mysql 学习笔记(二)
常用情景
标签:常见 面试 sql 习题
1、列出各个部门中工资高于本部门的平均工资的员工数和部门号,并按部门号排序
- 创建表:
mysql> CREATE TABLE employee921(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment ,
NAME VARCHAR(50) ,
salary BIGINT ,
deptid INT
);
- 插入实验数据:
mysql> INSERT INTO employee921
VALUES
(NULL , 'zs' , 1000 , 1) ,
(NULL , 'ls' , 1100 , 1) ,
(NULL , 'ww' , 1100 , 1) ,
(NULL , 'zl' , 900 , 1) ,
(NULL , 'zl' , 1000 , 2) ,
(NULL , 'zl' , 900 , 2) ,
(NULL , 'z
l' , 1000 , 2) ,
(NULL , 'zl' , 1100 , 2);
- 第一种方式先查高于平均分的员工然后再统计 group by 排序:
SELECT avg(salary) FROM employee921 GROUP BY deptid;mysql> SELECT employee921.id , employee921. NAME , employee921.salary , employee921.dep tid tid FROM employee921 WHERE salary >( SELECT avg(salary) FROM employee921 WHERE deptid = tid );
小贴士:效率低的一个语句,仅供学习参考使用(在group by之后不能使用where,只能使用having,在group by之前可以使用where,即表示对过滤后的结果分组)。
mysql> SELECT
count(*) ,
tid
FROM
(
SELECT
employee921.id ,
employee921. NAME ,
employee921.salary ,
employee921.deptid tid
FROM
employee921
WHERE
salary >(
SELECT
avg(salary)
FROM
employee921
WHERE
deptid = tid
)
) AS t
GROUP BY
tid;
- 另外一种方式:关联查询
SELECT
a.ename ,
a.salary ,
a.deptid
FROM
emp a ,
(
SELECT
deptid ,
avg(salary) avgsal
FROM
emp
GROUP BY
deptid
) b
WHERE
a.deptid = b.deptid
AND a.salary > b.avgsal;
2、存储过程与触发器必须会,经常被面试到?
create procedure insert_Student (_name varchar(50),_age int ,out _id int)
begin
insert into student value(null,_name,_age);
select max(stuId) into _id from student;
end;
call insert_Student('wfz',23,@id);
select @id;
mysql> create trigger update_Student BEFORE update on student FOR EACH ROW
-> select * from student;
# 触发器不允许返回结果
create trigger update_Student BEFORE update on student FOR EACH ROW
insert into student value(null,'zxx',28);
# mysql的触发器目前不能对当前表进行操作
create trigger update_Student BEFORE update on student FOR EACH ROW
delete from articles where id=8;
# 这个例子不是很好,最好是用删除一个用户时,顺带删除该用户的所有帖子
#这里要注意使用OLD.id
- 存储过程的实验步骤:
mysql> delimiter |
mysql> create procedure insertArticle_Procedure (pTitle varchar(50),pBid int,out
pId int)
-> begin
-> insert into article1 value(null,pTitle,pBid);
-> select max(id) into pId from article1;
-> end;
-> |
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> call insertArticle_Procedure('xiaoming',1,@pid);
-> |
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> delimiter ;
mysql> select @pid;
+------+
| @pid |
+------+
| 3 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from article1;
+----+--------------+------+
| id | title | bid |
+----+--------------+------+
| 1 | test | 1 |
| 2 | chuanzhiboke | 1 |
| 3 | xiaoming | 1 |
+----+--------------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 触发器的实验步骤:
create table board1(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50),ar
ticleCount int);
create table article1(id int primary key auto_increment,title varchar(50)
,bid int references board1(id));
delimiter |
create trigger insertArticle_Trigger after insert on article1 for each ro
w begin
-> update board1 set articleCount=articleCount+1 where id= NEW.bid;
-> end;
-> |
delimiter ;
insert into board1 value (null,'test',0);
insert into article1 value(null,'test',1);
小贴士:还有,每插入一个帖子,都希望将版面表中的最后发帖时间,帖子总数字段进行同步更新,用触发器做效率就很高。下次课设计这样一个案例,写触发器时,对于最后发帖时间可能需要用declare方式声明一个变量,或者是用NEW.posttime来生成。
3、说出一些数据库优化方面的经验?
