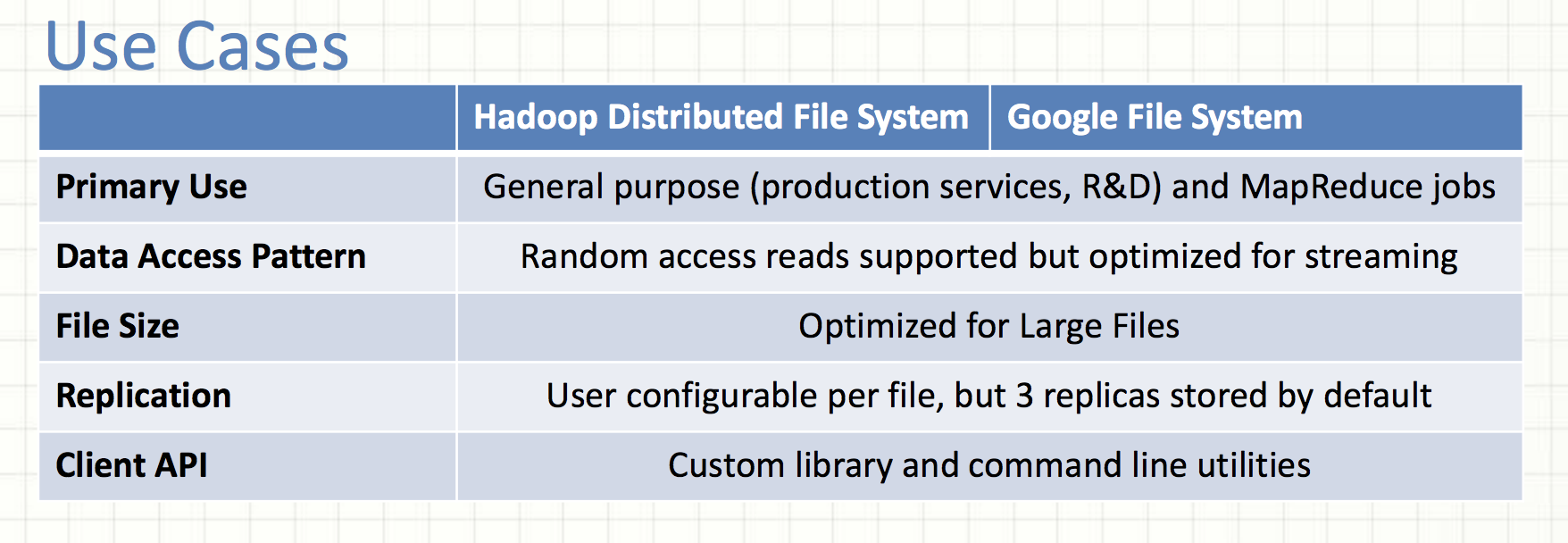
HDFS vs GFS
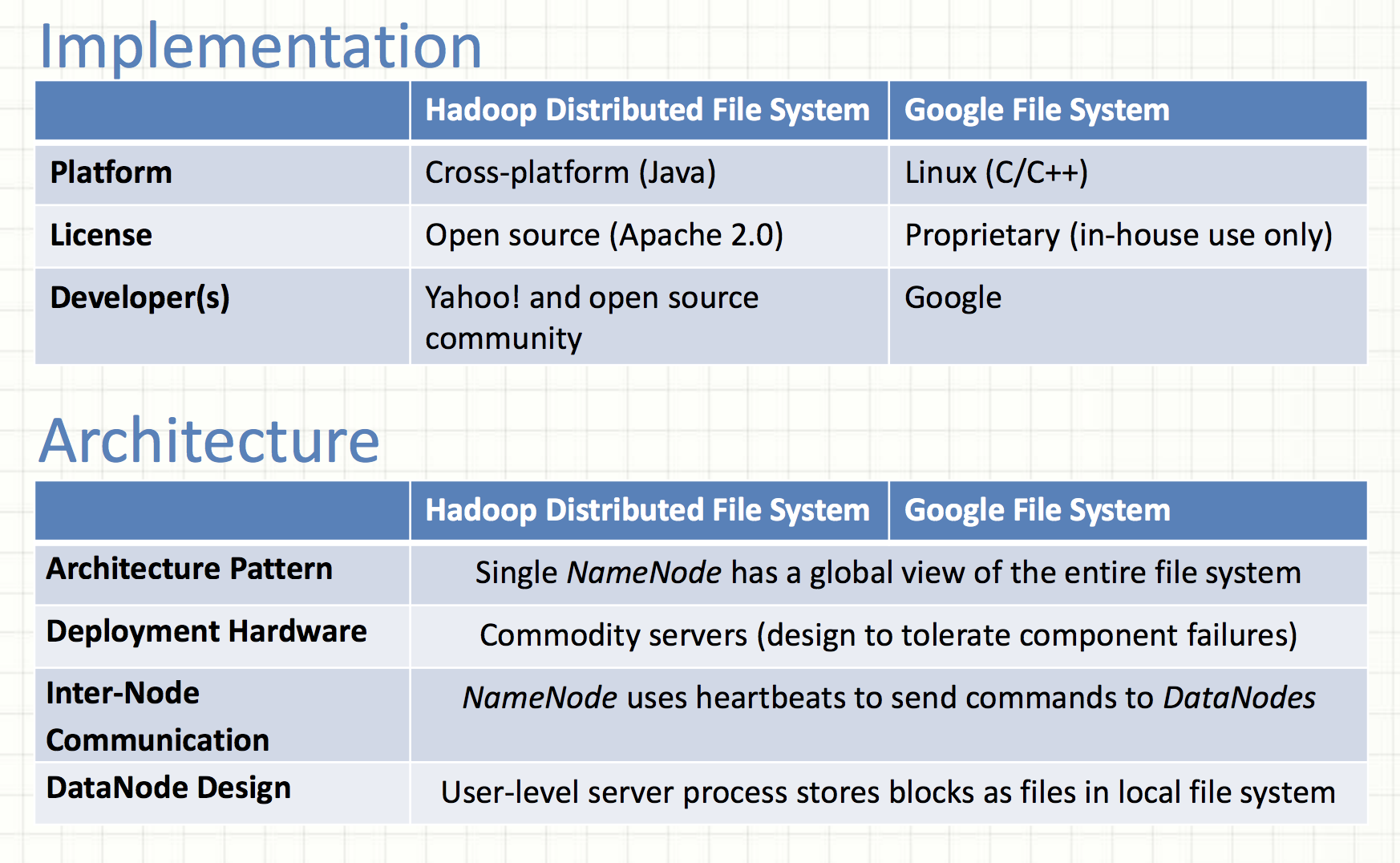
