莫队学习笔记
首先,贴上大佬的讲解WAMonster
然后大佬的卡常技巧一开始并没有看懂,经过多处查找。
下面的函数
int cmp(query a, query b) { return (belong[a.l] ^ belong[b.l]) ? belong[a.l] < belong[b.l] : ((belong[a.l] & 1) ? a.r < b.r : a.r > b.r); }
等同于
int cmp(query a, query b) {//对于左端点在同一奇数块的区间,右端点按升序排列,反之降序 return (belong[a.l]==belong[b.l]) ? ((belong[a.l] & 1) ? a.r < b.r : a.r > b.r):belong[a.l] < belong[b.l] ; }
然后饱受运算优先级折磨的我卑微的修改加上了注释(实在是看不懂)
while(l < ql) now -= (!--cnt[aa[l++]])/*del(l++)*/;//先cnt--,然后 !,然后++ while(l > ql) now += (!cnt[aa[--l]]++)/*add(--l)*/;//先--l,然后!,然后++ while(r < qr) now += (!cnt[aa[++r]]++)/*add(++r)*/;//先++r,然后!,然后++ while(r > qr) now -= (!--cnt[aa[r--]])/*del(r--)*/;//先cnt--,然后!,然后--
然后全部代码(并没有什么改动)
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define maxn 1010000 #define maxb 1010 #define isdigit(x) ((x) >= '0' && (x) <= '9') int aa[maxn], cnt[maxn], belong[maxn]; int n, m, size, bnum, now, ans[maxn]; struct query { int l, r, id; } q[maxn]; int cmp(query a, query b) {//对于左端点在同一奇数块的区间,右端点按升序排列,反之降序 return (belong[a.l]==belong[b.l]) ? ((belong[a.l] & 1) ? a.r < b.r : a.r > b.r):belong[a.l] < belong[b.l] ; } /*void add(int pos) { if(!cnt[aa[pos]]) ++now; ++cnt[aa[pos]]; } void del(int pos) { --cnt[aa[pos]]; if(!cnt[aa[pos]]) --now; }*/ int read() { int res = 0; char c = getchar(); while(!isdigit(c)) c = getchar(); while(isdigit(c)) res = (res << 1) + (res << 3) + c - 48, c = getchar(); return res; } void printi(int x) { if(x / 10) printi(x / 10); putchar(x % 10 + '0'); } int main() { scanf("%d", &n); size = sqrt(n); bnum =ceil((double)n / size); for(int i = 1; i <= bnum; ++i) for(int j = (i - 1) * size + 1; j <= i * size;j++) { belong[j] = i; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) aa[i] = read(); m = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { q[i].l = read(), q[i].r = read(); q[i].id = i; } sort(q + 1, q + m + 1, cmp); int l = 1, r = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { int ql = q[i].l, qr = q[i].r; while(l < ql) now -= (!--cnt[aa[l++]])/*del(l++)*/;//先cnt--,然后 !,然后++ while(l > ql) now += (!cnt[aa[--l]]++)/*add(--l)*/;//先--l,然后!,然后++ while(r < qr) now += (!cnt[aa[++r]]++)/*add(++r)*/;//先++r,然后!,然后++ while(r > qr) now -= (!--cnt[aa[r--]])/*del(r--)*/;//先cnt--,然后!,然后-- ans[q[i].id] = now; } for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) printi(ans[i]), putchar('\n'); return 0; }
接下来出场的是可修改莫队
好题(毒瘤)
这题似乎加强了数据搞的必须开O2才能过(题解里的神仙解法例外)
普通莫队要离线下来做,遇到这种带修改的题目直接就萎了,但是全国广大的OIer们在莫队的基础上,发明了带修莫队这种玄学算法。
对于某些允许离线的带修改区间查询来说,莫队还是能大展拳脚的。做法就是把莫队直接加上一维,变为带修莫队。
具体来说就是给修改和求值打上时间戳,然后在普通莫队双指针的基础上增加一个指针time指向时间,在这一个维度上面跳来跳去,直到跳到左指针指向左端点,右指针指向右端点,time指针指向当前求值的时间戳为止。
通俗地讲,就是再弄一指针,在修改操作上跳来跳去,如果当前修改多了就改回来,改少了就改过去,直到次数恰当为止。(来自大佬的言简意赅)Orz
带修改莫队的排序:
其实排序的主要方法还是跟普通莫队没两样,只不过是加了个关键字而已。
排序函数:
int cmp(ask a,ask b) { return (belong[a.l]==belong[b.l])?((belong[a.r]==belong[b.r])?a.time<b.time:belong[a.r]<belong[b.r]):belong[a.l]<belong[b.l]; }
主算法中的修改操作