用PreparedStatement 一般来说比Statement性能高:一个sql 发给服务器去执行,涉及步骤:语法检查、语义分析, 编译,缓存有外键约束会影响插入和删除性能,如果程序能够保证数据的完整性,那在设计数据库时就去掉外键。(比喻:就好比免检产品,就是为了提高效率,充分相信产品的制造商)
(对于hibernate来说,就应该有一个变化:empleyee->Deptment对象,现在设计时就成了employee->deptid)
4、看mysql帮助文档子查询章节的最后部分,例如,根据扫描的原理,下面的子查询语句要比第二条关联查询的效率高:
1. select e.name,e.salary where e.managerid=(select id from employee where name='zxx');
2. select e.name,e.salary,m.name,m.salary from employees e,employees m where
e.managerid = m.id and m.name='zxx';
5、军规
表中允许适当冗余,譬如,主题帖的回复数量和最后回复时间等
将姓名和密码单独从用户表中独立出来。这可以是非常好的一对一的案例哟!
** sql语句全部大写,特别是列名和表名都大写。特别是sql命令的缓存功能,更加需要统一大小写,sql语句发给oracle服务器,语法检查和编译成为内部指令,缓存和执行指令。根据缓存的特点,不要拼凑条件,而是用?和PreparedStatment**
还有索引对查询性能的改进也是值得关注的。
6、下面是关于性能的讨论举例
问题:4航班 3个城市
- m * n
select * from flight,city where flight.startcityid=city.cityid and city.name='beijing';
- m + n(两种方式)
1、select * from flight where startcityid = (select cityid from city where cityname='beijing');
2、select flight.id,'beijing',flight.flightTime from flight where startcityid = (select cityid from city where cityname='beijing')
7、union和union all有什么不同?
- 假设我们有一个表Student,包括以下字段与数据:
drop table student;
create table student
(
id int primary key,
name nvarchar2(50) not null,
score number not null
);
-- c插入数据
insert into student values(1,'Aaron',78);
insert into student values(2,'Bill',76);
insert into student values(3,'Cindy',89);
insert into student values(4,'Damon',90);
insert into student values(5,'Ella',73);
insert into student values(6,'Frado',61);
insert into student values(7,'Gill',99);
insert into student values(8,'Hellen',56);
insert into student values(9,'Ivan',93);
insert into student values(10,'Jay',90);
commit;
- Union和Union All的区别。
select *
from student
where id < 4
union
select *
from student
where id > 2 and id < 6
-- 结果将是
1 Aaron 78
2 Bill 76
3 Cindy 89
4 Damon 90
5 Ella 73
-- 如果换成Union All连接两个结果集,则返回结果是:
1 Aaron 78
2 Bill 76
3 Cindy 89
3 Cindy 89
4 Damon 90
5 Ella 73
-- 可以看到,Union和Union All的区别之一在于对重复结果的处理。
-
UNION在进行表链接后会筛选掉重复的记录,所以在表链接后会对所产生的结果集进行排序运算,删除重复的记录再返回结果。实际大部分应用中是不会产生重复的记录,最常见的是过程表与历史表UNION。如:
select * from gc_dfys union select * from ls_jg_dfys
8、分页语句
- 取出sql表中第31到40的记录(以自动增长ID为主键)
pageSize=20;
pageNo = 5;
sql server方案1:
select top 10 * from t where id not in (select top 30 id from t order by id ) orde by id
sql server方案2:
select top 10 * from t where id in (select top 40 id from t order by id) order by id desc
mysql方案:select * from t order by id limit 30,10
oracle方案:select * from (select rownum r,* from t where r<=40) where r>30
- 1.分页技术(直接利用sql语句进行分页,效率最高和最推荐的)
mysql: sql = "select * from articles limit " + (pageNo-1) * pageSize + "," + pageSize;
oracle: sql = "select * from " +
"(select rownum r,* from " +
"(select * from articles order by postime desc)" +