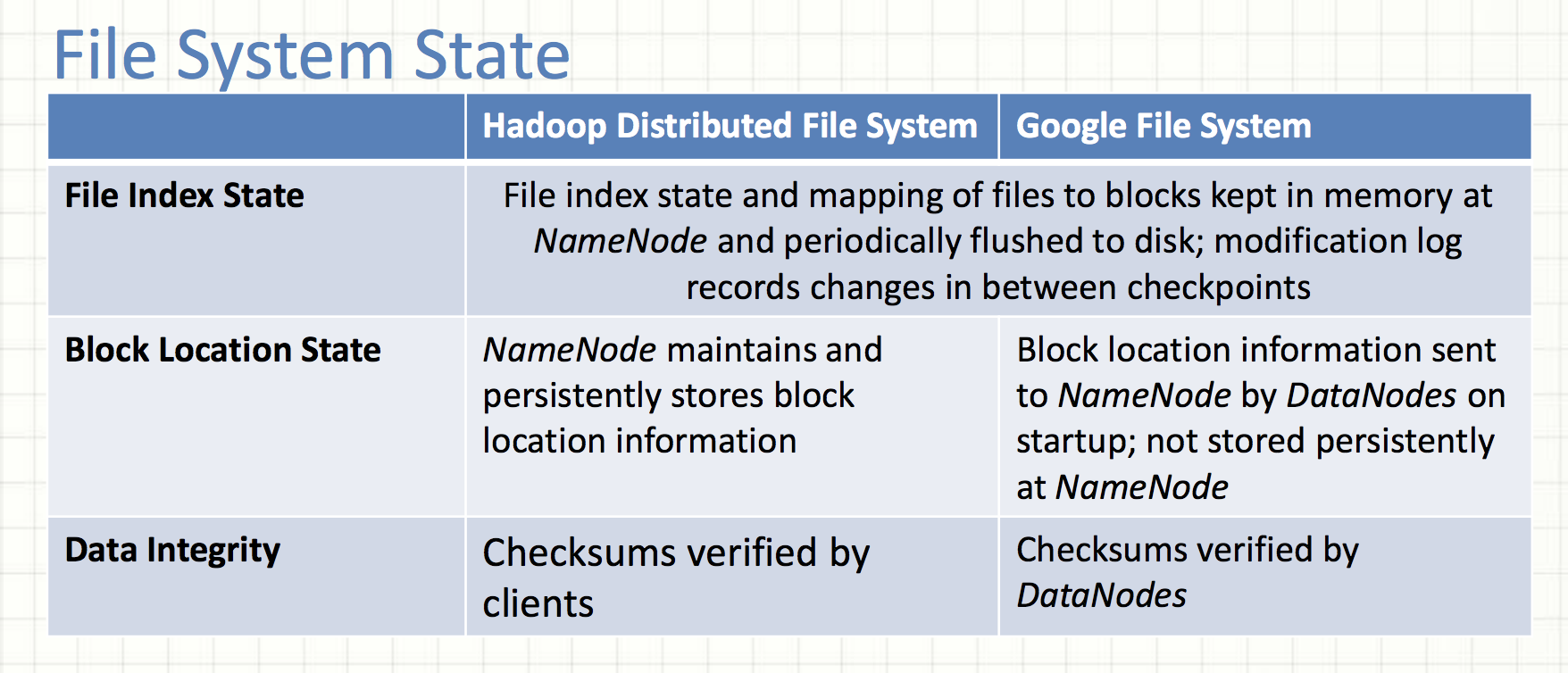
Block Location State
The statement above for HDFS is false.
