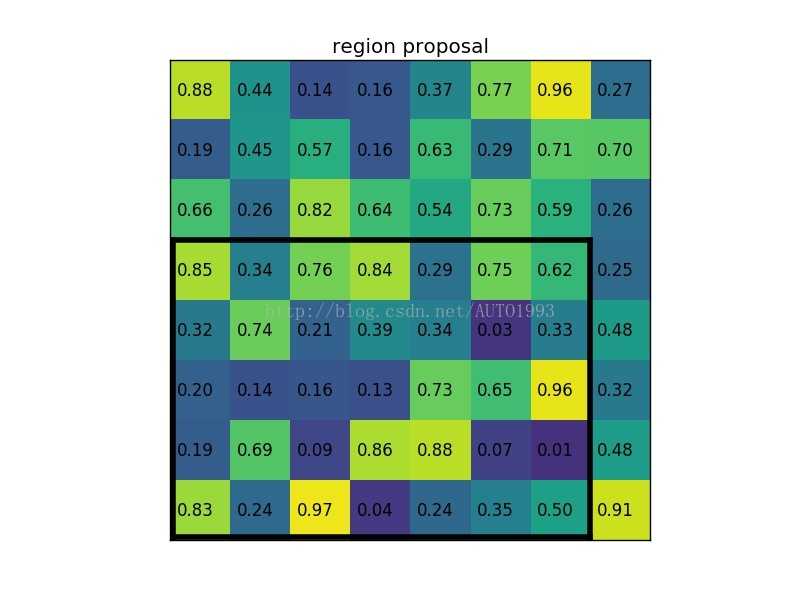
(3)将其划分为(2*2)个sections(因为输出大小为2*2),我们可以得到:
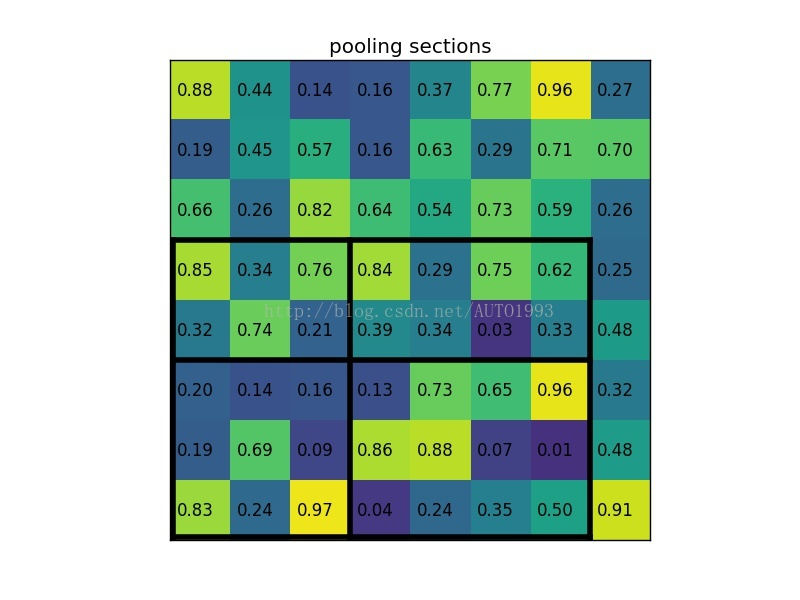
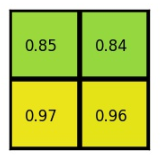
(4)对每个section做max pooling,可以得到:
下面上完整代码
** ## roi_pooling/src/roi_pooling.c ## **
1 #include <TH/TH.h> 2 #include <math.h> 3 4 int roi_pooling_forward(int pooled_height, int pooled_width, float spatial_scale, 5 THFloatTensor * features, THFloatTensor * rois, THFloatTensor * output) 6 { 7 // Grab the input tensor 8 float * data_flat = THFloatTensor_data(features); 9 float * rois_flat = THFloatTensor_data(rois); 10 11 float * output_flat = THFloatTensor_data(output); 12 13 // Number of ROIs 14 int num_rois = THFloatTensor_size(rois, 0); 15 int size_rois = THFloatTensor_size(rois, 1); 16 // batch size 17 int batch_size = THFloatTensor_size(features, 0); 18 if(batch_size != 1) 19 { 20 return 0; 21 } 22 // data height 23 int data_height = THFloatTensor_size(features, 1); 24 // data width 25 int data_width = THFloatTensor_size(features, 2); 26 // Number of channels 27 int num_channels = THFloatTensor_size(features, 3); 28 29 // Set all element of the output tensor to -inf. 30 THFloatStorage_fill(THFloatTensor_storage(output), -1); 31 32 // For each ROI R = [batch_index x1 y1 x2 y2]: max pool over R 33 int index_roi = 0; 34 int index_output = 0; 35 int n; 36 for (n = 0; n < num_rois; ++n) 37 { 38 int roi_batch_ind = rois_flat[index_roi + 0]; 39 int roi_start_w = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 1] * spatial_scale); 40 int roi_start_h = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 2] * spatial_scale); 41 int roi_end_w = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 3] * spatial_scale); 42 int roi_end_h = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 4] * spatial_scale); 43 // CHECK_GE(roi_batch_ind, 0); 44 // CHECK_LT(roi_batch_ind, batch_size); 45 46 int roi_height = fmaxf(roi_end_h - roi_start_h + 1, 1); 47 int roi_width = fmaxf(roi_end_w - roi_start_w + 1, 1); 48 float bin_size_h = (float)(roi_height) / (float)(pooled_height); 49 float bin_size_w = (float)(roi_width) / (float)(pooled_width); 50 51 int index_data = roi_batch_ind * data_height * data_width * num_channels; 52 const int output_area = pooled_width * pooled_height; 53 54 int c, ph, pw; 55 for (ph = 0; ph < pooled_height; ++ph) 56 { 57 for (pw = 0; pw < pooled_width; ++pw) 58 { 59 int hstart = (floor((float)(ph) * bin_size_h)); 60 int wstart = (floor((float)(pw) * bin_size_w)); 61 int hend = (ceil((float)(ph + 1) * bin_size_h)); 62 int wend = (ceil((float)(pw + 1) * bin_size_w)); 63 64 hstart = fminf(fmaxf(hstart + roi_start_h, 0), data_height); 65 hend = fminf(fmaxf(hend + roi_start_h, 0), data_height); 66 wstart = fminf(fmaxf(wstart + roi_start_w, 0), data_width); 67 wend = fminf(fmaxf(wend + roi_start_w, 0), data_width); 68 69 const int pool_index = index_output + (ph * pooled_width + pw); 70 int is_empty = (hend <= hstart) || (wend <= wstart); 71 if (is_empty) 72 { 73 for (c = 0; c < num_channels * output_area; c += output_area) 74 { 75 output_flat[pool_index + c] = 0; 76 } 77 } 78 else 79 { 80 int h, w, c; 81 for (h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) 82 { 83 for (w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) 84 { 85 for (c = 0; c < num_channels; ++c) 86 { 87 const int index = (h * data_width + w) * num_channels + c; 88 if (data_flat[index_data + index] > output_flat[pool_index + c * output_area]) 89 { 90 output_flat[pool_index + c * output_area] = data_flat[index_data + index]; 91 } 92 } 93 } 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 } 98 99 // Increment ROI index 100 index_roi += size_rois; 101 index_output += pooled_height * pooled_width * num_channels; 102 } 103 return 1; 104 }
ref:https://blog.csdn.net/auto1993/article/details/78514071
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43872578/article/details/86628515


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号