"where rownum<= " + pageNo*pageSize +") tmp " +
"where r>" + (pageNo-1)*pageSize;
注释:第7行保证rownum的顺序是确定的,因为oracle的索引会造成rownum返回不同的值
小提示:没有order by时,rownum按顺序输出,一旦有了order by,rownum不按顺序输出了,这说明rownum是排序前的编号。如果对order by从句中的字段建立了索引,那么,rownum也是按顺序输出的,因为这时候生成原始的查询结果集时会参照索引表的顺序来构建。
sqlserver:sql = "select top 10 * from id not id(select top " + (pageNo-1)*pageSize + "id from articles)"
DataSource ds = new InitialContext().lookup(jndiurl);
Connection cn = ds.getConnection();
//"select * from user where id=?" --->binary directive
PreparedStatement pstmt = cn.prepareSatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery()
while(rs.next())
{
out.println(rs.getString(1));
}
- 2.不可滚动的游标
pageSize=20;
pageNo = 5;
cn = null
stmt = null;
rs = null;
try
{
sqlserver:sql = "select * from articles";
DataSource ds = new InitialContext().lookup(jndiurl);
Connection cn = ds.getConnection();
//"select * from user where id=?" --->binary directive
PreparedStatement pstmt = cn.prepareSatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery()
for(int j=0;j<(pageNo-1)*pageSize;j++)
{
rs.next();
}
int i=0;
while(rs.next() && i<10)
{
i++;
out.println(rs.getString(1));
}
}
cacth(){}
finnaly
{
if(rs!=null)try{rs.close();}catch(Exception e){}
if(stm.........
if(cn............
}
- 3.可滚动的游标
pageSize=20;
pageNo = 5;
cn = null
stmt = null;
rs = null;
try
{
sqlserver:sql = "select * from articles";
DataSource ds = new InitialContext().lookup(jndiurl);
Connection cn = ds.getConnection();
//"select * from user where id=?" --->binary directive
PreparedStatement pstmt = cn.prepareSatement(sql,ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,...);
//根据上面这行代码的异常SQLFeatureNotSupportedException,就可判断驱动是否支持可滚动游标
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery()
rs.absolute((pageNo-1)*pageSize)
int i=0;
while(rs.next() && i<10)
{
i++;
out.println(rs.getString(1));
}
}
cacth(){}
finnaly
{
if(rs!=null)try{rs.close();}catch(Exception e){}
if(stm.........
if(cn............
}
9、用一条SQL语句 查询出每门课都大于80分的学生姓名
name kecheng fenshu
张三 语文 81
张三 数学 75
李四 语文 76
李四 数学 90
王五 语文 81
王五 数学 100
王五 英语 90
- 准备数据的sql代码:
create table score(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20),subject varchar(20),score int);
insert into score values
(null,'张三','语文',81),
(null,'张三','数学',75),
(null,'李四','语文',76),
(null,'李四','数学',90),
(null,'王五','语文',81),
(null,'王五','数学',100),
(null,'王五 ','英语',90);
提示:当百思不得其解时,请理想思维,把小变成大做,把大变成小做,
答案:
A: select distinct name from score where name not in (select distinct name from score where score >=80)
B:select distince name t1 from score where 80< all (select score from score where name=t1);
10、所有部门之间的比赛组合
一个叫department的表,里面只有一个字段name,一共有4条纪录,分别是a,b,c,d,对应四个球对,现在四个球对进行比赛,用一条sql语句显示所有可能的比赛组合.
