Codeforces Round #319 (Div. 2)
A:
Let's consider a table consisting of n rows and n columns. The cell located at the intersection of i-th row and j-th column contains numberi × j. The rows and columns are numbered starting from 1.
You are given a positive integer x. Your task is to count the number of cells in a table that contain number x.
The single line contains numbers n and x (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ x ≤ 109) — the size of the table and the number that we are looking for in the table.
Print a single number: the number of times x occurs in the table.
10 5
2
6 12
4
5 13
0
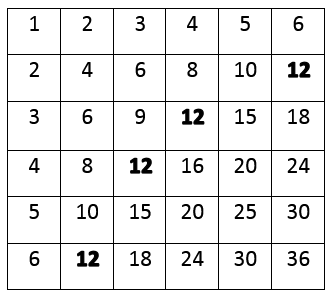
A table for the second sample test is given below. The occurrences of number 12 are marked bold.
题目大意:
就是说,有一个n*n的网格,格子中的每一个数字都是行号*列号,给你一个数字x,问x在这个网格中总共出现了多少次?
解题思路:
这题其实就是找1-n的数字中,任意两个数字相乘有多少个数字满足乘积是x,那我们只需要枚举i:1->n。然后在x%i==0和x/i<=n的情况下的所有的i就行了。
代码:
# include<cstdio>
# include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n,x;
cin>>n>>x;
int cnt = 0;
for ( int i = 1;i <= n;i++ )
{
if ( x%i==0&&x/i<=n )
cnt++;
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
return 0;
}
B题:
题目大意:
就是说,给你一个长度为n的序列,然后问其中是否存在子序列(不要求连续),使得这个子序列的和能够整除m。
解题思路:
一开始看到别人用的bitset做的。,,,自己太弱,不知道bitset该怎么用。
说下大概的做法吧。就是说,我们首先判断n和m的大小,如果n>=m,根据鸽巢原理,我们知道,一定有子序列的和满足%m==0这个条件。
当n<m的时候,我们转化为最简单的01背包问题。
状态:dp[i]表示长度为n的子序列中是否有一个子序列满足%m==i。
初值:dp[a[i]%m]==1;
这道题目实际要找的就是dp[0]是不是为1了。
代码:
# include<cstdio>
# include<iostream>
# include<cstring>
using namespace std;
# define MAX 1000004
int a[MAX];
int dp[MAX];
int tmp[MAX];
int main(void)
{
int n,m;
while ( scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF )
{
for ( int i = 0;i < n;i++ )
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
if( n>=m )
{
puts("YES");
continue;
}
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for ( int i = 0;i < n;i++ )
{
for ( int j = 0;j < m;j++ )
{
if ( dp[j] )
{
tmp[(j+a[i])%m] = 1;
}
}
tmp[a[i]%m] = 1;
for ( int j = 0;j < m;j++ )
{
dp[j] = tmp[j];
}
}
if ( dp[0] )
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}
C:
题目大意:
两个人玩游戏,其中一个人说一个1-n的数字,然后另外一个人来猜测,求那个人所需要的最少猜测次数和猜测过程中每次需要用到的数字,就是我们说的。这些数字都能否整除那个目标数。
解题思路:
用到了整数的唯一分解定理,任何一个大于1的整数都可以被分解成为多个素数的不同次幂的乘积。
首先预处理1-n中的所有的素数,然后判断p^k是不是小于等于n。如果是的话,就是我们要选择的数字。
代码:
# include<cstdio>
# include<cstring>
# include<iostream>
# include<vector>
using namespace std;
# define MAX 1234
int book[MAX],prime[MAX];
int num[MAX];
int len;
vector<int>v;
/*
void init()
{
for ( int i = 1;i < MAX;i++ )
book[i] = 1;
for ( int i = 2;i < MAX;i++ )
{
if ( book[i]==1 )
{
for ( int j = 2*i;j < MAX;j+=i )
{
book[j] = 0;
}
}
}
len = 0;
for ( int i = 2;i < MAX;i++ )
{
if ( book[i]==1 )
{
prime[len++] = 1;
}
}
}
*/
void init()
{
memset(prime,0,sizeof(prime));
prime[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= MAX; i++)
{
for(int j = 2*i; j <= MAX; j += i)
{
prime[j] = 1;
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
int n;
init();
while ( scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF )
{
int tmp;
for ( int i = 2;i <= n;i++ )
{
if ( prime[i]==0 )
{
tmp = i;
if( num[i]==0 )
{
v.push_back(i);
num[i] = 1;
}
while ( tmp*i <= n )
{
tmp*=i;
if ( num[tmp]==0 )
{
v.push_back(tmp);
num[tmp] = 1;
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",v.size());
for ( int i = 0;i < v.size();i++ )
{
printf("%d ",v[i]);
}
puts(" ");
}
return 0;
}