The GFS paper, 2.6.2 chunk locations: The master does not store chunck locations persistently.
Why? It was much simpler to request chunk location information from chunkservers at startup, and periodically thereafter.
- The problem of keeping the master and chunkservers in sync as chunkservers join and leave the cluster, change names, fail, restart, and so on.
- A chunkserver has the final word over what chunks it does or does not have on its own disks.
Data Integrity
Data corruption can occur because of faults in a storage device, network faults, or buggy software.
The statement above about HDFS is not accurate.
HDFS
- Checksum unit: a chunk (io.bytes.per.checksum, 512 bytes)
- End-to-end checksumming (checksums are generated at clients)
- HDFS clients compute checksums and store checksums in a separate hidden file on datanodes
- At rest, DataNodes continuously verify data against stored CRCs to detect and repair bit-rot. (scan period is 504 hrs in HDFS 3.1.2)
GFS
- Checksum unit: 64KB sized blocks (chunks are broken up into logical blocks)
- Checksums are generated at chunchsevers
- Each chunkserver must independently verify the integrity of its own copy by maintaining checksums.
- Checksums are kept in memory and stored persistently with logging, separate from user data.
- During idle periods, chunkservers scan and verify the contents of inactive chunks.
Note: 1. Read / write unit in GFS may be less than a checksumming block
2. Replicas of a chunk are not guaranteed to be bitwise identical in GFS
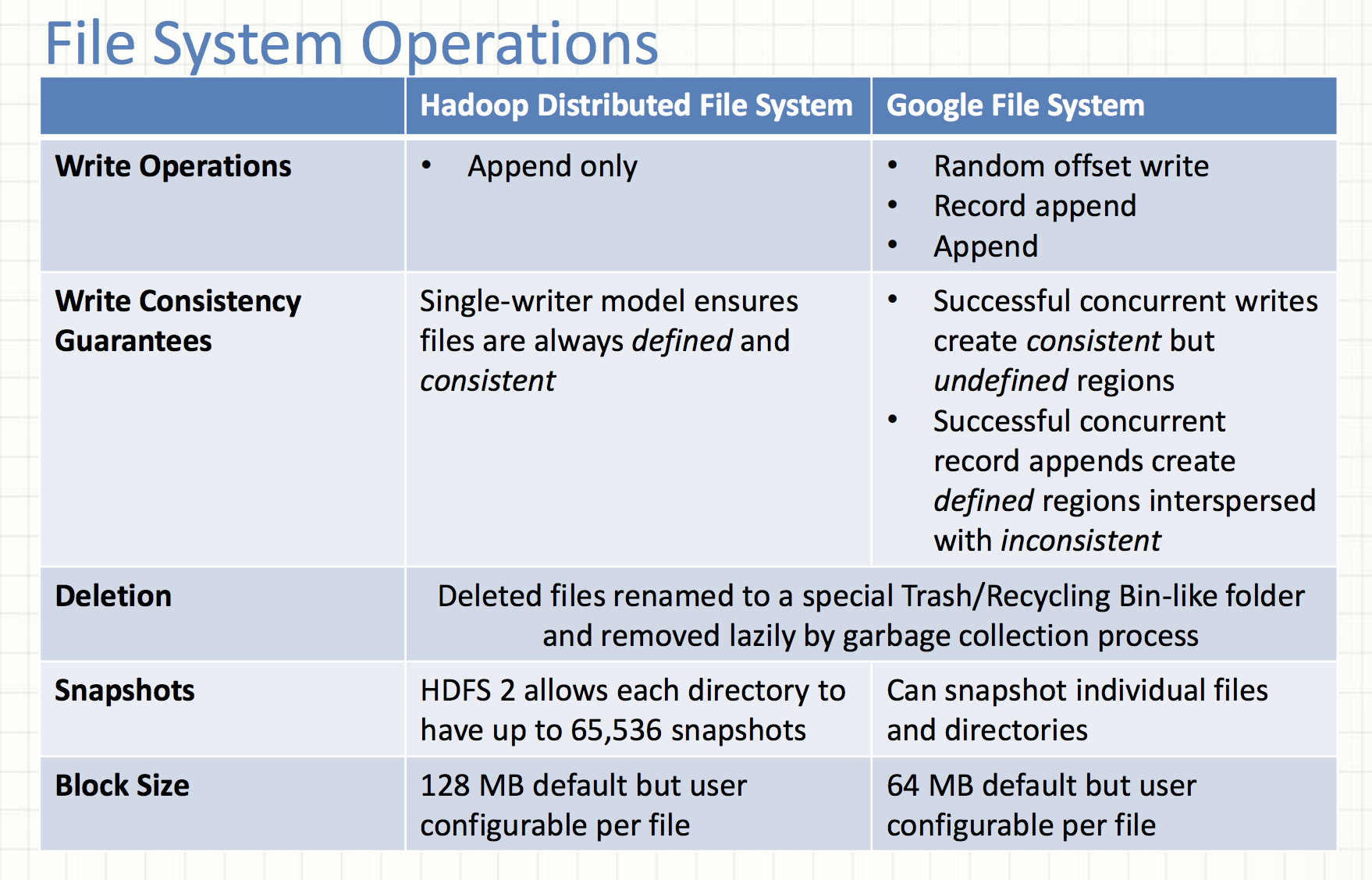
Write Consistency Guarantees
consistent
all clients see the same data, regardless of which replicas they read from.
defined
A file region is considered 'defined' after a file data mutation if:
-
- The file region is consistent
- clients will see what the mutation writes in its entirety.
The relaxed consistency model in GFS
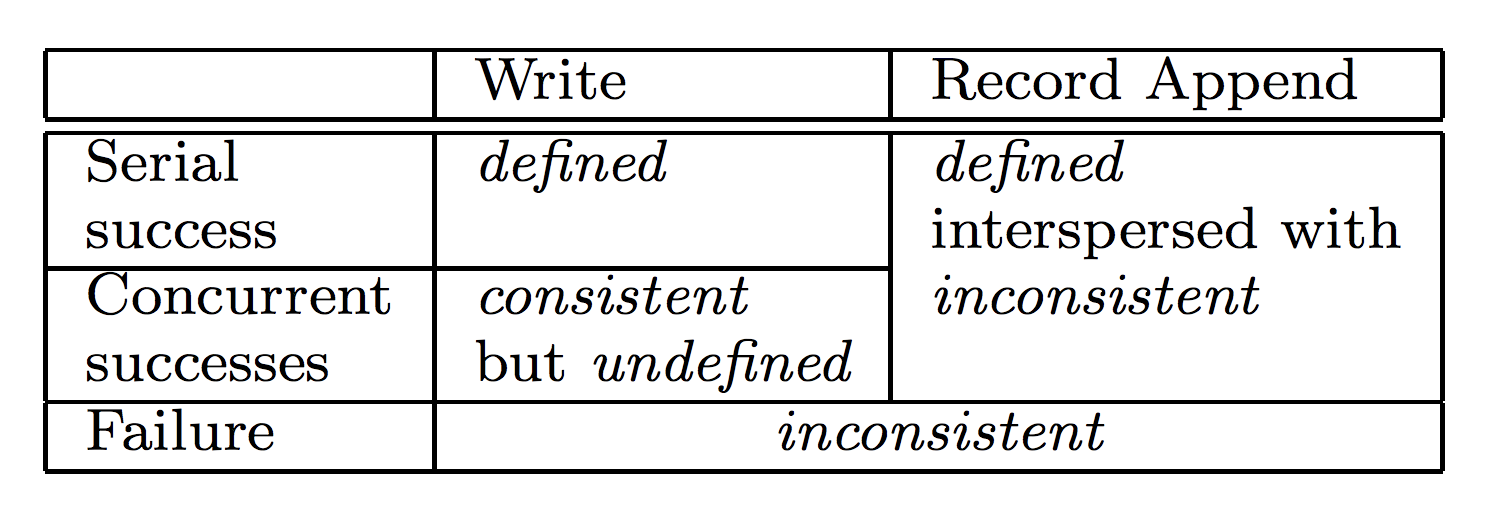
- Successful Concurrent Writes
- Write means random write!
- P1: w(offset_start: 0, offset_end: 100); P2: w(offset_start: 50, offset_end: 150)
- Record Appends
- Successfully written records are defined
- There may be paddings or duplicates between defined regions
HDFS only allows a single writer which performs serial writes
References
Shvachko, Konstantin, et al. "The hadoop distributed file system." MSST. Vol. 10. 2010. paper
Ghemawat, Sanjay, Howard Gobioff, and Shun-Tak Leung. "The Google file system." (2003).