DROP TABLE if EXISTS RANKS;
CREATE TABLE RANKS(NAME CHAR );
INSERT INTO RANKS VALUES('A'),('B'),('C'),('D');
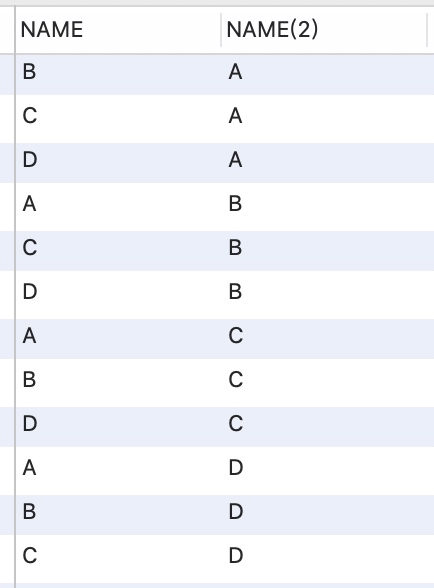
SELECT A.NAME ,B.NAME
FROM RANKS A,RANKS B
WHERE A.NAME <> B.NAME
-- 12
SELECT A.NAME,B.NAME
FROM RANKS A,RANKS B
WHERE A.NAME > B.NAME
-- 5
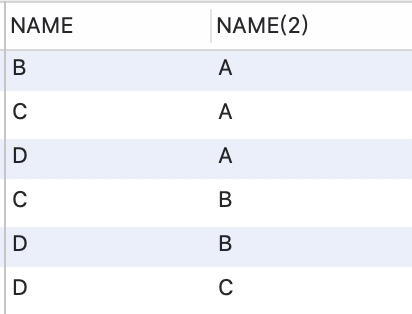
SELECT A.NAME,B.NAME
FROM RANKS A,RANKS B
WHERE A.NAME < B.NAME
-- 6 √

总结:
select a.name, b.name
from team a, team b
where a.name < b.name
11、每个月份的发生额都比101科目多的科目
请用SQL语句实现:从TestDB数据表中查询出所有月份的发生额都比101科目相应月份的发生额高的科目。请注意:TestDB中有很多科目,都有1-12月份的发生额。
AccID:科目代码,Occmonth:发生额月份,DebitOccur:发生额。
数据库名:JcyAudit,数据集:Select * from TestDB
- 准备数据的sql代码:
drop table if exists TestDB;
create table TestDB(id int primary key auto_increment,AccID varchar(20), Occmonth date, DebitOccur bigint);
insert into TestDB values
(null,'101','1988-1-1',100),
(null,'101','1988-2-1',110),
(null,'101','1988-3-1',120),
(null,'101','1988-4-1',100),
(null,'101','1988-5-1',100),
(null,'101','1988-6-1',100),
(null,'101','1988-7-1',100),
(null,'101','1988-8-1',100);
--复制上面的数据,故意把第一个月份的发生额数字改小一点
insert into TestDB values
(null,'102','1988-1-1',90),
(null,'102','1988-2-1',110),
(null,'102','1988-3-1',120),
(null,'102','1988-4-1',100),
(null,'102','1988-5-1',100),
(null,'102','1988-6-1',100),
(null,'102','1988-7-1',100),
(null,'102','1988-8-1',100);
--复制最上面的数据,故意把所有发生额数字改大一点
insert into TestDB values
(null,'103','1988-1-1',150),
(null,'103','1988-2-1',160),
(null,'103','1988-3-1',180),
(null,'103','1988-4-1',120),
(null,'103','1988-5-1',120),
(null,'103','1988-6-1',120),
(null,'103','1988-7-1',120),
(null,'103','1988-8-1',120);
--复制最上面的数据,故意把所有发生额数字改大一点
insert into TestDB values
(null,'104','1988-1-1',130),
(null,'104','1988-2-1',130),
(null,'104','1988-3-1',140),
(null,'104','1988-4-1',150),
(null,'104','1988-5-1',160),
(null,'104','1988-6-1',170),
(null,'104','1988-7-1',180),
(null,'104','1988-8-1',140);
--复制最上面的数据,故意把第二个月份的发生额数字改小一点
insert into TestDB values
(null,'105','1988-1-1',100),
(null,'105','1988-2-1',80),
(null,'105','1988-3-1',120),
(null,'105','1988-4-1',100),
(null,'105','1988-5-1',100),
(null,'105','1988-6-1',100),
(null,'105','1988-7-1',100),
(null,'105','1988-8-1',100);
答案:
select distinct AccID from TestDB
where AccID not in
(select TestDB.AccIDfrom TestDB,
(select * from TestDB where AccID='101') as db101
where TestDB.Occmonth=db101.Occmonth and TestDB.DebitOccur<=db101.DebitOccur
);
12、统计每年每月的信息
year month amount
1991 1 1.1
1991 2 1.2
1991 3 1.3
1991 4 1.4
1992 1 2.1
1992 2 2.2
1992 3 2.3
1992 4 2.4
查成这样一个结果
year m1 m2 m3 m4
1991 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4
1992 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4
提示:这个与工资条非常类似,与学生的科目成绩也很相似。
- 准备sql语句:
drop table if exists sales;
