List、Map、Set之间的联系与区别:
一、数组和集合的区别:
1.数组的大小是固定的,并且同一个数组只能是相同的数据类型
2.集合的大小是不固定的,在不知道会有多少数据的情况下可使用集合。
二、集合的三种类型:list(列表)、set(集)、map(映射)
List接口和Set接口属于Collection接口,Map接口和Collection接口并列存在(同级)。
List(元素可重复性,有序性):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> arraylist=new ArrayList<>(); arraylist.add(3); arraylist.add(22); arraylist.add(31); arraylist.add(345); arraylist.add(63); arraylist.add(3); //ArrayList底层是一个数组,输出时需要foreach遍历,查询快,增删慢,线层安全,效率高 System.out.print("arraylist:"); for (Integer test : arraylist) { System.out.print(test+" "); } System.out.println(); //换行 //Vector底层是一个实现自动增长的对象数组,元素会自动添加到数组中,查询快,增删慢,线层安全,效率低 Vector<Integer> vector=new Vector<>(); vector.add(3); vector.add(5); vector.add(25); vector.add(51); vector.add(5); System.out.println("vector:"+vector); //LinkedList底层是一个链表,查询慢,增删快,线层不安全,效率高 LinkedList<Integer> linkedList=new LinkedList<>(); linkedList.add(30); linkedList.add(30); linkedList.add(34); linkedList.add(55); System.out.println("linkedlist"+linkedList); |
运行结果:

Set(具有唯一性,无序性):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); LinkedHashSet<String> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<>(); TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(); for (String data : Arrays.asList("afaE", "afaE", "asfweD", "hfasfae", "aefaeA")) { hashSet.add(data); linkedHashSet.add(data); treeSet.add(data); } //HashSet:无序,随机输出。底层数据结构是哈希表,依赖hashCode()和equals()两个方法来保证唯一性。 System.out.println("Ordering in HashSet :" + hashSet); //LinkedHashSet:FIFO插入有序,先进先出。底层结构是链表和哈希表,由链表保证元素有序,哈希表保证元素唯一。 System.out.println("Order of element in LinkedHashSet :" + linkedHashSet); //TreeSet:有序,唯一。底层结构是红黑树,排序采用自然排序和比较容器排序,根据比较的返回值是否为0来判断元素唯一。 System.out.println("Order of objects in TreeSet :" + treeSet); } |
运行结果:
Map(采用键值对<key,value>存储元素,key键唯一):
hashmap:底层结构是数组+链表,无序,线程不安全,效率高,允许有null(key和value都允许),父类是AbstractMap
treemap:底层结构是红黑树,有序,将数据按照key排序,默认是升序排序。
hashtable:底层结构是哈希表,无序,线程安全,效率低,不允许有null值,父类是Dictionary
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | public static void main(String[] args) { // HashMap采用键值对存储数据,采用put()方法存放数据 Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>(); map.put(1, "中国"); map.put(2, "小日本"); map.put(3, "美国佬"); // foreach遍历方法,普遍使用,通过对key唯一的特性,进行key遍历 for (Integer key : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(key + "-->" + map.get(key)); } System.out.println("------------------------------------"); // 因为key唯一,key重复时会自动覆盖value之前存储的数据 map.put(3, "英国佬"); for (Integer key1 : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(key1 + "-->" + map.get(key1)); } System.out.println("------------------------------------"); // Map.Entry遍历key和value,同样是foreach方法,推荐容量大的时候使用 for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "-->" + entry.getValue()); } } |
运行结果: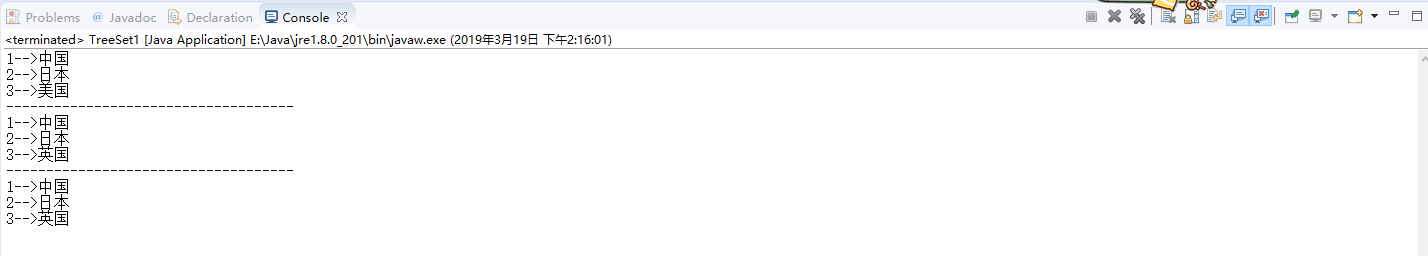
分类:
Java





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
2018-09-04 react+echarts/g2/bizcharts可视化图表