似乎与原来的修改区别不大,但值得一提的是,在修改的时候,由于我们的time指针可能“往回跳”,所以我们要记下来之前的值,因此我们可以直接swap这俩值,回来的时候就直接swap回来。(存下来也可以吧)
分块大小和复杂度
大佬证明:
块大小为 ![]() 可以达到最快的理论复杂度
可以达到最快的理论复杂度 ![]() ,证明如下
,证明如下
设分块大小为a,莫队算法时间复杂度主要为t轴移动,同r块l,r移动,l块间的r移动三部分
t轴移动的复杂度为 ![]() ,同r块l,r移动复杂度为
,同r块l,r移动复杂度为 ![]() ,l块间的r移动复杂度为
,l块间的r移动复杂度为 ![]()
三个函数max的最小值当a为 ![]() 取得,为
取得,为 ![]()
证明了当块的大小设n4t−−−√3n4t3时理论复杂度达到最优,而块大小取n−−√n时会退化成O(n2)O(n2),不建议使用。
然后就是毒瘤题的代码了并没有什么改动
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define maxn 1333340//毒瘤题数据加强了 #define maxc 1001000 int a[maxn],cnt[maxc],ans[maxn],belong[maxn]; struct ask{ int l, r, time, id; } q[maxn]; int read(){ int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9')ch=getchar(); while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(ch^48);ch=getchar();} return x*f; } struct modify{ int pos,color,last; } c[maxn]; int cntq, cntc, n, m, size, bnum; int cmp(ask a,ask b) { return (belong[a.l]==belong[b.l])?((belong[a.r]==belong[b.r])?a.time<b.time:belong[a.r]<belong[b.r]):belong[a.l]<belong[b.l]; } int main() { n=read(),m=read(); size=pow(n,2.0/3.0); bnum=ceil((double)n/size);//上取整函数 for(int i = 1; i <= bnum; ++i) for(int j=(i-1)*size+1;j<=i*size;++j)belong[j] = i; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { char opt; opt=getchar();getchar(); if(opt == 'Q') { q[++cntq].l=read(); q[cntq].r=read(); q[cntq].time=cntc; q[cntq].id =cntq; } else if(opt == 'R') { c[++cntc].pos=read(); c[cntc].color=read(); } } sort(q + 1, q + cntq + 1, cmp); int l = 1, r = 0, time = 0, now = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= cntq; ++i) { int ql = q[i].l, qr = q[i].r, qt = q[i].time; while(l<ql) now-= (!--cnt[a[l++]]); while(l>ql) now+= (!cnt[a[--l]]++); while(r<qr) now+= (!cnt[a[++r]]++); while(r>qr) now-= (!--cnt[a[r--]]); while(time < qt) { ++time; if(ql <= c[time].pos && c[time].pos <= qr) now -= (!--cnt[a[c[time].pos]] - !cnt[c[time].color]++); swap(a[c[time].pos], c[time].color); } while(time > qt) { if(ql <= c[time].pos && c[time].pos <= qr) now -= (!--cnt[a[c[time].pos]] - !cnt[c[time].color]++); swap(a[c[time].pos], c[time].color); --time; } ans[q[i].id] = now; } for(int i = 1; i <= cntq; ++i) printf("%d\n", ans[i]); return 0; }
莫队算法的扩展——树上莫队
路径上的统计
分析:
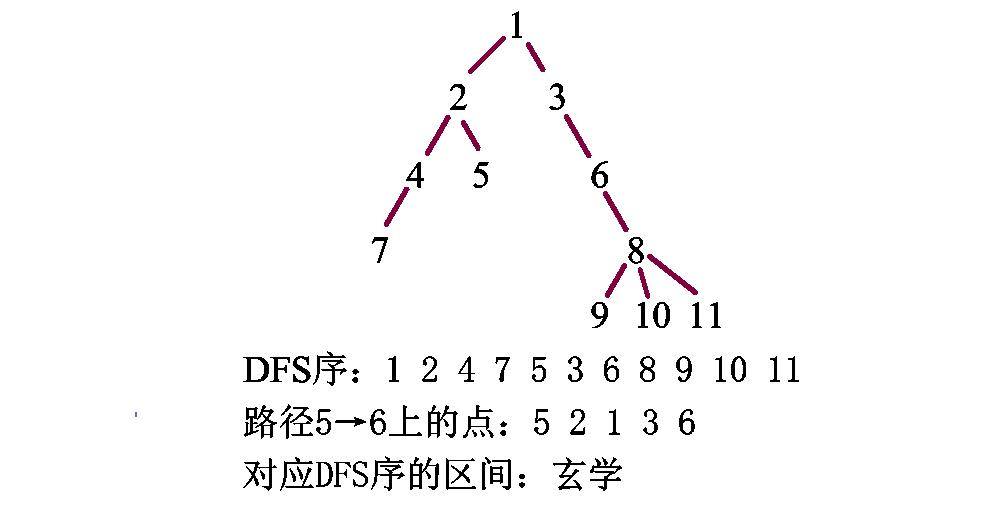

简单的DFS序并不能满足我们进行莫队的应用,因此我们需要用神奇的欧拉序图二来表示。
结论:树的欧拉序上两个相同编号(设为xx)之间的所有编号都出现两次,且都位于xx子树上Orz
大佬对于经过点是否加入答案的解释:树上路径的定义为:从xx到yy经过节点个数最少的路径。
若一个点kk出现两次,说明我们可以先访问kk,进入kk的子树中,然后出来,再到yy,很显然不访问kk是更优的。因此出现两次的点不能统计入答案
WAMonster大佬的具体做法非常详细:设每个点的编号aa首次出现的位置first[a]first[a],最后出现的位置为last[a]last[a],那么对于路径x→yx→y,设first[x]<=first[y]first[x]<=first[y]
(不满足则swap,这个操作的意义在于,如果xx、yy在一条链上,则xx一定是yy的祖先或等于yy),如果lca(x,y)=xlca(x,y)=x,则直接把[first[x],first[y]][first[x],first[y]]的区间扯过来用
,反之使用[last[x],first[y]][last[x],first[y]]区间(为什么不用[first[x],first[y]][first[x],first[y]]?因为(first[x],last[x])(first[x],last[x])不会在路径上,根据性质,里面的编号都会出现两次,考虑了等于没考虑),
但这个区间内不包含xx和yy的最近公共祖先,查询的时候加上即可。
注意:序列长度要*2避免越界