create table sales(id int auto_increment primary key,year varchar(10), month varchar(10), amount float(2,1));
insert into sales values
(null,'1991','1',1.1),
(null,'1991','2',1.2),
(null,'1991','3',1.3),
(null,'1991','4',1.4),
(null,'1992','1',2.1),
(null,'1992','2',2.2),
(null,'1992','3',2.3),
(null,'1992','4',2.4);
-- 答案
select sales.year ,
(select t.amount from sales t where t.month='1' and t.year= sales.year) '1',
(select t.amount from sales t where t.month='1' and t.year= sales.year) '2',
(select t.amount from sales t where t.month='1' and t.year= sales.year) '3',
(select t.amount from sales t where t.month='1' and t.year= sales.year) as '4'
from sales group by year;
13、显示文章标题,发帖人、最后回复时间
- 表
id,title,postuser,postdate,parentid
- 准备sql语句:
drop table if exists articles;
create table articles(id int auto_increment primary key,title varchar(50), postuser varchar(10), postdate datetime,parentid int references articles(id));
insert into articles values
(null,'第一条','张三','1998-10-10 12:32:32',null),
(null,'第二条','张三','1998-10-10 12:34:32',null),
(null,'第一条回复1','李四','1998-10-10 12:35:32',1),
(null,'第二条回复1','李四','1998-10-10 12:36:32',2),
(null,'第一条回复2','王五','1998-10-10 12:37:32',1),
(null,'第一条回复3','李四','1998-10-10 12:38:32',1),
(null,'第二条回复2','李四','1998-10-10 12:39:32',2),
(null,'第一条回复4','王五','1998-10-10 12:39:40',1);
-- 答案:
select a.title,a.postuser,
(select max(postdate) from articles where parentid=a.id) reply
from articles a where a.parentid is null;
注释:子查询可以用在选择列中,也可用于where的比较条件中,还可以用于from从句中。
14、删除除了id号不同,其他都相同的学生冗余信息
- 学生表 如下:
id号 学号 姓名 课程编号 课程名称 分数
1 2005001 张三 0001 数学 69
2 2005002 李四 0001 数学 89
3 2005001 张三 0001 数学 69
A: delete from tablename where id号 not in(select min(id号) from tablename group by 学号,姓名,课程编号,课程名称,分数)
- 实验:
create table student2(id int auto_increment primary key,code varchar(20),name varchar(20));
insert into student2 values(null,'2005001','张三'),(null,'2005002','李四'),(null,'2005001','张三');
//如下语句,mysql报告错误,可能删除依赖后面统计语句,而删除又导致统计语句结果不一致。
-- 但是,如下语句没有问题:
select * from student2 where id not in(select min(id) from student2 group by name);
-- 于是,我想先把分组的结果做成虚表,然后从虚表中选出结果,最后再将结果作为删除的条件数据。
delete from student2 where id not in(select mid from (select min(id) mid
from student2 group by name) as t);
-- 或者:
delete from student2 where id not in(select min(id) from (select * from s
tudent2) as t group by t.name);
15、航空网的几个航班查询题:
- 表结构如下:
flight { flightID ,
StartCityID ,
endCityID ,
StartTime } city { cityID ,
CityName
)
- 实验环境:
CREATE TABLE city(
cityID INT auto_increment PRIMARY KEY ,
cityName VARCHAR(20)
);
CREATE TABLE flight(
flightID INT auto_increment PRIMARY KEY ,
StartCityID INT REFERENCES city(cityID) ,
endCityID INT REFERENCES city(cityID) ,
StartTime TIMESTAMP
);
-- 航 班 本 来应该没有日期部分才 好 ,但 是 下面的题目当 中 涉及到了日期 INSERT INTO city
VALUES
(NULL , '北京') ,
(NULL , '上海') ,
(NULL , '广州');
INSERT INTO flight
VALUES
(NULL , 1 , 2 , '9:37:23') ,
(NULL , 1 , 3 , '9:37:23') ,
(NULL , 1 , 2 , '10:37:23') ,
(NULL , 2 , 3 , '10:37:23');
- 问题如下:
1、查询起飞城市是北京的所有航班,按到达城市的名字排序
参与运算的列是我起码能够显示出来的那些列,但最终我不一定把它们显示出来。各个表组合出来的中间结果字段中必须包含所有运算的字段。SELECT * FROM flight f , city c WHERE f.endcityid = c.cityid AND startcityid =( SELECT c1.cityid FROM city c1 WHERE c1.cityname = "北京" ) ORDER BY c.cityname ASC;
2、查询北京到上海的所有航班纪录(起飞城市,到达城市,起飞时间,航班号)mysql> SELECT flight.flightid , '北京' startcity , e.cityname FROM flight , city e wh ere flight.endcityid = e.cityid AND flight.startcityid =( SELECT cityid FROM city wh ere cityname = '北京' ); mysql> SELECT flight.flightid , s.cityname , e.cityname FROM flight , city s , city e wh ere flight.startcityid = s.cityid AND s.cityname = '北京' AND flight.endCityId = e.cit yID ORDER BY e.cityName DESC;
3、查询具体某一天(2005-5-8)的北京到上海的的航班次数SELECT c1.CityName , c2.CityName , f.StartTime , f.flightID FROM city c1 , city c2 , flight f WHERE f.StartCityID = c1.cityID AND f.endCityID = c2.cityID AND c1.cityName = '北京' AND c2.cityName = '上海'
mysql中提取日期部分进行比较的示例代码如下:SELECT count(*) FROM ( SELECT c1.CityName , c2.CityName , f.StartTime , f.flightID FROM city c1 , city c2 , flight f WHERE f.StartCityID = c1.cityID AND f.endCityID = c2.cityID AND c1.cityName = '北京' AND c2.cityName = '上海' AND 查帮助获得的某个日期处理函数(startTime) LIKE '2005-5-8%'select * from flight where date_format(starttime,'%Y-%m-%d')='1998-01-02'
16、查出比经理薪水还高的员工信息:
DROP TABLE
IF NOT EXISTS employees;
CREATE TABLE employees(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment ,
NAME VARCHAR(50) ,
salary INT ,
managerid INT REFERENCES employees(id)
);
INSERT INTO employees
VALUES
(NULL , ' lhm' , 10000 , NULL) ,
(NULL , ' zxx' , 15000 , 1) ,
(NULL , 'flx' , 9000 , 1) ,
(NULL , 'tg' , 10000 , 2) ,
(NULL , 'wzg' , 10000 , 3);
-
问题:Wzg大于flx,lhm大于zxx ?
-
解题思路:
根据sql语句的查询特点,是逐行进行运算,不可能两行同时参与运算。
涉及了员工薪水和经理薪水,所有,一行记录要同时包含两个薪水,所有想到要把这个表自关联组合一下。
首先要组合出一个包含有各个员工及该员工的经理信息的长记录,譬如,左半部分是员工,右半部分是经理。而迪卡尔积会组合出很多垃圾信息,先去除这些垃圾信息。 -
答案
SELECT
e.*
FROM
employees e ,
employees m
WHERE
e.managerid = m.id
AND e.sala ry > m.salary;
17、求出小于45岁的各个老师所带的大于12岁的学生人数
数据库中有3个表 teacher 表,student表,tea_stu关系表。
teacher 表 teaID name age
student 表 stuID name age
teacher_student表 teaID stuID
- 要求用一条sql查询出这样的结果
1.显示的字段要有老师name, age 每个老师所带的学生人数
2 只列出老师age为40以下,学生age为12以上的记录 - 预备知识:
1.sql语句是对每一条记录依次处理,条件为真则执行动作(select,insert,delete,update)
2.只要是迪卡尔积,就会产生“垃圾”信息,所以,只要迪卡尔积了,我们首先就要想到清除“垃圾”信息 - 实验准备:
DROP TABLE
IF EXISTS tea_stu;
DROP TABLE
IF EXISTS teacher;
DROP TABLE
IF EXISTS student;
CREATE TABLE teacher(
teaID INT PRIMARY KEY ,
NAME VARCHAR(50) ,
age INT
);
CREATE TABLE student(
stuID INT PRIMARY KEY ,