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define maxn 200200 #define isdigit(x) ((x) >= '0' && (x) <= '9') inline int read() { int res = 0; char c = getchar(); while(!isdigit(c)) c = getchar(); while(isdigit(c)) res = (res << 1) + (res << 3) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar(); return res; } int aa[maxn], cnt[maxn], first[maxn], last[maxn], ans[maxn]; int belong[maxn], inp[maxn], vis[maxn], ncnt, l = 1, r, now, size, bnum; //莫队相关 int ord[maxn], val[maxn], head[maxn], depth[maxn], fa[maxn][30], ecnt; int n, m; struct edge { int to, next; } e[maxn]; void adde(int u, int v) { e[++ecnt] = (edge){v, head[u]}; head[u] = ecnt; e[++ecnt] = (edge){u, head[v]}; head[v] = ecnt; } void dfs(int x) { ord[++ncnt] = x; first[x] = ncnt; for(int k = head[x]; k; k = e[k].next) { int to = e[k].to; if(to == fa[x][0]) continue; depth[to] = depth[x] + 1; fa[to][0] = x; for(int i = 1;(1 << i)<=depth[to]; ++i) fa[to][i] = fa[fa[to][i - 1]][i - 1]; dfs(to); } ord[++ncnt] = x; last[x] = ncnt; } int getlca(int x, int y) { if (depth[x] < depth[y]) { swap(x, y); } int dd = depth[x] - depth[y]; for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { if (dd >> i & 1) { x = fa[x][i]; } } if (x == y) { return x; } for (int i = 20 - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (fa[x][i] != fa[y][i]) { x = fa[x][i]; y = fa[y][i]; } } return fa[x][0]; } struct query { int l, r, lca, id; } q[maxn]; int cmp(query a, query b) {//对于左端点在同一奇数块的区间,右端点按升序排列,反之降序 return (belong[a.l]==belong[b.l]) ? ((belong[a.l] & 1) ? a.r < b.r : a.r > b.r):belong[a.l] < belong[b.l] ; } void work(int pos) { vis[pos] ? now -= !--cnt[val[pos]] : now += !cnt[val[pos]]++; vis[pos] ^= 1;//不进位加法,重复两次的点不记入答案 } int main() { n = read(); m = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) val[i] = inp[i] = read(); sort(inp + 1, inp + n + 1); int tot = unique(inp + 1, inp + n + 1) - inp - 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) val[i] = lower_bound(inp + 1, inp + tot + 1, val[i]) - inp; for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) adde(read(), read()); depth[1] = 1; dfs(1); size = sqrt(ncnt), bnum = ceil((double) ncnt / size); for(int i = 1; i <= bnum; ++i) for(int j = size * (i - 1) + 1; j <= i * size; ++j) belong[j] = i; for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { int L = read(), R = read(), lca = getlca(L, R); if(first[L] > first[R]) swap(L, R); if(L == lca) { q[i].l = first[L]; q[i].r = first[R]; } else { q[i].l = last[L]; q[i].r = first[R]; q[i].lca = lca; } q[i].id = i; } sort(q + 1, q + m + 1, cmp); for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { int ql = q[i].l, qr = q[i].r, lca = q[i].lca; while(l < ql) work(ord[l++]); while(l > ql) work(ord[--l]); while(r < qr) work(ord[++r]); while(r > qr) work(ord[r--]); if(lca) work(lca); ans[q[i].id] = now; if(lca) work(lca);//消除掉本次操作的影响避免对下一次查询区间的影响 } for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) printf("%d\n", ans[i]); return 0; }