NAME VARCHAR(50) ,
age INT
);
CREATE TABLE tea_stu(
teaID INT REFERENCES teacher(teaID) ,
stuID INT REFERENCES student(stuID)
);
INSERT INTO teacher
VALUES
(1 , 'zxx' , 45) ,
(2 , 'lhm' , 25) ,
(3 , 'wzg' , 26) ,
(4 , 'tg' , 27);
INSERT INTO student
VALUES
(1 , 'wy' , 11) ,
(2 , 'dh' , 25) ,
(3 , 'ysq' , 26) ,
(4 , 'mxc' , 27);
INSERT INTO tea_stu
VALUES
(1 , 1) ,
(1 , 2) ,
(1 , 3);
INSERT INTO tea_stu
VALUES
(2 , 2) ,
(2 , 3) ,
(2 , 4);
INSERT INTO tea_stu
VALUES
(3 , 3) ,
(3 , 4) ,
(3 , 1);
INSERT INTO tea_stu
VALUES
(4 , 4) ,
(4 , 1) ,
(4 , 2) ,
(4 , 3);
结果:2->3,3->2,4->3
- 解题思路:(真实面试答题时,也要写出每个分析步骤,如果纸张不够,就找别人要)
1、要会统计分组信息,统计信息放在中间表中:
2、接着其实应该是筛除掉小于12岁的学生,然后再进行统计,中间表必须与student关联才能得到12岁以下学生和把该学生记录从中间表中剔除,代码是:select teaid,count(*) from tea_stu group by teaid;
3、接着把上面的结果做成虚表与teacher进行关联,并筛除大于45的老师SELECT tea_stu.teaid , count(*) total FROM student , tea_stu WHERE student.stuid = tea_stu.stuid AND student.age > 12 GROUP BY tea_stu.teaidSELECT teacher.teaid , teacher. NAME , total FROM teacher , ( SELECT tea_stu.tea id , count(*) total FROM student , tea_stu WHERE student.stuid = tea_stu.stuid AND stu dent.age > 12 GROUP BY tea_stu.teaid ) AS tea_stu2 WHERE teacher.teaid = tea_stu2.tea id AND teacher.age < 45;
18.求出发帖最多的人:
select authorid,count(*) total from articles
group by authorid
having total=
(select max(total2) from (select count(*) total2 from articles group by authorid) as t);
select t.authorid,max(t.total) from
(select authorid,count(*) total from articles )as t
这条语句不行,因为max只有一列,不能与其他列混淆。
select authorid,count(*) total from articles
group by authorid having total=max(total)也不行。
19、一个用户表中有一个积分字段,假如数据库中有100多万个用户,若要在每年第一天凌晨将积分清零,你将考虑什么,你将想什么办法解决?
alter table drop column score;
alter table add colunm score int;
可能会很快,但是需要试验,试验不能拿真实的环境来操刀,并且要注意,
这样的操作时无法回滚的,在我的印象中,只有inert update delete等DML语句才能回滚,
对于create table,drop table ,alter table等DDL语句是不能回滚。
解决方案一
update user set score=0;
解决方案二,假设上面的代码要执行好长时间,超出我们的容忍范围,那我就
alter table user drop column score;alter table user add column score int。
下面代码实现每年的那个凌晨时刻进行清零。
Runnable runnable =
new Runnable(){
public void run(){
clearDb();
schedule(this,new Date(new Date().getYear()+1,0,0));
}
};
schedule(runnable,
new Date(new Date().getYear()+1,0,1));
小提示:千万注意场合---定时任务跑路不值当
20、一个用户具有多个角色,请查询出该表中具有该用户的所有角色的其他用户。
select count(*) as num,tb.id
from
tb,
(select role from tb where id=xxx) as t1
where
tb.role = t1.role and tb.id != t1.id
group by tb.id
having
num = select count(role) from tb where id=xxx;
21、xxx公司的sql面试
Table EMPLOYEES Structure:
EMPLOYEE_ID NUMBER Primary Key,
FIRST_NAME VARCHAR2(25),
LAST_NAME VARCHAR2(25),
Salary number(8,2),
HiredDate DATE,
Departmentid number(2)
Table Departments Structure:
Departmentid number(2) Primary Key,
DepartmentName VARCHAR2(25).
(1)基于上述EMPLOYEES表写出查询:写出雇用日期在今年的,或者工资在[1000,2000]之间的,或者员工姓名(last_name)以’Obama’打头的所有员工,列出这些员工的全部个人信息。(4分)
SELECT
*
FROM
employees
WHERE
YEAR(hiredDate) = YEAR(date())
OR(salary BETWEEN 1000 AND 200)
OR LEFT(last_name , 3) = 'abc';
(2) 基于上述EMPLOYEES表写出查询:查出部门平均工资大于1800元的部门的所有员工,列出这些员工的全部个人信息。(4分)
SELECT
id ,
NAME ,
salary ,
deptid did
FROM
employee1
WHERE
(
SELECT
avg(salary)
FROM
employee1
WHERE
deptid = did
) > 1800;
(3) 基于上述EMPLOYEES表写出查询:查出个人工资高于其所在部门平均工资的员工,列出这些员工的全部个人信息及该员工工资高出部门平均工资百分比。(5分)
SELECT
employee1.*,(employee1.salary - t.avgSalary) * 100 / employee1.salary
FROM
employee1 ,
(
SELECT
deptid ,
avg(salary) avgSalary
FROM
employee1
GROUP BY
deptid
) AS t
WHERE
employee1.deptid = t.deptid
AND employee1.salary > t.avgSalary;
22、oracle中除了数据库备份,还有什么方法备份?
Oracle数据库有三种标准的备份方法,它们分别是导出/导入(EXP/IMP)、热备份和冷备份。导出备份是一种逻辑备份,冷备份和热备份是物理备份。
23、truncate与delete的区别?(delete from table和truncate table tablea的区别!)
- truncate是DDL語言.delete是DML語言 DDL語言是自動提交的.命令完成就不可回滾.truncate的速度也比delete要快得多.
详细说明: - 相同点:truncate和不带where子句的delete, 以及drop都会删除表内的数据
- 不同点:
1、truncate和 delete只删除数据不删除表的结构(定义)
drop语句将删除表的结构被依赖的约束(constrain),触发器(trigger),索引(index); 依赖于该表的存储过程/函数将保留,但是变为invalid状态.
2、delete语句是dml,这个操作会放到rollback segement中,事务提交之后才生效;如果有相应的trigger,执行的时候将被触发.
truncate,drop是ddl, 操作立即生效,原数据不放到rollback segment中,不能回滚. 操作不触发trigger.
3、delete语句不影响表所占用的extent, 高水线(high watermark)保持原位置不动
显然drop语句将表所占用的空间全部释放
truncate 语句缺省情况下见空间释放到 minextents个 extent,除非使用reuse storage; truncate会将高水线复位(回到最开始).
4、速度,一般来说: drop> truncate > delete
5、安全性:小心使用drop 和truncate,尤其没有备份的时候.否则哭都来不及
使用上,想删除部分数据行用delete,注意带上where子句. 回滚段要足够大.
想删除表,当然用drop
想保留表而将所有数据删除. 如果和事务无关,用truncate即可. 如果和事务有关,或者想触发trigger,还是用delete.
24、racle冷备份的通常步骤
- 1、正常关闭数据库
- 2、备份所有重要的文件到备份目录(数据文件、控制文件、重做日志文件等)
- 3、完成备份后启动数据库用冷备份进行恢复时,只需要将所有文件恢复到原有位置,就可以启动数据库了
- 4、关闭数据库 SQL>shutdown 5 备份文件到备份的目录 6 然后启动数据库 #sqlplus "/as sysdba"SQL>startup 冷备份完毕!!
- 5、对数据库的访问是怎么实现的
将对持久层数据库的基本添加,修改,查找等操作提取到BaseDAO中,采用JavaBean对数据进行封装,以便对持久层的数据能够很好的处理,实现BaseDAO设计对数据库访问的便捷。业务组件通过DAO 的委托接口调用DAO对象,使得上层组件不 直接依赖于DAO的实现类.
25、数据库优化的方案
建立主键,为数据库创建索引,建立存储过程,触发器,可提高查询速度。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号